Abstract
Escherichia coli multi-locus sequence type ST131 is a globally distributed pandemic lineage that causes multidrug-resistant extra-intestinal infections. ST131 E. coli frequently produce extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs), which confer resistance to many β-lactam antibiotics and make infections difficult to treat. We sequenced the genomes of 154 ESBL-producing E. coli clinical isolates belonging to the ST131 lineage from patients at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC) between 2004 and 2018. Isolates belonged to the well described ST131 clades A (8%), B (3%), and C (89%). Time-dated phylogenetic analysis estimated that the most recent common ancestor (MRCA) for all clade C isolates emerged around 1989, consistent with previous studies. We identified multiple genes potentially under selection in clade C, including the cell wall assembly gene ftsI, the LPS biosynthesis gene arnC, and the yersiniabactin uptake receptor fyuA. Diverse ESBL-encoding genes belonging to the blaCTX-M, blaSHV, and blaTEM families were identified; these genes were found at varying numbers of loci and in variable numbers of copies across isolates. Analysis of ESBL flanking regions revealed diverse mobile elements that varied by ESBL type. Overall, our findings show that ST131 subclade C dominated among patients and uncover possible signals of ongoing adaptation within this ST131 lineage.
Keywords: Escherichia coli, Antimicrobial resistance, Comparative genomics, Mobile genetic elements
Subject terms: Clinical microbiology, Bacterial genomics
Introduction
Escherichia coli sequence type (ST) 131 is a globally distributed extra-intestinal pathogenic E. coli (ExPEC) lineage that causes bloodstream and urinary tract infections1. ST131 isolates commonly exhibit multidrug resistance and often produce extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs), which give them the ability to resist therapy with many β-lactam antibiotics including expanded-spectrum cephalosporins2. The emergence and global spread of ESBL-producing E. coli raise serious issues for clinical management.
Prior studies have shown that the E. coli ST131 population can be separated into three major phylogenetic clades3. Typing of the fimH locus has been traditionally used to classify isolates into clade A (fimH41), clade B (fimH22), and clade C (fimH30). Isolates belonging to clade A have been mostly found in Asia, whereas clade C isolates dominate in the United States4. The clade C population has further diverged into the nested subclades C1 (fimH30R) and C2 (fimH30Rx), with isolates in both subclades encoding mutations in the gyrA and parC genes that confer resistance to fluoroquinolones. Most isolates in the C2 subclade carry the ESBL gene blaCTX-M-15, while isolates in the C1 subclade often carry blaCTX-M-275. ESBL-encoding genes are frequently maintained on mobile genetic elements (MGEs)6, which are often carried on plasmids but can also be integrated into the chromosome7.
Here we survey the genomic diversity and evolution of ESBL-producing ST131 E. coli isolates at a single medical center in the Pittsburgh area over a 15-year period. We describe the distribution of subclades and the diversity of ESBL-encoding MGEs, as well as the evolution of clade C isolates specifically, at our hospital. Our results suggest that a diverse ST131 E. coli population circulates in our facility. We also found evidence that distinct ST131 subpopulations have persisted in our hospital for over a decade, suggesting that multiple subclades are stably maintained in this setting.
Results
The ESBL-producing E. coli ST131 population at UPMC is dominated by clade C
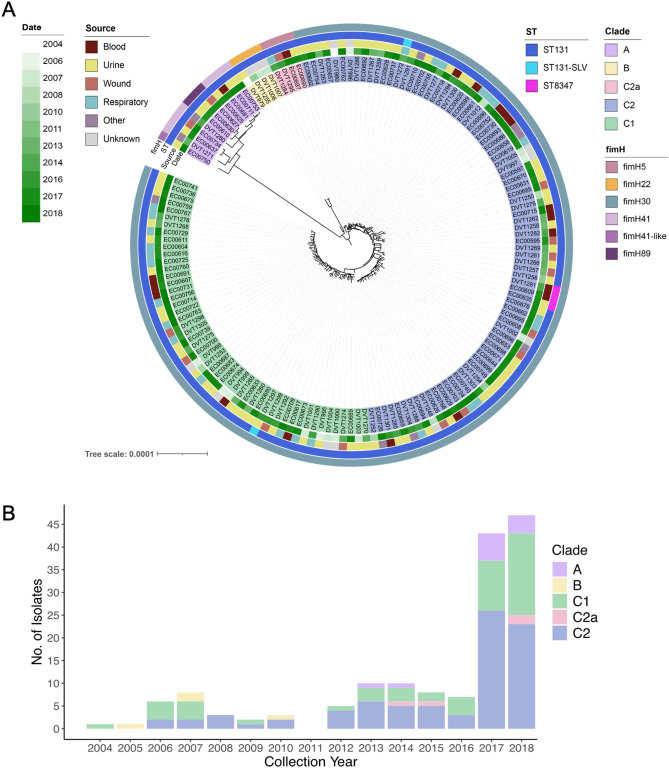
To survey the genomic diversity of ESBL-producing ST131 E. coli at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC), we sequenced the genomes of 154 clinical isolates collected from patients between 2004 and 2018 (Table S1). ESBL-producing E. coli isolates collected between 2004 and 2016 were tested with PCR using ST131-specific primers8, and up to ten ST131 isolates from each year were selected for whole genome sequencing. Beginning in 2016, isolates were identified as ST131 through analysis of whole genome sequence data9. We included isolates belonging to ST131 based on multi-locus sequence typing (MLST), as well as three isolates that belonged to ST8347 (a single locus variant of ST131) and two isolates that belonged to two additional single locus variants of ST131 that have not yet been assigned a sequence type (Fig. 1A).
Fig. 1.
Genetic diversity and timeline of collection of 154 ESBL-producing ST131 E. coli isolates. (A) The maximum likelihood phylogeny was constructed with RAxML from 18,734 core genome single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Background shading of each isolate indicates the ST131 clade (A, B), subclade (C2, C2), or subgroup (C2a). fimH allele type, multi-locus sequence type (ST), source, and date of isolation are shown for each isolate. (B) Total number of ST131 isolates collected each year colored by ST131 subclade.
A recombination-filtered phylogenetic tree based on variants found in the core genome of all 154 isolates was constructed using RAxML (Fig. 1A). As expected for the ST131 population4,6,10, isolates resided on three major branches. The first branch (clade A) contained twelve isolates (7.8%), including eight with fimH41, three with fimH89, and one with a novel fimH sequence that was most similar to fimH41 (Fig. 1A). These isolates were all collected in 2013 and later (Fig. 1B). An additional four isolates (2.6%) collected in 2005, 2007, and 2010 encoded fimH22 and belonged to clade B. The third branch consisted of the remaining 138 isolates (89.6%), including one group of four isolates that encoded fimH5. The rest of the isolates on this branch encoded fimH30, indicating that their clade could be assigned as clade C (Fig. 1A). Quinolone resistance-associated mutations in gyrA and parC were detected in all 138 clade C isolates. The 86 isolates carrying two additional mutations described previously4 were assigned to subclade C2. Within this clade, the four isolates encoding fimH5 were designated as subgroup C2a. The remaining 52 clade C isolates were classified as subclade C1. Clade C isolates were collected throughout the study period and there was no apparent difference in collection dates of subclade C1 versus C2 isolates (Fig. 1B).
