Abstract
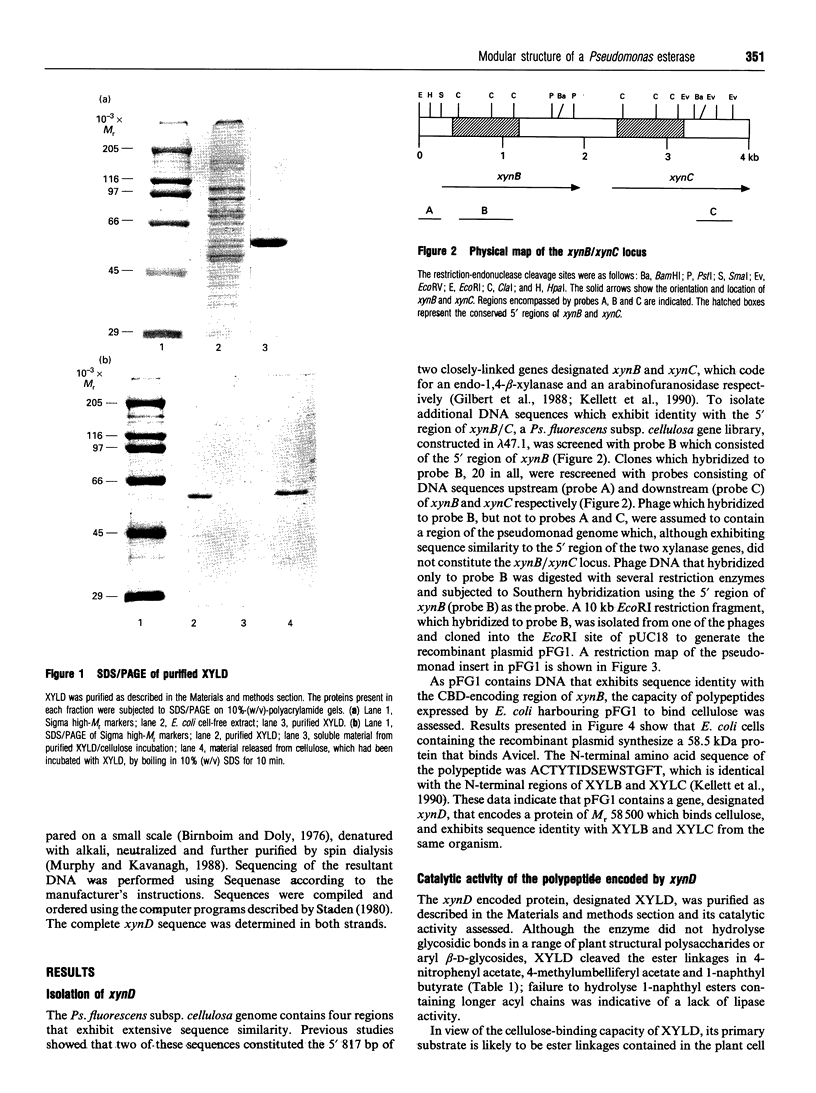
The 5' regions of genes xynB and xynC, coding for a xylanase and arabinofuranosidase respectively, are identical and are reiterated four times within the Pseudomonas fluorescens subsp. cellulosa genome. To isolate further copies of the reiterated xynB/C 5' region, a genomic library of Ps. fluorescens subsp. cellulosa DNA was screened with a probe constructed from the conserved region of xynB. DNA from one phage which hybridized to the probe, but not to sequences upstream or downstream of the reiterated xynB/C locus, was subcloned into pMTL22p to construct pFG1. The recombinant plasmid expressed a protein in Escherichia coli, designated esterase XYLD, of M(r) 58,500 which bound to cellulose but not to xylan. XYLD hydrolysed aryl esters, released acetate groups from acetylxylan and liberated 4-hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic acid from destarched wheat bran. The nucleotide sequence of the XYLD-encoding gene, xynD, revealed an open reading frame of 1752 bp which directed the synthesis of a protein of M(r) 60,589. The 5' 817 bp of xynD and the amino acid sequence between residues 37 and 311 of XYLD were almost identical with the corresponding regions of xynB and xynC and their encoded proteins XYLB and XYLC. Truncated derivatives of XYLD lacking the N-terminal conserved sequence retained the capacity to hydrolyse ester linkages, but did not bind cellulose. Expression of truncated derivatives of xynD, comprising the 5' 817 bp sequence, encoded a non-catalytic polypeptide that bound cellulose. These data indicate that XYLD has a modular structure comprising of a N-terminal cellulose-binding domain and a C-terminal catalytic domain.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borneman W. S., Ljungdahl L. G., Hartley R. D., Akin D. E. Purification and partial characterization of two feruloyl esterases from the anaerobic fungus Neocallimastix strain MC-2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Nov;58(11):3762–3766. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.11.3762-3766.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Béguin P. Molecular biology of cellulose degradation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:219–248. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers S. P., Prior S. E., Barstow D. A., Minton N. P. The pMTL nic- cloning vectors. I. Improved pUC polylinker regions to facilitate the use of sonicated DNA for nucleotide sequencing. Gene. 1988 Aug 15;68(1):139–149. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90606-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke J. H., Laurie J. I., Gilbert H. J., Hazlewood G. P. Multiple xylanases of Cellulomonas fimi are encoded by distinct genes. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Oct 15;67(3):305–309. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90493-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulds C. B., Williamson G. The purification and characterization of 4-hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic (ferulic) acid esterase from Streptomyces olivochromogenes. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Oct;137(10):2339–2345. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-10-2339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira L. M., Durrant A. J., Hall J., Hazlewood G. P., Gilbert H. J. Spatial separation of protein domains is not necessary for catalytic activity or substrate binding in a xylanase. Biochem J. 1990 Jul 1;269(1):261–264. doi: 10.1042/bj2690261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira L. M., Hazlewood G. P., Barker P. J., Gilbert H. J. The cellodextrinase from Pseudomonas fluorescens subsp. cellulosa consists of multiple functional domains. Biochem J. 1991 Nov 1;279(Pt 3):793–799. doi: 10.1042/bj2790793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert H. J., Hall J., Hazlewood G. P., Ferreira L. M. The N-terminal region of an endoglucanase from Pseudomonas fluorescens subspecies cellulosa constitutes a cellulose-binding domain that is distinct from the catalytic centre. Mol Microbiol. 1990 May;4(5):759–767. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00646.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert H. J., Hazlewood G. P., Laurie J. I., Orpin C. G., Xue G. P. Homologous catalytic domains in a rumen fungal xylanase: evidence for gene duplication and prokaryotic origin. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Aug;6(15):2065–2072. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert H. J., Jenkins G., Sullivan D. A., Hall J. Evidence for multiple carboxymethylcellulase genes in Pseudomonas fluorescens subsp. cellulosa. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(3):551–556. doi: 10.1007/BF00327211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert H. J., Sullivan D. A., Jenkins G., Kellett L. E., Minton N. P., Hall J. Molecular cloning of multiple xylanase genes from Pseudomonas fluorescens subsp. cellulosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Dec;134(12):3239–3247. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-12-3239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilkes N. R., Henrissat B., Kilburn D. G., Miller R. C., Jr, Warren R. A. Domains in microbial beta-1, 4-glycanases: sequence conservation, function, and enzyme families. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jun;55(2):303–315. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.2.303-315.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J., Gilbert H. J. The nucleotide sequence of a carboxymethylcellulase gene from Pseudomonas fluorescens subsp. cellulosa. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jul;213(1):112–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00333406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J., Hazlewood G. P., Barker P. J., Gilbert H. J. Conserved reiterated domains in Clostridium thermocellum endoglucanases are not essential for catalytic activity. Gene. 1988 Sep 15;69(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90375-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J., Hazlewood G. P., Huskisson N. S., Durrant A. J., Gilbert H. J. Conserved serine-rich sequences in xylanase and cellulase from Pseudomonas fluorescens subspecies cellulosa: internal signal sequence and unusual protein processing. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1211–1219. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00271.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazlewood G. P., Davidson K., Laurie J. I., Romaniec M. P., Gilbert H. J. Cloning and sequencing of the celA gene encoding endoglucanase A of Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens strain A46. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Oct;136(10):2089–2097. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-10-2089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrissat B., Claeyssens M., Tomme P., Lemesle L., Mornon J. P. Cellulase families revealed by hydrophobic cluster analysis. Gene. 1989 Sep 1;81(1):83–95. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hespell R. B., O'Bryan-Shah P. J. Esterase activities in Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Aug;54(8):1917–1922. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.8.1917-1922.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Hewick R. M., Dreyer W. J., Hood L. E. High-sensitivity sequencing with a gas-phase sequenator. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:399–413. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellett L. E., Poole D. M., Ferreira L. M., Durrant A. J., Hazlewood G. P., Gilbert H. J. Xylanase B and an arabinofuranosidase from Pseudomonas fluorescens subsp. cellulosa contain identical cellulose-binding domains and are encoded by adjacent genes. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 1;272(2):369–376. doi: 10.1042/bj2720369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüthi E., Love D. R., McAnulty J., Wallace C., Caughey P. A., Saul D., Bergquist P. L. Cloning, sequence analysis, and expression of genes encoding xylan-degrading enzymes from the thermophile "Caldocellum saccharolyticum". Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Apr;56(4):1017–1024. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.4.1017-1024.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino M., Davidson W. F., Fredrickson T. N., Hartley J. W., Morse H. C., 3rd Effects of non-MHC loci on resistance to retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency in mice. Immunogenetics. 1991;33(5-6):345–351. doi: 10.1007/BF00216693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rixon J. E., Ferreira L. M., Durrant A. J., Laurie J. I., Hazlewood G. P., Gilbert H. J. Characterization of the gene celD and its encoded product 1,4-beta-D-glucan glucohydrolase D from Pseudomonas fluorescens subsp. cellulosa. Biochem J. 1992 Aug 1;285(Pt 3):947–955. doi: 10.1042/bj2850947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A new computer method for the storage and manipulation of DNA gel reading data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3673–3694. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomme P., Van Tilbeurgh H., Pettersson G., Van Damme J., Vandekerckhove J., Knowles J., Teeri T., Claeyssens M. Studies of the cellulolytic system of Trichoderma reesei QM 9414. Analysis of domain function in two cellobiohydrolases by limited proteolysis. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 4;170(3):575–581. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13736.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utt E. A., Eddy C. K., Keshav K. F., Ingram L. O. Sequencing and expression of the Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens xylB gene encoding a novel bifunctional protein with beta-D-xylosidase and alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase activities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Apr;57(4):1227–1234. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.4.1227-1234.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]