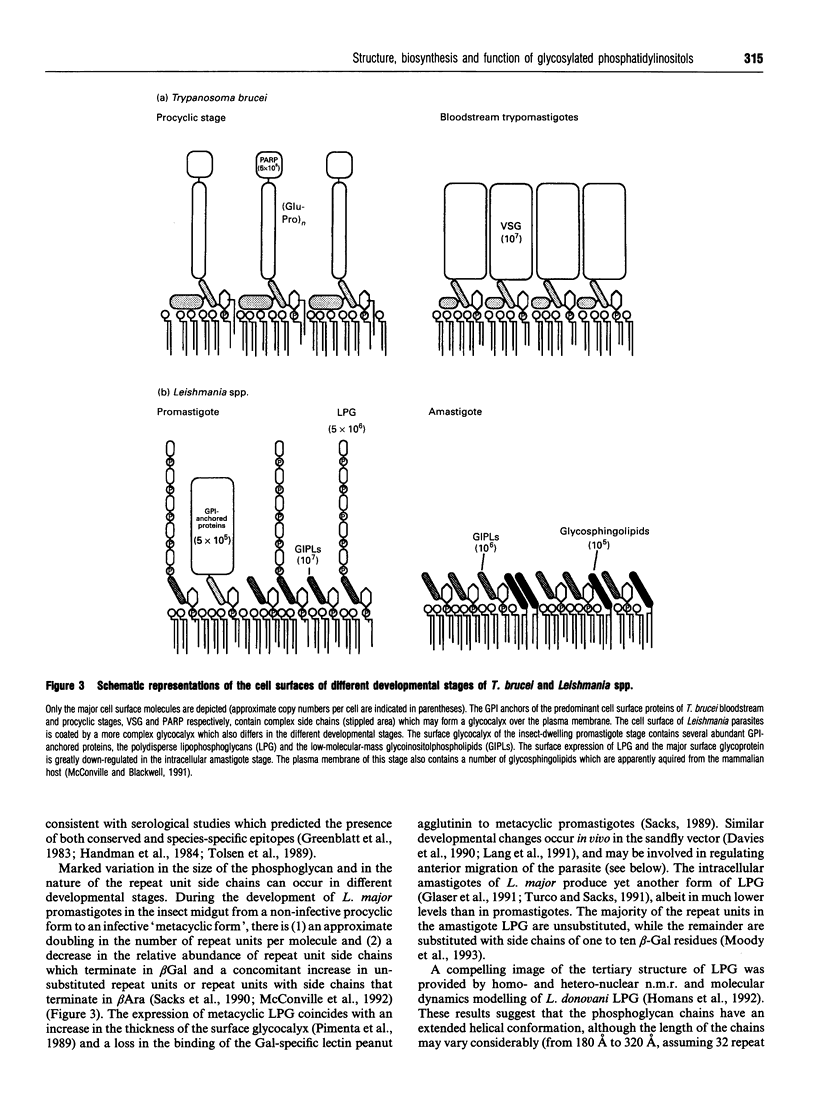
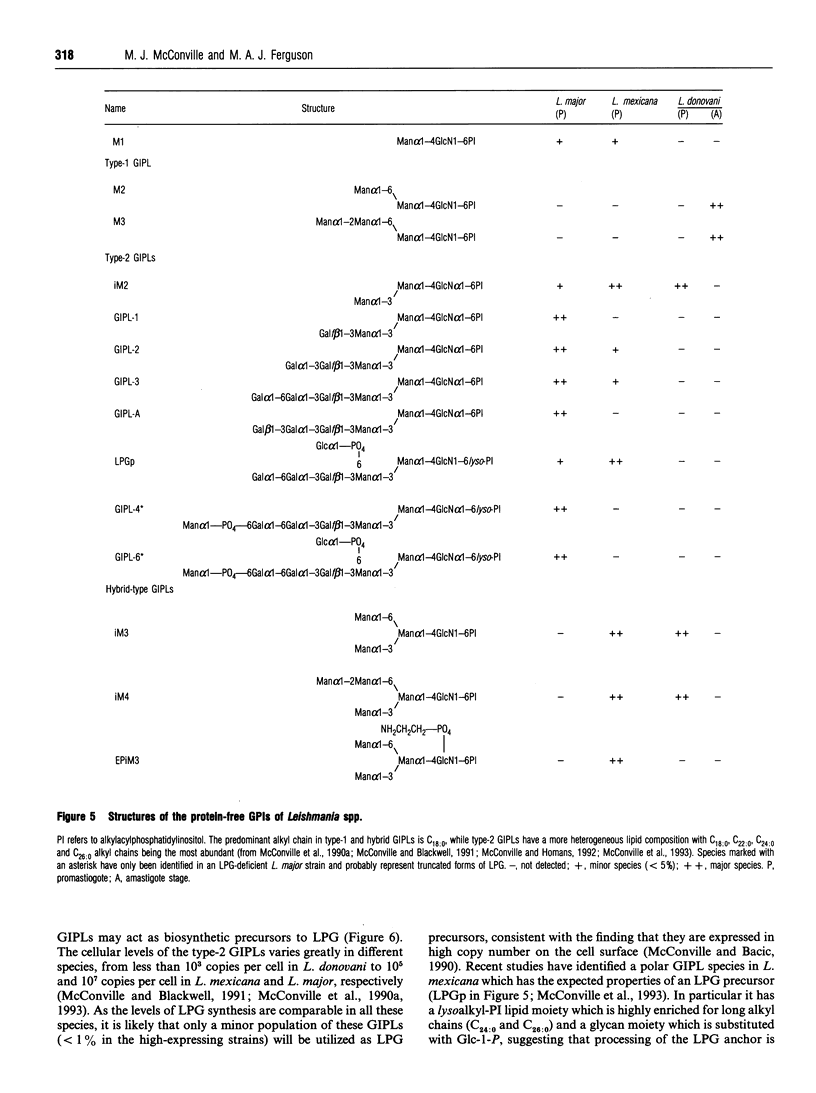
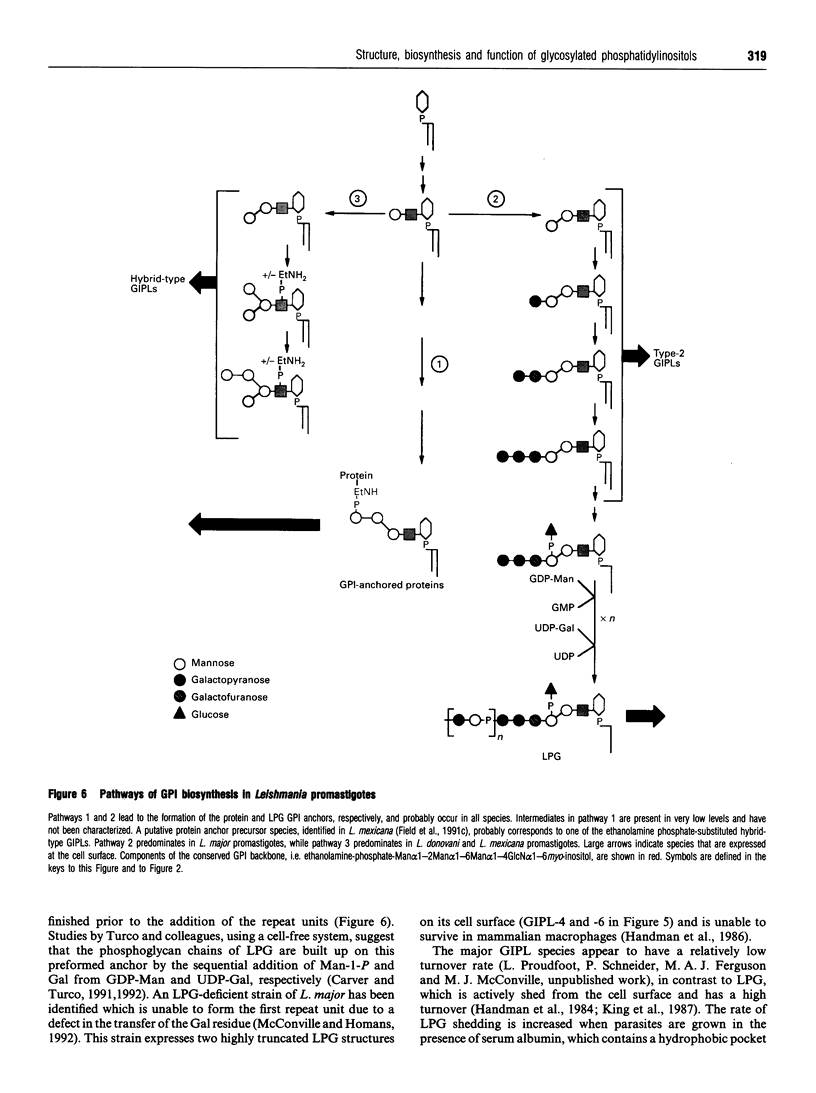
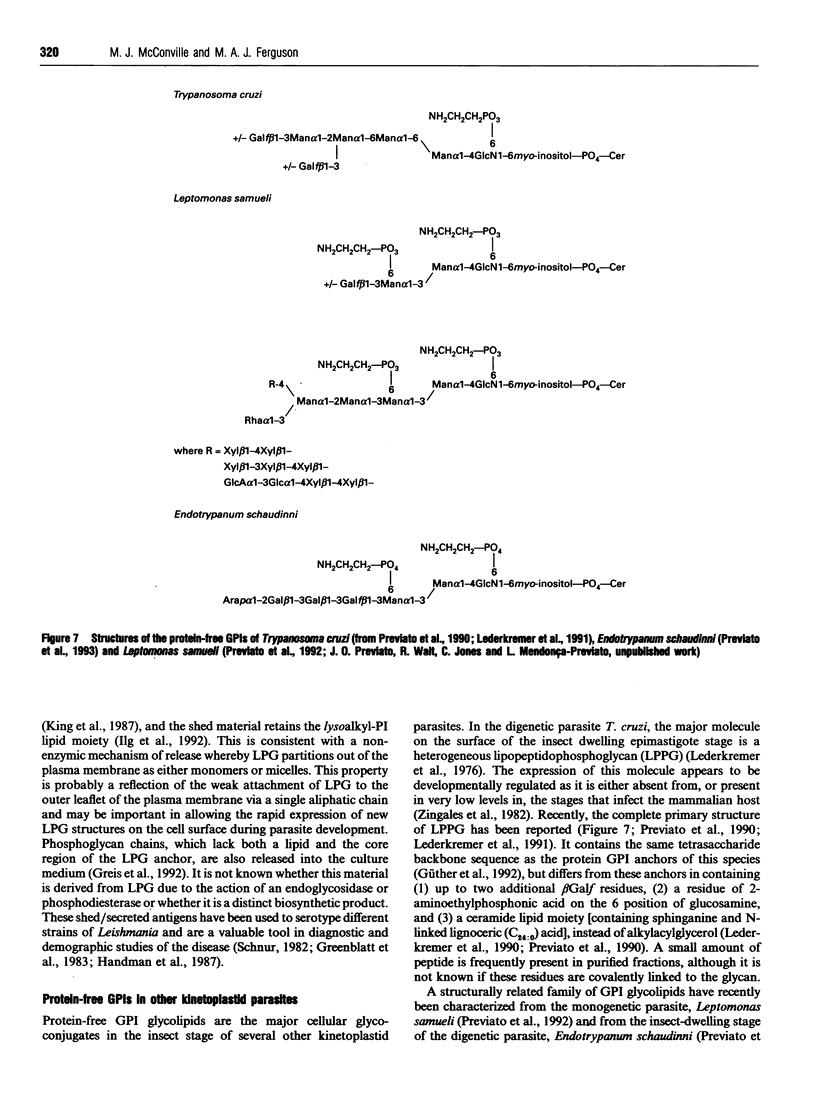
Full text
PDF
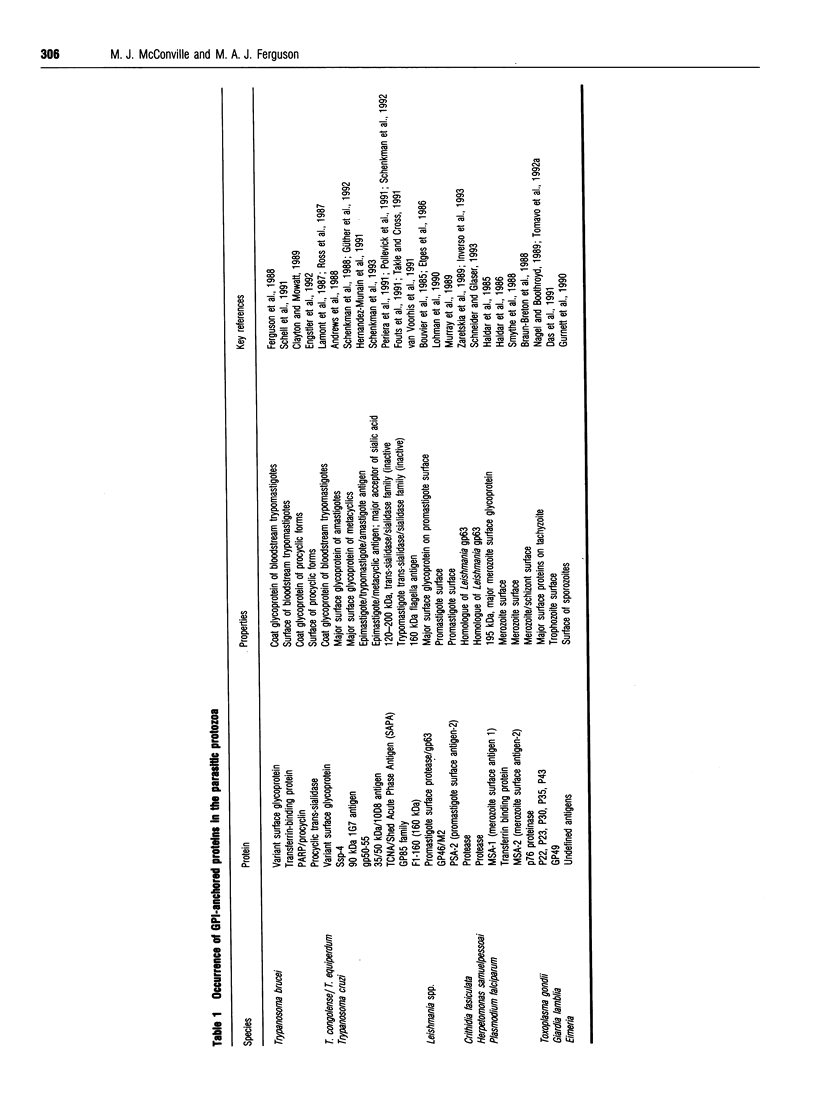

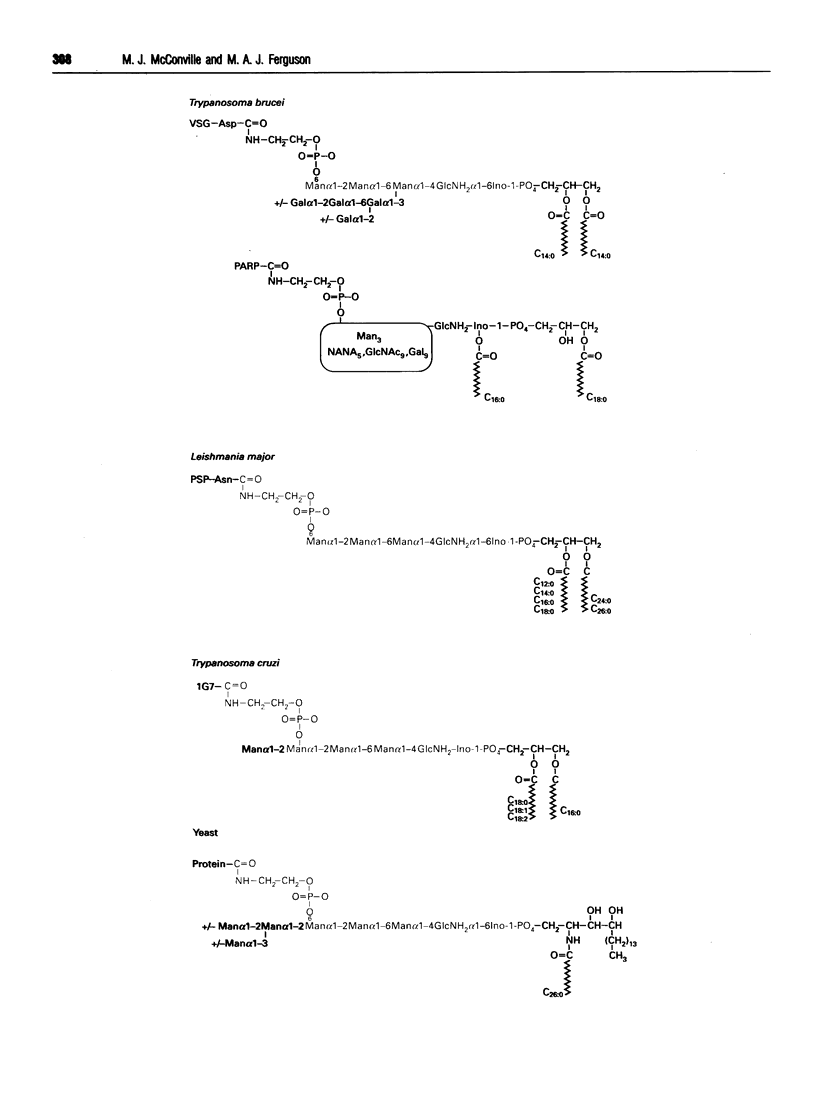
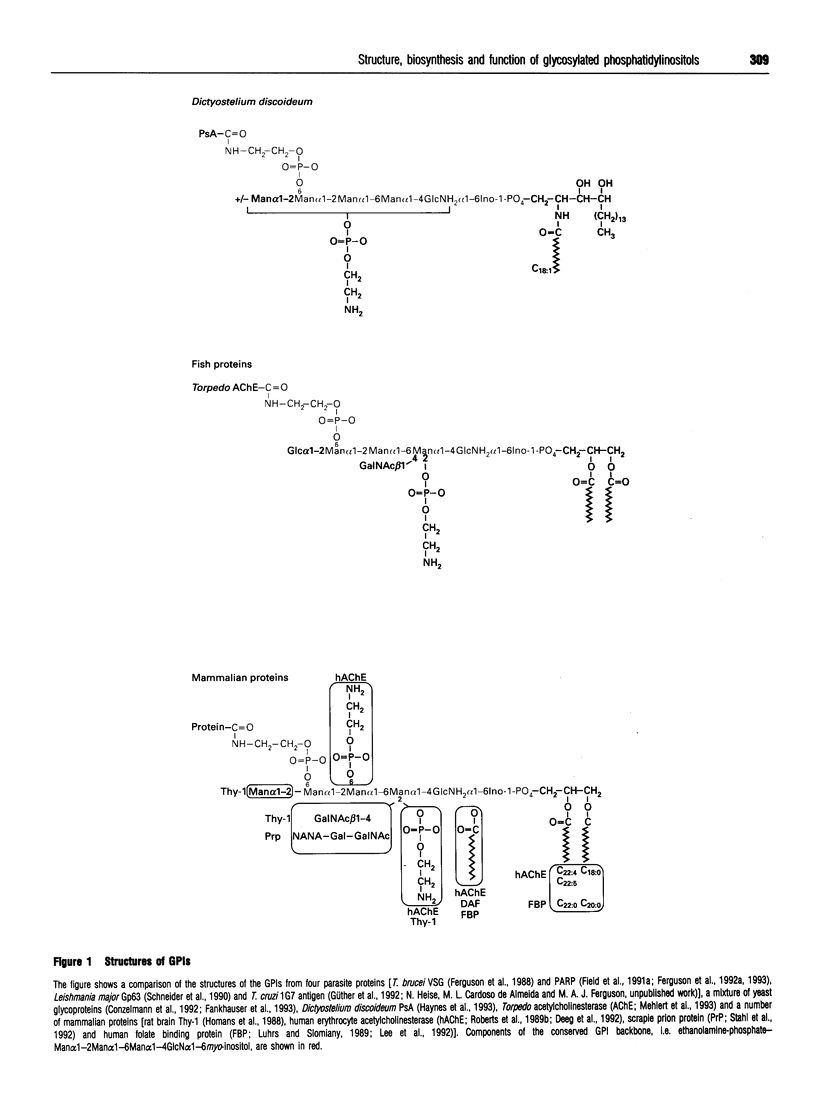
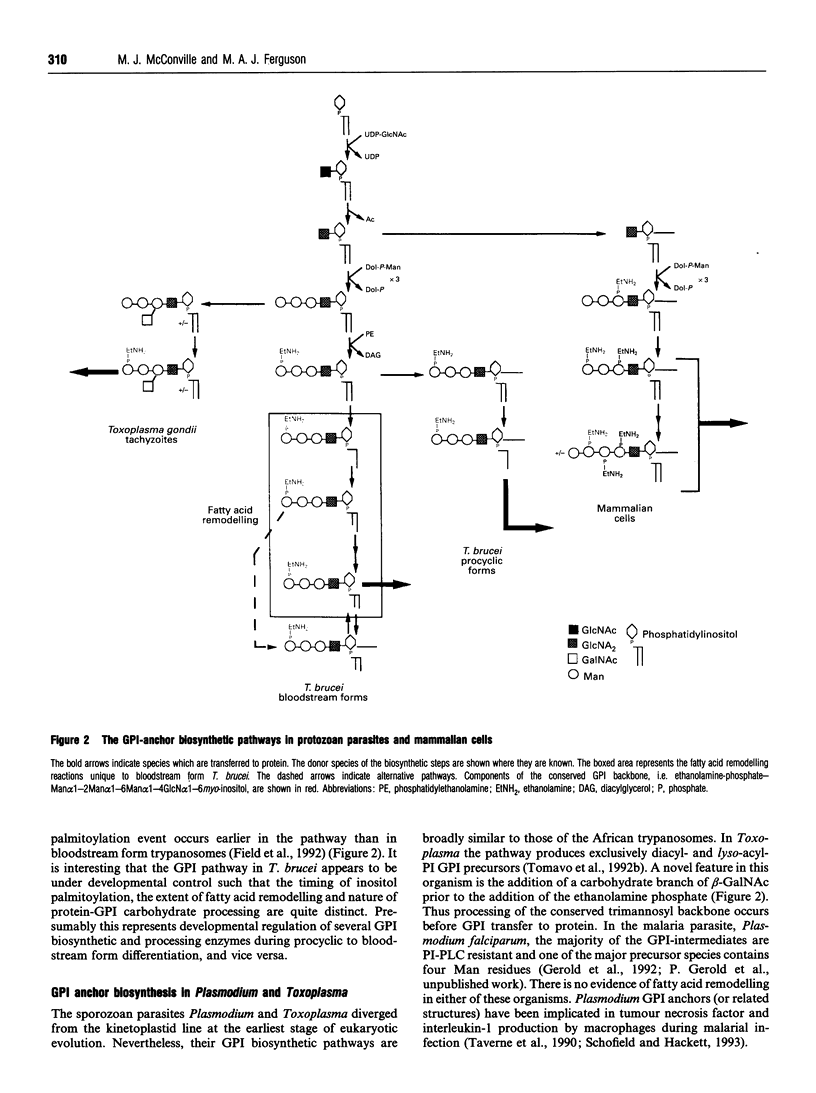










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abeijon C., Hirschberg C. B. Topography of glycosylation reactions in the endoplasmic reticulum. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jan;17(1):32–36. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90424-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amthauer R., Kodukula K., Brink L., Udenfriend S. Phosphatidylinositol-glycan (PI-G)-anchored membrane proteins: requirement of ATP and GTP for translation-independent COOH-terminal processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6124–6128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amthauer R., Kodukula K., Gerber L., Udenfriend S. Evidence that the putative COOH-terminal signal transamidase involved in glycosylphosphatidylinositol protein synthesis is present in the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3973–3977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. L., Shen L., Eicher D. M., Wewers M. D., Gill J. K. Phagocytosis mediated by three distinct Fc gamma receptor classes on human leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1990 Apr 1;171(4):1333–1345. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.4.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. G., Kamen B. A., Rothberg K. G., Lacey S. W. Potocytosis: sequestration and transport of small molecules by caveolae. Science. 1992 Jan 24;255(5043):410–411. doi: 10.1126/science.1310359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews N. W., Robbins E. S., Ley V., Hong K. S., Nussenzweig V. Developmentally regulated, phospholipase C-mediated release of the major surface glycoprotein of amastigotes of Trypanosoma cruzi. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):300–314. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C., Schubert J., Ueda E., Knez J. J., Gelperin D., Hirose S., Silber R., Hollan S., Schmidt R. E., Medof M. E. Affected paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria T lymphocytes harbor a common defect in assembly of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine inositol phospholipid corresponding to that in class A Thy-1- murine lymphoma mutants. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):25347–25351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avila J. L., Rojas M., Acosta A. Glycoinositol phospholipids from American Leishmania and Trypanosoma spp: partial characterization of the glycan cores and the human humoral immune response to them. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Oct;29(10):2305–2312. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.10.2305-2312.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahr V., Stierhof Y. D., Ilg T., Demar M., Quinten M., Overath P. Expression of lipophosphoglycan, high-molecular weight phosphoglycan and glycoprotein 63 in promastigotes and amastigotes of Leishmania mexicana. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 Mar;58(1):107–121. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90095-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamezai A., Goldmacher V. S., Rock K. L. Internalization of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored lymphocyte proteins. II. GPI-anchored and transmembrane molecules internalize through distinct pathways. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jan;22(1):15–21. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bangs J. D., Doering T. L., Englund P. T., Hart G. W. Biosynthesis of a variant surface glycoprotein of Trypanosoma brucei. Processing of the glycolipid membrane anchor and N-linked oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17697–17705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bangs J. D., Hereld D., Krakow J. L., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. Rapid processing of the carboxyl terminus of a trypanosome variant surface glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3207–3211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya A., Prasad R., Sacks D. L. Identification and partial characterization of a lipophosphoglycan from a pathogenic strain of Entamoeba histolytica. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Nov;56(1):161–168. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90163-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell J. M., Ezekowitz R. A., Roberts M. B., Channon J. Y., Sim R. B., Gordon S. Macrophage complement and lectin-like receptors bind Leishmania in the absence of serum. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):324–331. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier J., Etges R. J., Bordier C. Identification and purification of membrane and soluble forms of the major surface protein of Leishmania promastigotes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15504–15509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun-Breton C., Rosenberry T. L., da Silva L. P. Induction of the proteolytic activity of a membrane protein in Plasmodium falciparum by phosphatidyl inositol-specific phospholipase C. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):457–459. doi: 10.1038/332457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breton C. B., Blisnick T., Jouin H., Barale J. C., Rabilloud T., Langsley G., Pereira da Silva L. H. Plasmodium chabaudi p68 serine protease activity required for merozoite entry into mouse erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9647–9651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S., Thomson J. N., Pearse B. M. Coated pits act as molecular filters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4156–4159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A. Interactions between GPI-anchored proteins and membrane lipids. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;2(11):338–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Rose J. K. Sorting of GPI-anchored proteins to glycolipid-enriched membrane subdomains during transport to the apical cell surface. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):533–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90189-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölow R., Griffiths G., Webster P., Stierhof Y. D., Opperdoes F. R., Overath P. Intracellular localization of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C of Trypanosoma brucei. J Cell Sci. 1989 Jun;93(Pt 2):233–240. doi: 10.1242/jcs.93.2.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülow R., Nonnengässer C., Overath P. Release of the variant surface glycoprotein during differentiation of bloodstream to procyclic forms of Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Jan 1;32(1):85–92. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caras I. W. Probing the signal for glycophosphatidylinositol anchor attachment using decay accelerating factor as a model system. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1991 Sep;15(9):815–826. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(91)90035-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington M., Bülow R., Reinke H., Overath P. Sequence and expression of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C of Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Mar 15;33(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carver M. A., Turco S. J. Biosynthesis of lipophosphoglycan from Leishmania donovani: characterization of mannosylphosphate transfer in vitro. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Jun;295(2):309–317. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90523-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carver M. A., Turco S. J. Cell-free biosynthesis of lipophosphoglycan from Leishmania donovani. Characterization of microsomal galactosyltransferase and mannosyltransferase activities. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):10974–10981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J., Fujiwara T., Brennan P., McNeil M., Turco S. J., Sibille J. C., Snapper M., Aisen P., Bloom B. R. Microbial glycolipids: possible virulence factors that scavenge oxygen radicals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2453–2457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cinek T., Horejsí V. The nature of large noncovalent complexes containing glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-anchored membrane glycoproteins and protein tyrosine kinases. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 1;149(7):2262–2270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton C. E., Mowatt M. R. The procyclic acidic repetitive proteins of Trypanosoma brucei. Purification and post-translational modification. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):15088–15093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann A., Puoti A., Lester R. L., Desponds C. Two different types of lipid moieties are present in glycophosphoinositol-anchored membrane proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):457–466. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05075.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann A., Riezman H., Desponds C., Bron C. A major 125-kd membrane glycoprotein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is attached to the lipid bilayer through an inositol-containing phospholipid. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2233–2240. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03063.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costello L. C., Orlean P. Inositol acylation of a potential glycosyl phosphoinositol anchor precursor from yeast requires acyl coenzyme A. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8599–8603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Cellular and genetic aspects of antigenic variation in trypanosomes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:83–110. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.000503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Glycolipid anchoring of plasma membrane proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:1–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva R. P., Hall B. F., Joiner K. A., Sacks D. L. CR1, the C3b receptor, mediates binding of infective Leishmania major metacyclic promastigotes to human macrophages. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 15;143(2):617–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das S., Traynor-Kaplan A., Reiner D. S., Meng T. C., Gillin F. D. A surface antigen of Giardia lamblia with a glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):21318–21325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies C. R., Cooper A. M., Peacock C., Lane R. P., Blackwell J. M. Expression of LPG and GP63 by different developmental stages of Leishmania major in the sandfly Phlebotomus papatasi. Parasitology. 1990 Dec;101(Pt 3):337–343. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000060522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lederkremer R. M., Alves M. J., Fonseca G. C., Colli W. A lipopeptidophosphoglycan from Trypanosoma cruzi (epimastigota). Isolation, purification and carbohydrate composition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 24;444(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90226-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dearborn D. G., Smith S., Korn E. D. Lipophosphonoglycan of the plasma membrane of A canthamoeba castellanii. Inositol and phytosphingosine content and general structural features. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 25;251(10):2976–2982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeg M. A., Humphrey D. R., Yang S. H., Ferguson T. R., Reinhold V. N., Rosenberry T. L. Glycan components in the glycoinositol phospholipid anchor of human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Novel fragments produced by trifluoroacetic acid. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18573–18580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descoteaux A., Matlashewski G., Turco S. J. Inhibition of macrophage protein kinase C-mediated protein phosphorylation by Leishmania donovani lipophosphoglycan. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 1;149(9):3008–3015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Descoteaux A., Turco S. J., Sacks D. L., Matlashewski G. Leishmania donovani lipophosphoglycan selectively inhibits signal transduction in macrophages. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 15;146(8):2747–2753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doering T. L., Masterson W. J., Englund P. T., Hart G. W. Biosynthesis of the glycosyl phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor of the trypanosome variant surface glycoprotein. Origin of the non-acetylated glucosamine. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11168–11173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doering T. L., Masterson W. J., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. Biosynthesis of glycosyl phosphatidylinositol membrane anchors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):611–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doering T. L., Pessin M. S., Hoff E. F., Hart G. W., Raben D. M., Englund P. T. Trypanosome metabolism of myristate, the fatty acid required for the variant surface glycoprotein membrane anchor. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9215–9222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doering T. L., Raper J., Buxbaum L. U., Adams S. P., Gordon J. I., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. An analog of myristic acid with selective toxicity for African trypanosomes. Science. 1991 Jun 28;252(5014):1851–1854. doi: 10.1126/science.1829548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer C. A., Benjamins J. A. Glycolipids and transmembrane signaling: antibodies to galactocerebroside cause an influx of calcium in oligodendrocytes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):625–633. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilam Y., El-On J., Spira D. T. Leishmania major: excreted factor, calcium ions, and the survival of amastigotes. Exp Parasitol. 1985 Apr;59(2):161–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(85)90068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-On J., Bradley D. J., Freeman J. C. Leishmania donovani: action of excreted factor on hydrolytic enzyme activity of macrophages from mice with genetically different resistance to infection. Exp Parasitol. 1980 Apr;49(2):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(80)90114-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elhay M., Kelleher M., Bacic A., McConville M. J., Tolson D. L., Pearson T. W., Handman E. Lipophosphoglycan expression and virulence in ricin-resistant variants of Leishmania major. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 May;40(2):255–267. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90047-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englund P. T. The structure and biosynthesis of glycosyl phosphatidylinositol protein anchors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:121–138. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engstler M., Reuter G., Schauer R. Purification and characterization of a novel sialidase found in procyclic culture forms of Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Aug;54(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90091-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etges R., Bouvier J., Bordier C. The major surface protein of Leishmania promastigotes is anchored in the membrane by a myristic acid-labeled phospholipid. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):597–601. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04252.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A. Colworth Medal Lecture. Glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane anchors: the tale of a tail. Biochem Soc Trans. 1992 May;20(2):243–256. doi: 10.1042/bst0200243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Duszenko M., Lamont G. S., Overath P., Cross G. A. Biosynthesis of Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoproteins. N-glycosylation and addition of a phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):356–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Homans S. W., Dwek R. A., Rademacher T. W. Glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol moiety that anchors Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein to the membrane. Science. 