Abstract
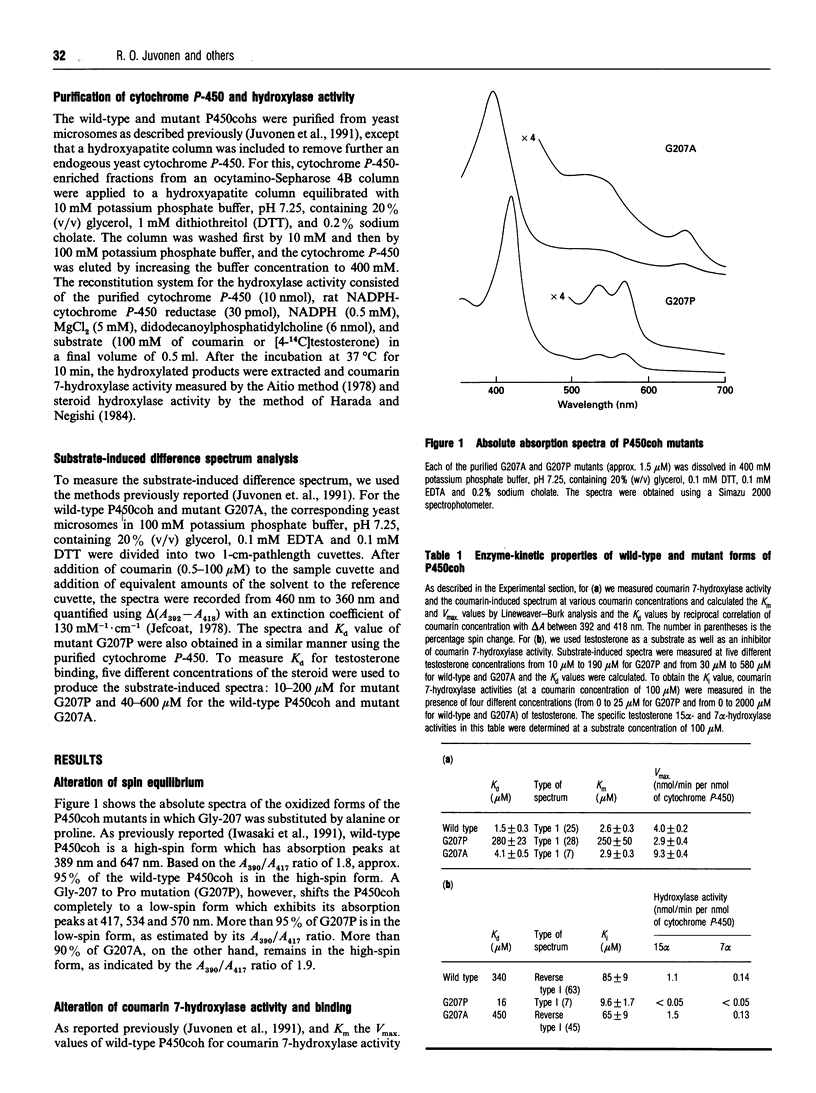
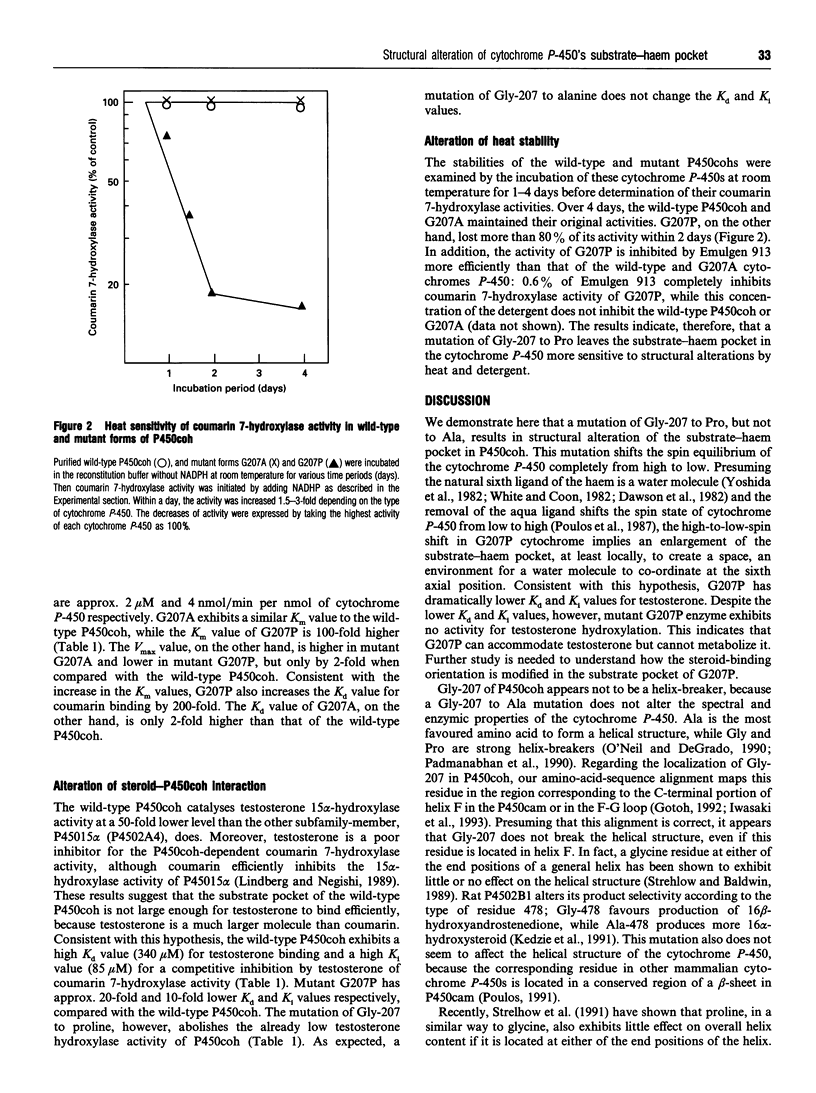
Mouse cytochrome P450coh is a high-spin haem protein which specifically catalyses coumarin 7-hydroxylase activity. A mutation of Gly-207 to Pro shifts the P450coh completely to the low-spin form, indicating that the sixth axial position of the haem is hexaco-ordinated with a water molecule in the mutant G207P. Moreover, the G207P mutation increases the Km value for coumarin 7-hydroxylase activity 100-fold and the Kd value for coumarin binding 200-fold. Conversely, the mutation decreases the Ki and Kd values 10- and 20-fold respectively when testosterone, a larger molecule, is used as a substrate. The results, therefore, are consistent with an idea that the substrate pocket may be larger in the mutant G207P than in the wild-type cytochrome P-450. A Gly-207 to Ala mutation (G207A) of P450coh (G207A), on the other hand, affects neither the spectral nor the enzymic properties of P450coh. Pro-207, through cis/trans isomerization or formation of a kink, may confer on the G207P a structural alteration of its substrate-haem pocket. Our previous studies [Iwasaki, Juvonen, Lindberg and Negishi (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266, 3380-3382; Juvonen, Iwasaki and Negishi (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266, 16431-16435] show that the residue at position 209 in P450coh resides close to the sixth axial position of the haem, and the spin equilibrium of the cytochrome P-450 shifts toward the high-spin state as residue 209 becomes more hydrophobic and larger. A Gly-207 to Pro mutation, therefore, results in the creation of a larger substrate pocket in the mutant cytochrome P-450 by altering the protein structure around residue 209 so that a water molecule and testosterone can be accommodated.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitio A. A simple and sensitive assay of 7-ethoxycoumarin deethylation. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):488–491. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90245-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alber T., Bell J. A., Sun D. P., Nicholson H., Wozniak J. A., Cook S., Matthews B. W. Replacements of Pro86 in phage T4 lysozyme extend an alpha-helix but do not alter protein stability. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):631–635. doi: 10.1126/science.3277275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandts J. F., Halvorson H. R., Brennan M. Consideration of the Possibility that the slow step in protein denaturation reactions is due to cis-trans isomerism of proline residues. Biochemistry. 