Evolution of clade C and stable maintenance of subclades C1 and C2 in the Pittsburgh area
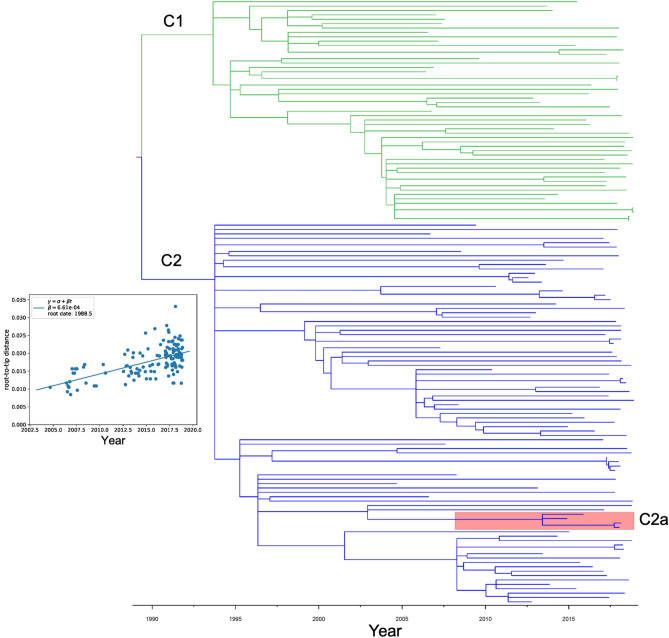
Prior studies have suggested that clade C emerged in approximately 19906,10,11. To examine the evolution of clade C in our hospital, we performed a time-calibrated phylogenetic analysis using TreeTime (Fig. 2)12. The estimated substitution rate was 1.76 core genome mutations per genome per year, and the estimated root date of clade C was 1986 (90% confidence interval: 1982–1991). In addition, when we re-rooted the phylogenetic tree to separate subclades C1 and C2, we confirmed that the C2a subgroup was embedded within subclade C2. The estimated date of emergence of this subgroup from the subclade C2 population was approximately 2013 (90% confidence interval: 2011–2015) (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
Time-calibrated phylogeny of 138 clade C isolates. The time-calibrated phylogeny was inferred from 2656 aligned SNPs and was constructed with TreeTime. Subclades C1 and C2 are indicated with green and blue branches, respectively. Subgroup C2a is shaded pink. The distribution of root-to-tip distances versus isolation date of all terminal nodes in the time-scaled tree is shown in the inset graph.
We identified a roughly 40%/60% split in the prevalence of isolates belonging to subclades C1 versus C2. Due to the persistence of both subclades, we investigated if these subclades differed in their isolation source and antimicrobial resistance (AMR) gene content. The only differences we observed in isolation source between the two clades, however, were slightly more blood isolates belonging to subclade C2 and slightly more respiratory isolates belonging to subclade C1 (Table S1). We next identified acquired AMR genes in all genomes in our dataset, and then examined the AMR gene content in subclade C1 versus C2 genomes (Table S2, Fig. S1). We found that subclade C1 isolate genomes encoded slightly more AMR genes compared to subclade C2 genomes, however the difference was not significant (mean 7.8 vs. 7.1 genes, P = 0.178). We also observed differences in the prevalence of individual genes conferring resistance to several different antibiotic classes between the different subclades, including aminoglycosides, antifolates, macrolides, and sulfonamides (Fig. S1).
Minimal gene enrichment in subclade C1 and C2 genomes
We performed a pan-genome analysis on the 138 genomes in clade C using Roary13 to identify genes that may be beneficial in clade persistence. Among the 11,587 genes in the clade C pangenome, 3,429 genes were shared among all clade C genomes, representing 70.3% of the average number of genes among genomes in this clade (Table S3). To assess gene enrichment among the clade C subclades, we used an 80%/20% enrichment cut-off and Fisher’s Exact Test to assess enrichment significance. We identified only 13 genes that were enriched among subclade C1 genomes (Table S4), and no genes were enriched among subclade C2 genomes, perhaps because this subclade was larger and more diverse than subclade C1. Nearly all the 13 genes enriched (P < 0.0001) among subclade C1 genomes appeared to be plasmid-encoded and were predicted to encode hypothetical proteins (Table S4).
Within subclade C2, we identified 56 genes that were specific to the fimH5 allele-carrying subgroup we designated as C2a (Fig. S2, Table S5). These genes appeared to be associated with several transposable units carrying carbohydrate and lipid metabolism genes as well as cell wall and cell membrane biogenesis genes (Table S5). We also identified a group of 27 subclade C2 genomes isolated between 2007 and 2018 that resided on the same phylogenetic branch, clustered together by accessory gene content, and carried 181 group-specific genes that we designated subgroup C2b (Fig. S2, Table S6). Approximately one third of these genes were associated with prophages, and 32 genes were predicted to reside within transposons. We further investigated prophages within our entire collection of 154 isolates by using PHASTEST to identify prophages predicted to be intact and questionable, which grouped into 90 different clusters of genetically similar prophage sequences (Table S7, Fig. S3). The most common prophage cluster was found in 76% of isolates. Other genes enriched in subgroup C2b had annotated functions including carbohydrate transport and metabolism genes, antibiotic and heavy metal resistance genes, toxin genes, and cell envelope-associated factors (Table S6).
