Abstract
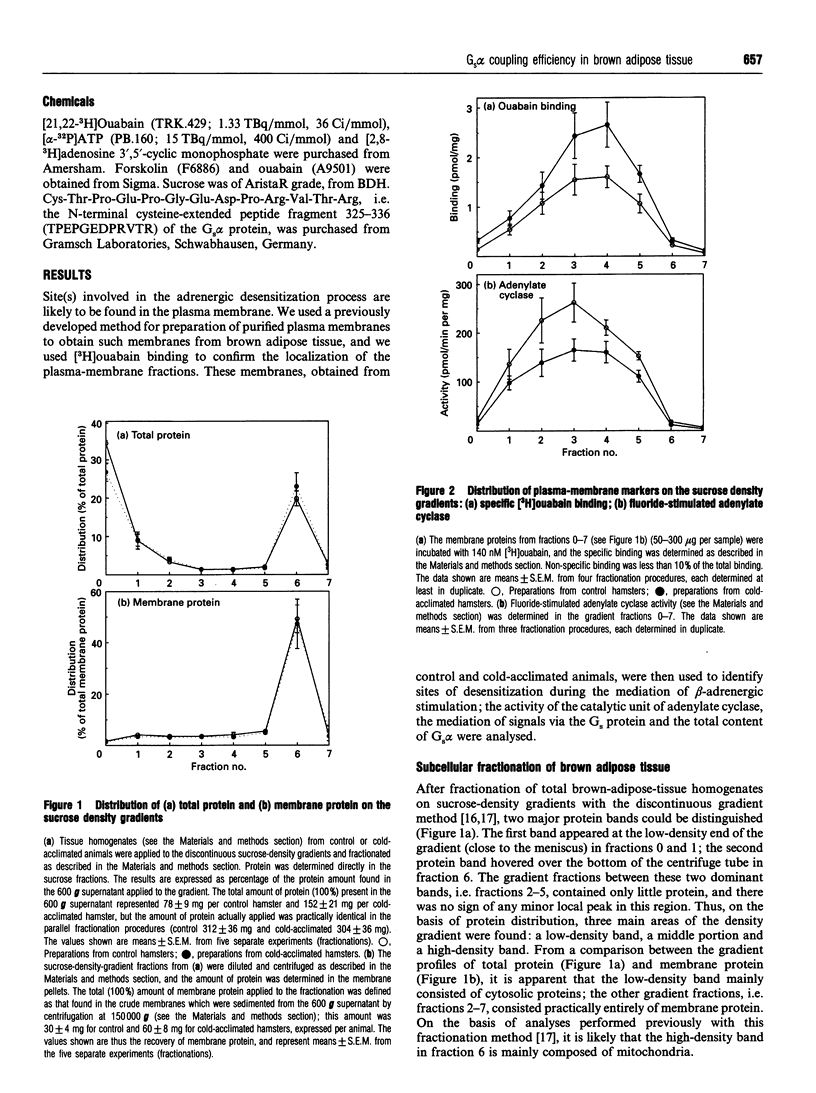
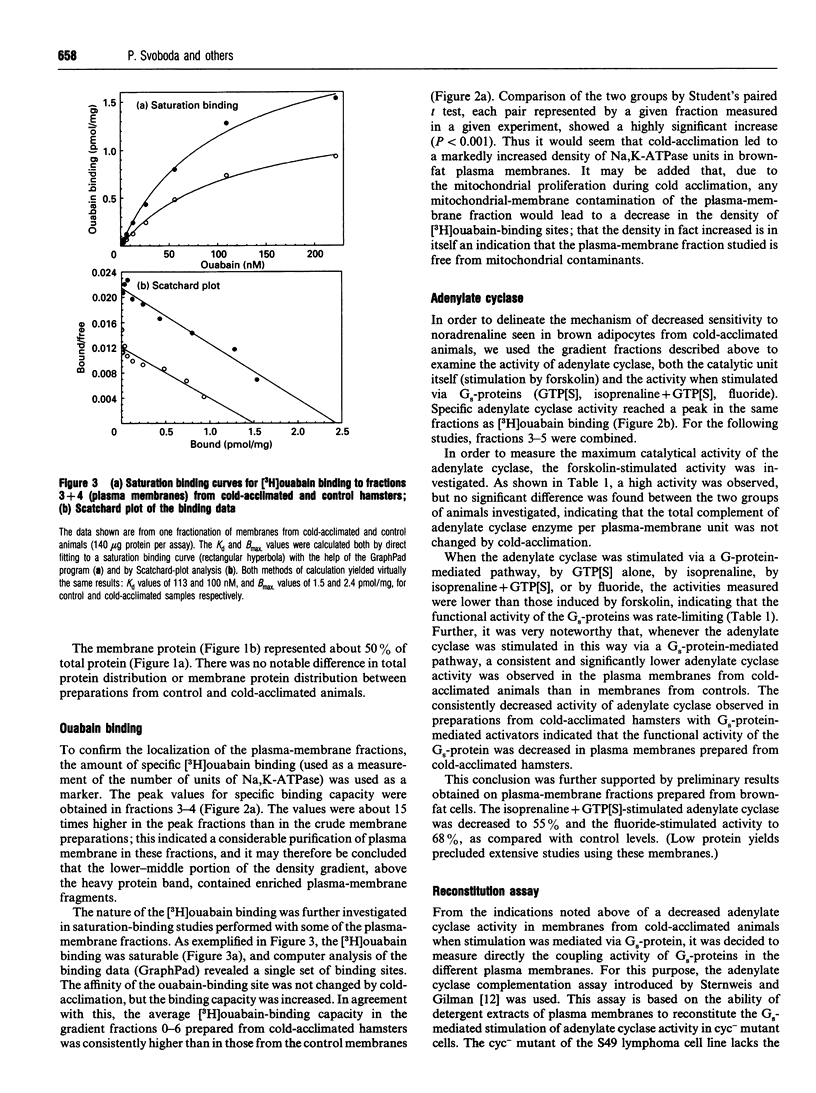
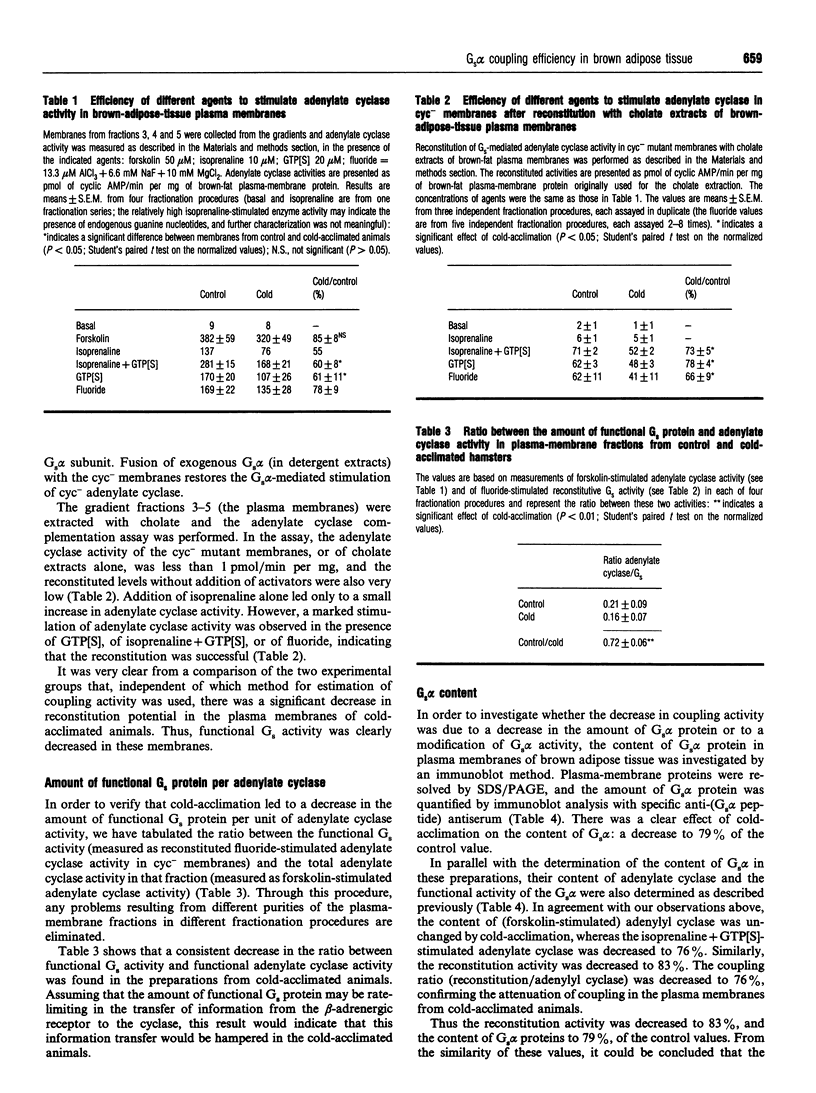
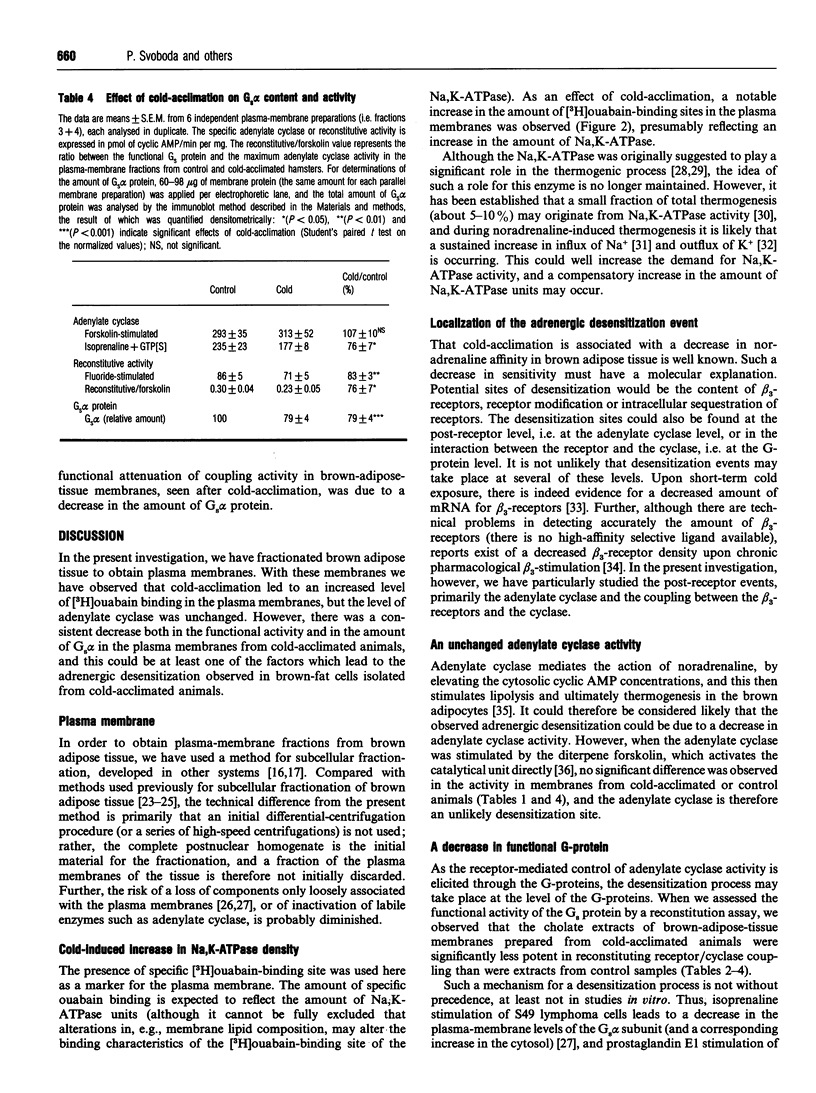
In order to localize site(s) of beta-adrenergic desensitization found in brown adipocytes from cold-acclimated animals, total brown-adipose-tissue homogenates (postnuclear supernatant) were obtained from control or cold-acclimated hamsters and were fractionated on discontinuous sucrose gradients. A low-density band (cytosolic proteins) and a high-density band (mitochondria) were obtained; in the middle fractions only low levels of protein were recovered. However, these fractions displayed a high level of specific [3H]ouabain binding, indicating that they represented fractions enriched in plasma membranes. The level of [3H]ouabain binding was significantly higher in plasma membranes from cold-acclimated animals, indicating an increased density of Na,K-ATPase units. The maximal activity of adenylate cyclase, as estimated with forskolin, was not changed by cold acclimation. However, the levels of cyclase activity observed after Gs-protein-mediated activation (with guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate, isoprenaline, both of these, or fluoride) were decreased, indicating a decreased coupling efficiency. Notably, a significant decrease was observed in the functional activity of the Gs protein, as directly measured by estimation of the ability of cholate extracts of brown-fat plasma membranes to reconstitute Gs-protein-mediated stimulation of adenylate cyclase in cyc- membranes. Further, a functionally significant decrease (to 72%) was observed in the ratio between the amount of functional Gs proteins and adenylate cyclase units. The total content of Gs alpha protein was decreased to the same extent as the coupling efficiency of the membranes, indicating that a lower content of functionally equivalent Gs alpha molecules could explain the decreased coupling. It could therefore be concluded that a decrease in Gs-protein-mediated coupling efficiency, owing to a decrease in the amount of Gs alpha, is at least one site of beta-adrenergic desensitization in cold-acclimated animals. This may, at least in part, explain that desensitization takes place despite the fact that the beta 3-adrenoceptor itself apparently lacks some of the sites known to be involved in the desensitization process in other beta-adrenergic receptors.