Abstract
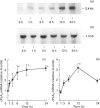
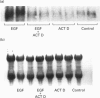
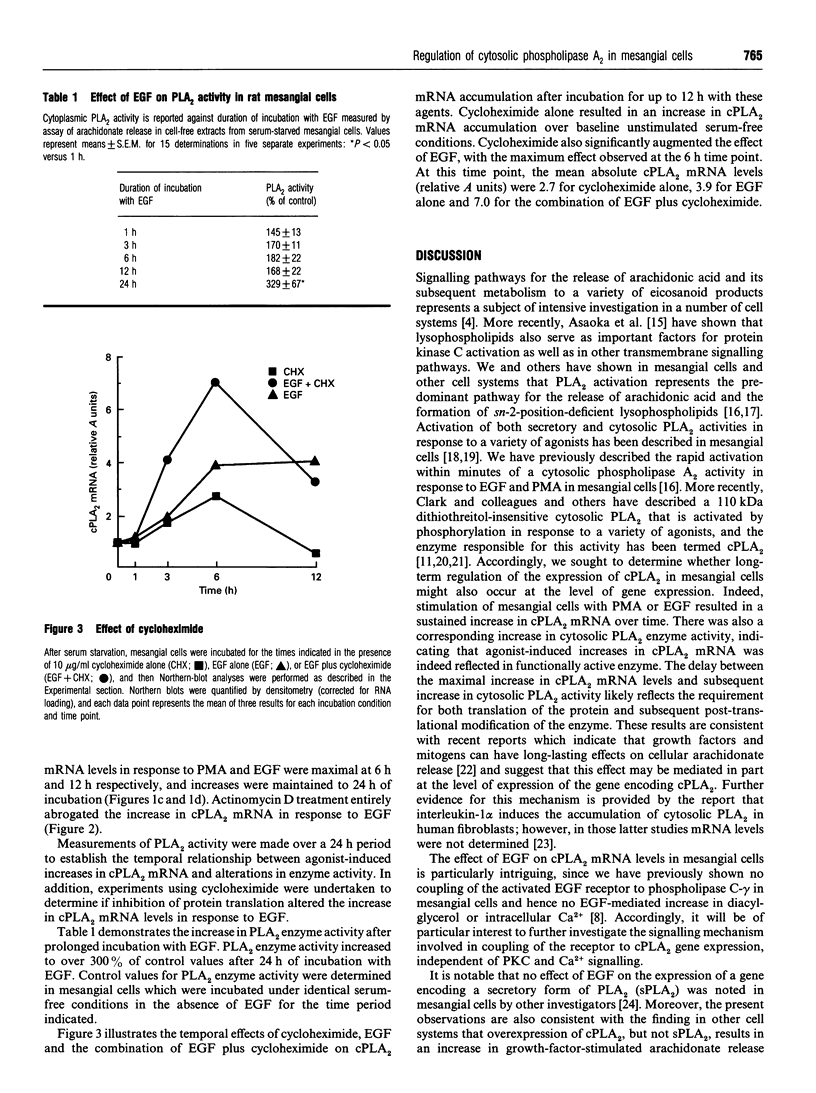
We have previously shown that phospholipase A2 (PLA2) activity is rapidly activated by epidermal growth factor (EGF) and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) in renal mesangial cells and other cell systems in a manner that suggests a covalent modification of the PLA2 enzyme(s). This PLA2 activity is cytosolic (cPLA2) and is distinct from secretory forms of PLA2, which are also stimulated in mesangial cells in response to cytokines and other agonists. However, longer-term regulation of cPLA2 in renal cells may also occur at the level of gene expression. Cultured rat mesangial cells were used as a model system to test the effects of EGF and PMA on the regulation of cPLA2 gene expression. EGF and PMA both produced sustained increases in cPLA2 mRNA levels, with a parallel increase in enzyme activity over time. Inhibition of protein synthesis by cycloheximide increased basal cPLA2 mRNA accumulation in serum-starved mesangial cells, and the combination of EGF and cycloheximide resulted in super-induction of cPLA2 gene expression compared with EGF alone. Actinomycin D treatment entirely abrogated the effect of EGF on cPLA2 mRNA accumulation. These findings suggest that regulation of cPLA2 is achieved by factors controlling gene transcription and possibly mRNA stability, in addition to previously characterized posttranslational modifications.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asaoka Y., Oka M., Yoshida K., Sasaki Y., Nishizuka Y. Role of lysophosphatidylcholine in T-lymphocyte activation: involvement of phospholipase A2 in signal transduction through protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6447–6451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre J. V., Gronich J. H., Nemenoff R. A. Epidermal growth factor enhances glomerular mesangial cell soluble phospholipase A2 activity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):4934–4938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre J. V. Phospholipase A2 and signal transduction. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1992 Aug;3(2):128–150. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V32128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. D., Lin L. L., Kriz R. W., Ramesha C. S., Sultzman L. A., Lin A. Y., Milona N., Knopf J. L. A novel arachidonic acid-selective cytosolic PLA2 contains a Ca(2+)-dependent translocation domain with homology to PKC and GAP. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90556-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. D., Milona N., Knopf J. L. Purification of a 110-kilodalton cytosolic phospholipase A2 from the human monocytic cell line U937. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7708–7712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven P. A., Patterson M. C., DeRubertis F. R. Role of enhanced arachidonate availability through phospholipase A2 pathway in mediation of increased prostaglandin synthesis by glomeruli from diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1988 Apr;37(4):429–435. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.4.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis E. A., Rhee S. G., Billah M. M., Hannun Y. A. Role of phospholipase in generating lipid second messengers in signal transduction. FASEB J. 1991 Apr;5(7):2068–2077. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.7.1901288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domin J., Rozengurt E. Platelet-derived growth factor stimulates a biphasic mobilization of arachidonic acid in Swiss 3T3 cells. The role of phospholipase A2. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8927–8934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falvey E., Schibler U. How are the regulators regulated? FASEB J. 1991 Mar 1;5(3):309–314. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.3.2001790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floege J., Burns M. W., Alpers C. E., Yoshimura A., Pritzl P., Gordon K., Seifert R. A., Bowen-Pope D. F., Couser W. G., Johnson R. J. Glomerular cell proliferation and PDGF expression precede glomerulosclerosis in the remnant kidney model. Kidney Int. 1992 Feb;41(2):297–309. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg H. J., Viegas M. M., Margolis B. L., Schlessinger J., Skorecki K. L. The tyrosine kinase activity of the epidermal-growth-factor receptor is necessary for phospholipase A2 activation. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 15;267(2):461–465. doi: 10.1042/bj2670461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodyer P. R., Fata J., Goodyer C. G. Excretion of epidermal growth factor-like material in acute Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis. Pediatr Nephrol. 1990 Mar;4(2):101–104. doi: 10.1007/BF00858818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronich J. H., Bonventre J. V., Nemenoff R. A. Identification and characterization of a hormonally regulated form of phospholipase A2 in rat renal mesangial cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16645–16651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronich J. H., Bonventre J. V., Nemenoff R. A. Purification of a high-molecular-mass form of phospholipase A2 from rat kidney activated at physiological calcium concentrations. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 1;271(1):37–43. doi: 10.1042/bj2710037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hack N., Margolis B. L., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Skorecki K. L. Distinct structural specificities for functional coupling of the epidermal growth factor receptor to calcium-signalling versus phospholipase A2 responses. Biochem J. 1991 May 1;275(Pt 3):563–567. doi: 10.1042/bj2750563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hack N., Margolis B., Schlessinger J., Skorecki K. Interaction of epidermal growth factor with vasoactive hormones in the regulation of phospholipase A2. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 1991 Jul-Sep;2(3):161–182. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp.1991.2.3.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. C., Hoover R. L., Jacobson H. R., Badr K. F. Evidence for glomerular actions of epidermal growth factor in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):1028–1039. doi: 10.1172/JCI113659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. C., Munger K. A., Badr K. F., Takahashi K. Mediation of renal vascular effects of epidermal growth factor by arachidonate metabolites. FASEB J. 1990 Apr 1;4(6):1654–1660. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.6.2138579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lianos E. A. Eicosanoids and the modulation of glomerular immune injury. Kidney Int. 1989 Apr;35(4):985–992. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. L., Lin A. Y., DeWitt D. L. Interleukin-1 alpha induces the accumulation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 and the release of prostaglandin E2 in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23451–23454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. L., Lin A. Y., Knopf J. L. Cytosolic phospholipase A2 is coupled to hormonally regulated release of arachidonic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6147–6151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L. L., Lin A. Y., Knopf J. L. Cytosolic phospholipase A2 is coupled to hormonally regulated release of arachidonic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6147–6151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier J. A., Hla T., Maciag T. Cyclooxygenase is an immediate-early gene induced by interleukin-1 in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):10805–10808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B. L., Bonventre J. V., Kremer S. G., Kudlow J. E., Skorecki K. L. Epidermal growth factor is synergistic with phorbol esters and vasopressin in stimulating arachidonate release and prostaglandin production in renal glomerular mesangial cells. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 15;249(2):587–592. doi: 10.1042/bj2490587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mené P., Simonson M. S., Dunn M. J. Phospholipids in signal transduction of mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 2):F375–F386. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.3.F375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mené P., Simonson M. S., Dunn M. J. Physiology of the mesangial cell. Physiol Rev. 1989 Oct;69(4):1347–1424. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.4.1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühl H., Geiger T., Pignat W., Märki F., van den Bosch H., Vosbeck K., Pfeilschifter J. PDGF suppresses the activation of group II phospholipase A2 gene expression by interleukin 1 and forskolin in mesangial cells. FEBS Lett. 1991 Oct 21;291(2):249–252. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81295-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellmayer A., Uedelhoven W. M., Weber P. C., Bonventre J. V. Endogenous non-cyclooxygenase metabolites of arachidonic acid modulate growth and mRNA levels of immediate-early response genes in rat mesangial cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3800–3807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal E. The molecular biology of mammalian arachidonic acid metabolism. Am J Physiol. 1991 Feb;260(2 Pt 1):L13–L28. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1991.260.2.L13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson M. S., Wolfe J. A., Konieczkowski M., Sedor J. R., Dunn M. J. Regulation of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase gene expression in cultured rat mesangial cells: induction by serum via a protein kinase-C-dependent mechanism. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Mar;5(3):441–451. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-3-441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka K., Takemura T., Murakami K., Akano N., Matsubara K., Aya N., Maki S. Identification and localization of epidermal growth factor and its receptor in the human glomerulus. Lab Invest. 1990 Aug;63(2):189–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]