Abstract
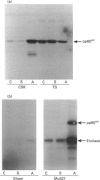
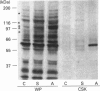
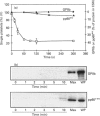
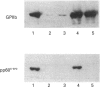
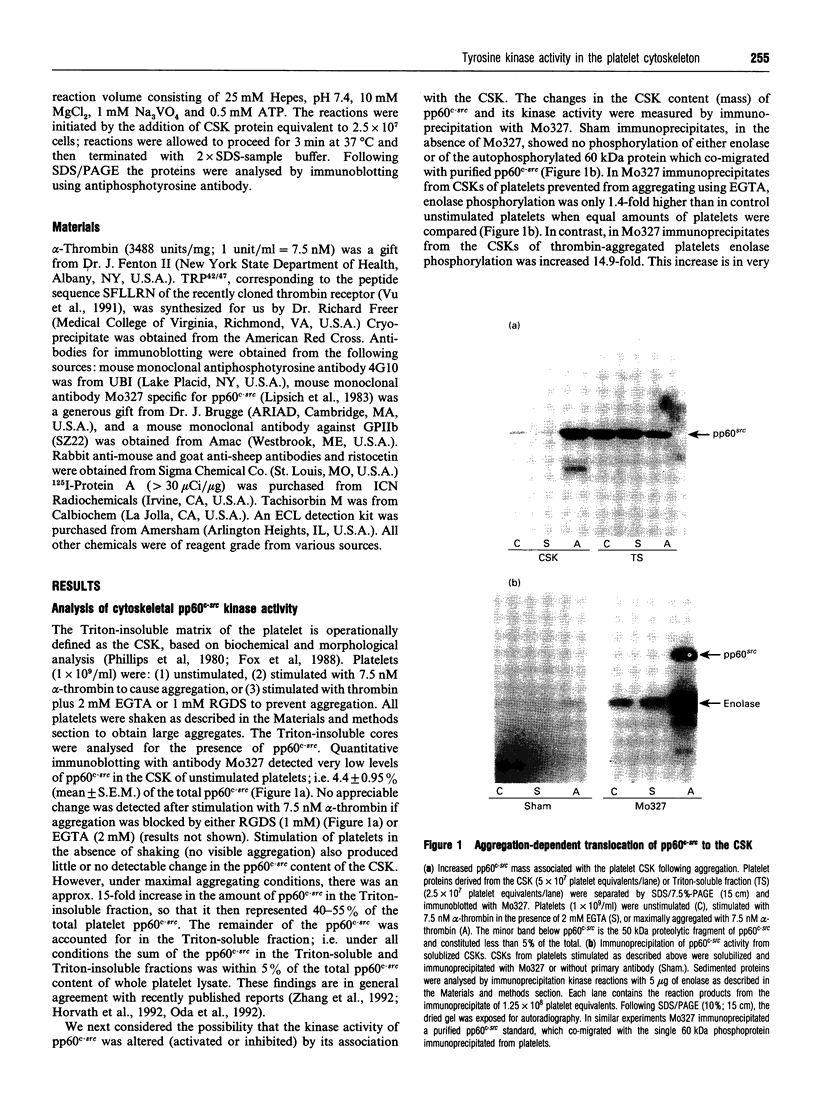
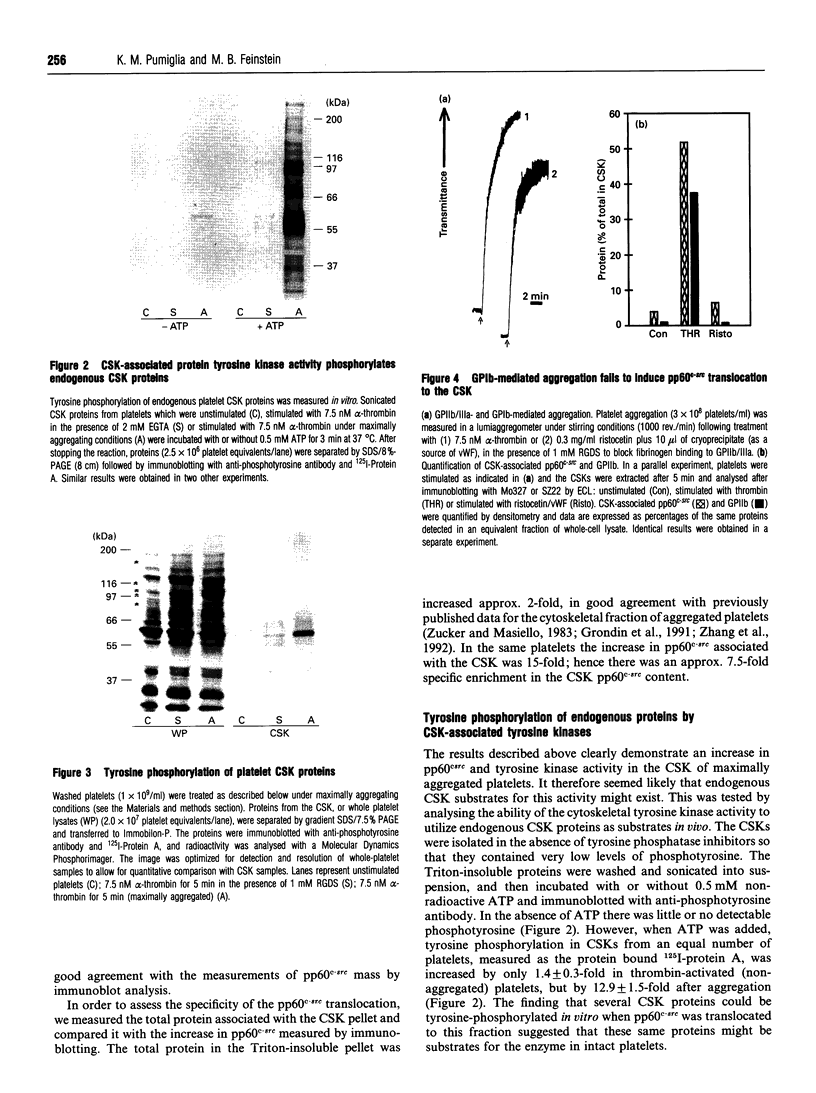
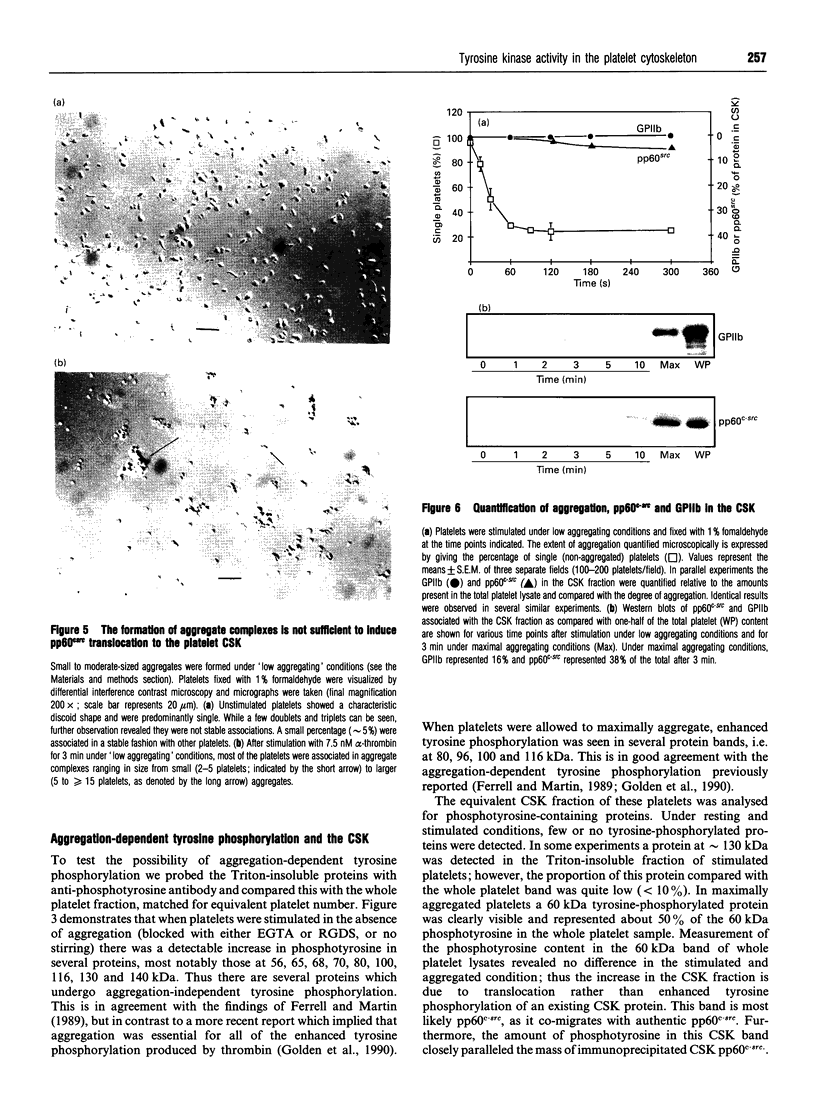
The maximal aggregation of platelets induced by alpha-thrombin or by the receptor agonist peptide thrombin-(42-47)-peptide (TRP42/47) rapidly increased the pp60c-src associated with the cytoskeleton fraction. There was good correlation between the tyrosine kinase activity and the mass of pp60c-src. Tyrosine kinase activity associated with the cytoskeleton phosphorylated several endogenous cytoskeleton-associated proteins, as revealed by immunoblotting with anti-phosphotyrosine antibody following incubation with ATP in vitro. However, with the exception of pp60c-src, few phosphotyrosine-containing proteins were retained in the cytoskeleton in intact platelets when compared with total platelet lysates. Translocation of pp60c-src to the cytoskeleton induced by alpha-thrombin and TRP42/47 is dependent on glycoprotein IIb/IIIa (GPIIb/IIIa)-fibrinogen-mediated aggregation, but does not occur when ristocetin/von Willebrand factor produces GPIb-mediated platelet aggregation. The translocation of GPIIb/IIIa and pp60c-src to the cytoskeleton is not necessary for aggregation, as it is not seen when clearly visible small to moderate-sized aggregates are initially formed after exposure to thrombin. The linkage of these proteins to the cytoskeleton occurs only after later extensive formation of large aggregates. Translocation of GPIIa/IIIa to the cytoskeleton is not sufficient for the cytoskeletal association of pp60c-src, as the former occurs independently in platelets stimulated with concanavalin A in the absence of aggregation. Linkage of the integrin GPIIb/IIIa and pp60c-src to the internal cytoskeleton structure, and the corresponding tyrosine phosphorylation of certain proteins upon formation of large aggregates, may be an example of mechanochemical transduction by integrin receptors and may represent a structure with the requisite tensile strength to stabilize large platelet aggregates against high shear stresses.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asijee G. M., Sturk A., Bruin T., Wilkinson J. M., Ten Cate J. W. Vinculin is a permanent component of the membrane skeleton and is incorporated into the (re)organising cytoskeleton upon platelet activation. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Apr 20;189(1):131–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar A., Paul A. K., Shukla S. D. Platelet-activating factor stimulation of tyrosine kinase and its relationship to phospholipase C in rabbit platelets: studies with genistein and monoclonal antibody to phosphotyrosine. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Apr;37(4):519–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du X. P., Plow E. F., Frelinger A. L., 3rd, O'Toole T. E., Loftus J. C., Ginsberg M. H. Ligands "activate" integrin alpha IIb beta 3 (platelet GPIIb-IIIa). Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):409–416. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90458-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Martin G. S. Platelet tyrosine-specific protein phosphorylation is regulated by thrombin. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3603–3610. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Martin G. S. Tyrosine-specific protein phosphorylation is regulated by glycoprotein IIb-IIIa in platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2234–2238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Boyles J. K., Berndt M. C., Steffen P. K., Anderson L. K. Identification of a membrane skeleton in platelets. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1525–1538. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudette D. C., Holub B. J. Effect of genistein, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, on U46619-induced phosphoinositide phosphorylation in human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 16;170(1):238–242. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91265-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Brugge J. S., Shattil S. J. Role of platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb-IIIa in agonist-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of platelet proteins. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):3117–3127. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.3117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Brugge J. S. Thrombin treatment induces rapid changes in tyrosine phosphorylation in platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):901–905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Nemeth S. P., Brugge J. S. Blood platelets express high levels of the pp60c-src-specific tyrosine kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):852–856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grondin P., Plantavid M., Sultan C., Breton M., Mauco G., Chap H. Interaction of pp60c-src, phospholipase C, inositol-lipid, and diacyglycerol kinases with the cytoskeletons of thrombin-stimulated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15705–15709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan J. L., Shalloway D. Regulation of focal adhesion-associated protein tyrosine kinase by both cellular adhesion and oncogenic transformation. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):690–692. doi: 10.1038/358690a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutkind J. S., Lacal P. M., Robbins K. C. Thrombin-dependent association of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase with p60c-src and p59fyn in human platelets. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3806–3809. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon J. T., Jamieson G. A. The glycocalicin portion of platelet glycoprotein Ib expresses both high and moderate affinity receptor sites for thrombin. A soluble radioreceptor assay for the interaction of thrombin with platelets. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13224–13229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horak I. D., Corcoran M. L., Thompson P. A., Wahl L. M., Bolen J. B. Expression of p60fyn in human platelets. Oncogene. 1990 Apr;5(4):597–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath A. R., Muszbek L., Kellie S. Translocation of pp60c-src to the cytoskeleton during platelet aggregation. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):855–861. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05123.