Abstract
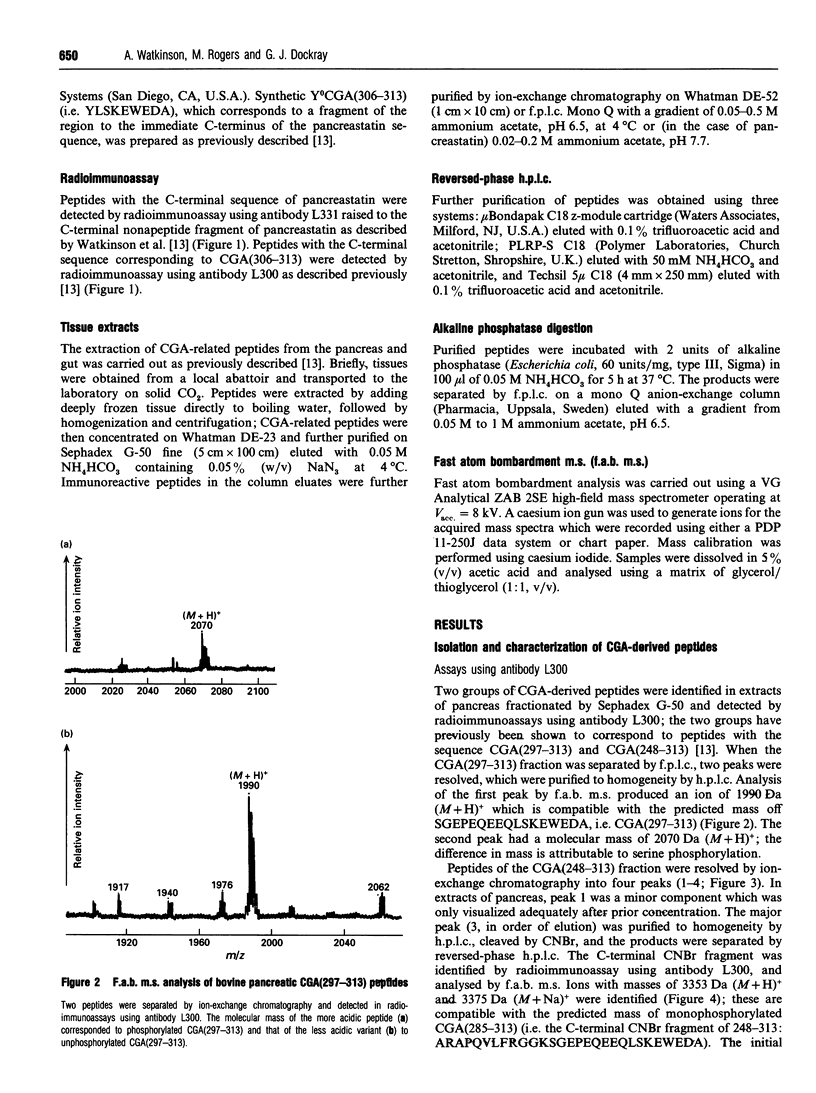
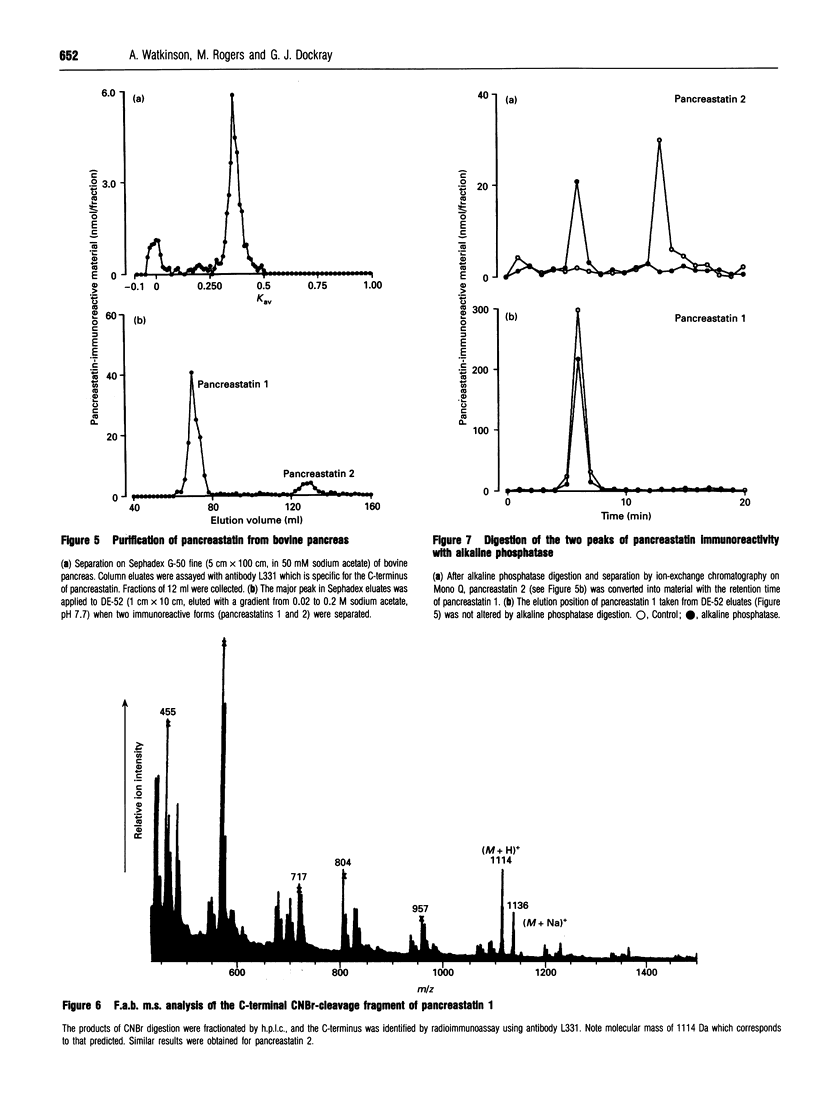
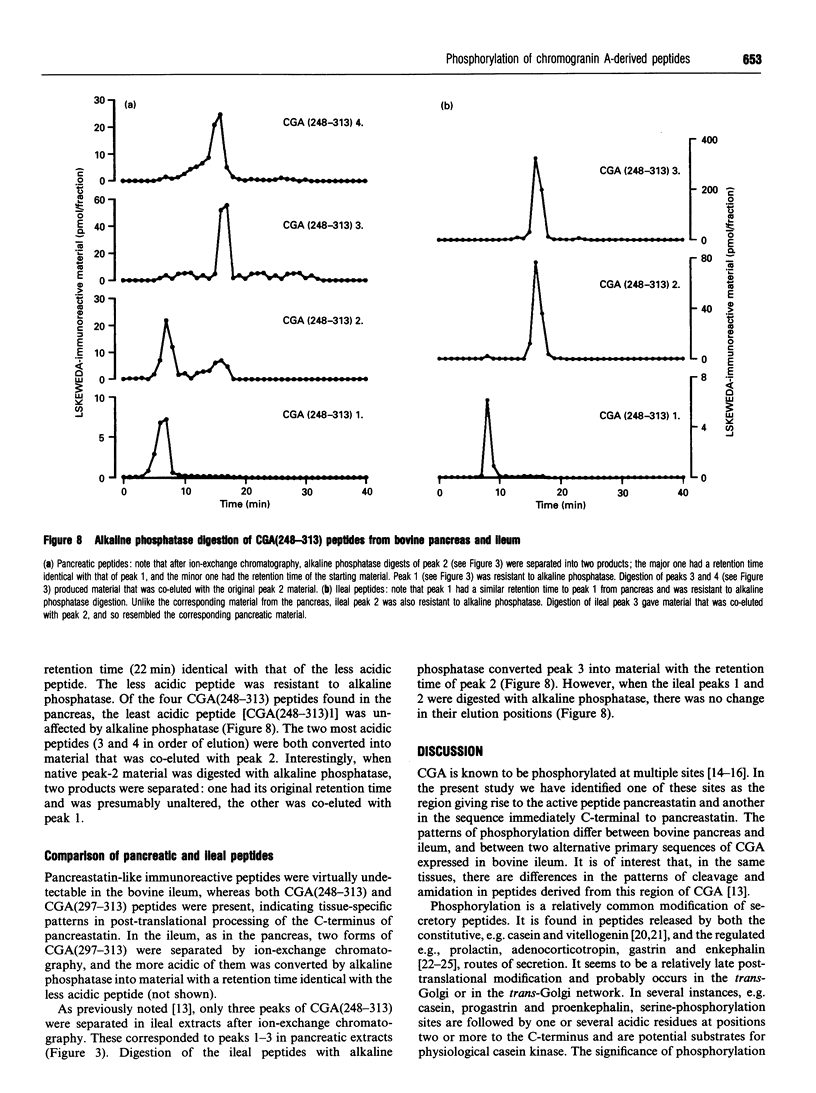
Chromogranin A is a secretory protein expressed widely in neuroendocrine cells. It is known to be phosphorylated but the precise sites of phosphorylation are not known. We have isolated, from bovine pancreas and ileum, chromogranin A fragments corresponding to a region giving rise to a biologically active product, pancreastatin. Phosphorylation patterns were determined by fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry and alkaline phosphatase digestion followed by ion-exchange chromatography and radioimmunoassay. In the pancreas, there were unmodified, mono- and di-phosphorylated forms of the fragment chromogranin A(248-313) with Arg and Glu at positions 293 and 301 respectively; in addition, there were small amounts of monophosphorylated peptide with an alternative primary sequence of His and Lys at 293 and 301 respectively. Two products of cleavage, pancreastatin and the fragment 297-313, were also found in unmodified and monophosphorylated forms. In the ileum, peptides with both alternative primary sequences were found, pancreastatin was absent, and phosphorylation was generally less than in the pancreas. Chromogranin A-derived peptides therefore exhibit tissue-specific patterns of phosphorylation and cleavage, and at least two phosphorylation sites occur in the region giving rise to a biologically active product.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn T. G., Cohn D. V., Gorr S. U., Ornstein D. L., Kashdan M. A., Levine M. A. Primary structure of bovine pituitary secretory protein I (chromogranin A) deduced from the cDNA sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):5043–5047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.5043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedum U. M., Baeuerle P. A., Konecki D. S., Frank R., Powell J., Mallet J., Huttner W. B. The primary structure of bovine chromogranin A: a representative of a class of acidic secretory proteins common to a variety of peptidergic cells. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1495–1502. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava G., Russell J., Sherwood L. M. Phosphorylation of parathyroid secretory protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):878–881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockray G. J., Varro A., Desmond H., Young J., Gregory H., Gregory R. A. Post-translational processing of the porcine gastrin precursor by phosphorylation of the COOH-terminal fragment. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8643–8647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efendić S., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Quan C., Chang D., Ostenson C. G. Pancreastatin and islet hormone release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7257–7260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorr S. U., Hamilton J. W., Cohn D. V. Sulfated secreted forms of bovine and porcine parathyroid chromogranin A (secretory protein-I). J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5780–5784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacangelo A. L., Grimes M., Eiden L. E. The bovine chromogranin A gene: structural basis for hormone regulation and generation of biologically active peptides. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Nov;5(11):1651–1660. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-11-1651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacangelo A., Affolter H. U., Eiden L. E., Herbert E., Grimes M. Bovine chromogranin A sequence and distribution of its messenger RNA in endocrine tissues. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):82–86. doi: 10.1038/323082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuka J., Asada I., Poston G. J., Lluis F., Tatemoto K., Greeley G. H., Jr, Thompson J. C. Effect of pancreastatin on pancreatic endocrine and exocrine secretion. Pancreas. 1989;4(3):277–281. doi: 10.1097/00006676-198906000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyasaka K., Funakoshi A., Kitani K., Tamamura H., Funakoshi S., Fujii N. Inhibitory effect of pancreastatin on pancreatic exocrine secretions. Pancreastatin inhibits central vagal nerve stimulation. Gastroenterology. 1990 Dec;99(6):1751–1756. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90483-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oetting W. S., Tuazon P. T., Traugh J. A., Walker A. M. Phosphorylation of prolactin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1649–1652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P., Hille A., Lee R. W., Zanini A., De Camilli P., Huttner W. B. Secretogranins I and II: two tyrosine-sulfated secretory proteins common to a variety of cells secreting peptides by the regulated pathway. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1999–2011. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P., Mantovani S., Rosboch R., Huttner W. B. Monensin and brefeldin A differentially affect the phosphorylation and sulfation of secretory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):12227–12232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P., Weiss U., Pepperkok R., Ansorge W., Niehrs C., Stelzer E. H., Huttner W. B. An antibody against secretogranin I (chromogranin B) is packaged into secretory granules. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):17–34. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saccuzzo J. E., Krzesicki R. F., Perini F., Ruddon R. W. Phosphorylation of the secreted, free alpha subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9493–9496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. P., Aunis D. Biochemistry of the chromogranin A protein family. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 15;262(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2620001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Efendić S., Mutt V., Makk G., Feistner G. J., Barchas J. D. Pancreastatin, a novel pancreatic peptide that inhibits insulin secretion. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):476–478. doi: 10.1038/324476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varro A., Desmond H., Pauwels S., Gregory H., Young J., Dockray G. J. The human gastrin precursor. Characterization of phosphorylated forms and fragments. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 15;256(3):951–957. doi: 10.1042/bj2560951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. Y., Williams D. L. Biosynthesis of the vitellogenins. Identification and characterization of nonphosphorylated precursors to avian vitellogenin I and vitellogenin II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3837–3846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkinson A., Jönsson A. C., Davison M., Young J., Lee C. M., Moore S., Dockray G. J. Heterogeneity of chromogranin A-derived peptides in bovine gut, pancreas and adrenal medulla. Biochem J. 1991 Jun 1;276(Pt 2):471–479. doi: 10.1042/bj2760471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkinson A., Young J., Varro A., Dockray G. J. The isolation and chemical characterization of phosphorylated enkephalin-containing peptides from bovine adrenal medulla. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3061–3065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Fischer-Colbrie R. The chromogranins A and B: the first 25 years and future perspectives. Neuroscience. 1992 Aug;49(3):497–528. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90222-N. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