1975 Nov 4;14(22):4953–4963. doi: 10.1021/bi00693a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Consler T. G., Tsolas O., Kaback H. R. Role of proline residues in the structure and function of a membrane transport protein. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 5;30(5):1291–1298. doi: 10.1021/bi00219a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson J. H., Andersson L. A., Sono M. Spectroscopic investigations of ferric cytochrome P-450-CAM ligand complexes. Identification of the ligand trans to cysteinate in the native enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3606–3617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh O. Substrate recognition sites in cytochrome P450 family 2 (CYP2) proteins inferred from comparative analyses of amino acid and coding nucleotide sequences. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):83–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki M., Darden T. A., Pedersen L. G., Davis D. G., Juvonen R. O., Sueyoshi T., Negishi M. Engineering mouse P450coh to a novel corticosterone 15 alpha-hydroxylase and modeling steroid-binding orientation in the substrate pocket. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):759–762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki M., Juvonen R., Lindberg R., Negishi M. Alteration of high and low spin equilibrium by a single mutation of amino acid 209 in mouse cytochromes P450. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3380–3382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juvonen R. O., Iwasaki M., Negishi M. Structural function of residue-209 in coumarin 7-hydroxylase (P450coh). Enzyme-kinetic studies and site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16431–16435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedzie K. M., Balfour C. A., Escobar G. Y., Grimm S. W., He Y. A., Pepperl D. J., Regan J. W., Stevens J. C., Halpert J. R. Molecular basis for a functionally unique cytochrome P450IIB1 variant. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22515–22521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg R. L., Negishi M. Alteration of mouse cytochrome P450coh substrate specificity by mutation of a single amino-acid residue. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):632–634. doi: 10.1038/339632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Strobel H. W. Secondary structure prediction of 52 membrane-bound cytochromes P450 shows a strong structural similarity to P450cam. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):656–660. