Abstract
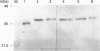
The tetrameric extracellular superoxide dismutase (EC-SOD) in human tissues and plasma has previously been found to be heterogenous with regard to heparin affinity and could be divided into at least three classes: A, lacking heparin affinity; B, with weak affinity; and C, with strong affinity. Using rigorous extraction conditions and an extensive set of anti-proteolytic agents, tissue EC-SOD is now shown to be almost exclusively of native homotetrameric C-class. Plasma EC-SOD on the other hand is shown to be mainly composed of a complex mixture of heterotetramers with modifications probably residing in the C-terminal heparin-binding domain. Proteolytic truncations appear to be a major cause of this heterogeneity. The findings suggest that, since 99% of the EC-SOD in the human body exists in the extravascular space of tissue, EC-SOD is primarily synthesized in tissues and secreted as homotetrameric native EC-SOD C. This tissue EC-SOD C should exist almost completely sequestered by heparin sulphate proteoglycans. C-terminal modifications subsequently occurring in the EC-SOD C would weaken the binding to heparan sulphate proteoglycan, facilitate entrance to the vasculature through capillaries and lymph flow, and finally result in the heterogeneous plasma EC-SOD pattern. With the new extraction and analysis procedure, the tissue content of EC-SOD is found to be higher than previously reported. It is found, for example, when compared with Mn-SOD, to be higher in umbilical cord and uterus, about equal in placenta and testis and as high as that of CuZn-SOD in umbilical cord. The findings suggest that the protection level against superoxide radicals provided by EC-SOD in the tissue interstitial space, given the small distribution volume, is not much less prominent than that bestowed on the intracellular space by CuZn-SOD and Mn-SOD.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi T., Marklund S. L. Interactions between human extracellular superoxide dismutase C and sulfated polysaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8537–8541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adachi T., Ohta H., Hayashi K., Hirano K., Marklund S. L. The site of nonenzymic glycation of human extracellular-superoxide dismutase in vitro. Free Radic Biol Med. 1992 Sep;13(3):205–210. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(92)90016-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adachi T., Ohta H., Hirano K., Hayashi K., Marklund S. L. Non-enzymic glycation of human extracellular superoxide dismutase. Biochem J. 1991 Oct 1;279(Pt 1):263–267. doi: 10.1042/bj2790263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjalmarsson K., Marklund S. L., Engström A., Edlund T. Isolation and sequence of complementary DNA encoding human extracellular superoxide dismutase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6340–6344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson K., Edlund A., Sandström J., Marklund S. L. Proteolytic modification of the heparin-binding affinity of extracellular superoxide dismutase. Biochem J. 1993 Mar 1;290(Pt 2):623–626. doi: 10.1042/bj2900623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson K., Lindahl U., Marklund S. L. Binding of human extracellular superoxide dismutase C to sulphated glycosaminoglycans. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 15;256(1):29–33. doi: 10.1042/bj2560029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson K., Marklund S. L. Binding of human extracellular-superoxide dismutase C to cultured cell lines and to blood cells. Lab Invest. 1989 May;60(5):659–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson K., Marklund S. L. Extracellular superoxide dismutase in the vascular system of mammals. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):223–228. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson K., Marklund S. L. Heparin-induced release of extracellular superoxide dismutase to human blood plasma. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 15;242(1):55–59. doi: 10.1042/bj2420055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson K., Marklund S. L. Plasma clearance of human extracellular-superoxide dismutase C in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):762–766. doi: 10.1172/JCI113676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin Y., Skidgel R. A., Erdös E. G. Isolation and characterization of the subunits of human plasma carboxypeptidase N (kininase i). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4618–4622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marklund S. L., Bjelle A., Elmqvist L. G. Superoxide dismutase isoenzymes of the synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis and in reactive arthritides. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Oct;45(10):847–851. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.10.847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marklund S. L. Expression of extracellular superoxide dismutase by human cell lines. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 15;266(1):213–219. doi: 10.1042/bj2660213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marklund S. L. Extracellular superoxide dismutase and other superoxide dismutase isoenzymes in tissues from nine mammalian species. Biochem J. 1984 Sep 15;222(3):649–655. doi: 10.1042/bj2220649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marklund S. L. Extracellular superoxide dismutase in human tissues and human cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1398–1403. doi: 10.1172/JCI111550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marklund S. L., Holme E., Hellner L. Superoxide dismutase in extracellular fluids. Clin Chim Acta. 1982 Nov 24;126(1):41–51. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(82)90360-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marklund S. L. Human copper-containing superoxide dismutase of high molecular weight. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7634–7638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marklund S. Spectrophotometric study of spontaneous disproportionation of superoxide anion radical and sensitive direct assay for superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7504–7507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6049–6055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandström J., Carlsson L., Marklund S. L., Edlund T. The heparin-binding domain of extracellular superoxide dismutase C and formation of variants with reduced heparin affinity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):18205–18209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan F., Chan S. J., Steiner D. F., Schilling J. W., Skidgel R. A. Molecular cloning and sequencing of the cDNA for human membrane-bound carboxypeptidase M. Comparison with carboxypeptidases A, B, H, and N. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13165–13170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibell L., Hjalmarsson K., Edlund T., Skogman G., Engström A., Marklund S. L. Expression of human extracellular superoxide dismutase in Chinese hamster ovary cells and characterization of the product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6634–6638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]