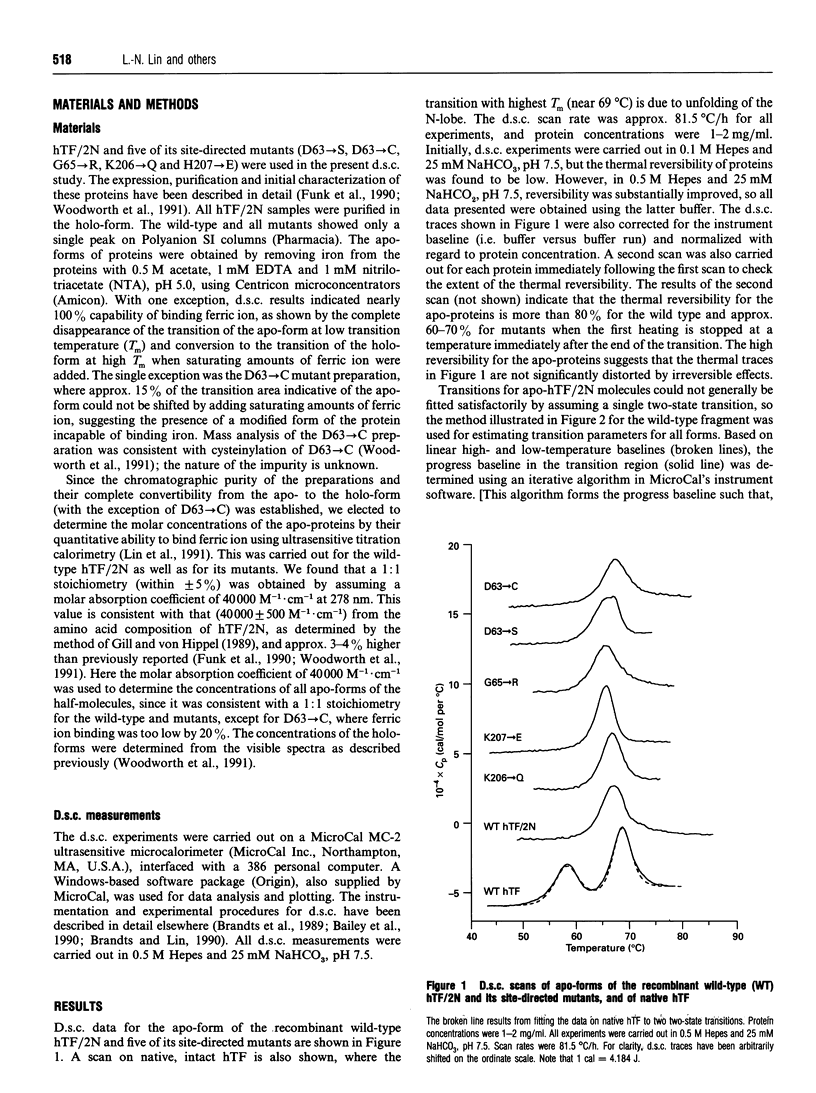
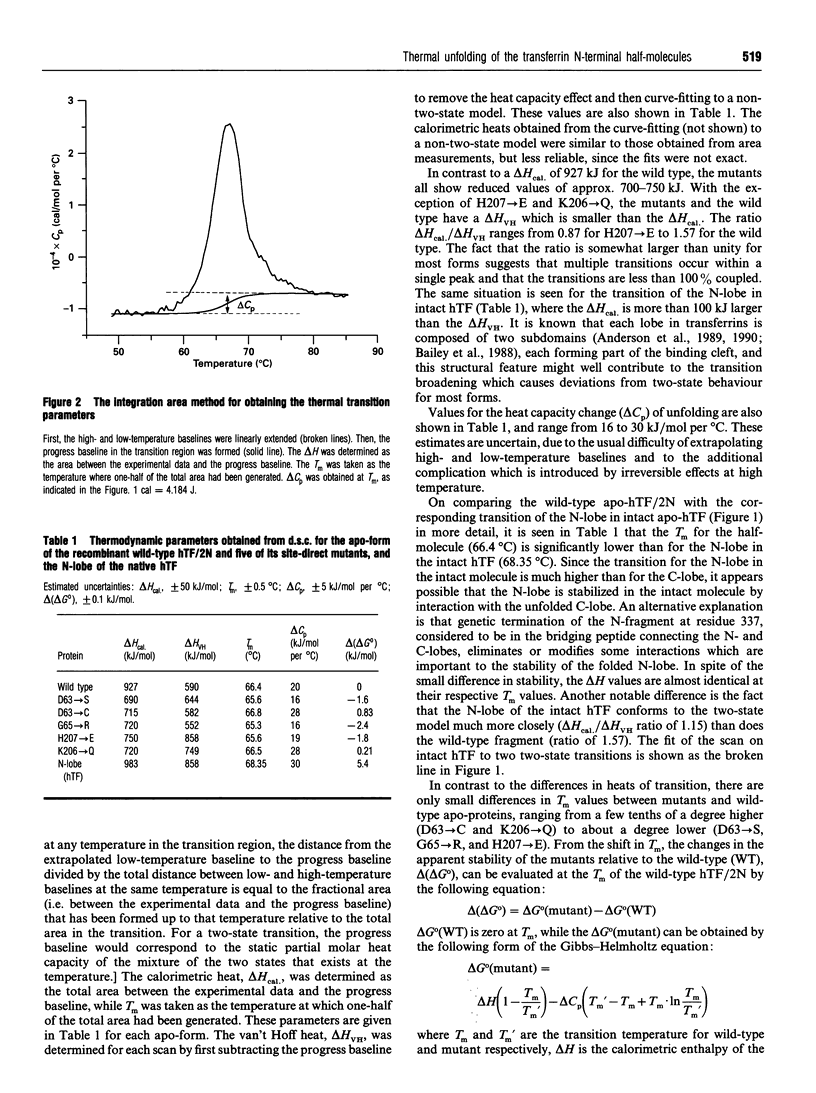
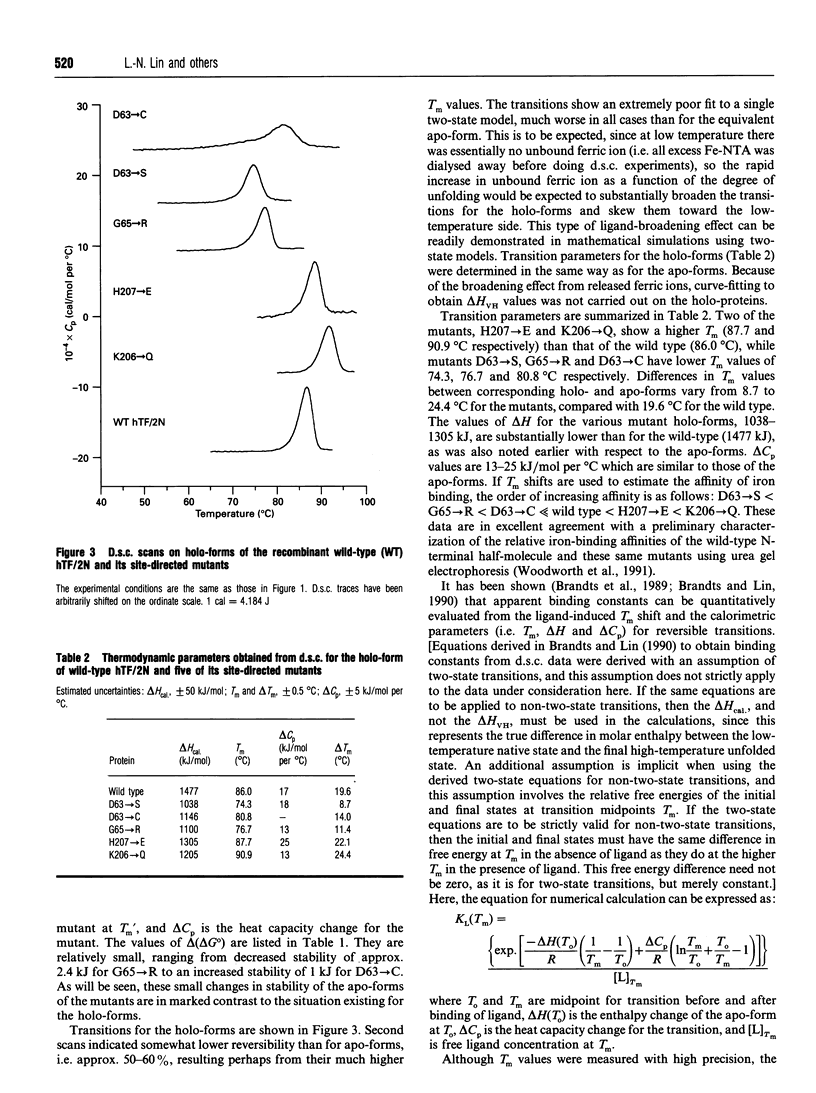
Abstract
The effects of single amino acid substitution on the thermal stability of the N-terminal half-molecule of human transferrin and its iron-binding affinity have been studied by high-sensitivity scanning calorimetry. All site-directed mutations are located on the surface of the binding cleft, and they are D63-->S, D63-->C, G65-->R, H207-->E and K206-->Q. Differential scanning calorimetry results show that the mutations do not significantly alter the conformational stability of the apo-forms of the proteins. The changes in free energy of unfolding relative to the wild-type protein range from 0.83 to -2.4 kJ/mol. The D63-->S, G54-->R and H207-->E mutations slightly destabilize the apo-protein, while the D63-->C and K206-->Q mutations increase its stability by a small amount. However, there are large compensating enthalpy-entropy changes caused by all mutations. All mutants bind ferric ion, but with different affinities. Replacement of Asp-63 by either Ser or Cys decreases the apparent binding constant by 5-6 orders of magnitude. The G65-->R mutation also decreases the apparent binding constant by 5 orders of magnitude. The K206-->Q mutation increases the apparent binding constant by 20-fold, while the H207-->E mutation does not significantly change the apparent iron-binding affinity of the half-molecule.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aisen P., Leibman A., Zweier J. Stoichiometric and site characteristics of the binding of iron to human transferrin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):1930–1937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson B. F., Baker H. M., Norris G. E., Rice D. W., Baker E. N. Structure of human lactoferrin: crystallographic structure analysis and refinement at 2.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1989 Oct 20;209(4):711–734. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90602-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson B. F., Baker H. M., Norris G. E., Rumball S. V., Baker E. N. Apolactoferrin structure demonstrates ligand-induced conformational change in transferrins. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):784–787. doi: 10.1038/344784a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Lin L. N., Brandts J. F., Mas M. T. Substitution of a proline for alanine 183 in the hinge region of phosphoglycerate kinase: effects on catalysis, activation by sulfate, and thermal stability. J Protein Chem. 1990 Feb;9(1):59–67. doi: 10.1007/BF01024985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey S., Evans R. W., Garratt R. C., Gorinsky B., Hasnain S., Horsburgh C., Jhoti H., Lindley P. F., Mydin A., Sarra R. Molecular structure of serum transferrin at 3.3-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 26;27(15):5804–5812. doi: 10.1021/bi00415a061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandts J. F., Hu C. Q., Lin L. N., Mos M. T. A simple model for proteins with interacting domains. Applications to scanning calorimetry data. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 17;28(21):8588–8596. doi: 10.1021/bi00447a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandts J. F., Lin L. N. Study of strong to ultratight protein interactions using differential scanning calorimetry. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 24;29(29):6927–6940. doi: 10.1021/bi00481a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly P., Ghosaini L., Hu C. Q., Kitamura S., Tanaka A., Sturtevant J. M. A differential scanning calorimetric study of the thermal unfolding of seven mutant forms of phage T4 lysozyme. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 19;30(7):1887–1891. doi: 10.1021/bi00221a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day C. L., Stowell K. M., Baker E. N., Tweedie J. W. Studies of the N-terminal half of human lactoferrin produced from the cloned cDNA demonstrate that interlobe interactions modulate iron release. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):13857–13862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funk W. D., MacGillivray R. T., Mason A. B., Brown S. A., Woodworth R. C. Expression of the amino-terminal half-molecule of human serum transferrin in cultured cells and characterization of the recombinant protein. Biochemistry. 1990 Feb 13;29(6):1654–1660. doi: 10.1021/bi00458a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill S. C., von Hippel P. H. Calculation of protein extinction coefficients from amino acid sequence data. Anal Biochem. 1989 Nov 1;182(2):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90602-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris W. R. Equilibrium constants for the complexation of metal ions by serum transferrin. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1989;249:67–93. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-9111-1_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Grutter M. G., Schellman J. Thermodynamic stability and point mutations of bacteriophage T4 lysozyme. J Mol Biol. 1984 May 15;175(2):195–212. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90474-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht M. H., Sturtevant J. M., Sauer R. T. Effect of single amino acid replacements on the thermal stability of the NH2-terminal domain of phage lambda repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5685–5689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrand D., Mazurier J., Colavizza D., Montreuil J., Spik G. Properties of the iron-binding site of the N-terminal lobe of human and bovine lactotransferrins. Importance of the glycan moiety and of the non-covalent interactions between the N- and C-terminal lobes in the stability of the iron-binding site. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 1;266(2):575–581. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. N., Mason A. B., Woodworth R. C., Brandts J. F. Calorimetric studies of the binding of ferric ions to ovotransferrin and interactions between binding sites. Biochemistry. 1991 Dec 17;30(50):11660–11669. doi: 10.1021/bi00114a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lineback-Zins J., Brew K. Preparation and characterization of an NH2-terminal fragment of human serum transferrin containing a single iron-binding site. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):708–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose T. M., Plowman G. D., Teplow D. B., Dreyer W. J., Hellström K. E., Brown J. P. Primary structure of the human melanoma-associated antigen p97 (melanotransferrin) deduced from the mRNA sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1261–1265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D., Meeker A. K., Freire E. Stability mutants of staphylococcal nuclease: large compensating enthalpy-entropy changes for the reversible denaturation reaction. Biochemistry. 1988 Jun 28;27(13):4761–4768. doi: 10.1021/bi00413a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth R. C., Mason A. B., Funk W. D., MacGillivray R. T. Expression and initial characterization of five site-directed mutants of the N-terminal half-molecule of human transferrin. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 12;30(45):10824–10829. doi: 10.1021/bi00109a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


