Abstract
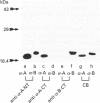
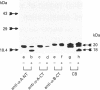
Recent studies have demonstrated that the alpha-crystallins can protect other proteins against heat-induced denaturation and aggregation. To determine the possible involvement of the C-terminal region in this activity, the alpha-crystallins were subjected to limited tryptic digestion, and the amount of cleavage from the N-terminal and C-terminal regions of the alpha-A and alpha-B crystallin chains was assessed using antisera specific for these regions. Limited tryptic digestion resulted in cleavage only from the C-terminal region of alpha-A crystallin. This trypsin-treated alpha-A crystallin preparation showed a decreased ability to protect proteins from heat-induced aggregation using an in vitro assay. Together, these results demonstrate that the C-terminal region of alpha-A crystallin is important for its ability to protect against heat-induced aggregation, which is consistent with the hypothesis that post-translational changes that are known to occur at the C-terminal region may have significant effects on the ability of alpha-A crystallin to protect against protein denaturation in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloemendal H. The vertebrate eye lens. Science. 1977 Jul 8;197(4299):127–138. doi: 10.1126/science.877544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons T., Takemoto L. Age-dependent loss of the C-terminal amino acid from alpha crystallin. Exp Eye Res. 1992 Oct;55(4):551–554. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(05)80167-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz J. Alpha-crystallin can function as a molecular chaperone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10449–10453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz J., Emmons T., Takemoto L. The ability of lens alpha crystallin to protect against heat-induced aggregation is age-dependent. Curr Eye Res. 1992 Aug;11(8):817–822. doi: 10.3109/02713689209000754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ifeanyi F., Takemoto L. Involvement of the N-terminal region in alpha-crystallin-lens membrane recognition. Exp Eye Res. 1991 Sep;53(3):305–308. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(91)90234-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia T. D., Craig E. A. Four small Drosophila heat shock proteins are related to each other and to mammalian alpha-crystallin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2360–2364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramps J. A., de Man B. M., de Jong W. W. The primary structure of the B2 chain of human alpha-crystallin. FEBS Lett. 1977 Feb 15;74(1):82–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80757-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J., Horwich A. L., Hartl F. U. Prevention of protein denaturation under heat stress by the chaperonin Hsp60. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):995–998. doi: 10.1126/science.1359644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merck K. B., De Haard-Hoekman W. A., Oude Essink B. B., Bloemendal H., De Jong W. W. Expression and aggregation of recombinant alpha A-crystallin and its two domains. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Apr 6;1130(3):267–276. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90439-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. E., Abraham E. C. High-performance liquid chromatographic separation of lens crystallins and their subunits. J Chromatogr. 1986 Jan 3;351(1):103–110. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)83476-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siezen R. J., Hoenders H. J. Limited tryptic digestion of alpha-crystallin from calf eye lens: Possible correlation between in vivo and in vitro degradation. FEBS Lett. 1977 Aug 1;80(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80410-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto L. J., Emmons T., Granstrom D., Griffin P. R., Shabanowitz J., Hunt D. F. Analysis of tryptic peptides from the C-terminal region of alpha-crystallin from cataractous and normal human lenses. Exp Eye Res. 1990 Jun;50(6):695–702. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(90)90116-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto L. J., Hansen J. S., Horwitz J. Antisera to synthetic peptides of lens MIP26K (major intrinsic polypeptide): characterization and use as site-specific probes of membrane changes in the aging human lens. Exp Eye Res. 1985 Sep;41(3):415–422. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(85)80032-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto L., Emmons T. Truncation of alpha A-crystallin from the human lens. Exp Eye Res. 1991 Dec;53(6):811–813. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(91)90119-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto L., Horwitz J., Emmons T. Oxidation of the N-terminal methionine of lens alpha-A crystallin. Curr Eye Res. 1992 Jul;11(7):651–655. doi: 10.3109/02713689209000738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Ouderaa F. J., De Jong W. W., Hilderink A., Bloemendal H. The amino-acids sequence of the alphaB2 chain of bovine alpha-crystallin. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Nov 1;49(1):157–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03821.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Kleef F. S., De Jong W. W., Hoenders H. J. Stepwise degradations and deamidation of the eye lens protein alpha-crystallin in ageing. Nature. 1975 Nov 20;258(5532):264–266. doi: 10.1038/258264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voorter C. E., Roersma E. S., Bloemendal H., de Jong W. W. Age-dependent deamidation of chicken alpha A-crystallin. FEBS Lett. 1987 Sep 14;221(2):249–252. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80935-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong W. W., Leunissen J. A., Leenen P. J., Zweers A., Versteeg M. Dogfish alpha-crystallin sequences. Comparison with small heat shock proteins and Schistosoma egg antigen. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5141–5149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong W. W., Terwindt E. C., Bloemendal H. The amino acid sequence of the A chain of human alpha-crystallin. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):310–313. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80286-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]