Abstract
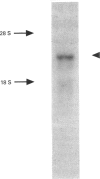
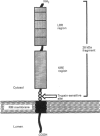
Protein p34 is a non-glycosylated membrane protein characteristic of rough microsomes and is believed to play a role in the ribosome-membrane association. In the present study we isolated cDNA encoding p34 from a rat liver cDNA library and determined its complete amino acid sequence. p34 mRNA is 3.2 kb long and encodes a polypeptide of 307 amino acids with a molecular mass of about 34.9 kDa. Primary sequence analysis, coupled with biochemical studies on the topology, suggested that p34 is a type II signal-anchor protein; it is composed of a large cytoplasmic domain, a membrane-spanning segment and a 38-amino-acid-long luminally disposed C-terminus. The cytoplasmic domain of p34 has several noteworthy structural features, including a region of 4.5 tandem repeats of 23-24 amino acids. The repeated motif shows structural similarity to the leucine-rich repeat which is found in a variety of proteins widely distributed among eukaryotic cells and which potentially functions in mediating protein-protein interactions. The cytoplasmic domain also contains a characteristic hydrophilic region with abundant charged amino acids. These structural regions may be important for the observed ribosome-binding activity of the p34 protein.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blochberger T. C., Vergnes J. P., Hempel J., Hassell J. R. cDNA to chick lumican (corneal keratan sulfate proteoglycan) reveals homology to the small interstitial proteoglycan gene family and expression in muscle and intestine. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):347–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgese N., Mok W., Kreibich G., Sabatini D. D. Ribosomal-membrane interaction: in vitro binding of ribosomes to microsomal membranes. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 25;88(3):559–580. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90408-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. G., Gilmore R. Ribosome binding to the endoplasmic reticulum: a 180-kD protein identified by crosslinking to membrane-bound ribosomes is not required for ribosome binding activity. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(4):639–649. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.4.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dai J., Baxter R. C. Molecular cloning of the acid-labile subunit of the rat insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Oct 15;188(1):304–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92385-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher L. W., Termine J. D., Young M. F. Deduced protein sequence of bone small proteoglycan I (biglycan) shows homology with proteoglycan II (decorin) and several nonconnective tissue proteins in a variety of species. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4571–4576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flick J. S., Johnston M. GRR1 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is required for glucose repression and encodes a protein with leucine-rich repeats. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5101–5112. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fresco L. D., Harper D. S., Keene J. D. Leucine periodicity of U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle (snRNP) A' protein is implicated in snRNP assembly via protein-protein interactions. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1578–1589. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Frehel C., Gouin E., Cossart P. Entry of L. monocytogenes into cells is mediated by internalin, a repeat protein reminiscent of surface antigens from gram-positive cocci. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1127–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90009-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlich D., Prehn S., Hartmann E., Kalies K. U., Rapoport T. A. A mammalian homolog of SEC61p and SECYp is associated with ribosomes and nascent polypeptides during translocation. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):489–503. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90517-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa M., Titani K., Holland L. Z., Roberts J. R., Ruggeri Z. M. The von Willebrand factor-binding domain of platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib. Characterization by monoclonal antibodies and partial amino acid sequence analysis of proteolytic fragments. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12579–12585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto C., Hudson K. L., Anderson K. V. The Toll gene of Drosophila, required for dorsal-ventral embryonic polarity, appears to encode a transmembrane protein. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):269–279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90516-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey M. J., Williams S. A., Roth G. J. Human platelet glycoprotein IX: an adhesive prototype of leucine-rich glycoproteins with flank-center-flank structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6773–6777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofsteenge J., Kieffer B., Matthies R., Hemmings B. A., Stone S. R. Amino acid sequence of the ribonuclease inhibitor from porcine liver reveals the presence of leucine-rich repeats. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 15;27(23):8537–8544. doi: 10.1021/bi00423a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hortsch M., Avossa D., Meyer D. I. Characterization of secretory protein translocation: ribosome-membrane interaction in endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):241–253. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichimura T., Ohsumi T., Shindo Y., Ohwada T., Yagame H., Momose Y., Omata S., Sugano H. Isolation and some properties of a 34-kDa-membrane protein that may be responsible for ribosome binding in rat liver rough microsomes. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jan 13;296(1):7–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80391-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Broek D., Wigler M. DNA sequence and characterization of the S. cerevisiae gene encoding adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):493–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krantz D. E., Zipursky S. L. Drosophila chaoptin, a member of the leucine-rich repeat family, is a photoreceptor cell-specific adhesion molecule. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1969–1977. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08325.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krusius T., Ruoslahti E. Primary structure of an extracellular matrix proteoglycan core protein deduced from cloned cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7683–7687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauffer L., Garcia P. D., Harkins R. N., Coussens L., Ullrich A., Walter P. Topology of signal recognition particle receptor in endoplasmic reticulum membrane. 1985 Nov 28-Dec 4Nature. 318(6044):334–338. doi: 10.1038/318334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F. S., Fox E. A., Zhou H. M., Strydom D. J., Vallee B. L. Primary structure of human placental ribonuclease inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 15;27(23):8545–8553. doi: 10.1021/bi00423a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong S. R., Baxter R. C., Camerato T., Dai J., Wood W. I. Structure and functional expression of the acid-labile subunit of the insulin-like growth factor-binding protein complex. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Jun;6(6):870–876. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.6.1379671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W., Vergnes J. P., Cornuet P. K., Hassell J. R. cDNA clone to chick corneal chondroitin/dermatan sulfate proteoglycan reveals identity to decorin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Jul;296(1):190–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90562-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez J. A., Chung D. W., Fujikawa K., Hagen F. S., Davie E. W., Roth G. J. The alpha and beta chains of human platelet glycoprotein Ib are both transmembrane proteins containing a leucine-rich amino acid sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2135–2139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez J. A., Chung D. W., Fujikawa K., Hagen F. S., Papayannopoulou T., Roth G. J. Cloning of the alpha chain of human platelet glycoprotein Ib: a transmembrane protein with homology to leucine-rich alpha 2-glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5615–5619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland K. C., Sprengel R., Phillips H. S., Köhler M., Rosemblit N., Nikolics K., Segaloff D. L., Seeburg P. H. Lutropin-choriogonadotropin receptor: an unusual member of the G protein-coupled receptor family. Science. 1989 Aug 4;245(4917):494–499. doi: 10.1126/science.2502842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikol D. D., Gulcher J. R., Stefansson K. The oligodendrocyte-myelin glycoprotein belongs to a distinct family of proteins and contains the HNK-1 carbohydrate. J Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;110(2):471–479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.2.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neame P. J., Choi H. U., Rosenberg L. C. The primary structure of the core protein of the small, leucine-rich proteoglycan (PG I) from bovine articular cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8653–8661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nose A., Mahajan V. B., Goodman C. S. Connectin: a homophilic cell adhesion molecule expressed on a subset of muscles and the motoneurons that innervate them in Drosophila. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):553–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90426-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkura H., Yanagida M. S. pombe gene sds22+ essential for a midmitotic transition encodes a leucine-rich repeat protein that positively modulates protein phosphatase-1. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90216-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldberg A., Antonsson P., Lindblom K., Heinegård D. A collagen-binding 59-kd protein (fibromodulin) is structurally related to the small interstitial proteoglycans PG-S1 and PG-S2 (decorin). EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2601–2604. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08399.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang Q., Hays J. B., Rajagopal I. A plant cDNA that partially complements Escherichia coli recA mutations predicts a polypeptide not strongly homologous to RecA proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8073–8077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks G. D., Lamb R. A. Topology of eukaryotic type II membrane proteins: importance of N-terminal positively charged residues flanking the hydrophobic domain. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):777–787. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90507-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patthy L. Detecting homology of distantly related proteins with consensus sequences. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 20;198(4):567–577. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90200-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Bentley R. C., Keene J. D. A common RNA recognition motif identified within a defined U1 RNA binding domain of the 70K U1 snRNP protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinke R., Krantz D. E., Yen D., Zipursky S. L. Chaoptin, a cell surface glycoprotein required for Drosophila photoreceptor cell morphogenesis, contains a repeat motif found in yeast and human. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):291–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90518-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revelard P., Lips S., Pays E. A gene from the VSG expression site of Trypanosoma brucei encodes a protein with both leucine-rich repeats and a putative zinc finger. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7299–7303. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross D. T., Raibaud A., Florent I. C., Sather S., Gross M. K., Storm D. R., Eisen H. The trypanosome VSG expression site encodes adenylate cyclase and a leucine-rich putative regulatory gene. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2047–2053. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07735.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth G. J., Church T. A., McMullen B. A., Williams S. A. Human platelet glycoprotein V: a surface leucine-rich glycoprotein related to adhesion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 16;170(1):153–161. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91253-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg J. M., Jacobs J. R., Goodman C. S., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. slit: an extracellular protein necessary for development of midline glia and commissural axon pathways contains both EGF and LRR domains. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2169–2187. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi M., Tomiyoshi R., Kuroiwa T., Mihara K., Omura T. Functions of signal and signal-anchor sequences are determined by the balance between the hydrophobic segment and the N-terminal charge. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):16–19. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders S. L., Schekman R. Polypeptide translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):13791–13794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savitz A. J., Meyer D. I. Identification of a ribosome receptor in the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):540–544. doi: 10.1038/346540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R., Schweiger M. The yeast DNA repair proteins RAD1 and RAD7 share similar putative functional domains. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jun 3;283(2):203–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80588-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura T., Fujimura K., Maehama S., Takemoto M., Oda K., Fujimoto T., Oyama R., Suzuki M., Ichihara-Tanaka K., Titani K. Rapid purification and characterization of human platelet glycoprotein V: the amino acid sequence contains leucine-rich repetitive modules as in glycoprotein Ib. Blood. 1990 Jun 15;75(12):2349–2356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinomura T., Kimata K. Proteoglycan-Lb, a small dermatan sulfate proteoglycan expressed in embryonic chick epiphyseal cartilage, is structurally related to osteoinductive factor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1265–1270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shires T. K., Narurkar L., Pitot H. C. The association in vitro of polyribosomes with ribonuclease-treated derivatives of hepatic rough endoplasmic reticulum. Characteristics of the membrane binding sites and factors influencing association. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(1):67–79. doi: 10.1042/bj1250067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillekens P. T., Beijer R. P., Habets W. J., van Verooij W. J. Molecular cloning of the cDNA for the human U2 snRNA-specific A' protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1893–1906. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. M., Blobel G. A protein-conducting channel in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):371–380. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90455-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Choe H. R., Nishida Y., Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Ohnishi S., Tamaoki T., Kataoka T. Leucine-rich repeats and carboxyl terminus are required for interaction of yeast adenylate cyclase with RAS proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8711–8715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima S., Lauffer L., Rath V. L., Walter P. The signal recognition particle receptor is a complex that contains two distinct polypeptide chains. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1167–1178. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Takahashi Y., Putnam F. W. Periodicity of leucine and tandem repetition of a 24-amino acid segment in the primary structure of leucine-rich alpha 2-glycoprotein of human serum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1906–1910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. C., Lim L. Novel brain-specific bovine cDNA for a developmentally regulated mRNA encoding a putative new member of the leucine-rich glycoprotein (LRG) family. Neurochem Res. 1992 Sep;17(9):907–916. doi: 10.1007/BF00993267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan F., Weerasinghe D. K., Skidgel R. A., Tamei H., Kaul R. K., Roninson I. B., Schilling J. W., Erdös E. G. The deduced protein sequence of the human carboxypeptidase N high molecular weight subunit reveals the presence of leucine-rich tandem repeats. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):13–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazawa S., Unuma M., Tondokoro N., Asano Y., Ohsumi T., Ichimura T., Sugano H. Identification of a membrane protein responsible for ribosome binding in rough microsomal membranes. J Biochem. 1991 Jan;109(1):89–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicki A. N., Clemetson K. J. Structure and function of platelet membrane glycoproteins Ib and V. Effects of leukocyte elastase and other proteases on platelets response to von Willebrand factor and thrombin. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Nov 15;153(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09259.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Tamaoki T., Choe H. R., Tanaka H., Kataoka T. Adenylate cyclases in yeast: a comparison of the genes from Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5693–5697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]