Convergent evolution in subclades C1 and C2
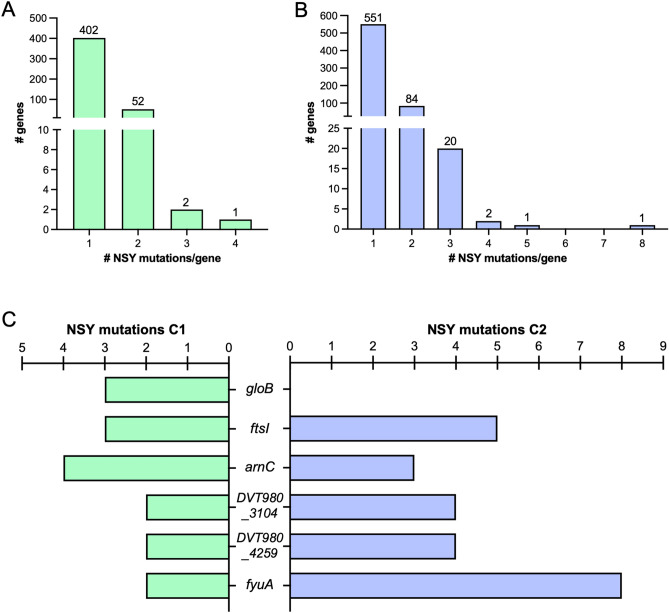
To investigate genes potentially under selection in clade C, we analyzed core genome non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in non-recombined genes among all isolates in each subclade to identify genes with multiple, independent SNPs in different isolates (Fig. 3, Table S8, Table S9). We focused on genes that had at least three non-synonymous SNPs among subclade C1 genomes (Fig. 3A), and at least four non-synonymous SNPs among subclade C2 genomes (Fig. 3B), as these genes would be unlikely to accrue so many mutations due to chance alone. Among subclade C1 genomes, the hydroxyacylglutathione hydrolase gene gloB and the peptidoglycan D,D-transpeptidase gene ftsI (also referred as PBP3) both possessed three different non-synonymous SNPs in three different isolates, and the undecaprenyl-phosphate 4-deoxy-4-formamido-L-arabinose transferase gene arnC possessed four different non-synonymous SNPs in five different isolates (Fig. 3C, Table S8). Both ftsI and arnC contribute to cell wall assembly, while gloB is involved in methylglyoxal detoxification14. Among subclade C2 genomes, two genes encoding hypothetical proteins (DVT980_3104 and DVT980_4259) each possessed four different non-synonymous SNPs (Fig. 3C). One of these proteins (DVT980_3104) was similar to the ribosome association toxin encoded by ratA and was mutated in four different isolates, while the other protein (DVT980_4259) was similar to the enterobactin siderophore exporter encoded by entS and was mutated in 19 isolates (Table S9). The peptidoglycan D,D-transpeptidase gene ftsI possessed five different non-synonymous SNPs in five different subclade C2 isolates, none of which overlapped with the three ftsI mutations detected in subclade C1 isolates. Two different mutations were detected at amino acid position 413 in ftsI (Ala413Val and Ala413Thr), strongly suggesting adaptive evolution of this gene. Finally, the yersiniabactin/pesticin outer membrane receptor gene fyuA possessed eight different non-synonymous SNPs in nine different subclade C2 isolates; such a high number of independent mutations also suggests strong selection acting on this gene.
Fig. 3.
Genes putatively under selection among clade C ST131 E. coli isolates. Enrichment of nonsynonymous (NSY) mutations among subclade (A) C1 and (B) C2 genomes. Frequency distributions show the number of genes with one or more NSY mutations detected. (C) Genes with at least three unique NSY mutations in subclade C1 genomes or at least four unique NSY mutations in subclade C2 genomes. The number of different mutations detected in each gene among the genomes in each subclade is shown.
ST131 clades carry diverse ESBL genes on both plasmids and the chromosome
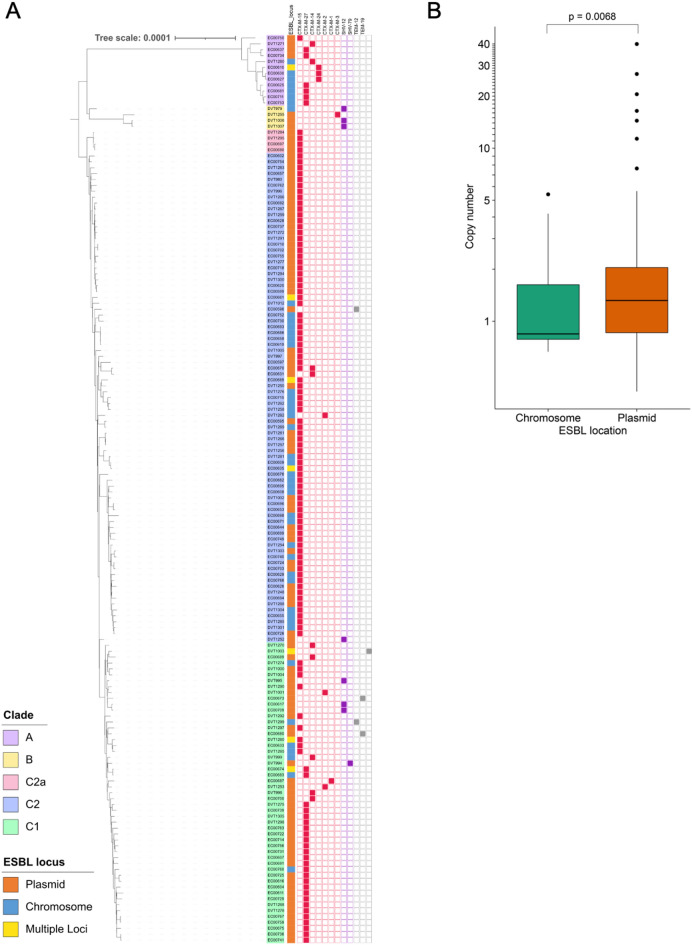
To examine the diversity of ESBL genes carried by the isolates we collected, we performed BLASTP searches against the ResFinder database15. A total of twelve different ESBLs were detected, including CTX-M, SHV, and TEM family enzymes (Fig. 4A, Table S10). The most common ESBL enzyme detected was CTX-M-15, which was found in 94 genomes and was dominant in subclade C2 (80/83, 96.4%). Outside of subclade C2, CTX-M-15 was also found in nine subclade C1 genomes and in one clade A genome (Fig. 4A). The second most common ESBL enzyme detected was CTX-M-27, which was found in 32 genomes and was the most prevalent enzyme detected in subclade C1 (26/51, 50.98%) and clade A (6/12, 50%). CTX-M-27 was first detected in 2013, and was the dominant ESBL type identified in subclade C1 and in clade A in 2017 and 2018 (Table S1). The third most common enzyme we detected was CTX-M-14, which was found in nine genomes and was not associated with any specific clade or subclade (Fig. 4A). The remaining ESBL enzymes detected were CTX-M-2 (n = 3), CTX-M-24 (n = 3), CTX-M-1 (n = 1), CTX-M-3 (n = 1), SHV-12 (n = 7), SHV-79 (n = 1), TEM-19 (n = 2), TEM-12 (n = 2), and TEM-10 (n = 2). One isolate (EC00670, belonging to subclade C2) was found to encode both CTX-M-14 and CTX-M-15 enzymes.
Fig. 4.