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. M., Bolen J. B., Barnwell J. W., Shattil S. J., Brugge J. S. Membrane glycoprotein IV (CD36) is physically associated with the Fyn, Lyn, and Yes protein-tyrosine kinases in human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7844–7848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inazu T., Taniguchi T., Yanagi S., Yamamura H. Protein-tyrosine phosphorylation and aggregation of intact human platelets by vanadate with H2O2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 16;170(1):259–263. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91268-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingber D. Integrins as mechanochemical transducers. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;3(5):841–848. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouns W. C., Fox C. F., Lamoreaux W. J., Coons L. B., Jennings L. K. The effect of glycoprotein IIb-IIIa receptor occupancy on the cytoskeleton of resting and activated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13891–13900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll M. H., Schafer A. I. Biochemical mechanisms of platelet activation. Blood. 1989 Sep;74(4):1181–1195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung L. L. Role of thrombospondin in platelet aggregation. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1764–1772. doi: 10.1172/JCI111595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipfert L., Haimovich B., Schaller M. D., Cobb B. S., Parsons J. T., Brugge J. S. Integrin-dependent phosphorylation and activation of the protein tyrosine kinase pp125FAK in platelets. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(4):905–912. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.4.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsich L. A., Lewis A. J., Brugge J. S. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies that recognize the transforming proteins of avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.352-360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahas N., Plantavid M., Mauco G., Chap H. Association of phosphatidylinositol kinase and phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate kinase activities with the cytoskeleton in human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 27;246(1-2):30–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda A., Druker B. J., Smith M., Salzman E. W. Association of pp60src with Triton X-100-insoluble residue in human blood platelets requires platelet aggregation and actin polymerization. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20075–20081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta S., Taniguchi T., Asahi M., Kato Y., Nakagawara G., Yamamura H. Protein-tyrosine kinase p72syk is activated by wheat germ agglutinin in platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jun 30;185(3):1128–1132. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91743-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter R. G., Ginsberg M. Concanavalin A induces interactions between surface glycoproteins and the platelet cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):565–573. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Jennings L. K., Edwards H. H. Identification of membrane proteins mediating the interaction of human platelets. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jul;86(1):77–86. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E., Marguerie G. A., Ginsberg M. H. The effect of Arg-Gly-Asp-containing peptides on fibrinogen and von Willebrand factor binding to platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8057–8061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pumiglia K. M., Huang C. K., Feinstein M. B. Elevation of cAMP, but not cGMP, inhibits thrombin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation in human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 14;171(2):738–745. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91208-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pumiglia K. M., Lau L. F., Huang C. K., Burroughs S., Feinstein M. B. Activation of signal transduction in platelets by the tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor pervanadate (vanadyl hydroperoxide). Biochem J. 1992 Sep 1;286(Pt 2):441–449. doi: 10.1042/bj2860441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salari H., Duronio V., Howard S. L., Demos M., Jones K., Reany A., Hudson A. T., Pelech S. L. Erbstatin blocks platelet activating factor-induced protein-tyrosine phosphorylation, polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis, protein kinase C activation, serotonin secretion and aggregation of rabbit platelets. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 9;263(1):104–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80715-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage B., Shattil S. J., Ruggeri Z. M. Modulation of platelet function through adhesion receptors. A dual role for glycoprotein IIb-IIIa (integrin alpha IIb beta 3) mediated by fibrinogen and glycoprotein Ib-von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):11300–11306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller M. D., Borgman C. A., Cobb B. S., Vines R. R., Reynolds A. B., Parsons J. T. pp125FAK a structurally distinctive protein-tyrosine kinase associated with focal adhesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5192–5196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassallo R. R., Jr, Kieber-Emmons T., Cichowski K., Brass L. F. Structure-function relationships in the activation of platelet thrombin receptors by receptor-derived peptides. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6081–6085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu T. K., Hung D. T., Wheaton V. I., Coughlin S. R. Molecular cloning of a functional thrombin receptor reveals a novel proteolytic mechanism of receptor activation. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1057–1068. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90261-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Fry M. J., Waterfield M. D., Jaken S., Liao L., Fox J. E., Rittenhouse S. E. Activated phosphoinositide 3-kinase associates with membrane skeleton in thrombin-exposed platelets. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4686–4692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B., Masiello N. C. The Triton X-100-insoluble residue ("cytoskeleton") of aggregated platelets contains increased lipid phosphorus as well as 125I-labeled glycoproteins. Blood. 1983 Apr;61(4):676–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]