Abstract
Recombinant insulin-like growth factor-II (IGF-II) and two structural analogues, des(1-6)IGF-II and [Arg6]-IGF-II, were produced to investigate the role of N-terminal residues in binding to IGF-binding proteins (IGFBPs) and hence the biological properties of the modified peptides. The growth factors were modelled on two previously characterized variants of IGF-I, des(1-3)IGF-I and [Arg3]-IGF-I, which both show substantially decreased binding to IGFBPs and were expressed as fusion proteins in Escherichia coli. The biological activities of the corresponding analogues of IGF-I and IGF-II were compared in rat L6 myoblasts and H35B hepatoma cells. In the L6-myoblast protein-synthesis assay, the IGF-II analogues, des(1-6)IGF-II and [Arg6]-IGF-II, were slightly more potent than IGF-II but about 10-fold less potent than IGF-I and 100-fold less potent than the respective IGF-I analogues, des(1-3)IGF-I and [Arg3]IGF-I. In H35 hepatoma cells the anabolic response measured was the inhibition of protein breakdown, and the potency order was insulin >>> [Arg3]-IGF-I > des(1-3)IGF-I > [Arg6]-IGF-II > des(1-6)IGF-II > IGF-I > IGF-II. Binding of the IGFs and their analogues to the type 1 IGF receptor in L6 myoblasts and to the insulin receptor in H35 hepatoma cells did not fully explain the observed anabolic potency differences. Moreover, binding of all four analogues to the IGFBPs secreted by L6 myoblasts and H35B hepatoma cells was greatly decreased compared with the parent IGF. We conclude that the observed anabolic response to each IGF was determined by their relative binding to the competing cell receptor and IGFBP binding sites present.
Full text
PDF

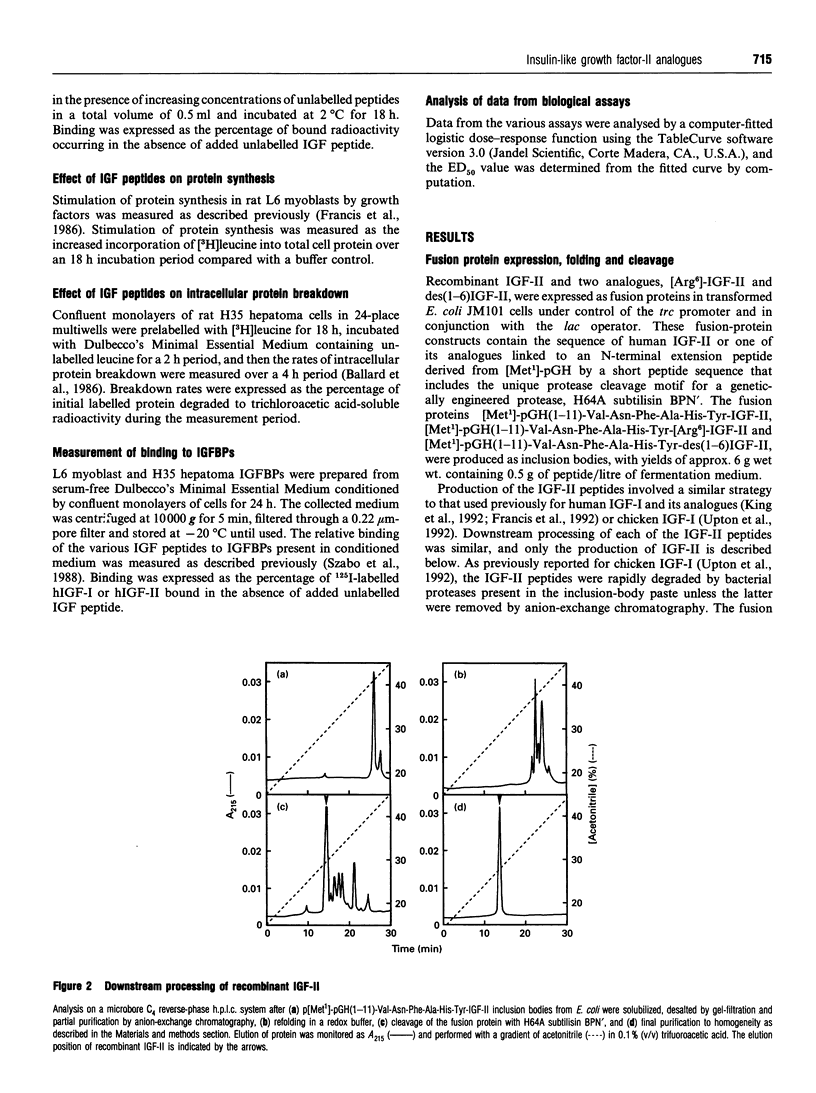
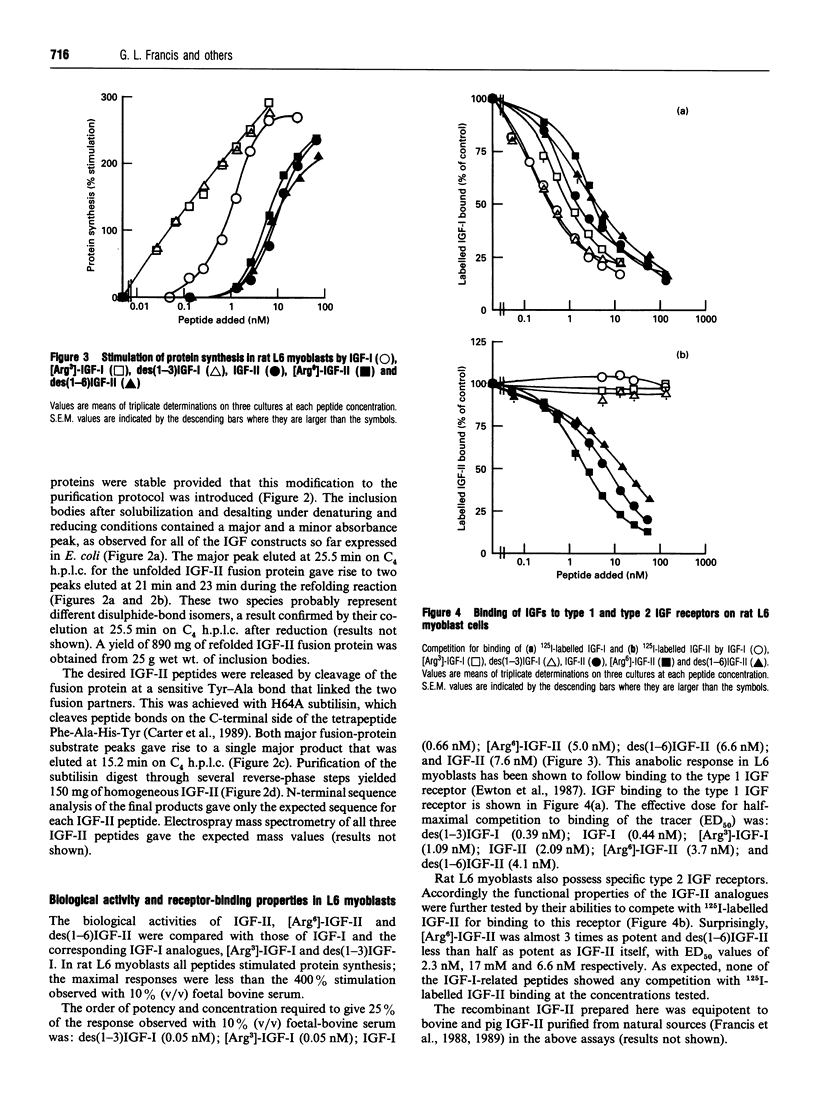
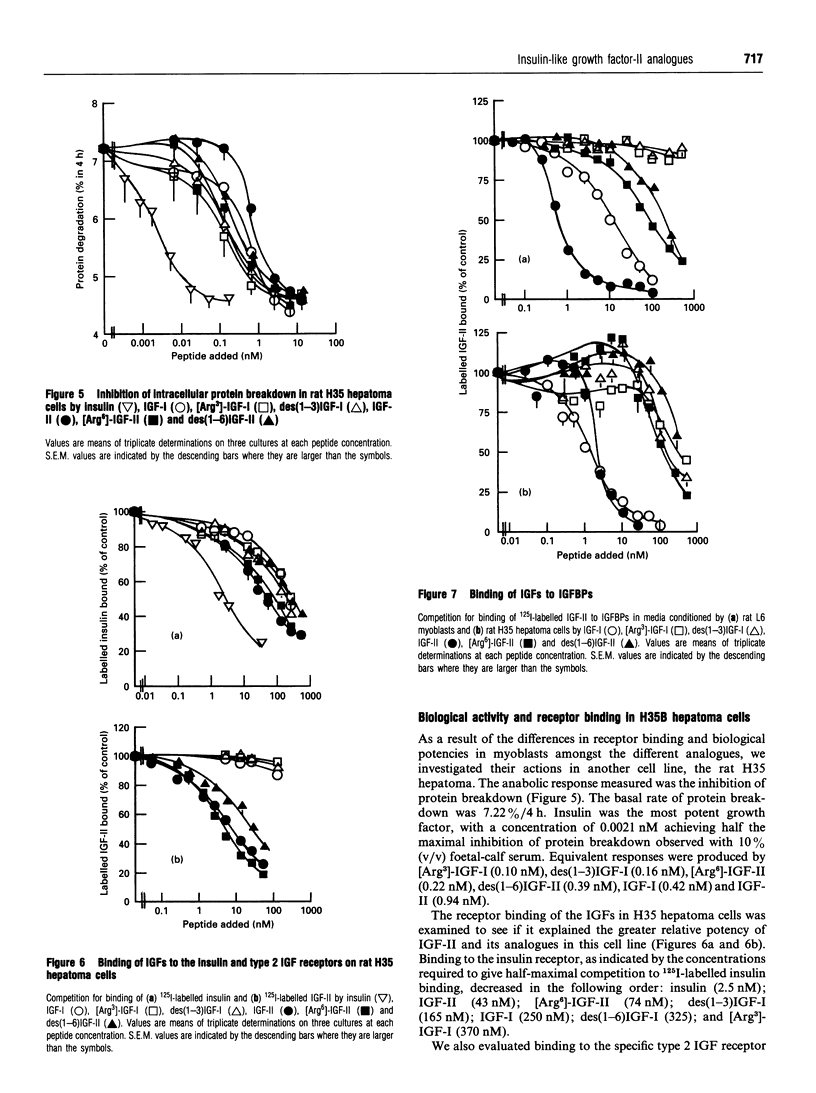
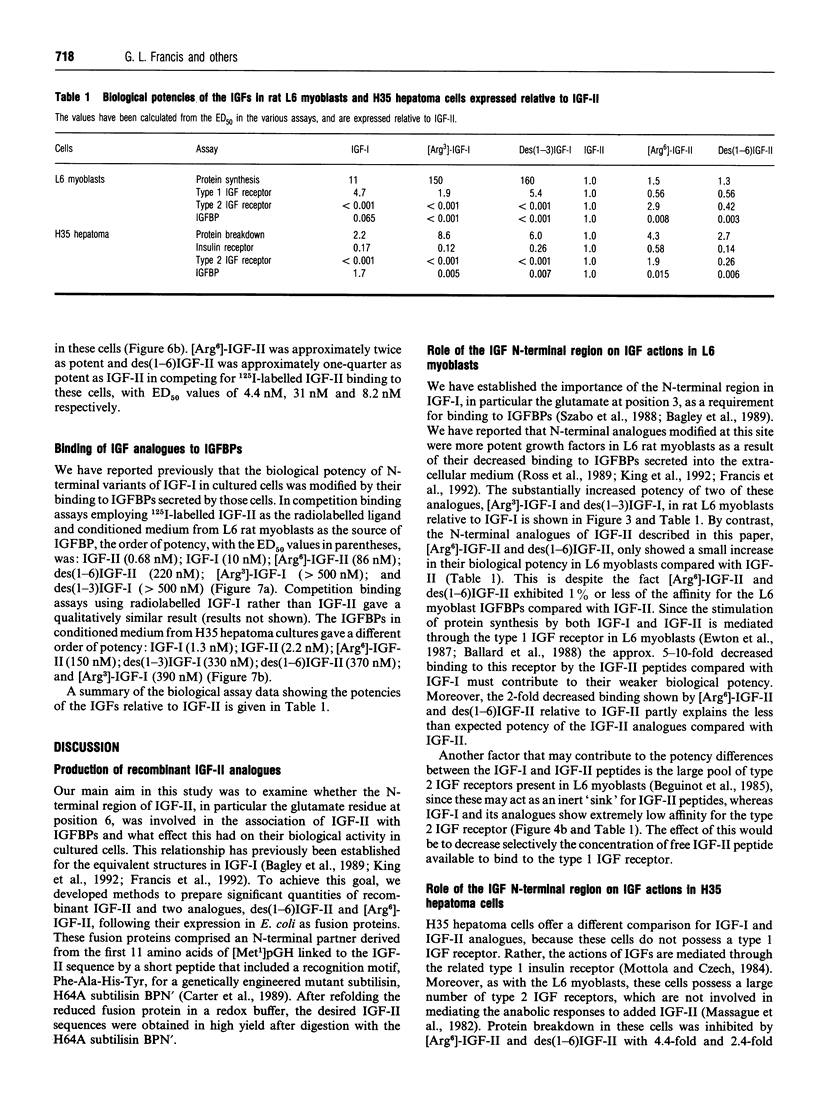