ESBL gene diversity, genomic location, and copy number variation. (A) Distribution of ESBL genes. ESBL locations (plasmid/chromosome/multiple loci) and types are shown as color blocks next to the isolate names, which are ordered based on their phylogenetic placement. (B) Box plot showing ESBL gene copy number in isolates predicted to encode an ESBL gene on the chromosome or on a plasmid. P-value was calculated using a two-tailed t-test.
While ESBL genes are carried on MGEs, these elements can reside on plasmids or be integrated into the chromosome1. We assigned a putative genomic location of the ESBL enzyme in each isolate in our dataset using the MOB-RECON tool in MOB-Suite, which predicted whether ESBL-encoding contigs in each genome represented plasmid or chromosome sequences16,17. The majority of isolates (105/154, 68%) were predicted to carry ESBL genes on plasmids, while 46/154 (30%) were predicted to carry ESBL genes on the chromosome (Fig. 4A). The remaining isolates (3/154, 2%) were predicted to encode ESBL enzymes on both plasmids and the chromosome. Next, we used the 45 genomes that were hybrid assembled to examine the diversity and distribution of ESBL-encoding plasmids in our dataset. Among these 45 genomes, we identified 35 ESBL-encoding plasmids, most of which belonged to the IncF family (Table S10). We then searched for each of these plasmids in all genomes in our dataset, and found that 11 plasmids were likely present in more than one isolate (Fig. S4). Four different blaCTX-M-15-carrying plasmids were found among subclade C2 genomes exclusively, while six of the other seven plasmids were found in isolates belonging to multiple clades. A total of 33 isolates that had ESBL enzymes predicted to be plasmid-encoded did not match to any of the 35 resolved ESBL-encoding plasmids using the identity and coverage cut-offs we employed (detailed further in the "Methods"), and likely contain different plasmid sequences.
Of the 35 ESBL-encoding plasmids, three plasmids were most common in our collection: DVT1294_4 (n = 21, unknown replicon type), DVT1284_2 (n = 9, IncFIA, IncFIC, IncFII), and EC00675_2 (n = 8, IncFIA, IncFIA, IncFIB). All isolates encoding the DVT1294_4 or DVT1284_2 plasmids were identified in subclade C2. Conversely, nearly all (n = 7) isolates encoding the EC00675_2 plasmid were identified in subclade C1. To compare these plasmids to those previously reported, we compared them with plasmid sequences in NCBI using BLASTN. Plasmid DVT1294_4 showed 100% identity and coverage to 3 different plasmids, p418 (MK295833.1), p396 (MK295831.1), and p461 (MK295823.1), all of which were collected from ST131 E. coli human blood isolates in 2007 from Israel. DVT1284_2 showed highest similarity (100% coverage, 99.97% identity) to plasmid pDog168 (MZ634324.1) carried by an ST131 E. coli strain found in dog feces, with year and geolocation unknown. EC00675_2 was most similar (100% coverage and 99.92% identity) to plasmid p1-S1-KEN-05-A (CP145690.1) carried by an ST131 E.coli strain from human stool in Switzerland in 2022. Lastly, we investigated IncF incompatibility group enrichment among the EBSL-encoding plasmids across clade C, and identified an enrichment of IncFIA, IncFIB, and IncFII groups within subclade C1 isolates, while IncFII_1 was enriched within subclade C2 (P < 0.05). Together these data suggest that many of the ESBL-encoding plasmids we identified were not unique to our setting, and that different incompatibility groups might be more compatible with particular ST131 clade C subclades.
Among the 45 hybrid assembled genomes, we identified eight genomes that had ESBL genes at more than one locus (Fig. 4A). The EC00610 genome carried three separate loci encoding CTX-M-24, all of which were on the chromosome. The EC00661 genome carried three loci encoding CTX-M-15, two of which were on the chromosome and one of which was on a plasmid. The DVT1260 genome also carried two chromosomal loci encoding CTX-M-15, while the EC00685 and EC00635 genomes both encoded one CTX-M-15 locus on the chromosome and another locus on a plasmid. The EC00670 genome encoded one CTX-M-14 locus and one CTX-M-15 locus, each on two different plasmids, and the DVT1003 genome carried two loci encoding TEM-10 on two different plasmids. Finally, the EC00674 genome carried two loci encoding CTX-M-27 on the same plasmid.
To assess ESBL copy number variation in the isolates we collected, we quantified the estimated ESBL gene copy number in each genome by comparing Illumina sequencing read depth of the ESBL gene with the read depth of all single copy genes in the core genome (Table S11). We found that estimated ESBL gene copy numbers varied from 0.39× to 40×, with a median copy number of 1.15×. Isolates with chromosomal ESBL genes had an average ESBL gene copy number of 1.34 × and a standard deviation of 1.06×, while isolates with plasmid-encoded ESBL genes had an average ESBL gene copy number of 2.73× and a standard deviation of 5.28x (Fig. 4B). ESBL gene copy numbers were significantly higher among isolates with plasmid-encoded ESBLs (P = 0.0068).
ESBLs are flanked by mobile elements that vary by enzyme type
To understand the genetic diversity of the elements carrying ESBL genes among the isolates we collected, we analyzed the genetic regions flanking the ESBL genes in each isolate in our study. We used the term “mobile genetic element” (MGE) to represent these small mobile elements carrying ESBL genes, which themselves are carried by plasmids or on the chromosome. Most assembled genomes allowed for examination of the genes immediately upstream and downstream of the ESBL enzyme (Fig. 5, Fig. S5). We found that blaCTX-M-15, which was present in 94% of subclade C2 isolates, very frequently resided in a conserved 3-kb region that was integrated into both plasmids and the chromosomes of different isolates (Fig. 5). We classified the blaCTX-M-15-flanking regions based on similarities in their gene organization and orientation, and identified four different MGE types. The first blaCTX-M-15-harboring MGE was found in isolates of clades A and C, and consisted of an ISEcp1 transposase and a small ORF with unknown function upstream of blaCTX-M-15 (Fig. 5A). This MGE was similar to the ISEcp1-blaCTX-M-15-ORF477 transposition unit reported by Stoesser et al. and Lartigue et al.6,18. The second MGE included the same upstream ISEcp1 transposase gene and small ORF with unknown function, as well as a Tn2 transposase gene downstream of blaCTX-M-15 (Fig. 5B). This MGE was similar to the putative blaCTX-M-15 source element (Tn2-ISEcp1-blaCTX-M-15-ORF477-Tn2) reported by Stoesser et al6. A third MGE was found exclusively on plasmids, and was flanked on either side by IS26 elements (Fig. 5C). The fourth MGE was only present in subclade C2 genomes, and was found on predicted chromosomal contigs, however it appears to have integrated at different chromosomal positions in different isolates (Fig. 5D).
Fig. 5.
