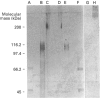
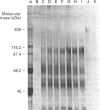
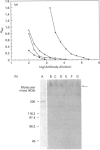
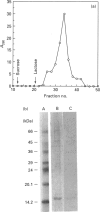
Abstract
The S-type lectins have been shown to be components of mucosal scrapings, and in avian systems these lectins have been localized immunohistochemically to the mucosal surface and goblet cells of the intestine. The interaction of lectin specifically with purified mucin has not, however, been established. Quail intestinal mucin was purified by two subsequent isopycnic density-gradient centrifugations in CsCl and chromatography on Sepharose Cl-2B. Purified mucin, obtained from the void volume of the Sepharose column, was characterized by SDS/PAGE, amino acid and carbohydrate analyses, sensitivity to thiol reduction, and cross-reactivity with antibody preparations to rat and human intestinal mucins on Western blots. Antibody raised against purified quail mucin partially cross-reacts with purified rat, rabbit and human intestinal mucins, and specifically labels the mucosal surface and goblet cells of quail intestine by the immunoperoxidase technique. Protein eluted by lactose from an affinity matrix composed of quail intestinal mucin possessed the same molecular mass on SDS/PAGE as intestinal lectin and reacted on Western blots with a lectin-specific antibody. The data clearly demonstrate the co-localization of lectin and mucin in the quail intestine and also the ability of the lectin to specifically interact with the purified mucin, raising the question of the role of endogenous lectins in secretions.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beyer E. C., Barondes S. H. Chicken tissue binding sites for a purified chicken lectin. J Supramol Struct. 1980;13(2):219–227. doi: 10.1002/jss.400130210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer E. C., Tokuyasu K. T., Barondes S. H. Localization of an endogenous lectin in chicken liver, intestine, and pancreas. J Cell Biol. 1979 Aug;82(2):565–571. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.2.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bols N. C., Roberson M. M., Haywood-Reid P. L., Cerra R. F., Barondes S. H. Secretion of a cytoplasmic lectin from Xenopus laevis skin. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):492–499. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceri H., Hwang W. S., Rabin H. Structure, secretion, and bacterial specificity of an endogenous lectin from cystic fibrosis lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Jul;5(1):51–55. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerra R. F., Gitt M. A., Barondes S. H. Three soluble rat beta-galactoside-binding lectins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10474–10477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadee K., Keller K., Forstner J., Innes D. J., Ravdin J. I. Mucin and nonmucin secretagogue activity of Entamoeba histolytica and cholera toxin in rat colon. Gastroenterology. 1991 Apr;100(4):986–997. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90274-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin M. F. A rapid and sensitive method for the analysis of carbohydrate components in glycoproteins using gas-liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jul 1;123(2):336–341. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90455-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerch L. B., Whitney P., Hass M., Brew K., Miller T., Werner R., Massaro D. Sequence of a full-length cDNA for rat lung beta-galactoside-binding protein: primary and secondary structure of the lectin. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 26;27(2):692–699. doi: 10.1021/bi00402a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. S., Rossoll R., Cabelli V. J., Yang S. L., Laux D. C. Relationship between the mouse colonizing ability of a human fecal Escherichia coli strain and its ability to bind a specific mouse colonic mucous gel protein. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):62–69. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.62-69.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang R. X., Ceri H. Characterization of an endogenous quail intestinal lectin. Biochem Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;68(2):471–475. doi: 10.1139/o90-066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendimenico G. J., Bouquin P. L., Tramposch K. M. Diphenylamine-colorimetric method for DNA assay: a shortened procedure by incubating samples at 50 degrees C. Anal Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;173(1):45–48. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90156-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison F. L., FitzGerald J. E., Catt J. W. Endogenous beta-galactoside-specific lectins in rabbit tissues. J Cell Sci. 1984 Dec;72:147–162. doi: 10.1242/jcs.72.1.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. M., Berry A. Mechanism of action of porphobilinogen deaminase. The participation of stable enzyme substrate covalent intermediates between porphobilinogen and the porphobilinogen deaminase from Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Biochem J. 1981 Apr 1;195(1):177–181. doi: 10.1042/bj1950177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffler H., Masiarz F. R., Barondes S. H. Soluble lactose-binding vertebrate lectins: a growing family. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 14;28(23):9222–9229. doi: 10.1021/bi00449a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev B., Ward H., Keusch G. T., Pereira M. E. Lectin activation in Giardia lamblia by host protease: a novel host-parasite interaction. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):71–73. doi: 10.1126/science.3513312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack D. R., Sherman P. M. Mucin isolated from rabbit colon inhibits in vitro binding of Escherichia coli RDEC-1. Infect Immun. 1991 Mar;59(3):1015–1023. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.3.1015-1023.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantle M., Allen A. A colorimetric assay for glycoproteins based on the periodic acid/Schiff stain [proceedings]. Biochem Soc Trans. 1978;6(3):607–609. doi: 10.1042/bst0060607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantle M., Basaraba L., Peacock S. C., Gall D. G. Binding of Yersinia enterocolitica to rabbit intestinal brush border membranes, mucus, and mucin. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3292–3299. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3292-3299.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantle M. Effects of hydrogen peroxide, mild trypsin digestion and partial reduction on rat intestinal mucin and its disulphide-bound 118 kDa glycoprotein. Biochem J. 1991 Mar 15;274(Pt 3):679–685. doi: 10.1042/bj2740679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantle M., Forstner G. G., Forstner J. F. Antigenic and structural features of goblet-cell mucin of human small intestine. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 1;217(1):159–167. doi: 10.1042/bj2170159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantle M., Thakore E., Atkins E., Mathison R., Davison J. S. Effects of streptozotocin-diabetes on rat intestinal mucin and goblet cells. Gastroenterology. 1989 Jul;97(1):68–75. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91417-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantle M., Thakore E. Rabbit intestinal and colonic mucins: isolation, partial characterization, and measurement of secretion using an enzyme-linked immunoassay. Biochem Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;66(10):1045–1054. doi: 10.1139/o88-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSweegan E., Walker R. I. Identification and characterization of two Campylobacter jejuni adhesins for cellular and mucous substrates. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):141–148. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.141-148.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouricout M. A., Julien R. A. Pilus-mediated binding of bovine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli to calf small intestinal mucins. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1216–1223. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1216-1223.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Jackson T. F., Gathiram V., Kress K., Saffer L. D., Snodgrass T. L., Chapman M. D., Keren Z., Mirelman D. Pathogenic and nonpathogenic strains of Entamoeba histolytica can be differentiated by monoclonal antibodies to the galactose-specific adherence lectin. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1802–1806. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1802-1806.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffer L. D., Petri W. A., Jr Role of the galactose lectin of Entamoeba histolytica in adherence-dependent killing of mammalian cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4681–4683. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4681-4683.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajjan S. U., Forstner J. F. Characteristics of binding of Escherichia coli serotype O157:H7 strain CL-49 to purified intestinal mucin. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):860–867. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.860-867.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajjan S. U., Forstner J. F. Role of the putative "link" glycopeptide of intestinal mucin in binding of piliated Escherichia coli serotype O157:H7 strain CL-49. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):868–873. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.868-873.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford B. A., Thomas V. L., Ramsay M. A. Binding of staphylococci to mucus in vivo and in vitro. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3735–3742. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3735-3742.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiomi K., Uematsu H., Yamanaka H., Kikuchi T. Purification and characterization of a galactose-binding lectin from the skin mucus of the conger eel Conger myriaster. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1989;92(2):255–261. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(89)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparrow C. P., Leffler H., Barondes S. H. Multiple soluble beta-galactoside-binding lectins from human lung. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7383–7390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanke C. A., Cronan S., Goss C., Chadee K., Guerrant R. L. Characterization of binding of Escherichia coli strains which are enteropathogens to small-bowel mucin. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):794–800. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.794-800.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G., Huan L. J., Khatri I. A., Wang D., Bennick A., Fahim R. E., Forstner G. G., Forstner J. F. cDNA for the carboxyl-terminal region of a rat intestinal mucin-like peptide. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5401–5407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Yokota T. Electron microscopic study of Vibrio cholerae O1 adherence to the mucus coat and villus surface in the human small intestine. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2753–2759. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2753-2759.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]