Abstract
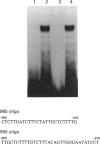
The far upstream region of the rat androgen receptor (AR) gene has been cloned, and the nucleotide sequence up to -2656 bp established. Nested deletion mutants of rat AR 5' flanking sequences were ligated to the luciferase reporter gene, and their promoter activities were examined in transfected COS1 cells. Results show a critical cis-acting domain located between positions -960 and -940. Deletion of this cis element resulted in a greater than 90% decrease in the promoter activity. A nuclear protein that specifically binds to this 21-nucleotide sequence was identified by gel mobility shift analysis. The -960/-940 cis element has no identify to the binding sequence of any known transcription factor. Furthermore, the cognate binding protein is present in both rat and human (HeLa) cell nuclear extracts. We conclude that a novel trans-activator interacting at the -960/-940 region plays a critical role in the regulation of AR gene expression.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baarends W. M., Themmen A. P., Blok L. J., Mackenbach P., Brinkmann A. O., Meijer D., Faber P. W., Trapman J., Grootegoed J. A. The rat androgen receptor gene promoter. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1990 Nov 12;74(1):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(90)90207-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankier A. T., Weston K. M., Barrell B. G. Random cloning and sequencing by the M13/dideoxynucleotide chain termination method. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:51–93. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Tjian R. Transcription factors and the control of Drosophila development. Trends Genet. 1989 Nov;5(11):377–383. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90173-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. S., Kokontis J., Liao S. T. Molecular cloning of human and rat complementary DNA encoding androgen receptors. Science. 1988 Apr 15;240(4850):324–326. doi: 10.1126/science.3353726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy B., Nathans D. DNA binding site of the growth factor-inducible protein Zif268. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8737–8741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey D. S., Pienta K. J. New concepts in studying the control of normal and cancer growth of the prostate. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1987;239:1–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colvard D. S., Eriksen E. F., Keeting P. E., Wilson E. M., Lubahn D. B., French F. S., Riggs B. L., Spelsberg T. C. Identification of androgen receptors in normal human osteoblast-like cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):854–857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Franza B. R., Jr Fos and Jun: the AP-1 connection. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Encío I. J., Detera-Wadleigh S. D. The genomic structure of the human glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):7182–7188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber P. W., van Rooij H. C., van der Korput H. A., Baarends W. M., Brinkmann A. O., Grootegoed J. A., Trapman J. Characterization of the human androgen receptor transcription unit. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):10743–10749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. V., Jacob P. E., Ringold G. M., Lee F. Expression and regulation of Escherichia coli lacZ gene fusions in mammalian cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):101–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huckaby C. S., Conneely O. M., Beattie W. G., Dobson A. D., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Structure of the chromosomal chicken progesterone receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8380–8384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issemann I., Green S. Activation of a member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily by peroxisome proliferators. Nature. 1990 Oct 18;347(6294):645–650. doi: 10.1038/347645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenster G., van der Korput J. A., Trapman J., Brinkmann A. O. Functional domains of the human androgen receptor. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1992 Mar;41(3-8):671–675. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(92)90402-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Celada A., Van Beveren C., Maki R. A. The macrophage and B cell-specific transcription factor PU.1 is related to the ets oncogene. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclerc S., Xie B. X., Roy R., Govindan M. V. Purification of a human glucocorticoid receptor gene promoter-binding protein. Production of polyclonal antibodies against the purified factor. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8711–8719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubahn D. B., Joseph D. R., Sullivan P. M., Willard H. F., French F. S., Wilson E. M. Cloning of human androgen receptor complementary DNA and localization to the X chromosome. Science. 1988 Apr 15;240(4850):327–330. doi: 10.1126/science.3353727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. E., Piette J., Yaniv M., Tang W. J., Folk W. R. Activation of the polyomavirus enhancer by a murine activator protein 1 (AP1) homolog and two contiguous proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5839–5843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEwen B. S. Binding and metabolism of sex steroids by the hypothalamic-pituitary unit: physiological implications. Annu Rev Physiol. 1980;42:97–110. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.42.030180.000525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milin B., Roy A. K. Androgen "receptor" in rat liver: cytosol "receptor" deficiency in pseudohermaphrodite male rats. Nat New Biol. 1973 Apr 25;242(121):248–250. doi: 10.1038/newbio242248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmark J. R., Hardy D. O., Tonb D. C., Carter B. S., Epstein J. I., Isaacs W. B., Brown T. R., Barrack E. R. Androgen receptor gene mutations in human prostate cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6319–6323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley B. The steroid receptor superfamily: more excitement predicted for the future. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;4(3):363–369. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-3-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pajunen A. E., Isomaa V. V., Jänne O. A., Bardin C. W. Androgenic regulation of ornithine decarboxylase activity in mouse kidney and its relationship to changes in cytosol and nuclear androgen receptor concentrations. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8190–8198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinsky L., Kaufman M. Genetics of steroid receptors and their disorders. Adv Hum Genet. 1987;16:299–472. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0620-8_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prestridge D. S. SIGNAL SCAN: a computer program that scans DNA sequences for eukaryotic transcriptional elements. Comput Appl Biosci. 1991 Apr;7(2):203–206. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/7.2.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Brasier A. R., Wright K. A., Tate J. E., Habener J. F. An inducible 50-kilodalton NF kappa B-like protein and a constitutive protein both bind the acute-phase response element of the angiotensinogen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1023–1032. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song C. S., Rao T. R., Demyan W. F., Mancini M. A., Chatterjee B., Roy A. K. Androgen receptor messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) in the rat liver: changes in mRNA levels during maturation, aging, and calorie restriction. Endocrinology. 1991 Jan;128(1):349–356. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-1-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilley W. D., Marcelli M., McPhaul M. J. Expression of the human androgen receptor gene utilizes a common promoter in diverse human tissues and cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13776–13781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarbrough W. G., Quarmby V. E., Simental J. A., Joseph D. R., Sar M., Lubahn D. B., Olsen K. L., French F. S., Wilson E. M. A single base mutation in the androgen receptor gene causes androgen insensitivity in the testicular feminized rat. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8893–8900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]