Abstract
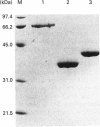
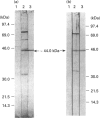
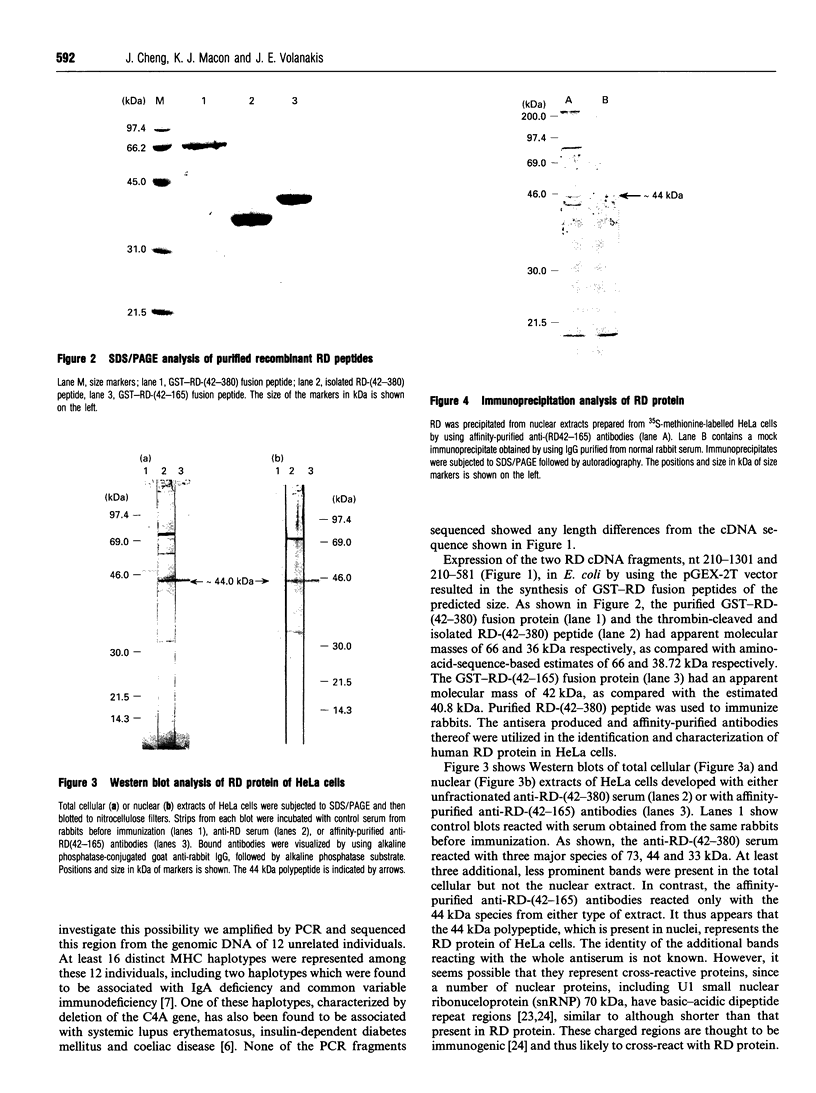
The RD gene, initially defined in the mouse, has been mapped between the Bf and C4A genes in the human major histocompatibility complex class III region. Using the mouse cDNA as a probe, we isolated and sequenced human RD cDNA clones. The composite nucleotide sequence consisted of 1301 nucleotides, excluding a poly(A) tail at the 3' end. It contained a single open reading frame encoding a polypeptide of 380 amino acid residues with a calculated molecular mass of 42274 Da. The most striking structural feature of the deduced amino acid sequence is a region consisting entirely of 24 tandem repeats of an Arg-Asp (or Glu) dipeptide. The human RD cDNA was expressed in Escherichia coli as a fusion protein with glutathione S-transferase and used to produce antisera in rabbits. Western blot analysis and immunoprecipitation of lysates of biosynthetically labelled HeLa cells indicated that RD is a 44 kDa nuclear protein.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brendel V., Dohlman J., Blaisdell B. E., Karlin S. Very long charge runs in systemic lupus erythematosus-associated autoantigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1536–1540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douvas A., Sobelman S. Multiple overlapping homologies between two rheumatoid antigens and immunosuppressive viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6328–6332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French M. A., Dawkins R. L. Central MHC genes, IgA deficiency and autoimmune disease. Immunol Today. 1990 Aug;11(8):271–274. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90110-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Factor required for mammalian spliceosome assembly is localized to discrete regions in the nucleus. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):437–441. doi: 10.1038/343437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Royle N. J., Wilson V., Wong Z. Spontaneous mutation rates to new length alleles at tandem-repetitive hypervariable loci in human DNA. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):278–281. doi: 10.1038/332278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall E., Sargent C. A., Campbell R. D. Human major histocompatibility complex contains a new cluster of genes between the HLA-D and complement C4 loci. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7251–7257. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Structural features in eukaryotic mRNAs that modulate the initiation of translation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):19867–19870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévi-Strauss M., Carroll M. C., Steinmetz M., Meo T. A previously undetected MHC gene with an unusual periodic structure. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):201–204. doi: 10.1126/science.3353717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. R., Kramer F. R. Structure-independent nucleotide sequence analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2232–2235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragoussis J., Monaco A., Mockridge I., Kendall E., Campbell R. D., Trowsdale J. Cloning of the HLA class II region in yeast artificial chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3753–3757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. Protein composition of mammalian spliceosomes assembled in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8031–8035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent C. A., Dunham I., Campbell R. D. Identification of multiple HTF-island associated genes in the human major histocompatibility complex class III region. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2305–2312. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08357.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheets M. D., Ogg S. C., Wickens M. P. Point mutations in AAUAAA and the poly (A) addition site: effects on the accuracy and efficiency of cleavage and polyadenylation in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5799–5805. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speiser P. W., White P. C. Structure of the human RD gene: a highly conserved gene in the class III region of the major histocompatibility complex. DNA. 1989 Dec;8(10):745–751. doi: 10.1089/dna.1989.8.745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spies T., Blanck G., Bresnahan M., Sands J., Strominger J. L. A new cluster of genes within the human major histocompatibility complex. Science. 1989 Jan 13;243(4888):214–217. doi: 10.1126/science.2911734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spies T., Bresnahan M., Strominger J. L. Human major histocompatibility complex contains a minimum of 19 genes between the complement cluster and HLA-B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8955–8958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surowy C. S., Hoganson G., Gosink J., Strunk K., Spritz R. A. The human RD protein is closely related to nuclear RNA-binding proteins and has been highly conserved. Gene. 1990 Jun 15;90(2):299–302. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90194-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes B. C. DNA in heritable disease. Lancet. 1983 Oct 1;2(8353):787–788. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92314-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volanakis J. E., Zhu Z. B., Schaffer F. M., Macon K. J., Palermos J., Barger B. O., Go R., Campbell R. D., Schroeder H. W., Jr, Cooper M. D. Major histocompatibility complex class III genes and susceptibility to immunoglobulin A deficiency and common variable immunodeficiency. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jun;89(6):1914–1922. doi: 10.1172/JCI115797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., Vitek J., Lahita R. G., Speiser P. W. Polymorphism in the RD (D6S45) gene. Hum Genet. 1992 May;89(2):243–244. doi: 10.1007/BF00217132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]