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arch J. R. The brown adipocyte beta-adrenoceptor. Proc Nutr Soc. 1989 Jul;48(2):215–223. doi: 10.1079/pns19890032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Strasser R. H., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: identification of a novel protein kinase that phosphorylates the agonist-occupied form of the receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2797–2801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L., Abramowitz J., Brown A. M. Receptor-effector coupling by G proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 7;1031(2):163–224. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(90)90007-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhry A., Granneman J. G. Adrenergic regulation of neonatal brown fat adenylyl cyclase and Gs alpha activity. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jul;263(1 Pt 2):R34–R38. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1992.263.1.R34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhry A., Granneman J. G. Developmental changes in adenylyl cyclase and GTP binding proteins in brown fat. Am J Physiol. 1991 Aug;261(2 Pt 2):R403–R411. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1991.261.2.R403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhry A., Granneman J. G. Subcellular distribution of adenylyl cyclase and Gs alpha in rat brown adipose tissue. Metabolism. 1991 Apr;40(4):432–437. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(91)90156-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. B., Friedman J., Prashad N., Ruoho A. E. Epinephrine-induced sequestration of the beta-adrenergic receptor in cultured S49 WT and cyc- lymphoma cells. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1985;10(1):97–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly E., Nånberg E., Nedergaard J. Norepinephrine-induced Na+ influx in brown adipocytes is cyclic AMP-mediated. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14377–14385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emorine L. J., Feve B., Pairault J., Briend-Sutren M. M., Marullo S., Delavier-Klutchko C., Strosberg D. A. Structural basis for functional diversity of beta 1-, beta 2- and beta 3-adrenergic receptors. 1991 Mar 15-Apr 1Biochem Pharmacol. 41(6-7):853–859. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90188-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacobino J. P. Subcellular fractionation of brown adipose tissue. J Supramol Struct. 1979;11(4):445–449. doi: 10.1002/jss.400110403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardier L., Seydoux J., Clausen T. Membrane potential of brown adipose tissue. A suggested mechanism for the regulation of thermogenesis. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Dec;52(6):925–940. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.6.