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil K. T., DeGrado W. F. A thermodynamic scale for the helix-forming tendencies of the commonly occurring amino acids. Science. 1990 Nov 2;250(4981):646–651. doi: 10.1126/science.2237415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oeda K., Sakaki T., Ohkawa H. Expression of rat liver cytochrome P-450MC cDNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. DNA. 1985 Jun;4(3):203–210. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabhan S., Marqusee S., Ridgeway T., Laue T. M., Baldwin R. L. Relative helix-forming tendencies of nonpolar amino acids. Nature. 1990 Mar 15;344(6263):268–270. doi: 10.1038/344268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piela L., Némethy G., Scheraga H. A. Proline-induced constraints in alpha-helices. Biopolymers. 1987 Sep;26(9):1587–1600. doi: 10.1002/bip.360260910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos T. L., Finzel B. C., Howard A. J. High-resolution crystal structure of cytochrome P450cam. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 5;195(3):687–700. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos T. L. Modeling of mammalian P450s on basis of P450cam X-ray structure. Methods Enzymol. 1991;206:11–30. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)06073-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S., Richardson D. C. Amino acid preferences for specific locations at the ends of alpha helices. Science. 1988 Jun 17;240(4859):1648–1652. doi: 10.1126/science.3381086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strehlow K. G., Baldwin R. L. Effect of the substitution Ala----Gly at each of five residue positions in the C-peptide helix. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 7;28(5):2130–2133. doi: 10.1021/bi00431a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strehlow K. G., Robertson A. D., Baldwin R. L. Proline for alanine substitutions in the C-peptide helix of ribonuclease A. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 11;30(23):5810–5814. doi: 10.1021/bi00237a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. E., Coon M. J. Heme ligand replacement reactions of cytochrome P-450. Characterization of the bonding atom of the axial ligand trans to thiolate as oxygen. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3073–3083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida Y., Imai Y., Hashimoto-Yutsudo C. Spectrophotometric examination of exogenous-ligand complexes of ferric cytochrome P-450. Characterization of the axial ligand trans to thiolate in the native ferric low-spin form. J Biochem. 1982 May;91(5):1651–1659. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


