Abstract
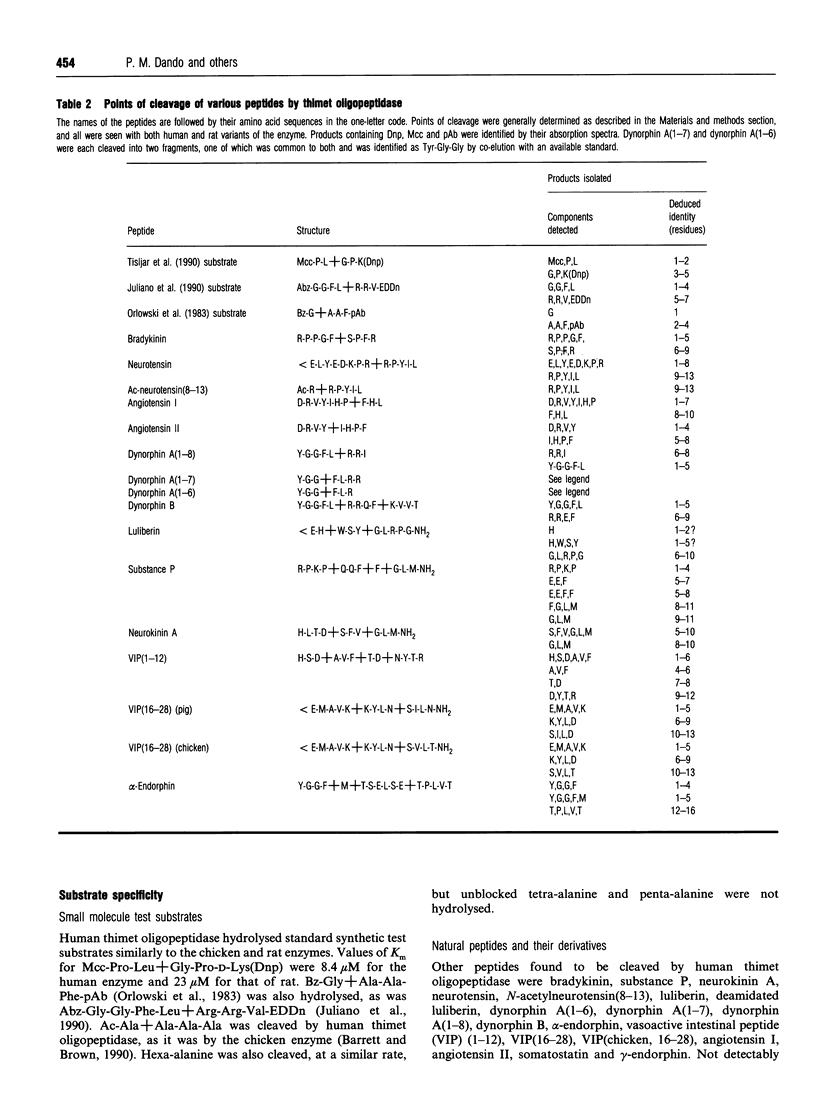
We have purified human thimet oligopeptidase to homogeneity from erythrocytes, and compared it with the enzyme from rat testis and chicken liver. An antiserum raised against rat thimet oligopeptidase also recognized the human and chicken enzymes, suggesting that the structure of the enzyme has been strongly conserved in evolution. Consistent with this, the properties of the human enzyme were very similar to those for the other species. Thus human thimet oligopeptidase also is a thiol-dependent metallo-oligopeptidase with M(r) about 75,000. Specificity for cleavage of a number of peptides was indistinguishable from that of the rat enzyme, but Ki values for the four potent reversible inhibitors tested were lower. In discussing the results, we consider the determinants of the complex substrate specificity of thimet oligopeptidase. We question whether substrates containing more than 17 amino acid residues are cleaved, as has been suggested. We also point out that the favourable location of a proline residue and a free C-terminus in the substrate may be as important as the hydrophobic residues in the P2, P1 and P3' positions that have been emphasized in the past.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anastasi A., Knight C. G., Barrett A. J. Characterization of the bacterial metalloendopeptidase pitrilysin by use of a continuous fluorescence assay. Biochem J. 1993 Mar 1;290(Pt 2):601–607. doi: 10.1042/bj2900601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Brown M. A. Chicken liver Pz-peptidase, a thiol-dependent metallo-endopeptidase. Biochem J. 1990 Nov 1;271(3):701–706. doi: 10.1042/bj2710701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Knight C. G., Brown M. A., Tisljar U. A continuous fluorimetric assay for clostridial collagenase and Pz-peptidase activity. Biochem J. 1989 May 15;260(1):259–263. doi: 10.1042/bj2600259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. Thimet oligopeptidase (EC 3.4.24.15): the same by any name? Biochem J. 1991 Jul 1;277(Pt 1):295–296. doi: 10.1042/bj2770295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Tisljar U. Pz-peptidase is not a matrix metalloproteinase. Matrix Suppl. 1992;1:95–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Tisljar U. The activities of 'Pz-peptidase' and 'endopeptidase 24.15' are due to a single enzyme. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 1;261(3):1047–1050. doi: 10.1042/bj2611047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttle D. J., Abrahamson M., Burnett D., Mort J. S., Barrett A. J., Dando P. M., Hill S. L. Human sputum cathepsin B degrades proteoglycan, is inhibited by alpha 2-macroglobulin and is modulated by neutrophil elastase cleavage of cathepsin B precursor and cystatin C. Biochem J. 1991 Jun 1;276(Pt 2):325–331. doi: 10.1042/bj2760325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camargo A. C., Caldo H., Emson P. C. Degradation of neurotensin by rabbit brain endo-oligopeptidase A and endo-oligopeptidase B (proline-endopeptidase). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Nov 15;116(3):1151–1159. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho K. M., Camargo A. C. Purification of rabbit brain endooligopeptidases and preparation of anti-enzyme antibodies. Biochemistry. 1981 Dec 8;20(25):7082–7088. doi: 10.1021/bi00528a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu T. G., Orlowski M. Soluble metalloendopeptidase from rat brain: action on enkephalin-containing peptides and other bioactive peptides. Endocrinology. 1985 Apr;116(4):1418–1425. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-4-1418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicilini M. A., Ribeiro M. J., de Oliveira E. B., Mortara R. A., de Camargo A. C. Endooligopeptidase A activity in rabbit heart: generation of enkephalin from enkephalin containing peptides. Peptides. 1988 Sep-Oct;9(5):945–955. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(88)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahms P., Mentlein R. Purification of the main somatostatin-degrading proteases from rat and pig brains, their action on other neuropeptides, and their identification as endopeptidases 24.15 and 24.16. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Aug 15;208(1):145–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17168.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camargo A. C., Da Fonseca M. J., Caldo H., De Morais Carvalho K. Influence of the carboxyl terminus of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone and bradykinin on hydrolysis by brain endo-oligopeptidases. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9265–9267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dive V., Lai A., Valensin G., Saba G., Yiotakis A., Toma F. Proton and tritium NMR relaxation studies of peptide inhibitor binding to bacterial collagenase: conformation and dynamics. Biopolymers. 1991 Feb 15;31(3):305–317. doi: 10.1002/bip.360310305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidrich H. G., Kronschnabl O., Hannig K. Eine Endopeptidase aus der Matrix von Rattenlebermitochondrien. Isolierung, Reinigung und Charakterisierung des Enzyms. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1973 Oct-Nov;354(10-11):1399–1404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juliano L., Chagas J. R., Hirata I. Y., Carmona E., Sucupira M., Oliveira E. S., Oliveira E. B., Camargo A. C. A selective assay for endooligopeptidase A based on the cleavage of fluorogenic substrate structurally related to enkephalin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 14;173(2):647–652. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight C. G. A quenched fluorescent substrate for thimet peptidase containing a new fluorescent amino acid, DL-2-amino-3-(7-methoxy-4-coumaryl)propionic acid. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 15;274(Pt 1):45–48. doi: 10.1042/bj2740045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight C. G., Barrett A. J. Structure/function relationships in the inhibition of thimet oligopeptidase by carboxyphenylpropyl-peptides. FEBS Lett. 1991 Dec 9;294(3):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80664-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermott J. R., Biggins J. A., Gibson A. M. Human brain peptidase activity with the specificity to generate the N-terminus of the Alzheimer beta-amyloid protein from its precursor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jun 15;185(2):746–752. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91689-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermott J. R., Gibson A. M., Turner J. D. Involvement of endopeptidase 24.15 in the inactivation of bradykinin by rat brain slices. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jul 15;146(1):154–158. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90704-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros M. S., Iazigi N., Camargo A. C., Oliveira E. B. Distribution and properties of endo-oligopeptidases A and B in the human neuroendocrine system. J Endocrinol. 1992 Dec;135(3):579–588. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1350579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morales T. I., Woessner J. F., Jr PZ-peptidase from chick embryos. Purification, properties, and action on collagen peptides. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4855–4860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira E. B., Martins A. R., Camargo A. C. Isolation of brain endopeptidases: influence of size and sequence of substrates structurally related to bradykinin. Biochemistry. 1976 May 4;15(9):1967–1974. doi: 10.1021/bi00654a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Michaud C., Chu T. G. A soluble metalloendopeptidase from rat brain. Purification of the enzyme and determination of specificity with synthetic and natural peptides. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Sep 1;135(1):81–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Michaud C., Molineaux C. J. Substrate-related potent inhibitors of brain metalloendopeptidase. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 26;27(2):597–602. doi: 10.1021/bi00402a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Reznik S., Ayala J., Pierotti A. R. Endopeptidase 24.15 from rat testes. Isolation of the enzyme and its specificity toward synthetic and natural peptides, including enkephalin-containing peptides. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 1;261(3):951–958. doi: 10.1042/bj2610951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings N. D., Barrett A. J. FLUSYS: a software package for the collection and analysis of kinetic and scanning data from Perkin-Elmer fluorimeters. Comput Appl Biosci. 1990 Apr;6(2):118–119. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/6.2.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakyo K., Kobayashi J., Ito A., Mori Y. Partial purification and characterization of gelatinase and metal dependent peptidase from rabbit uterus and their synergistic action on gelatin in vitro. J Biochem. 1983 Dec;94(6):1913–1923. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöcker W., Ng M., Auld D. S. Fluorescent oligopeptide substrates for kinetic characterization of the specificity of Astacus protease. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 13;29(45):10418–10425. doi: 10.1021/bi00497a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisljar U., Knight C. G., Barrett A. J. An alternative quenched fluorescence substrate for Pz-peptidase. Anal Biochem. 1990 Apr;186(1):112–115. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90582-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisljar U., de Camargo A. C., da Costa C. A., Barrett A. J. Activity of Pz-peptidase and endo-oligopeptidase are due to the same enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):1460–1464. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90838-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toffoletto O., Camargo A. C., Oliveira E. B., Metters K. M., Rossier J. Liberation of enkephalins from enkephalin-containing peptides by brain endo-oligopeptidase A. Biochimie. 1988 Jan;70(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90157-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