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman J. G., Bannon M. J. Neural control of the alpha-subunit of Gs messenger ribonucleic acid in rat brown adipose tissue. Endocrinology. 1989 Nov;125(5):2328–2334. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-5-2328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman J. G., Haverstick D. M., Chaudhry A. Relationship between Gs alpha messenger ribonucleic acid splice variants and the molecular forms of Gs alpha protein in rat brown adipose tissue. Endocrinology. 1990 Oct;127(4):1596–1601. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-4-1596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman J. G., Lahners K. N., Chaudhry A. Molecular cloning and expression of the rat beta 3-adrenergic receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;40(6):895–899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman J. G., Lahners K. N. Differential adrenergic regulation of beta 1- and beta 3-adrenoreceptor messenger ribonucleic acids in adipose tissues. Endocrinology. 1992 Jan;130(1):109–114. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.1.1309320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman J. G., MacKenzie R. G. Neural modulation of the stimulatory regulatory protein of adenylate cyclase in rat brown adipose tissue. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Jun;245(3):1068–1074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman J. G. Norepinephrine infusions increase adenylate cyclase responsiveness in brown adipose tissue. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Jun;245(3):1075–1080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A., Johnson J. L., Milligan G. Down-regulation of Gi sub-types by prolonged incubation of adipocytes with an A1 adenosine receptor agonist. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5206–5210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A., Milligan G., Dobias S. B. Gi down-regulation as a mechanism for heterologous desensitization in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3223–3229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausdorff W. P., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Turning off the signal: desensitization of beta-adrenergic receptor function. FASEB J. 1990 Aug;4(11):2881–2889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler J. R., Gilman A. G. G proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):383–387. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90005-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz B. A. Ouabain-sensitive component of brown fat thermogenesis. Am J Physiol. 