Regions flanking blaCTX-M-15 among ST131 E. coli isolates. (A–D) Genomic context of different blaCTX-M-15-carrying MGEs is shown. Isolate names are shaded based on their phylogenetic clade assignments (clade A = purple; subclade C2 = blue; subclade C1 = green; subgroup C2a = pink). The genomic location of each sequence is indicated (C = chromosome, P = plasmid) and blaCTX-M-15 genes are colored red. Genes were annotated with Prokka, and genes with predicted functions are labeled. Genes associated with MGEs and transposases are highlighted with black outlines and are colored if found in more than one region. Regions that were used for MGE classification are shaded in each panel.
Apart from blaCTX-M-15, a variety of different MGEs were found to carry the other ESBL genes we detected (Fig. S5). blaCTX-M-27 was found on at least three different MGEs, and was associated with IS15 and Tn3 elements (Fig. S5A). Both blaCTX-M-14 and blaCTX-M-24 were found on the ISEcp1 MGE that also carried blaCTX-M-15 (Fig. S5B, S5C). Finally, blaSHV-12 was frequently found on a larger MGE that was flanked by IS26 and contained additional carbohydrate metabolism genes (Fig. S5D).
Discussion
In this 15-year study, we examined the genomic diversity and evolutionary dynamics of 154 ESBL-producing ST131 E. coli isolates from UPMC, a large healthcare system. Due to the multidrug resistance reported in ST131, numerous groups have characterized the clade structure of this pandemic lineage. Prior studies have suggested that clade C emerged around 19906,10,11. Similarly, we identified the estimated root date to be midway through 1988, although the 90% confidence interval spanned from 1982 to 1991. Our collection was dominated by isolates belonging to subclades C1 (fimH30-R) and C2 (fimH30-Rx) at an approximate 2:3 ratio, respectively. This finding suggests that these two subclades can coexist within the patient population that we sampled. We did not identify a significant difference in the number of AMR genes between the two clades, however, we did observe differences in the prevalence of individual genes conferring resistance to several different antibiotic classes. These data suggest that while subclade C1 and C2 isolates do not differ in their total AMR gene abundance, more subtle differences in the types of resistance genes they encode might contribute to their coexistence in the patient population that we sampled19.
We sought to further investigate why the C1 and C2 subclades have stably coexisted over the last 30 years. While our data suggest that subclades C1 and C2 do not harbor clade-specific gene signatures, within subclade C2 we identified two groups that were each enriched for genes with potentially useful functions. These enriched genes may contribute to ongoing adaptation of subclade C2 in the Pittsburgh area. Previous studies have identified an enrichment of phage-related genes in ST131 clades B and C compared to clade A20. Although we only performed gene enrichment analyses on clade C isolates, we did identify an enrichment of prophage genes in subclade C2b, suggesting that prophages may play a role in this subclade’s success. In agreement with previous reports, we identified a strong association between CTX-M-15 and subclade C2 and between CTX-M-27 and subclade C14,19,21. The first isolate harboring CTX-M-27 in our collection was identified in 2013, coinciding with the recent emergence of CTX-M-27 documented in Europe and Asia5,22,23. When we predicted the location of the 154 ESBL-positive isolates, roughly a third were identified on the chromosome. A similarly high incidence of ESBL chromosomal integration was observed in a prior study of clinical E. coli isolates from diverse geographical locations24. This finding suggests that the integration of the ESBL enzyme onto the chromosomal might enhance stable propagation and expression.
In addition to subclade-specifying genes, we also investigated whether distinct genes might be under positive selection in subclade C1 versus C2 genomes. We identified missense variants in gloB were only detected in subclade C1 genomes, suggesting that perhaps mutating this gene was only beneficial in the subclade C1 genetic background. Multiple independent mutations in ftsI and arnC were detected in both subclades, and might affect bacterial susceptibility to other cell wall-targeting antibiotics like carbapenems25, or membrane-targeting antibiotics like colistin26, respectively. The ratA-like toxin and entS-like siderophore exporter genes were also independently mutated in multiple isolates across both subclades. These mutations might serve to decrease bacterial virulence, which frequently occurs during chronic infection and host adaptation27. Lastly, mutations in fyuA were also detected in both subclades, however they were heavily biased toward subclade C2 genomes. Prior studies have shown that fyuA function is critical for biofilm formation in iron-poor environments like the urinary tract28; mutations that alter or abrogate fyuA function would be predicted to decrease iron scavenging and biofilm formation. Future studies of the functional consequences of fyuA mutations on bacterial virulence and host–pathogen interactions may produce additional insights as to why these mutations appear to be under selection in ESBL-producing ST131 E. coli from our setting.
In addition to carrying a wide variety of ESBL genes, the ST131 E. coli isolates we sampled also carried a large diversity of ESBL-encoding plasmids. Some of these were specific to individual ST131 subclades, while others were identified widely throughout the lineage. We found that only 13% of isolates in our collection carried the same plasmid (DVT1294_4, n = 21), suggesting a low prevalence of plasmid transmission in contrast to prior studies29. While we did not observe individual plasmids that were associated with different ST131 subclades, we did find that different IncF incompatibility groups were enriched in the two clade C subclades. Prior work has also identified enrichment of IncF types among subclades, suggesting that particular IncF types may play a role in the dissemination of particular ESBL types30. Highlighting the global dissemination of EBSL-encoding plasmids, we identified instances of high genetic similarity between plasmids identified at our center and those identified across different countries, hosts, and collection years. We also identified instances where isolates carried multiple ESBLs, either on different plasmids and/or integrated onto the chromosome. These data suggest that ESBL enzymes are frequently present at multiple loci within ST131 genomes, however these features can be difficult to resolve from Illumina draft genome assemblies. Given that nearly 20% of our hybrid assembled genomes encoded ESBL enzymes at more than one locus, it is very likely that there are additional isolates in our dataset that also encode ESBL genes at multiple loci. Additionally, our findings of variable ESBL copy number among the isolates we sequenced suggests that antibiotic selection might further increased the ESBL-encoding plasmid copy number in some isolates, as observed previously31,32. The significance of this is unclear but could be due to gene dosage, plasmid instability, and/or shifting selective pressures during infection and antibiotic treatment33,34.
ESBLs in ST131 E. coli are most often encoded within MGEs carrying insertion sequences and transposons, and these mobile elements are integrated into plasmids or the chromosome35,36. Through characterizing a variety of different MGEs with ESBLs, we found that ESBL genes in the isolates from our medical center are likely shuttled between bacteria by MGEs that vary by enzyme type. Additionally, these elements appear to have integrated at different locations on both the plasmid and chromosome. It is notable that we observed a wide variety of different MGEs among the ST131 ESBL-producing E. coli sampled from a single geographic location. This suggests that as in other locations37,38, no single ESBL enzyme or MGE type was dominant at our center during the study period.
