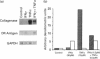Abstract
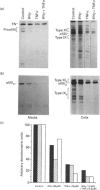
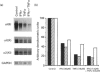
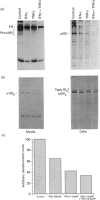
To examine the possibility that cytokines produced in inflamed joint tissues may contribute to the loss of articular cartilage by causing inhibition of synthesis of cartilage-specific matrix macromolecules, we studied the effects of interferon gamma (IFN gamma) and tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha), alone and in combination, on the expression of the genes for types-II, -IX and -XI collagens in cultured human chondrocytes. Chondrocytes isolated from human fetal epiphyseal cartilage by sequential enzymic digestions were cultured in the presence of IFN gamma (30 pM), TNF alpha (15 pM) or a combination of suboptimal concentrations of both cytokines (1.5 pM IFN gamma plus 0.3 pM TNF alpha). IFN gamma caused a maximal decrease of 23.3-32.6% in the biosynthesis of collagen by chondrocytes. TNF alpha was a more potent inhibitor causing a 42.8-45.3% decrease at one-half the concentration of IFN gamma. A synergistic inhibitory effect of 58.2% was observed with the combination of 1.5 pM IFN gamma plus 0.3 pM TNF alpha. Electrophoretic analysis of the biosynthesized proteins showed a co-ordinate decrease in the production of the three cartilage-specific collagen types II, IX and XI. These effects were accompanied by parallel changes in the steady-state levels of their corresponding mRNAs. In vitro transcription assays showed that the collagen inhibitory effects of the cytokines occurred largely at the transcriptional level. Similar effects of the cytokines were observed on biosynthesis of types-II, -IX and -XI collagens and steady-state mRNA levels for type-II collagen by chondrocytes obtained from adult articular cartilage. These observations indicate that IFN gamma and TNF alpha can induce a synergistic inhibition of the synthesis of cartilage-specific collagens by fetal and adult human chondrocytes and suggest that these effects may contribute to the articular cartilage loss that occurs in inflammatory joint diseases.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amento E. P., Bhan A. K., McCullagh K. G., Krane S. M. Influences of gamma interferon on synovial fibroblast-like cells. Ia induction and inhibition of collagen synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):837–848. doi: 10.1172/JCI112041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin C. T., Reginato A. M., Smith C., Jimenez S. A., Prockop D. J. Structure of cDNA clones coding for human type II procollagen. The alpha 1(II) chain is more similar to the alpha 1(I) chain than two other alpha chains of fibrillar collagens. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 1;262(2):521–528. doi: 10.1042/bj2620521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendtzen K., Petersen J., Halkjaer-Kristensen J., Ingemann-Hansen T. Interleukin-1-like activities in synovial fluids of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and traumatic synovitis. Rheumatol Int. 1985;5(2):79–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00270301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruckner P., Mendler M., Steinmann B., Huber S., Winterhalter K. H. The structure of human collagen type IX and its organization in fetal and infant cartilage fibrils. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16911–16917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesario T. C., Andrews B. S., Martin D. A., Jason M., Treadwell T., Friou G., Tilles J. G. Interferon in synovial fluid and serum of patients with rheumatic disease. J Rheumatol. 1983 Aug;10(4):647–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor stimulates collagenase and prostaglandin E2 production by human synovial cells and dermal fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):2163–2168. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., Bréard J., Chess L., Krane S. M. Participation of monocyte-macrophages and lymphocytes in the production of a factor that stimulates collagenase and prostaglandin release by rheumatoid synovial cells. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1386–1392. doi: 10.1172/JCI109596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., Demczuk S. Cytokines and other mediators in rheumatoid arthritis. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1984;7(4):387–413. doi: 10.1007/BF00201968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGré M., Mellbye O. J., Clarke-Jenssen O. Immune interferon in serum and synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis and related disorders. Ann Rheum Dis. 1983 Dec;42(6):672–676. doi: 10.1136/ard.42.6.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingle J. T., Horner A., Shield M. The sensitivity of synthesis of human cartilage matrix to inhibition by IL-1 suggests a mechanism for the development of osteoarthritis. Cell Biochem Funct. 1991 Apr;9(2):99–102. doi: 10.1002/cbf.290090206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestein G. S., Zvaifler N. J. Peripheral blood and synovial fluid monocyte activation in inflammatory arthritis. II. Low levels of synovial fluid and synovial tissue interferon suggest that gamma-interferon is not the primary macrophage activating factor. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Aug;30(8):864–871. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldring M. B., Sandell L. J., Stephenson M. L., Krane S. M. Immune interferon suppresses levels of procollagen mRNA and type II collagen synthesis in cultured human articular and costal chondrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):9049–9055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gowen M., Wood D. D., Ihrie E. J., Meats J. E., Russell R. G. Stimulation by human interleukin 1 of cartilage breakdown and production of collagenase and proteoglycanase by human chondrocytes but not by human osteoblasts in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Feb 14;797(2):186–193. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90121-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr, DiBona D. R., Krane S. M. A mechanism for cartilage destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1970;83:267–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins S. J., Meager A. Cytokines in synovial fluid: II. The presence of tumour necrosis factor and interferon. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Jul;73(1):88–92. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasin H. E., Dingle J. T. Human mononuclear cell factors mediate cartilage matrix degradation through chondrocyte activation. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):571–581. doi: 10.1172/JCI110290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez S. A., Yankowski R., Reginato A. M. Quantitative analysis of type X-collagen biosynthesis by embryonic-chick sternal cartilage. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):357–367. doi: 10.1042/bj2330357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krane S. M., Conca W., Stephenson M. L., Amento E. P., Goldring M. B. Mechanisms of matrix degradation in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;580:340–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb17943.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre V., Peeters-Joris C., Vaes G. Modulation by interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha of production of collagenase, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases and collagen types in differentiated and dedifferentiated articular chondrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 22;1052(3):366–378. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90145-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the ovalbumin and conalbumin genes by steroid hormones in chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9050–9058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nouri A. M., Panayi G. S., Goodman S. M. Cytokines and the chronic inflammation of rheumatic disease. I. The presence of interleukin-1 in synovial fluids. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Feb;55(2):295–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky B., Diegelmann R. Use of a mixture of proteinase-free collagenases for the specific assay of radioactive collagen in the presence of other proteins. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 16;10(6):988–994. doi: 10.1021/bi00782a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfizenmaier K., Scheurich P., Schlüter C., Krönke M. Tumor necrosis factor enhances HLA-A,B,C and HLA-DR gene expression in human tumor cells. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):975–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pujol-Borrell R., Todd I., Doshi M., Bottazzo G. F., Sutton R., Gray D., Adolf G. R., Feldmann M. HLA class II induction in human islet cells by interferon-gamma plus tumour necrosis factor or lymphotoxin. Nature. 1987 Mar 19;326(6110):304–306. doi: 10.1038/326304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggiero V., Tavernier J., Fiers W., Baglioni C. Induction of the synthesis of tumor necrosis factor receptors by interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2445–2450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rédini F., Lafuma C., Pujol J. P., Robert L., Hornebeck W. Effect of cytokines and growth factors on the expression of elastase activity by human synoviocytes, dermal fibroblasts and rabbit articular chondrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 15;155(2):786–793. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80564-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saklatvala J. Tumour necrosis factor alpha stimulates resorption and inhibits synthesis of proteoglycan in cartilage. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):547–549. doi: 10.1038/322547a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxne T., Palladino M. A., Jr, Heinegård D., Talal N., Wollheim F. A. Detection of tumor necrosis factor alpha but not tumor necrosis factor beta in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid and serum. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Aug;31(8):1041–1045. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby M. R., Aggarwal B. B., Rinderknecht E., Svedersky L. P., Finkle B. S., Palladino M. A., Jr Activation of human polymorphonuclear neutrophil functions by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factors. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2069–2073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor exerts endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine control of inflammatory responses. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1269–1277. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinmei M., Masuda K., Kikuchi T., Shimomura Y. Interleukin 1, tumor necrosis factor, and interleukin 6 as mediators of cartilage destruction. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Feb;18(3 Suppl 1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(89)90081-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson M. L., Krane S. M., Amento E. P., McCroskery P. A., Byrne M. Immune interferon inhibits collagen synthesis by rheumatoid synovial cells associated with decreased levels of the procollagen mRNAs. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 21;180(1):43–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. A. Articular cartilage cultured with catabolin (pig interleukin 1) synthesizes a decreased number of normal proteoglycan molecules. Biochem J. 1985 May 1;227(3):869–878. doi: 10.1042/bj2270869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. A., Benton H. P. Synthesis of type II collagen is decreased in cartilage cultured with interleukin 1 while the rate of intracellular degradation remains unchanged. Coll Relat Res. 1988 Sep;8(5):393–405. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(88)80013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Long E. O., Strubin M., Gross N., Accolla R., Carrel S., Mach B. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding HLA-DR alpha chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6979–6983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt F. M., Dudhia J. Prolonged expression of differentiated phenotype by chondrocytes cultured at low density on a composite substrate of collagen and agarose that restricts cell spreading. Differentiation. 1988 Jul;38(2):140–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1988.tb00208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitham S. E., Murphy G., Angel P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Smith B. J., Lyons A., Harris T. J., Reynolds J. J., Herrlich P., Docherty A. J. Comparison of human stromelysin and collagenase by cloning and sequence analysis. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):913–916. doi: 10.1042/bj2400913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Goeddel D. V. Tumour necrosis factors alpha and beta inhibit virus replication and synergize with interferons. 1986 Oct 30-Nov 5Nature. 323(6091):819–822. doi: 10.1038/323819a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yocum D. E., Esparza L., Dubry S., Benjamin J. B., Volz R., Scuderi P. Characteristics of tumor necrosis factor production in rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Immunol. 1989 Aug;122(1):131–145. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]