Abstract
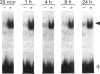
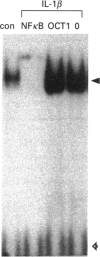
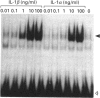
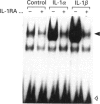
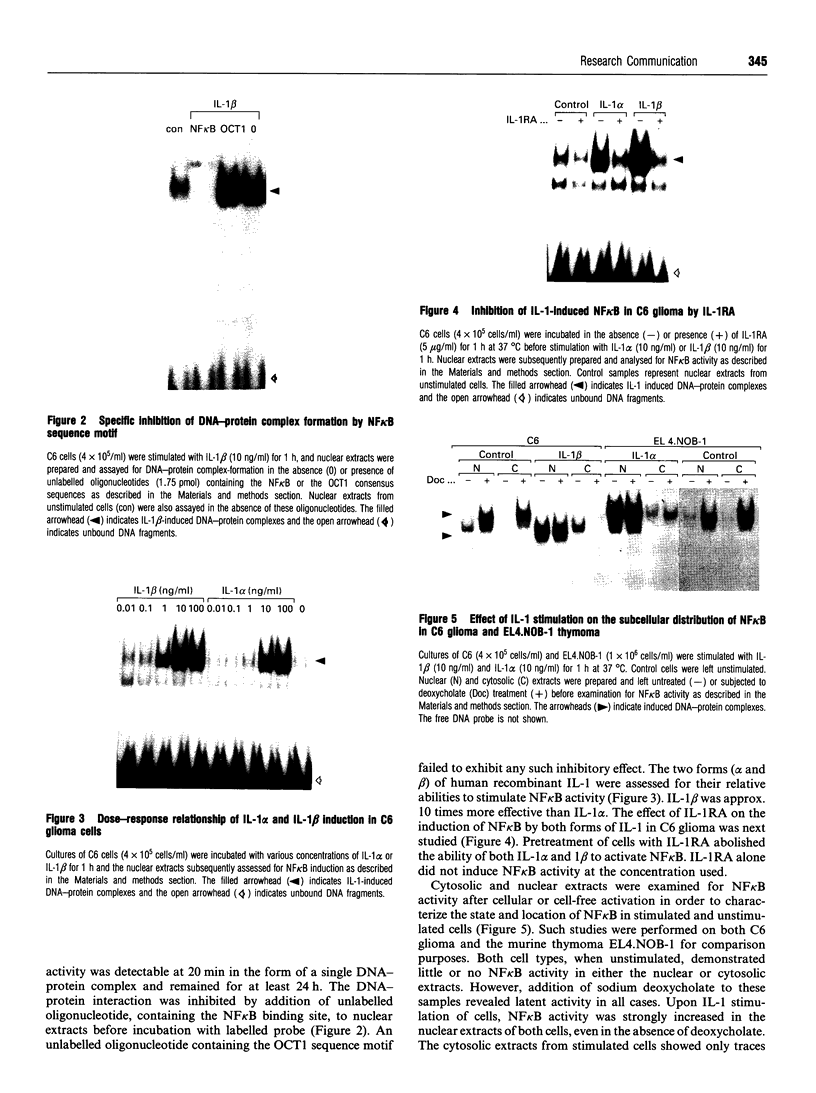
Recombinant human interleukin-1 (IL-1) alpha and beta were found to activate a latent cytosolic form of the transcription factor NF kappa B in rat C6 glioma. IL-1 beta was 10 times more potent than IL-1 alpha for this activity and both were inhibited by the IL-1 receptor antagonist. The activation was detectable from 20 min and remained sustained for up to 24 h. The electrophoretic mobility of the activated complex was shown to be different from that of the corresponding complexes in another IL-1-responsive cell line, the murine thymoma line EL4.NOB-1. C6 cells, when transiently transfected with five NF kappa B consensus sequence repeats linked to the reporter gene chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT), demonstrated increased CAT activity in response to IL-1 beta treatment. The activation of NF kappa B in glial cells may thus represent an early step in IL-1 signalling in brain and is likely to have consequences for IL-1-induced gene expression in these cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):540–546. doi: 10.1126/science.3140380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S. L., Halden N. F., Lenardo M. J., Leonard W. J. Functionally distinct NF-kappa B binding sites in the immunoglobulin kappa and IL-2 receptor alpha chain genes. Science. 1989 Apr 28;244(4903):466–469. doi: 10.1126/science.2497520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 antagonism. Blood. 1991 Apr 15;77(8):1627–1652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Lorenzetti B. B., Bristow A. F., Poole S. Interleukin-1 beta as a potent hyperalgesic agent antagonized by a tripeptide analogue. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):698–700. doi: 10.1038/334698a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin G. E., Leung K., Folks T. M., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Activation of HIV gene expression during monocyte differentiation by induction of NF-kappa B. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):70–73. doi: 10.1038/339070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami K., Scheidereit C., Roeder R. G. Identification and purification of a human immunoglobulin-enhancer-binding protein (NF-kappa B) that activates transcription from a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promoter in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4700–4704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent S., Bluthé R. M., Kelley K. W., Dantzer R. Sickness behavior as a new target for drug development. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Jan;13(1):24–28. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90012-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B. Interleukin 1 and T cell activation. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:51–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill L. A. How does interleukin-1 activate cells? Kidney Int. 1992 Mar;41(3):546–549. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 stimulate the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer by activation of the nuclear factor kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2336–2340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. The location of cis-acting regulatory sequences in the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III (HTLV-III/LAV) long terminal repeat. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):813–823. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg Z. F., Fauci A. S. Immunopathogenic mechanisms of HIV infection: cytokine induction of HIV expression. Immunol Today. 1990 May;11(5):176–180. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90070-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparacio S. M., Zhang Y., Vilcek J., Benveniste E. N. Cytokine regulation of interleukin-6 gene expression in astrocytes involves activation of an NF-kappa B-like nuclear protein. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Aug;39(3):231–242. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90257-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stylianou E., O'Neill L. A., Rawlinson L., Edbrooke M. R., Woo P., Saklatvala J. Interleukin 1 induces NF-kappa B through its type I but not its type II receptor in lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15836–15841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban M. B., Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. NF-kappa B contacts DNA by a heterodimer of the p50 and p65 subunit. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1817–1825. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07707.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao D. M., Levine L. Stimulation of arachidonic acid metabolism: differences in potencies of recombinant human interleukin-1 alpha and interleukin-1 beta on two cell types. Prostaglandins. 1986 Nov;32(5):709–718. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(86)90193-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]