In conclusion, this study describes ongoing adaptation of the ST131 E. coli population sampled from clinical cultures of patients in a single hospital in Pittsburgh. While the vast majority of isolates we collected belonged to ST131 clade C, both subclades C1 and C2 appear to be stably maintained over time in our facility. Despite this stable maintenance, we found an abundant diversity of ESBL enzyme types and a vast array of different mobile elements carrying these enzymes on both plasmids and the chromosome. The diversity of antimicrobial resistance genes, movement of plasmids and other MGEs, and signals of adaptation we identified will be the focus of our future work in this area.
Methods
Sample collection
Clinical bacterial isolates were collected from patients at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC), an adult tertiary care hospital with over 750 beds, 150 critical care unit beds, more than 32,000 yearly inpatient admissions, and over 400 solid organ transplants per year. Bacterial isolates included in this study were collected from patients as part of routine clinical care and were collected before they otherwise would have been discarded. Isolates represent both community-acquired and hospital-acquired infections. The study was designated by the University of Pittsburgh institutional review board as being exempt from informed consent, and all methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations. Isolates were collected from 2004 to 2018, and were identified as E. coli initially by the clinical microbiology laboratory. From all ESBL-producing E. coli collected between 2004 and 2016, ST131 isolates were identified with PCR using lineage-specific primers8, and up to 10 ST131 isolates per year were selected for whole genome sequencing. For isolates collected in 2017 and 2018, ST131 E. coli isolates were identified through analysis of whole genome sequences generated by the Enhanced Detection System for Healthcare-Associated Transmission (EDS-HAT)9. Collection of bacterial isolates was approved by the University of Pittsburgh institutional review board. ESBL phenotypes were inferred by the presence of an intact β-lactamase enzyme predicted to have ESBL activity within the genome of each isolate. Single bacterial colonies were isolated, and were grown on blood agar plates or in Lysogeny Broth (LB) media prior to genomic DNA extraction.
Whole-genome sequencing
Genomic DNA was extracted from each isolate using a Qiagen DNeasy Tissue Kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Qiagen, Germantown, MD). Illumina library construction and sequencing were conducted using an Illumina Nextera DNA Sample Prep Kit with 150-bp paired-end reads, and libraries were sequenced on the NextSeq 550 sequencing platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA) at the Microbial Genome Sequencing Center (MiGS). A total of 45 isolates were also sequenced on a MinION device (Oxford Nanopore Technologies, Oxford, United Kingdom). Long-read sequencing libraries were prepared and multiplexed using a rapid multiplex barcoding kit (catalog SQK-RBK004) and were sequenced on R9.4.1 flow cells. Base-calling on raw reads was performed using Albacore v2.3.3 or Guppy v2.3.1 (Oxford Nanopore Technologies, Oxford, UK).
Short and long reads (or short reads alone) were used as inputs for Unicycler to generate draft genomes39. Plasmid and chromosomal contigs were predicted with the MOB-RECON tool in MOB-Suite v3.1.716,17, and Prokka 1.14.5 was used for genome annotation40. Illumina raw reads and genome assemblies for all isolates have been submitted to NCBI under BioProjects PRJNA475751 and PRJNA874473. NCBI accession numbers for genome sequence data are listed in Table S1.
MLST, fimH, gyrA/parC, and clade C2 SNP genotyping
Multi-locus sequence typing (MLST) was performed with SRST241. Typing of the fimH locus was performed by running BLASTN against the fimH sequence database downloaded from FimTyper42,43. To detect quinolone resistance-determining region (QRDR) mutations, amino acid residues 81–87 of gyrA and the 78–84 of parC were extracted and compared44. To detect clade C2-specific single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), targeted regions of primer sets described previously4 were extracted from all genomes and were compared with BLASTN.
Phylogenetic trees and the time-scaled phylogeny
Among hybrid assembled genomes, the earliest collected isolate (DVT980) was used as a reference genome for Snippy v 4.6.0 to identify SNPs among the isolates using short read data and to generate a core SNP alignment (https://github.com/tseemann/snippy). The alignments were used as input for RAxMLHPC v 8.2.12 with [-m ASC_GTRCAT –asc-corr = lewis -V] flags to generate phylogenetic trees45. ClonalFrameML v1.12 was then used to filter recombinogenic regions46. Resulting trees were visualized with iTOL v6.347 or FigTree v1.4.4 (https://github.com/rambaut/figtree/). Branch bootstraps supporting the clade C phylogeny were evaluated using RaxMLHPC with 100 rapid bootstrapping replicates with [-m ASC_GTRCAT -f a –asc-corr lewis -V] flags. Estimation of evolutionary rate and a time scaled phylogeny of clade C isolates was generated with TreeTime v0.9.212, using a phylogenetic tree, ClonalFrameML-trimmed alignment, and the collection dates of the 138 isolates in clade C as input.
ESBL gene detection and copy number variation
Amino acid sequences of all protein coding genes annotated by Prokka were used as queries to run BLASTP against the ResFinder amino acid database15,43. Hits with 100% identity and 100% length coverage to the reference amino acid sequence were then filtered and manually curated to only include ESBL genes. Isolates with less than perfect matches to a database entry were compared with the NCBI non-redundant protein sequences (nr) database with BLASTP. To estimate the copy number of the ESBL gene(s) in each genome, Illumina raw reads were mapped to the assembled draft genome using BWA with default parameters48. The read depth covering each gene was then calculated via the MULTICOV function of BEDTOOLS v2.30.0, with the input BAM file generated by BWA and the BED file that includes all protein coding genes, tRNAs, and rRNAs49. To normalize read coverage, we used an AWK pipeline to calculate the reads per kilobase per million mapped reads (RPKM) for each gene based on the depth list output of BEDTOOLS. A list of single copy genes shared by all genomes included in this study was extracted from the < gene_presence_absence.csv > output file of Roary v3.13.013. For each genome, the median RPKM value of the single copy genes was calculated using the median() function in R. ESBL gene copy number in each genome was estimated by dividing the RPKM value of the ESBL gene(s) by the median RPKM value of single copy genes for the same genome.