1973 Feb;224(2):352–355. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.2.352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaziro Y., Itoh H., Kozasa T., Nakafuku M., Satoh T. Structure and function of signal-transducing GTP-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:349–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Andexinger S., Pitcher J., Trukawinski S., Codina J., Faure J. P., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Receptor-specific desensitization with purified proteins. Kinase dependence and receptor specificity of beta-arrestin and arrestin in the beta 2-adrenergic receptor and rhodopsin systems. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8558–8564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie F. R., Milligan G. Prostaglandin E1-mediated, cyclic AMP-independent, down-regulation of Gs alpha in neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17084–17093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohell N., Connolly E., Nedergaard J. Distinction between mechanisms underlying alpha 1- and beta-adrenergic respiratory stimulation in brown fat cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 1):C301–C308. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.2.C301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S. M., Gilman A. G. Synthetic peptide antisera with determined specificity for G protein alpha or beta subunits. Methods Enzymol. 1991;195:215–233. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)95168-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S. M., Kahn R. A., Manning D. R., Gilman A. G. Antisera of designed specificity for subunits of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):265–269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedergaard J. Catecholamine sensitivity in brown fat cells from cold-acclimated hamsters and rats. Am J Physiol. 1982 Mar;242(3):C250–C257. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.242.3.C250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedergaard J., Lindberg O. The brown fat cell. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;74:187–286. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61173-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nånberg E., Connolly E., Nedergaard J. Presence of a Ca2+-dependent K+ channel in brown adipocytes. Possible role in maintenance of alpha 1-adrenergic stimulation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jan 18;844(1):42–49. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(85)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obregón M. J., Jacobsson A., Kirchgessner T., Schotz M. C., Cannon B., Nedergaard J. Postnatal recruitment of brown adipose tissue is induced by the cold stress experienced by the pups. An analysis of mRNA levels for thermogenin and lipoprotein lipase. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 15;259(2):341–346. doi: 10.1042/bj2590341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransnäs L. A., Svoboda P., Jasper J. R., Insel P. A. Stimulation of beta-adrenergic receptors of S49 lymphoma cells redistributes the alpha subunit of the stimulatory G protein between cytosol and membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7900–7903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revelli J. P., Muzzin P., Giacobino J. P. Modulation in vivo of beta-adrenergic-receptor subtypes in rat brown adipose tissue by the thermogenic agonist Ro 16-8714. Biochem J. 1992 Sep 15;286(Pt 3):743–746. doi: 10.1042/bj2860743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Maguire M. E., Sturgill T. W., Biltonen R. L., Gilman A. G. Relationship between the beta-adrenergic receptor and adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5761–5775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. Reconstitution of catecholamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Reconstitution of the uncoupled variant of the S40 lymphoma cell. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3333–3340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svartengren J., Svoboda P., Cannon B. Desensitisation of beta-adrenergic responsiveness in vivo. Decreased coupling between receptors and adenylate cyclase in isolated brown-fat cells. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Nov 15;128(2-3):481–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda P., Amler E., Teisinger J. Different sensitivity of ATP + Mg + Na (I) and Pi + Mg (II) dependent types of ouabain binding to phospholipase A2. J Membr Biol. 1988 Sep;104(3):211–221. doi: 10.1007/BF01872323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda P., Kvapil P., Insel P. A., Ransnäs L. A. Plasma-membrane-independent pool of the alpha subunit of the stimulatory guanine-nucleotide-binding regulatory protein in a low-density-membrane fraction of S49 lymphoma cells. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Sep 15;208(3):693–698. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unelius L., Mohell N., Nedergaard J. Cold acclimation induces desensitization to adenosine in brown fat cells without changing receptor binding. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 1):C818–C826. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.5.C818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