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagley C. J., May B. L., Szabo L., McNamara P. J., Ross M., Francis G. L., Ballard F. J., Wallace J. C. A key functional role for the insulin-like growth factor 1 N-terminal pentapeptide. Biochem J. 1989 May 1;259(3):665–671. doi: 10.1042/bj2590665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Read L. C., Francis G. L., Bagley C. J., Wallace J. C. Binding properties and biological potencies of insulin-like growth factors in L6 myoblasts. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 1;233(1):223–230. doi: 10.1042/bj2330223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard F. J., Ross M., Upton F. M., Francis G. L. Specific binding of insulin-like growth factors 1 and 2 to the type 1 and type 2 receptors respectively. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 1;249(3):721–726. doi: 10.1042/bj2490721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beguinot F., Kahn C. R., Moses A. C., Smith R. J. Distinct biologically active receptors for insulin, insulin-like growth factor I, and insulin-like growth factor II in cultured skeletal muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15892–15898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blundell T. L., Bedarkar S., Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. Insulin-like growth factor: a model for tertiary structure accounting for immunoreactivity and receptor binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):180–184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P., Nilsson B., Burnier J. P., Burdick D., Wells J. A. Engineering subtilisin BPN' for site-specific proteolysis. Proteins. 1989;6(3):240–248. doi: 10.1002/prot.340060306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewton D. Z., Falen S. L., Florini J. R. The type II insulin-like growth factor (IGF) receptor has low affinity for IGF-I analogs: pleiotypic actions of IGFs on myoblasts are apparently mediated by the type I receptor. Endocrinology. 1987 Jan;120(1):115–123. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-1-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis G. L., Owens P. C., McNeil K. A., Wallace J. C., Ballard F. J. Purification, amino acid sequences and assay cross-reactivities of porcine insulin-like growth factor-I and -II. J Endocrinol. 1989 Sep;122(3):681–687. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1220681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis G. L., Read L. C., Ballard F. J., Bagley C. J., Upton F. M., Gravestock P. M., Wallace J. C. Purification and partial sequence analysis of insulin-like growth factor-1 from bovine colostrum. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 1;233(1):207–213. doi: 10.1042/bj2330207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis G. L., Ross M., Ballard F. J., Milner S. J., Senn C., McNeil K. A., Wallace J. C., King R., Wells J. R. Novel recombinant fusion protein analogues of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I indicate the relative importance of IGF-binding protein and receptor binding for enhanced biological potency. J Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Jun;8(3):213–223. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0080213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis G. L., Upton F. M., Ballard F. J., McNeil K. A., Wallace J. C. Insulin-like growth factors 1 and 2 in bovine colostrum. Sequences and biological activities compared with those of a potent truncated form. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 1;251(1):95–103. doi: 10.1042/bj2510095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gargosky S. E., Walton P. E., Wallace J. C., Ballard F. J. Characterization of insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins in rat serum, lymph, cerebrospinal and amniotic fluids, and in media conditioned by liver, bone and muscle cells. J Endocrinol. 1990 Dec;127(3):391–400. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1270391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humbel R. E. Insulin-like growth factors I and II. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jul 5;190(3):445–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15595.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Hewick R. M., Dreyer W. J., Hood L. E. High-sensitivity sequencing with a gas-phase sequenator. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:399–413. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R., Wells J. R., Krieg P., Snoswell M., Brazier J., Bagley C. J., Wallace J. C., Ballard F. J., Ross M., Francis G. L. Production and characterization of recombinant insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and potent analogues of IGF-I, with Gly or Arg substituted for Glu3, following their expression in Escherichia coli as fusion proteins. J Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Feb;8(1):29–41. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0080029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüthi C., Roth B. V., Humbel R. E. Mutants of human insulin-like growth factor II (IGF II). Expression and characterization of truncated IGF II and of two naturally occurring variants. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Apr 15;205(2):483–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16804.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. G., Pfeffer S. R., Coussens L., Tepper M. A., Brocklebank C. M., Mole J. E., Anderson J. K., Chen E., Czech M. P., Ullrich A. A single receptor binds both insulin-like growth factor II and mannose-6-phosphate. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1134–1137. doi: 10.1126/science.2964083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Blinderman L. A., Czech M. P. The high affinity insulin receptor mediates growth stimulation in rat hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):13958–13963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mottola C., Czech M. P. The type II insulin-like growth factor receptor does not mediate increased DNA synthesis in H-35 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12705–12713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross M., Francis G. L., Szabo L., Wallace J. C., Ballard F. J. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding proteins inhibit the biological activities of IGF-1 and IGF-2 but not des-(1-3)-IGF-1. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 15;258(1):267–272. doi: 10.1042/bj2580267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano K., Enjoh T., Numata F., Fujiwara H., Marumoto Y., Higashihashi N., Sato Y., Perdue J. F., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y. The design, expression, and characterization of human insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) mutants specific for either the IGF-II/cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor or IGF-I receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):20626–20635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo L., Mottershead D. G., Ballard F. J., Wallace J. C. The bovine insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein purified from conditioned medium requires the N-terminal tripeptide in IGF-1 for binding. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 29;151(1):207–214. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90580-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomas F. M., Knowles S. E., Owens P. C., Chandler C. S., Francis G. L., Read L. C., Ballard F. J. Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and especially IGF-I variants are anabolic in dexamethasone-treated rats. Biochem J. 1992 Feb 15;282(Pt 1):91–97. doi: 10.1042/bj2820091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upton F. Z., Francis G. L., Ross M., Wallace J. C., Ballard F. J. Production and characterization of recombinant chicken insulin-like growth factor-I from Escherichia coli. J Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Aug;9(1):83–92. doi: 10.1677/jme.0.0090083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