ESBL-encoding plasmid detection and analysis of flanking regions
A list of ESBL-encoding reference plasmids was first generated from all hybrid assembled genomes and plasmid contigs identified by MOB-RECON v3.1.716,17. Contigs predicted to be circular by Unicycler v0.5.0 but not recognized as plasmids were not included in the reference plasmid list. To reduce redundancy, plasmids sharing > 95% nucleotide similarity (defined as the product of query coverage and nucleotide identity) and encoding the same ESBL gene were combined and only the longest plasmid was retained. The remaining reference plasmids were then queried in all genomes using BLASTN and hits that had > 95% nucleotide similarity were retained. Results were then manually curated to remove hits in genomes predicted to encode ESBLs on the chromosome only and hits to reference plasmids harboring a different ESBL. Among Illumina-only genomes, if there were hits to multiple reference plasmids with the same ESBL, only the longest reference plasmid was reported. To assess ESBL flanking regions, DNA segments containing up to 15 genes upstream and downstream of each ESBL gene were visualized via the R package genoPlotR, and were manually aligned centering on the ESBL gene to visualize conservation and enable classification of ESBL-containing MGEs50. Associations between ESBL plasmid replicon/incompatibility type and ST131 subclades were assessed using a Fisher’s Exact test.
Identification of subclade-specific genes and SNPs for clade C
The 138 annotated genomes belonging to clade C, including four genomes in clade C2a, were used for pangenome analysis. The pangenome analysis tool ROARY was used to generate a gene presence and absence matrix (gene_presence_absence.csv). Genes enriched in each clade were identified as those that were present in more than 80% of isolates within the clade and less than 20% of isolates outside the clade. We further assessed the significance of enriched genes by performing a Fisher’s Exact test. The pangenome matrix was visualized using the heatmap() function in R. Genes associated with prophages and transposons were identified using PHASTER and MobileElementFinder, respectively51–53. Snippy was used to identify SNPs among clade C1 and C2 isolates using the DVT980 (earliest collected isolate) hybrid assembled genome as a reference. SNPs found in genomic regions identified by ClonalFrameML as putative recombinations were then masked. SNPs located in clade C core genes were annotated with gene description and locus tag of the reference genome. SNPs were then examined manually to identify genes with repeated and independent mutations within each subclade. Prophages were identified using PHASTEST54. Sequences of prophages predicted to be intact or questionable were extracted from genomes and compared to one another with all-by-all BLASTN. Clusters of genetically related prophages were identified as those with ≥ 90% nucleotide identity and ≥ 90% sequence coverage, as in55.
Supplementary Information
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge Jane Marsh, Akansha Pradhan, and Alecia Rokes for their helpful input throughout the course of this study. This work was supported by grant R01AI127472 from the National Institutes of Health (L.H.H.), grant DAA3-19-65600-1 from the US Civilian Research & Development Foundation (D.V.T), and by the Department of Medicine at the University of Pittsburgh, School of Medicine (D.V.T.). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author contributions
SC and DVT designed the study. LHH and YD provided bacterial isolates. SC, MPG, HRN, and CLM performed experiments and generated results. SC, EGM, and DVT wrote the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript and approved of its contents.
Data availability
Illumina raw reads and genome assemblies for all isolates have been submitted to NCBI under BioProjects PRJNA475751 and PRJNA874473. NCBI accession numbers for genome sequence data are listed in Table S1. All other data are provided in the supplementary information accompanying the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41598-024-70540-1.
References
- 1.Nicolas-Chanoine, M. H., Bertrand, X. & Madec, J. Y. Escherichia coli ST131, an intriguing clonal group. Clin Microbiol Rev27, 543–574. 10.1128/CMR.00125-13 (2014). 10.1128/CMR.00125-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nicolas-Chanoine, M. H. et al. Intercontinental emergence of Escherichia coli clone O25:H4-ST131 producing CTX-M-15. J Antimicrob Chemother61, 273–281. 10.1093/jac/dkm464 (2008). 10.1093/jac/dkm464 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Adams-Sapper, S., Diep, B. A., Perdreau-Remington, F. & Riley, L. W. Clonal composition and community clustering of drug-susceptible and -resistant Escherichia coli isolates from bloodstream infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother57, 490–497. 10.1128/AAC.01025-12 (2013). 10.1128/AAC.01025-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Price, L. B. et al. The epidemic of extended-spectrum-beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli ST131 is driven by a single highly pathogenic subclone H30-Rx. mBio4, e00377-e1313. 10.1128/mBio.00377-13 (2013). 10.1128/mBio.00377-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Matsumura, Y. et al. Global Escherichia coli sequence type 131 clade with blaCTX-M-27 gene. Emerg Infect Dis22, 1900–1907. 10.3201/eid2211.160519 (2016). 10.3201/eid2211.160519 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Stoesser, N. et al. Evolutionary history of the global emergence of the Escherichia coli epidemic clone ST131. MBio7, e02162. 10.1128/mBio.02162-15 (2016). 10.1128/mBio.02162-15 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zhang, C. Z. et al. The emergence of chromosomally located bla CTX-M-55 in salmonella from foodborne animals in China. Front Microbiol10, 1268. 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01268 (2019). 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01268 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Matsumura, Y. et al. Rapid identification of different Escherichia coli sequence type 131 clades. Antimicrob Agents Chemother10.1128/AAC.00179-17 (2017). 10.1128/AAC.00179-17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sundermann, A. J. et al. Whole genome sequencing surveillance and machine learning of the electronic health record for enhanced healthcare outbreak detection. Clin Infect Dis10.1093/cid/ciab946 (2021). 10.1093/cid/ciab946 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ludden, C. et al. Genomic surveillance of Escherichia coli ST131 identifies local expansion and serial replacement of subclones. Microb Genom10.1099/mgen.0.000352 (2020). 10.1099/mgen.0.000352 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kallonen, T. et al. Systematic longitudinal survey of invasive Escherichia coli in England demonstrates a stable population structure only transiently disturbed by the emergence of ST131. Genome Res10.1101/gr.216606.116 (2017). 10.1101/gr.216606.116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sagulenko, P., Puller, V. & Neher, R. A. TreeTime: maximum-likelihood phylodynamic analysis. Virus Evol4, vex042. 10.1093/ve/vex042 (2018). 10.1093/ve/vex042 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Page, A. J. et al. Roary: rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinformatics31, 3691–3693. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv421 (2015). 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv421 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Reiger, M., Lassak, J. & Jung, K. Deciphering the role of the type II glyoxalase isoenzyme YcbL (GlxII-2) in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett362, 1–7. 10.1093/femsle/fnu014 (2015). 10.1093/femsle/fnu014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bortolaia, V. et al. ResFinder 4.0 for predictions of phenotypes from genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother.75, 3491–3500. 10.1093/jac/dkaa345 (2020). 10.1093/jac/dkaa345 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Robertson, J. & Nash, J. H. E. MOB-suite: software tools for clustering, reconstruction and typing of plasmids from draft assemblies. Microb. Genom.10.1099/mgen.0.000206 (2018). 