Abstract
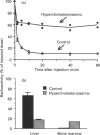
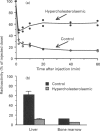
The accumulation of cholesterol-rich beta-very-low-density lipoproteins (beta-VLDL) in the plasma of rabbits fed on a high-fat high-cholesterol diet is due to a defect in the clearance of these lipoprotein remnants from circulation by the liver. In view of the evidence that hepatic lipase participates in the process of rapid removal of remnants from circulation, and considering that rabbits are naturally deficient in hepatic lipase, we examined whether this defect in the clearance of beta-VLDL could be reversed by exogenous hepatic lipase. We report that treatment in vitro of [3H]cholesterol-labelled beta-VLDL, or rat chylomicrons, with hepatic lipase resulted in the formation of particles that were rapidly cleared from circulation by the liver when injected intravenously into hypercholesterolaemic rabbits. These results are consistent with the notion that, in addition to the well-established requirement for lipoprotein lipase activity, the generation of remnants capable of being efficiently taken up by the liver also requires the action of hepatic lipase. Lipoprotein lipase acts on triacylglycerol-rich lipoproteins to transform them into particles (remnants) which bind to the surface of liver cells, where they become accessible to hepatic lipase. Hepatocyte endocytosis of these remnants occurs only after further modification by hepatic lipase. According to this scheme, the results presented suggest that the accumulation of beta-VLDL in the circulation of rabbits fed on a high-fat high-cholesterol diet is the result of the saturation of the available hepatic lipase by abnormally high levels of lipoprotein-lipase-generated chylomicron remnants.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABEL L. L., LEVY B. B., BRODIE B. B., KENDALL F. E. A simplified method for the estimation of total cholesterol in serum and demonstration of its specificity. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):357–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borensztajn J., Getz G. S., Kotlar T. J. Uptake of chylomicron remnants by the liver: further evidence for the modulating role of phospholipids. J Lipid Res. 1988 Aug;29(8):1087–1096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borensztajn J., Kotlar T. J., Chang S. Y. Apoprotein-independent binding of chylomicron remnants to rat liver membranes. Biochem J. 1991 Nov 1;279(Pt 3):769–773. doi: 10.1042/bj2790769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borensztajn J., Kotlar T. J. Liver uptake of chylomicron remnants with high and low apoprotein E:C ratios. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5863–5866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borensztajn J., Kotlar T. J., McNeill B. J. Uptake of phospholipid-depleted chylomicrons by the perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1980 Dec 15;192(3):845–851. doi: 10.1042/bj1920845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borensztajn J., Kotlar T. J. Phospholipids as modulators of hepatic recognition of chylomicron remnants. Observations with emulsified lipoprotein lipids. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 15;269(2):539–542. doi: 10.1042/bj2690539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breckenridge W. C., Little J. A., Alaupovic P., Wang C. S., Kuksis A., Kakis G., Lindgren F., Gardiner G. Lipoprotein abnormalities associated with a familial deficiency of hepatic lipase. Atherosclerosis. 1982 Nov;45(2):161–179. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(82)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrella M., Cooper A. D. High affinity binding of chylomicron remnants to rat liver plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):338–342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clay M. A., Hopkins G. J., Ehnholm C. P., Barter P. J. The rabbit as an animal model of hepatic lipase deficiency. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Apr 3;1002(2):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90284-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly P. W., Maguire G. F., Lee M., Little J. A. Plasma lipoproteins in familial hepatic lipase deficiency. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 Jan-Feb;10(1):40–48. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. D., Erickson S. K., Nutik R., Shrewsbury M. A. Characterization of chylomicron remnant binding to rat liver membranes. J Lipid Res. 1982 Jan;23(1):42–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daggy B. P., Bensadoun A. Enrichment of apolipoprotein B-48 in the LDL density class following in vivo inhibition of hepatic lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 27;877(2):252–261. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90302-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florén C. H., Nilsson A. Uptake and degradation of iodine-labelled chylomicron remnant particles by monolayers of rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 15;174(3):827–838. doi: 10.1042/bj1740827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. S., Mayes P. A. Comparison of the metabolism of chylomicrons and chylomicron remnants by the perfused liver. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 15;170(1):47–55. doi: 10.1042/bj1700047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I. J., Le N. A., Paterniti J. R., Jr, Ginsberg H. N., Lindgren F. T., Brown W. V. Lipoprotein metabolism during acute inhibition of hepatic triglyceride lipase in the cynomolgus monkey. J Clin Invest. 1982 Dec;70(6):1184–1192. doi: 10.1172/JCI110717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guldur T., Mayes P. A. Comparative hepatic metabolism of chylomicron remnants prepared in vivo or in vitro. Biochem Soc Trans. 1991 Aug;19(3):326S–326S. doi: 10.1042/bst019326s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui D. Y., Innerarity T. L., Milne R. W., Marcel Y. L., Mahley R. W. Binding of chylomicron remnants and beta-very low density lipoproteins to hepatic and extrahepatic lipoprotein receptors. A process independent of apolipoprotein B48. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15060–15068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain M. M., Mahley R. W., Boyles J. K., Lindquist P. A., Brecht W. J., Innerarity T. L. Chylomicron metabolism. Chylomicron uptake by bone marrow in different animal species. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17931–17938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita T., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Watanabe Y., Hornick C. A., Havel R. J. Hepatic uptake of chylomicron remnants in WHHL rabbits: a mechanism genetically distinct from the low density lipoprotein receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3623–3627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovanen P. T., Brown M. S., Basu S. K., Bilheimer D. W., Goldstein J. L. Saturation and suppression of hepatic lipoprotein receptors: a mechanism for the hypercholesterolemia of cholesterol-fed rabbits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1396–1400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo M., Matsuzawa Y., Sudo H., Ishikawa K., Yamamoto A., Tarui S. Specific modification of hepatic triglyceride lipase activity by ultracentrifugally separated serum lipoprotein fractions. J Biochem. 1980 Sep;88(3):905–908. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murase T., Itakura H. Accumulation of intermediate density lipoprotein in plasma after intravenous administration of hepatic triglyceride lipase antibody in rats. Atherosclerosis. 1981 Jun;39(3):293–300. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(81)90015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata Y., Chen J., Cooper A. D. Role of low density lipoprotein receptor-dependent and -independent sites in binding and uptake of chylomicron remnants in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):15151–15158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross A. C., Zilversmit D. B. Chylomicron remnant cholesteryl esters as the major constituent of very low density lipoproteins in plasma of cholesterol-fed rabbits. J Lipid Res. 1977 Mar;18(2):169–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultan F., Lagrange D., Griglio S. In vitro binding and in vivo uptake of chylomicron remnants after their hydrolysis by hepatic lipase. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991;285:311–317. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5904-3_37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultan F., Lagrange D., Jansen H., Griglio S. Inhibition of hepatic lipase activity impairs chylomicron remnant-removal in rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jan 16;1042(1):150–152. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(90)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultan F., Lagrange D., Le Liepvre X., Griglio S. Chylomicron-remnant uptake by freshly isolated hepatocytes. Effect of heparin and of hepatic triacylglycerol lipase. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 1;258(2):587–594. doi: 10.1042/bj2580587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren R. J., Ebert D. L., Mitchell A., Barter P. J. Rabbit hepatic lipase cDNA sequence: low activity is associated with low messenger RNA levels. J Lipid Res. 1991 Aug;32(8):1333–1339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windler E. E., Greeve J., Daerr W. H., Greten H. Binding of rat chylomicrons and their remnants to the hepatic low-density-lipoprotein receptor and its role in remnant removal. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 1;252(2):553–561. doi: 10.1042/bj2520553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dijk M. C., Ziere G. J., van Berkel T. J. Characterization of the chylomicron-remnant-recognition sites on parenchymal and Kupffer cells of rat liver. Selective inhibition of parenchymal cell recognition by lactoferrin. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Apr 15;205(2):775–784. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16842.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]