1988 Feb 12;239(4841 Pt 1):753–759. doi: 10.1126/science.3340856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Murray P., Rutherford H., McConville M. J. A simple purification of procyclic acidic repetitive protein and demonstration of a sialylated glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor. Biochem J. 1993 Apr 1;291(Pt 1):51–55. doi: 10.1042/bj2910051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A. Site of palmitoylation of a phospholipase C-resistant glycosylphosphatidylinositol membrane anchor. Biochem J. 1992 Jun 1;284(Pt 2):297–300. doi: 10.1042/bj2840297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Williams A. F. Cell-surface anchoring of proteins via glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol structures. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:285–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M. C., Medina-Acosta E., Cross G. A. Characterization of a glycosylphosphatidylinositol membrane protein anchor precursor in Leishmania mexicana. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Oct;48(2):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90118-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M. C., Menon A. K., Cross G. A. A glycosylphosphatidylinositol protein anchor from procyclic stage Trypanosoma brucei: lipid structure and biosynthesis. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2731–2739. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07821.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M. C., Menon A. K., Cross G. A. Developmental variation of glycosylphosphatidylinositol membrane anchors in Trypanosoma brucei. Identification of a candidate biosynthetic precursor of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor of the major procyclic stage surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8392–8400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M. C., Menon A. K., Cross G. A. Developmental variation of glycosylphosphatidylinositol membrane anchors in Trypanosoma brucei. In vitro biosynthesis of intermediates in the construction of the GPI anchor of the major procyclic surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5324–5329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouts D. L., Ruef B. J., Ridley P. T., Wrightsman R. A., Peterson D. S., Manning J. E. Nucleotide sequence and transcription of a trypomastigote surface antigen gene of Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Jun;46(2):189–200. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankenburg S., Leibovici V., Mansbach N., Turco S. J., Rosen G. Effect of glycolipids of Leishmania parasites on human monocyte activity. Inhibition by lipophosphoglycan. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4284–4289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber L. D., Kodukula K., Udenfriend S. Phosphatidylinositol glycan (PI-G) anchored membrane proteins. Amino acid requirements adjacent to the site of cleavage and PI-G attachment in the COOH-terminal signal peptide. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):12168–12173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser T. A., Moody S. F., Handman E., Bacic A., Spithill T. W. An antigenically distinct lipophosphoglycan on amastigotes of Leishmania major. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Apr;45(2):337–344. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90102-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt C. L., Slutzky G. M., de Ibarra A. A., Snary D. Monoclonal antibodies for serotyping Leishmania strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):191–193. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.191-193.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greis K. D., Turco S. J., Thomas J. R., McConville M. J., Homans S. W., Ferguson M. A. Purification and characterization of an extracellular phosphoglycan from Leishmania donovani. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5876–5881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurnett A., Dulski P., Hsu J., Turner M. J. A family of glycolipid linked proteins in Eimeria tenella. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Jun;41(2):177–185. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90180-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güther M. L., de Almeida M. L., Yoshida N., Ferguson M. A. Structural studies on the glycosylphosphatidylinositol membrane anchor of Trypanosoma cruzi 1G7-antigen. The structure of the glycan core. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6820–6828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldar K., Ferguson M. A., Cross G. A. Acylation of a Plasmodium falciparum merozoite surface antigen via sn-1,2-diacyl glycerol. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4969–4974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldar K., Henderson C. L., Cross G. A. Identification of the parasite transferrin receptor of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes and its acylation via 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8565–8569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. F., Webster P., Ma A. K., Joiner K. A., Andrews N. W. Desialylation of lysosomal membrane glycoproteins by Trypanosoma cruzi: a role for the surface neuraminidase in facilitating parasite entry into the host cell cytoplasm. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):313–325. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Goding J. W. The Leishmania receptor for macrophages is a lipid-containing glycoconjugate. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):329–336. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03633.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Greenblatt C. L., Goding J. W. An amphipathic sulphated glycoconjugate of Leishmania: characterization with monoclonal antibodies. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2301–2306. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02130.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Mitchell G. F., Goding J. W. Leishmania major: a very sensitive dot-blot ELISA for detection of parasites in cutaneous lesions. Mol Biol Med. 1987 Dec;4(6):377–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handman E., Schnur L. F., Spithill T. W., Mitchell G. F. Passive transfer of Leishmania lipopolysaccharide confers parasite survival in macrophages. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 1;137(11):3608–3613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannan L. A., Lisanti M. P., Rodriguez-Boulan E., Edidin M. Correctly sorted molecules of a GPI-anchored protein are clustered and immobile when they arrive at the apical surface of MDCK cells. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(2):353–358. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.2.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereld D., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. cDNA encoding the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C of Trypanosoma brucei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8914–8918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Munaín C., Fernández M. A., Alcina A., Fresno M. Characterization of a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-anchored membrane protein from Trypanosoma cruzi. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1409–1416. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1409-1416.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose S., Prince G. M., Sevlever D., Ravi L., Rosenberry T. L., Ueda E., Medof M. E. Characterization of putative glycoinositol phospholipid anchor precursors in mammalian cells. Localization of phosphoethanolamine. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):16968–16974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homans S. W., Edge C. J., Ferguson M. A., Dwek R. A., Rademacher T. W. Solution structure of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol membrane anchor glycan of Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 4;28(7):2881–2887. doi: 10.1021/bi00433a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homans S. W., Ferguson M. A., Dwek R. A., Rademacher T. W., Anand R., Williams A. F. Complete structure of the glycosyl phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor of rat brain Thy-1 glycoprotein. Nature. 1988 May 19;333(6170):269–272. doi: 10.1038/333269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homans S. W., Mehlert A., Turco S. J. Solution structure of the lipophosphoglycan of Leishmania donovani. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 28;31(3):654–661. doi: 10.1021/bi00118a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M. More than just a membrane anchor. Curr Biol. 1992 Nov;2(11):617–619. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(92)90183-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper N. M., Turner A. J. Ectoenzymes of the kidney microvillar membrane. Differential solubilization by detergents can predict a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 15;250(3):865–869. doi: 10.1042/bj2500865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman R. Somatic genetic analysis of the expression of cell surface molecules. Trends Genet. 1988 Jan;4(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90120-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilg T., Etges R., Overath P., McConville M. J., Thomas-Oates J., Thomas J., Homans S. W., Ferguson M. A. Structure of Leishmania mexicana lipophosphoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6834–6840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inverso J. A., Medina-Acosta E., O'Connor J., Russell D. G., Cross G. A. Crithidia fasciculata contains a transcribed leishmanial surface proteinase (gp63) gene homologue. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 Jan;57(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90242-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamitani T., Menon A. K., Hallaq Y., Warren C. D., Yeh E. T. Complexity of ethanolamine phosphate addition in the biosynthesis of glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchors in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24611–24619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karp C. L., Turco S. J., Sacks D. L. Lipophosphoglycan masks recognition of the Leishmania donovani promastigote surface by human kala-azar serum. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 15;147(2):680–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher M., Bacic A., Handman E. Identification of a macrophage-binding determinant on lipophosphoglycan from Leishmania major promastigotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):6–10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller G. A., Siegel M. W., Caras I. W. Endocytosis of glycophospholipid-anchored and transmembrane forms of CD4 by different endocytic pathways. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):863–874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05124.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King D. L., Chang Y. D., Turco S. J. Cell surface lipophosphoglycan of Leishmania donovani. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 May;24(1):47–53. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90114-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodukula K., Cines D., Amthauer R., Gerber L., Udenfriend S. Biosynthesis of phosphatidylinositol-glycan (PI-G)-anchored membrane proteins in cell-free systems: cleavage of the nascent protein and addition of the PI-G moiety depend on the size of the COOH-terminal signal peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1350–1353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakow J. L., Doering T. L., Masterson W. J., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. A glycolipid from Trypanosoma brucei related to the variant surface glycoprotein membrane anchor. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Oct;36(3):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. A., de la Cruz V. F., Ferreira P. C., Morel C., Simpson L. Evolution of parasitism: kinetoplastid protozoan history reconstructed from mitochondrial rRNA gene sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4779–4783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamont G. S., Fox J. A., Cross G. A. Glycosyl-sn-1,2-dimyristylphosphatidylinositol is the membrane anchor for Trypanosoma equiperdum and T. (Nannomonas) congolense variant surface glycoproteins. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Jun;24(2):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang T., Warburg A., Sacks D. L., Croft S. L., Lane R. P., Blackwell J. M. Transmission and scanning EM-immunogold labeling of Leishmania major lipophosphoglycan in the sandfly Phlebotomus papatasi. Eur J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;55(2):362–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. C., Shoda R., Krall J. A., Foster J. D., Selhub J., Rosenberry T. L. Folate binding protein from kidney brush border membranes contains components characteristic of a glycoinositol phospholipid anchor. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 31;31(12):3236–3243. doi: 10.1021/bi00127a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehuen A., Monteiro R. C., Kearney J. F. Identification of a surface protein (p100) associated with two glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-linked molecules (Thy-1 and ThB) by natural anti-lymphocyte autoantibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Sep;22(9):2373–2380. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemansky P., Fatemi S. H., Gorican B., Meyale S., Rossero R., Tartakoff A. M. Dynamics and longevity of the glycolipid-anchored membrane protein, Thy-1. J Cell Biol. 1990 May;110(5):1525–1531. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.5.1525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisanti M. P., Caras I. W., Gilbert T., Hanzel D., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Vectorial apical delivery and slow endocytosis of a glycolipid-anchored fusion protein in transfected MDCK cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7419–7423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisanti M. P., Field M. C., Caras I. W., Menon A. K., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Mannosamine, a novel inhibitor of glycosylphosphatidylinositol incorporation into proteins. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):1969–1977. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07726.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohman K. L., Langer P. J., McMahon-Pratt D. Molecular cloning and characterization of the immunologically protective surface glycoprotein GP46/M-2 of Leishmania amazonensis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8393–8397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G. The glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol anchor of membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 6;988(3):427–454. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luhrs C. A., Slomiany B. L. A human membrane-associated folate binding protein is anchored by a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol tail. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21446–21449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund-Johansen F., Olweus J., Horejsi V., Skubitz K. M., Thompson J. S., Vilella R., Symington F. W. Activation of human phagocytes through carbohydrate antigens (CD15, sialyl-CD15, CDw17, and CDw65). J Immunol. 1992 May 15;148(10):3221–3229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masco D., Van de Walle M., Spiegel S. Interaction of ganglioside GM1 with the B subunit of cholera toxin modulates growth and differentiation of neuroblastoma N18 cells. J Neurosci. 1991 Aug;11(8):2443–2452. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-08-02443.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masterson W. J., Doering T. L., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. A novel pathway for glycan assembly: biosynthesis of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol anchor of the trypanosome variant surface glycoprotein. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):793–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90684-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masterson W. J., Ferguson M. A. Phenylmethanesulphonyl fluoride inhibits GPI anchor biosynthesis in the African trypanosome. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2041–2045. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07734.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masterson W. J., Raper J., Doering T. L., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. Fatty acid remodeling: a novel reaction sequence in the biosynthesis of trypanosome glycosyl phosphatidylinositol membrane anchors. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90241-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayor S., Menon A. K., Cross G. A., Ferguson M. A., Dwek R. A., Rademacher T. W. Glycolipid precursors for the membrane anchor of Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoproteins. I. Can structure of the phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C sensitive and resistant glycolipids. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6164–6173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayor S., Menon A. K., Cross G. A. Galactose-containing glycosylphosphatidylinositols in Trypanosoma brucei. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):754–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayor S., Menon A. K., Cross G. A. Glycolipid precursors for the membrane anchor of Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoproteins. II. Lipid structures of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C sensitive and resistant glycolipids. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6174–6181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayor S., Menon A. K., Cross G. A. Transfer of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane anchors to polypeptide acceptors in a cell-free system. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(1):61–71. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConville M. J., Bacic A. A family of glycoinositol phospholipids from Leishmania major. Isolation, characterization, and antigenicity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):757–766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConville M. J., Bacic A., Mitchell G. F., Handman E. Lipophosphoglycan of Leishmania major that vaccinates against cutaneous leishmaniasis contains an alkylglycerophosphoinositol lipid anchor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8941–8945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConville M. J., Blackwell J. M. Developmental changes in the glycosylated phosphatidylinositols of Leishmania donovani. Characterization of the promastigote and amastigote glycolipids. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15170–15179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConville M. J. Glycosylated-phosphatidylinositols as virulence factors in Leishmania. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1991 Sep;15(9):779–798. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(91)90033-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConville M. J., Homans S. W. Identification of the defect in lipophosphoglycan biosynthesis in a non-pathogenic strain of Leishmania major. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5855–5861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConville M. J., Homans S. W., Thomas-Oates J. E., Dell A., Bacic A. Structures of the glycoinositolphospholipids from Leishmania major. A family of novel galactofuranose-containing glycolipids. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7385–7394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConville M. J., Thomas-Oates J. E., Ferguson M. A., Homans S. W. Structure of the lipophosphoglycan from Leishmania major. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19611–19623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConville M. J., Turco S. J., Ferguson M. A., Sacks D. L. Developmental modification of lipophosphoglycan during the differentiation of Leishmania major promastigotes to an infectious stage. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3593–3600. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05443.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeely T. B., Rosen G., Londner M. V., Turco S. J. Inhibitory effects on protein kinase C activity by lipophosphoglycan fragments and glycosylphosphatidylinositol antigens of the protozoan parasite Leishmania. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 15;259(2):601–604. doi: 10.1042/bj2590601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeely T. B., Turco S. J. Inhibition of protein kinase C activity by the Leishmania donovani lipophosphoglycan. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 29;148(2):653–657. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90926-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeely T. B., Turco S. J. Requirement of lipophosphoglycan for intracellular survival of Leishmania donovani within human monocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2745–2750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medina-Acosta E., Karess R. E., Russell D. G. Structurally distinct genes for the surface protease of Leishmania mexicana are developmentally regulated. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 Jan;57(1):31–45. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90241-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medina-Acosta E., Karess R. E., Schwartz H., Russell D. G. The promastigote surface protease (gp63) of Leishmania is expressed but differentially processed and localized in the amastigote stage. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Dec;37(2):263–273. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehlert A., Silman I., Homans S. W., Ferguson M. A. The structure of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor from Torpedo californica acetylcholinesterase. Biochem Soc Trans. 1993 Feb;21(1):43S–43S. doi: 10.1042/bst021043s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon A. K. Biosynthesis of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1991 Nov;15(11):1007–1021. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(91)90053-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon A. K., Eppinger M., Mayor S., Schwarz R. T. Phosphatidylethanolamine is the donor of the terminal phosphoethanolamine group in trypanosome glycosylphosphatidylinositols. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1907–1914. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05839.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon A. K., Mayor S., Schwarz R. T. Biosynthesis of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol lipids in Trypanosoma brucei: involvement of mannosyl-phosphoryldolichol as the mannose donor. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4249–4258. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07873.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon A. K., Schwarz R. T., Mayor S., Cross G. A. Cell-free synthesis of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol precursors for the glycolipid membrane anchor of Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoproteins. Structural characterization of putative biosynthetic intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9033–9042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon A. K., Stevens V. L. Phosphatidylethanolamine is the donor of the ethanolamine residue linking a glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor to protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15277–15280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mensa-Wilmot K., Englund P. T. Glycosyl phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C of Trypanosoma brucei: expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Dec;56(2):311–321. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90180-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf P., Blum M., Freymann D., Turner M., Wiley D. C. Two variant surface glycoproteins of Trypanosoma brucei of different sequence classes have similar 6 A resolution X-ray structures. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):84–86. doi: 10.1038/325084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne K. G., Ferguson M. A., Masterson W. J. Inhibition of the GlcNAc transferase of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor biosynthesis in African trypanosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Sep 1;208(2):309–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17188.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata T., Takeda J., Iida Y., Yamada N., Inoue N., Takahashi M., Maeda K., Kitani T., Kinoshita T. The cloning of PIG-A, a component in the early step of GPI-anchor biosynthesis. Science. 1993 Feb 26;259(5099):1318–1320. doi: 10.1126/science.7680492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser D. M., Springer T. A., Diamond M. S. Leishmania promastigotes require opsonic complement to bind to the human leukocyte integrin Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18). J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):511–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. J., Spithill T. W., Handman E. The PSA-2 glycoprotein complex of Leishmania major is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-linked promastigote surface antigen. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):4221–4226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel S. D., Boothroyd J. C. The major surface antigen, P30, of Toxoplasma gondii is anchored by a glycolipid. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5569–5574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishihara M., Utagawa M., Akutsu H., Koga Y. Archaea contain a novel diether phosphoglycolipid with a polar head group identical to the conserved core of eucaryal glycosyl phosphatidylinositol. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12432–12435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlandi P. A., Jr, Turco S. J. Structure of the lipid moiety of the Leishmania donovani lipophosphoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10384–10391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki L. S., Svec P., Nussenzweig R. S., Nussenzweig V., Godson G. N. Structure of the plasmodium knowlesi gene coding for the circumsporozoite protein. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):815–822. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90538-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan Y. T., Kamitani T., Bhuvaneswaran C., Hallaq Y., Warren C. D., Yeh E. T., Elbein A. D. Inhibition of glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor formation by mannosamine. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 15;267(29):21250–21255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul E., Leblond F. A., LeBel D. In resting conditions, the pancreatic granule membrane protein GP-2 is secreted by cleavage of its glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor. Biochem J. 1991 Aug 1;277(Pt 3):879–881. doi: 10.1042/bj2770879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira M. E., Mejia J. S., Ortega-Barria E., Matzilevich D., Prioli R. P. The Trypanosoma cruzi neuraminidase contains sequences similar to bacterial neuraminidases, YWTD repeats of the low density lipoprotein receptor, and type III modules of fibronectin. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):179–191. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Ravetch J. V. Fc gamma RIII (CD16) on human macrophages is a functional product of the Fc gamma RIII-2 gene. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Feb;21(2):425–429. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimenta P. F., Saraiva E. M., Sacks D. L. The comparative fine structure and surface glycoconjugate expression of three life stages of Leishmania major. Exp Parasitol. 1991 Feb;72(2):191–204. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(91)90137-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimenta P. F., Turco S. J., McConville M. J., Lawyer P. G., Perkins P. V., Sacks D. L. Stage-specific adhesion of Leishmania promastigotes to the sandfly midgut. Science. 1992 Jun 26;256(5065):1812–1815. doi: 10.1126/science.1615326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimenta P. F., da Silva R. P., Sacks D. L., da Silva P. P. Cell surface nanoanatomy of Leishmania major as revealed by fracture-flip. A surface meshwork of 44 nm fusiform filaments identifies infective developmental stage promastigotes. Eur J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;48(2):180–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pingel S., Duszenko M. Identification of two distinct galactosyltransferase activities acting on the variant surface glycoprotein of Trypanosoma brucei. Biochem J. 1992 Apr 15;283(Pt 2):479–485. doi: 10.1042/bj2830479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipaon C., Santos A., Perez-Castillo A. Thyroid hormone up-regulates NGFI-A gene expression in rat brain during development. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):21–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollevick G. D., Affranchino J. L., Frasch A. C., Sánchez D. O. The complete sequence of a shed acute-phase antigen of Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Aug;47(2):247–250. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontes de Carvalho L. C., Tomlinson S., Vandekerckhove F., Bienen E. J., Clarkson A. B., Jiang M. S., Hart G. W., Nussenzweig V. Characterization of a novel trans-sialidase of Trypanosoma brucei procyclic trypomastigotes and identification of procyclin as the main sialic acid acceptor. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):465–474. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Previato J. O., Gorin P. A., Mazurek M., Xavier M. T., Fournet B., Wieruszesk J. M., Mendonça-Previato L. Primary structure of the oligosaccharide chain of lipopeptidophosphoglycan of epimastigote forms of Trypanosoma cruzi. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2518–2526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Previato J. O., Mendonça-Previato L., Jones C., Wait R., Fournet B. Structural characterization of a novel class of glycophosphosphingolipids from the protozoan Leptomonas samueli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24279–24286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puentes S. M., Da Silva R. P., Sacks D. L., Hammer C. H., Joiner K. A. Serum resistance of metacyclic stage Leishmania major promastigotes is due to release of C5b-9. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4311–4316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puentes S. M., Sacks D. L., da Silva R. P., Joiner K. A. Complement binding by two developmental stages of Leishmania major promastigotes varying in expression of a surface lipophosphoglycan. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):887–902. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puoti A., Conzelmann A. Characterization of abnormal free glycophosphatidylinositols accumulating in mutant lymphoma cells of classes B, E, F, and H. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):7215–7224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puoti A., Conzelmann A. Structural characterization of free glycolipids which are potential precursors for glycophosphatidylinositol anchors in mouse thymoma cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22673–22680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramamoorthy R., Donelson J. E., Paetz K. E., Maybodi M., Roberts S. C., Wilson M. E. Three distinct RNAs for the surface protease gp63 are differentially expressed during development of Leishmania donovani chagasi promastigotes to an infectious form. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1888–1895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richier P., Arpagaus M., Toutant J. P. Glycolipid-anchored acetylcholinesterases from rabbit lymphocytes and erythrocytes differ in their sensitivity to phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Nov 23;1112(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(92)90257-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. L., Myher J. J., Kuksis A., Low M. G., Rosenberry T. L. Lipid analysis of the glycoinositol phospholipid membrane anchor of human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Palmitoylation of inositol results in resistance to phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18766–18775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. L., Santikarn S., Reinhold V. N., Rosenberry T. L. Structural characterization of the glycoinositol phospholipid membrane anchor of human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase by fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18776–18784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. J. Phosphatidylinositol membrane anchors and T-cell activation. Immunol Today. 1991 Jan;12(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90110-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roditi I., Schwarz H., Pearson T. W., Beecroft R. P., Liu M. K., Richardson J. P., Bühring H. J., Pleiss J., Bülow R., Williams R. O. Procyclin gene expression and loss of the variant surface glycoprotein during differentiation of Trypanosoma brucei. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):737–746. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Boulan E., Powell S. K. Polarity of epithelial and neuronal cells. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:395–427. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen G., Londner M. V., Sevlever D., Greenblatt C. L. Leishmania major: glycolipid antigens recognized by immune human sera. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Jan 1;27(1):93–99. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen G., Påhlsson P., Londner M. V., Westerman M. E., Nilsson B. Structural analysis of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol antigens of Leishmania major. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10457–10463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg I., Prioli R. P., Ortega-Barria E., Pereira M. E. Stage-specific phospholipase C-mediated release of Trypanosoma cruzi neuraminidase. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Jun;46(2):303–305. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90054-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., Cardoso de Almeida M. L., Turner M. J. Variant surface glycoproteins of Trypanosoma congolense bloodstream and metacyclic forms are anchored by a glycolipid tail. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Jan 15;22(2-3):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90045-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg K. G., Heuser J. E., Donzell W. C., Ying Y. S., Glenney J. R., Anderson R. G. Caveolin, a protein component of caveolae membrane coats. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):673–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90143-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg K. G., Ying Y. S., Kamen B. A., Anderson R. G. Cholesterol controls the clustering of the glycophospholipid-anchored membrane receptor for 5-methyltetrahydrofolate. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):2931–2938. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks D. L., Brodin T. N., Turco S. J. Developmental modification of the lipophosphoglycan from Leishmania major promastigotes during metacyclogenesis. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Sep-Oct;42(2):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90165-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks D. L. Metacyclogenesis in Leishmania promastigotes. Exp Parasitol. 1989 Jul;69(1):100–103. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. E., Brogle N. L., Edberg J. C., Kimberly R. P. Fc gamma receptor III induces actin polymerization in human neutrophils and primes phagocytosis mediated by Fc gamma receptor II. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 1;146(3):997–1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell D., Evers R., Preis D., Ziegelbauer K., Kiefer H., Lottspeich F., Cornelissen A. W., Overath P. A transferrin-binding protein of Trypanosoma brucei is encoded by one of the genes in the variant surface glycoprotein gene expression site. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1061–1066. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08045.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkman S., Ferguson M. A., Heise N., de Almeida M. L., Mortara R. A., Yoshida N. Mucin-like glycoproteins linked to the membrane by glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor are the major acceptors of sialic acid in a reaction catalyzed by trans-sialidase in metacyclic forms of Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 Jun;59(2):293–303. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90227-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkman S., Pontes de Carvalho L., Nussenzweig V. Trypanosoma cruzi trans-sialidase and neuraminidase activities can be mediated by the same enzymes. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):567–575. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkman S., Yoshida N., Cardoso de Almeida M. L. Glycophosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins in metacyclic trypomastigotes of Trypanosoma cruzi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Jun;29(2-3):141–151. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90069-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlein Y., Schnur L. F., Jacobson R. L. Released glycoconjugate of indigenous Leishmania major enhances survival of a foreign L. major in Phlebotomus papatasi. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1990 May-Jun;84(3):353–355. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(90)90315-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider P., Ferguson M. A., McConville M. J., Mehlert A., Homans S. W., Bordier C. Structure of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor of the Leishmania major promastigote surface protease. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16955–16964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider P., Glaser T. A. Characterization of a surface metalloprotease from Herpetomonas samuelpessoai and comparison with Leishmania major promastigote surface protease. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993 Apr;58(2):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90049-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider P., Rosat J. P., Bouvier J., Louis J., Bordier C. Leishmania major: differential regulation of the surface metalloprotease in amastigote and promastigote stages. Exp Parasitol. 1992 Sep;75(2):196–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(92)90179-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield L., Hackett F. Signal transduction in host cells by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol toxin of malaria parasites. J Exp Med. 1993 Jan 1;177(1):145–153. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sevlever D., Påhlsson P., Rosen G., Nilsson B., Londner M. V. Structural analysis of a glycosylphosphatidylinositol glycolipid of Leishmania donovani. Glycoconj J. 1991 Aug;8(4):321–329. doi: 10.1007/BF00731344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyfang A., Mecke D., Duszenko M. Degradation, recycling, and shedding of Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. J Protozool. 1990 Nov-Dec;37(6):546–552. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1990.tb01263.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. Z., Webster P. Coated vesicles from the protozoan parasite Trypanosoma brucei: purification and characterization. J Protozool. 1989 Jul-Aug;36(4):344–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1989.tb05524.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh N., Singleton D., Tartakoff A. M. Anchoring and degradation of glycolipid-anchored membrane proteins by L929 versus by LM-TK- mouse fibroblasts: implications for anchor biosynthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2362–2374. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smythe J. A., Coppel R. L., Brown G. V., Ramasamy R., Kemp D. J., Anders R. F. Identification of two integral membrane proteins of Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5195–5199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soares M. J., Souto-Padrón T., De Souza W. Identification of a large pre-lysosomal compartment in the pathogenic protozoon Trypanosoma cruzi. J Cell Sci. 1992 May;102(Pt 1):157–167. doi: 10.1242/jcs.102.1.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogin M. L., Gunderson J. H., Elwood H. J., Alonso R. A., Peattie D. A. Phylogenetic meaning of the kingdom concept: an unusual ribosomal RNA from Giardia lamblia. Science. 1989 Jan 6;243(4887):75–77. doi: 10.1126/science.2911720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler J., Keenan T. W., Bauer G., Gerisch G. The contact site A glycoprotein of Dictyostelium discoideum carries a phospholipid anchor of a novel type. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):371–377. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Baldwin M. A., Hecker R., Pan K. M., Burlingame A. L., Prusiner S. B. Glycosylinositol phospholipid anchors of the scrapie and cellular prion proteins contain sialic acid. Biochemistry. 1992 Jun 2;31(21):5043–5053. doi: 10.1021/bi00136a600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley S. L., Jr, Huizenga H., Li E. Isolation and partial characterization of a surface glycoconjugate of Entamoeba histolytica. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Jan;50(1):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90250-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanová I., Horejsí V., Ansotegui I. J., Knapp W., Stockinger H. GPI-anchored cell-surface molecules complexed to protein tyrosine kinases. Science. 1991 Nov 15;254(5034):1016–1019. doi: 10.1126/science.1719635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens V. L., Raetz C. R. Defective glycosyl phosphatidylinositol biosynthesis in extracts of three Thy-1 negative lymphoma cell mutants. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10039–10042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Takeda J., Hirose S., Hyman R., Inoue N., Miyata T., Ueda E., Kitani T., Medof M. E., Kinoshita T. Deficient biosynthesis of N-acetylglucosaminyl-phosphatidylinositol, the first intermediate of glycosyl phosphatidylinositol anchor biosynthesis, in cell lines established from patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):517–521. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takle G. B., Cross G. A. An 85-kilodalton surface antigen gene family of Trypanosoma cruzi encodes polypeptides homologous to bacterial neuraminidases. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Oct;48(2):185–198. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90114-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talamás-Rohana P., Wright S. D., Lennartz M. R., Russell D. G. Lipophosphoglycan from Leishmania mexicana promastigotes binds to members of the CR3, p150,95 and LFA-1 family of leukocyte integrins. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4817–4824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A. M., Singh N. How to make a glycoinositol phospholipid anchor. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Nov;17(11):470–473. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90491-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taverne J., Bate C. A., Playfair J. H. Malaria exoantigens induce TNF, are toxic and are blocked by T-independent antibody. Immunol Lett. 1990 Aug;25(1-3):207–212. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(90)90116-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. R., Dwek R. A., Rademacher T. W. Structure, biosynthesis, and function of glycosylphosphatidylinositols. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 12;29(23):5413–5422. doi: 10.1021/bi00475a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. R., McConville M. J., Thomas-Oates J. E., Homans S. W., Ferguson M. A., Gorin P. A., Greis K. D., Turco S. J. Refined structure of the lipophosphoglycan of Leishmania donovani. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6829–6833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. M., Samelson L. E. The glycophosphatidylinositol-anchored Thy-1 molecule interacts with the p60fyn protein tyrosine kinase in T cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):12317–12322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolson D. L., Turco S. J., Beecroft R. P., Pearson T. W. The immunochemical structure and surface arrangement of Leishmania donovani lipophosphoglycan determined using monoclonal antibodies. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Jun 15;35(2):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomavo S., Dubremetz J. F., Schwarz R. T. A family of glycolipids from Toxoplasma gondii. Identification of candidate glycolipid precursor(s) for Toxoplasma gondii glycosylphosphatidylinositol membrane anchors. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11721–11728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson S., Pontes de Carvalho L., Vandekerckhove F., Nussenzweig V. Resialylation of sialidase-treated sheep and human erythrocytes by Trypanosoma cruzi trans-sialidase: restoration of complement resistance of desialylated sheep erythrocytes. Glycobiology. 1992 Dec;2(6):549–551. doi: 10.1093/glycob/2.6.549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toutant J. P., Richards M. K., Krall J. A., Rosenberry T. L. Molecular forms of acetylcholinesterase in two sublines of human erythroleukemia K562 cells. Sensitivity or resistance to phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C and biosynthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jan 12;187(1):31–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco S. J., Descoteaux A. The lipophosphoglycan of Leishmania parasites. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1992;46:65–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.46.100192.000433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco S. J., Hull S. R., Orlandi P. A., Jr, Shepherd S. D., Homans S. W., Dwek R. A., Rademacher T. W. Structure of the major carbohydrate fragment of the Leishmania donovani lipophosphoglycan. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 22;26(19):6233–6238. doi: 10.1021/bi00393a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco S. J., Orlandi P. A., Jr, Homans S. W., Ferguson M. A., Dwek R. A., Rademacher T. W. Structure of the phosphosaccharide-inositol core of the Leishmania donovani lipophosphoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6711–6715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco S. J., Sacks D. L. Expression of a stage-specific lipophosphoglycan in Leishmania major amastigotes. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Mar;45(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90030-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udenfriend S., Micanovic R., Kodukula K. Structural requirements of a nascent protein for processing to a PI-G anchored form: studies in intact cells and cell-free systems. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1991 Sep;15(9):739–759. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(91)90030-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urakaze M., Kamitani T., DeGasperi R., Sugiyama E., Chang H. M., Warren C. D., Yeh E. T. Identification of a missing link in glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor biosynthesis in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6459–6462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Voorhis W. C., Schlekewy L., Trong H. L. Molecular mimicry by Trypanosoma cruzi: the F1-160 epitope that mimics mammalian nerve can be mapped to a 12-amino acid peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):5993–5997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.5993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidugiriene J., Menon A. K. Early lipid intermediates in glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol anchor assembly are synthesized in the ER and located in the cytoplasmic leaflet of the ER membrane bilayer. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;121(5):987–996. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.5.987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel M., Kowalewski H., Zimmermann H., Hooper N. M., Turner A. J. Soluble low-Km 5'-nucleotidase from electric-ray (Torpedo marmorata) electric organ and bovine cerebral cortex is derived from the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-anchored ectoenzyme by phospholipase C cleavage. Biochem J. 1992 Jun 15;284(Pt 3):621–624. doi: 10.1042/bj2840621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter E. I., Roberts W. L., Rosenberry T. L., Ratnoff W. D., Medof M. E. Structural basis for variations in the sensitivity of human decay accelerating factor to phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C cleavage. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 1;144(3):1030–1036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster P., Grab D. J. Intracellular colocalization of variant surface glycoprotein and transferrin-gold in Trypanosoma brucei. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):279–288. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster P., Russo D. C., Black S. J. The interaction of Trypanosoma brucei with antibodies to variant surface glycoproteins. J Cell Sci. 1990 Jun;96(Pt 2):249–255. doi: 10.1242/jcs.96.2.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinhart U., Thomas J. R., Pak Y. B., Thompson G. A., Jr, Ferguson M. A. Structural characterization of a novel glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol from the protozoan Tetrahymena mimbres. Biochem J. 1991 Oct 15;279(Pt 2):605–608. doi: 10.1042/bj2790605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zingales B., Martin N. F., de Lederkremer R. M., Colli W. Endogenous and surface labeling of glycoconjugates from the three differentiation stages of Trypanosoma cruzi. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jun 7;142(2):238–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80143-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lederkremer R. M., Lima C., Ramirez M. I., Casal O. L. Structural features of the lipopeptidophosphoglycan from Trypanosoma cruzi common with the glycophosphatidylinositol anchors. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Sep 11;192(2):337–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]