Abstract
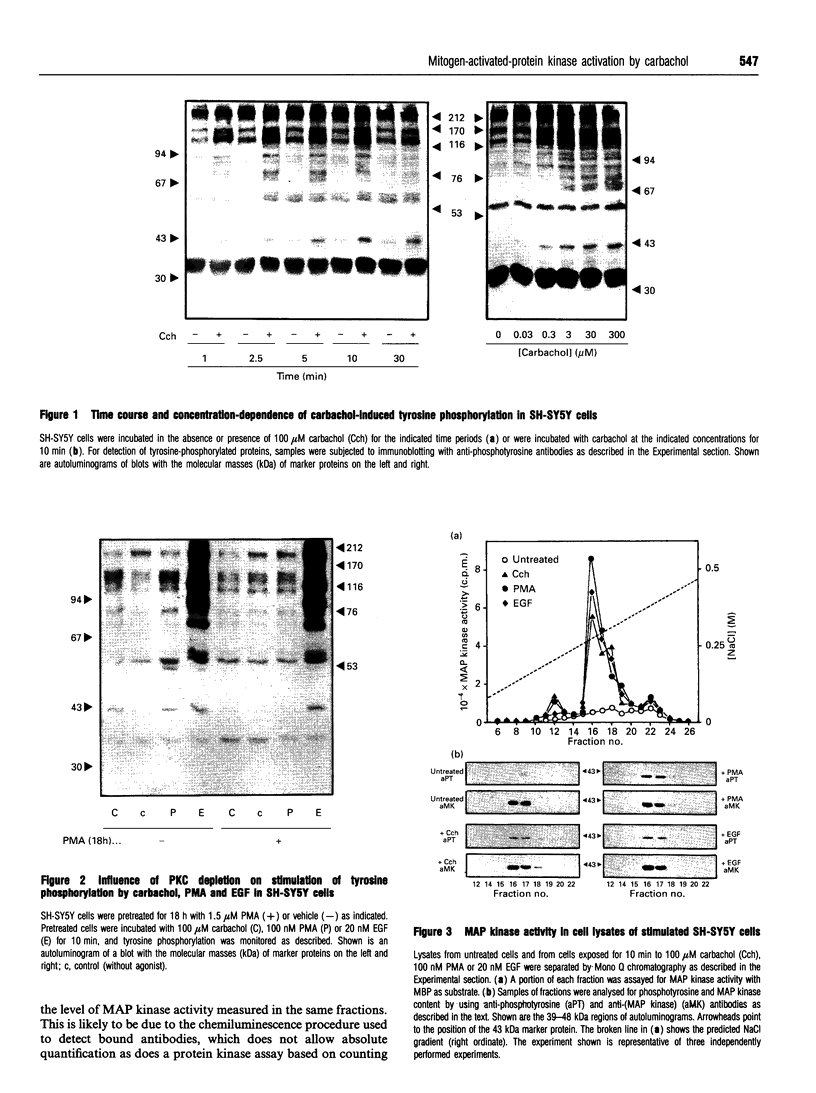
Activation of the G-protein-coupled muscarinic (M3) receptor in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells is known to lead to phosphoinositol hydrolysis and noradrenaline release. In this study, the effect of carbachol on tyrosine phosphorylation and mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase activity in SH-SY5Y cells was examined. Carbachol concentration-dependently induced tyrosine phosphorylation of several proteins, including one of 42 kDa. This tyrosine-phosphorylated 42 kDa protein co-eluted from a Mono Q anion-exchange column with MAP kinase activity and with immunologically detected MAP kinase. Stimulation of tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of MAP kinase were also observed after incubation of cells with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and epidermal growth factor (EGF). Down-regulation or inhibition of protein kinase C (PKC) abolished the stimulatory effects of both carbachol and PMA on MAP kinase activity, whereas EGF-stimulated MAP kinase activity remained unaffected. Thus carbachol acting through the muscarinic (M3) receptor PKC-dependently induced tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of a 42 kDa MAP kinase in SH-SY5Y cells, whereas EGF-induced MAP kinase activation occurred independently of PKC.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. D., Parker P. J. Activation of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase by a MAP kinase-kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13135–13137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahn N. G., Seger R., Bratlien R. L., Diltz C. D., Tonks N. K., Krebs E. G. Multiple components in an epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein kinase cascade. In vitro activation of a myelin basic protein/microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4220–4227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. G., Kilgour E., Sturgill T. W. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase in BC3H1 myocytes by fluoroaluminate. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10131–10135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. G., Maller J. L., Tonks N. K., Sturgill T. W. Requirement for integration of signals from two distinct phosphorylation pathways for activation of MAP kinase. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):651–653. doi: 10.1038/343651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Gregory J. S., Cobb M. H. Purification and properties of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1, an insulin-stimulated microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 8;30(1):278–286. doi: 10.1021/bi00215a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H., Boulton T. G., Robbins D. J. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases: ERKs in progress. Cell Regul. 1991 Dec;2(12):965–978. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.12.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Alessandrini A., Erikson R. L. The primary structure of MEK, a protein kinase that phosphorylates the ERK gene product. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):478–480. doi: 10.1126/science.1411546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent P., Haser W., Haystead T. A., Vincent L. A., Roberts T. M., Sturgill T. W. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase by v-Raf in NIH 3T3 cells and in vitro. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1404–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.1326789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson A. K., Payne D. M., Martino P. A., Rossomando A. J., Shabanowitz J., Weber M. J., Hunt D. F., Sturgill T. W. Identification by mass spectrometry of threonine 97 in bovine myelin basic protein as a specific phosphorylation site for mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19728–19735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallego C., Gupta S. K., Heasley L. E., Qian N. X., Johnson G. L. Mitogen-activated protein kinase activation resulting from selective oncogene expression in NIH 3T3 and rat 1a cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7355–7359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Nemeth S. P., Brugge J. S. Blood platelets express high levels of the pp60c-src-specific tyrosine kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):852–856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh Y., Nishida E., Yamashita T., Hoshi M., Kawakami M., Sakai H. Microtubule-associated-protein (MAP) kinase activated by nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor in PC12 cells. Identity with the mitogen-activated MAP kinase of fibroblastic cells. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 13;193(3):661–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. K., Gallego C., Johnson G. L., Heasley L. E. MAP kinase is constitutively activated in gip2 and src transformed rat 1a fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):7987–7990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutkind J. S., Novotny E. A., Brann M. R., Robbins K. C. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes as agonist-dependent oncogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4703–4707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe L. R., Leevers S. J., Gómez N., Nakielny S., Cohen P., Marshall C. J. Activation of the MAP kinase pathway by the protein kinase raf. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90361-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huckle W. R., Dy R. C., Earp H. S. Calcium-dependent increase in tyrosine kinase activity stimulated by angiotensin II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8837–8841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. A., Walseth T. F. The enzymatic preparation of [alpha-32P]ATP, [alpha-32P]GTP, [32P]cAMP, and [32P]cGMP, and their use in the assay of adenylate and guanylate cyclases and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:135–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Identification of multiple novel polypeptide substrates of the v-src, v-yes, v-fps, v-ros, and v-erb-B oncogenic tyrosine protein kinases utilizing antisera against phosphotyrosine. Oncogene. 1988 Apr;2(4):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., App H., Zhang X. F., Banerjee P., Brautigan D. L., Rapp U. R., Avruch J. Raf-1 activates MAP kinase-kinase. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):417–421. doi: 10.1038/358417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert D. G., Challiss R. A., Nahorski S. R. Accumulation and metabolism of Ins(1,4,5)P3 and Ins(1,3,4,5)P4 in muscarinic-receptor-stimulated SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 1;273(Pt 3):791–794. doi: 10.1042/bj2730791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert D. G., Ghataorre A. S., Nahorski S. R. Muscarinic receptor binding characteristics of a human neuroblastoma SK-N-SH and its clones SH-SY5Y and SH-EP1. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Jun 8;165(1):71–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90771-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laugwitz K. L., Offermanns S., Spicher K., Schultz G. mu and delta opioid receptors differentially couple to G protein subtypes in membranes of human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Neuron. 1993 Feb;10(2):233–242. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90314-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum E., Parker P. J., Carozzi A. The PtdIns-PLC superfamily and signal transduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 19;1092(1):49–71. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90177-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy N. P., Ball S. G., Vaughan P. F. Potassium- and carbachol-evoked release of [3H]noradrenaline from human neuroblastoma cells, SH-SY5Y. J Neurochem. 1991 May;56(5):1810–1815. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02085.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson N. M. Molecular properties of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1987;10:195–236. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.10.030187.001211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offermanns S., Bombien E., Schultz G. Thrombin Ca(2+)-dependently stimulates protein tyrosine phosphorylation in BC3H1 muscle cells. Biochem J. 1993 Feb 15;290(Pt 1):27–32. doi: 10.1042/bj2900027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offermanns S., Seifert R., Metzger J. W., Jung G., Lieberknecht A., Schmidt U., Schultz G. Lipopeptides are effective stimulators of tyrosine phosphorylation in human myeloid cells. Biochem J. 1992 Mar 1;282(Pt 2):551–557. doi: 10.1042/bj2820551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta S., Inazu T., Taniguchi T., Nakagawara G., Yamamura H. Protein-tyrosine phosphorylations induced by concanavalin A and N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine in human neutrophils. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jun 15;206(3):895–900. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16998.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrow V., Nånberg E., Heikkilä J., Hammerling U., Påhlman S. Protein kinase C remains functionally active during TPA induced neuronal differentiation of SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Sep;152(3):536–544. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041520313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Sanghera J. S. Mitogen-activated protein kinases: versatile transducers for cell signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jun;17(6):233–238. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)80005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp U. R. Role of Raf-1 serine/threonine protein kinase in growth factor signal transduction. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):495–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossomando A. J., Payne D. M., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Evidence that pp42, a major tyrosine kinase target protein, is a mitogen-activated serine/threonine protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6940–6943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossomando A., Wu J., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. The phorbol ester-dependent activator of the mitogen-activated protein kinase p42mapk is a kinase with specificity for the threonine and tyrosine regulatory sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5221–5225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorge L. K., Levy B. T., Maness P. F. pp60c-src is developmentally regulated in the neural retina. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Wu J. Recent progress in characterization of protein kinase cascades for phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 17;1092(3):350–357. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(97)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sözeri O., Vollmer K., Liyanage M., Frith D., Kour G., Mark G. E., 3rd, Stabel S. Activation of the c-Raf protein kinase by protein kinase C phosphorylation. Oncogene. 1992 Nov;7(11):2259–2262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T. Use and specificity of staurosporine, UCN-01, and calphostin C as protein kinase inhibitors. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:340–347. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01030-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Kitagawa H., Yasue S., Yanagi S., Sakai K., Asahi M., Ohta S., Takeuchi F., Nakamura S., Yamamura H. Protein-tyrosine kinase p72syk is activated by thrombin and is negatively regulated through Ca2+ mobilization in platelets. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2277–2279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. MAP kinase by any other name smells just as sweet. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):3–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90199-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Harrison J. K., Vincent L. A., Haystead C., Haystead T. A., Michel H., Hunt D. F., Lynch K. R., Sturgill T. W. Molecular structure of a protein-tyrosine/threonine kinase activating p42 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase: MAP kinase kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):173–177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachary I., Sinnett-Smith J., Rozengurt E. Stimulation of tyrosine kinase activity in anti-phosphotyrosine immune complexes of Swiss 3T3 cell lysates occurs rapidly after addition of bombesin, vasopressin, and endothelin to intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):24126–24133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]