10.1099/mgen.0.000206 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Robertson, J., Bessonov, K., Schonfeld, J. & Nash, J. H. E. Universal whole-sequence-based plasmid typing and its utility to prediction of host range and epidemiological surveillance. Microb. Genom.10.1099/mgen.0.000435 (2020). 10.1099/mgen.0.000435 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lartigue, M. F., Poirel, L. & Nordmann, P. Diversity of genetic environment of bla(CTX-M) genes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett.234, 201–207. 10.1016/j.femsle.2004.01.051 (2004). 10.1016/j.femsle.2004.01.051 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mills, E. G. et al. A one-year genomic investigation of Escherichia coli epidemiology and nosocomial spread at a large US healthcare network. Genome Med.14, 147. 10.1186/s13073-022-01150-7 (2022). 10.1186/s13073-022-01150-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.McNally, A. et al. Diversification of colonization factors in a multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli lineage evolving under negative frequency-dependent selection. mBio10.1128/mBio.00644-19 (2019). 10.1128/mBio.00644-19 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wilson, H. & Torok, M. E. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing and carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Microb. Genom.10.1099/mgen.0.000197 (2018). 10.1099/mgen.0.000197 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Merino, I. et al. Emergence of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli ST131-C1-M27 clade colonizing patients in Europe. J. Antimicrob. Chemother.73, 2973–2980. 10.1093/jac/dky296 (2018). 10.1093/jac/dky296 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Peirano, G. & Pitout, J. D. D. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing enterobacteriaceae: Update on molecular epidemiology and treatment options. Drugs79, 1529–1541. 10.1007/s40265-019-01180-3 (2019). 10.1007/s40265-019-01180-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Coque, T. M. et al. Dissemination of clonally related Escherichia coli strains expressing extended-spectrum beta-lactamase CTX-M-15. Emerg Infect Dis14, 195–200. 10.3201/eid1402.070350 (2008). 10.3201/eid1402.070350 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Adler, M., Anjum, M., Andersson, D. I. & Sandegren, L. Combinations of mutations in envZ, ftsI, mrdA, acrB and acrR can cause high-level carbapenem resistance in Escherichia coli. J Antimicrob Chemother71, 1188–1198. 10.1093/jac/dkv475 (2016). 10.1093/jac/dkv475 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sundaramoorthy, N. S., Suresh, P., Selva Ganesan, S., GaneshPrasad, A. & Nagarajan, S. Restoring colistin sensitivity in colistin-resistant E. coli: Combinatorial use of MarR inhibitor with efflux pump inhibitor. Sci. Rep.9, 19845. 10.1038/s41598-019-56325-x (2019). 10.1038/s41598-019-56325-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gatt, Y. E. & Margalit, H. Common adaptive strategies underlie within-host evolution of bacterial pathogens. Mol. Biol. Evol.38, 1101–1121. 10.1093/molbev/msaa278 (2021). 10.1093/molbev/msaa278 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hancock, V., Ferrieres, L. & Klemm, P. The ferric yersiniabactin uptake receptor FyuA is required for efficient biofilm formation by urinary tract infectious Escherichia coli in human urine. Microbiology (Reading)154, 167–175. 10.1099/mic.0.2007/011981-0 (2008). 10.1099/mic.0.2007/011981-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Woodford, N. et al. Complete nucleotide sequences of plasmids pEK204, pEK499, and pEK516, encoding CTX-M enzymes in three major Escherichia coli lineages from the United Kingdom, all belonging to the international O25:H4-ST131 clone. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.53, 4472–4482. 10.1128/AAC.00688-09 (2009). 10.1128/AAC.00688-09 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Johnson, T. J. et al. Separate F-Type plasmids have shaped the evolution of the H30 subclone of Escherichia coli sequence type 131. mSphere10.1128/mSphere.00121-16 (2016). 10.1128/mSphere.00121-16 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.San Millan, A., Escudero, J. A., Gifford, D. R., Mazel, D. & MacLean, R. C. Multicopy plasmids potentiate the evolution of antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Nat. Ecol. Evol.1, 10. 10.1038/s41559-016-0010 (2016). 10.1038/s41559-016-0010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sun, S., Berg, O. G., Roth, J. R. & Andersson, D. I. Contribution of gene amplification to evolution of increased antibiotic resistance in Salmonella typhimurium. Genetics182, 1183–1195. 10.1534/genetics.109.103028 (2009). 10.1534/genetics.109.103028 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hong, J. S. et al. Molecular characterization of fecal extended-spectrum beta-lactamase- and AmpC beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli from healthy companion animals and cohabiting humans in South Korea. Front Microbiol11, 674. 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00674 (2020). 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00674 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Dimitriu, T., Matthews, A. C. & Buckling, A. Increased copy number couples the evolution of plasmid horizontal transmission and plasmid-encoded antibiotic resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A10.1073/pnas.2107818118 (2021). 10.1073/pnas.2107818118 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Harmer, C. J. & Hall, R. M. IS26-mediated formation of transposons carrying antibiotic resistance genes. mSphere10.1128/mSphere.00038-16 (2016). 10.1128/mSphere.00038-16 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Shawa, M. et al. Novel chromosomal insertions of ISEcp1-blaCTX-M-15 and diverse antimicrobial resistance genes in Zambian clinical isolates of Enterobacter cloacae and Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control10, 79. 10.1186/s13756-021-00941-8 (2021). 10.1186/s13756-021-00941-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kanamori, H. et al. Genomic analysis of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli from North Carolina community hospitals: ongoing circulation of CTX-M-producing ST131-H30Rx and ST131-H30R1 strains. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.10.1128/AAC.00912-17 (2017). 10.1128/AAC.00912-17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ny, S., Sandegren, L., Salemi, M. & Giske, C. G. Genome and plasmid diversity of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli ST131 - tracking phylogenetic trajectories with Bayesian inference. Sci Rep9, 10291. 10.1038/s41598-019-46580-3 (2019). 10.1038/s41598-019-46580-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wick, R. R., Judd, L. M., Gorrie, C. L. & Holt, K. E. Unicycler: Resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput. Biol.13, e1005595. 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005595 (2017). 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005595 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Seemann, T. Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics30, 2068–2069. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu153 (2014). 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu153 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Inouye, M. et al. SRST2: Rapid genomic surveillance for public health and hospital microbiology labs. Genome Med6, 90. 10.1186/s13073-014-0090-6 (2014). 10.1186/s13073-014-0090-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Roer, L. et al. Development of a web tool for Escherichia coli subtyping based on fimH alleles. J Clin Microbiol55, 2538–2543. 10.1128/JCM.00737-17 (2017). 10.1128/JCM.00737-17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Camacho, C. et al. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinf.10, 421. 10.1186/1471-2105-10-421 (2009). 10.1186/1471-2105-10-421 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Aoike, N. et al. Molecular characterization of extraintestinal Escherichia coli isolates in Japan: Relationship between sequence types and mutation patterns of quinolone resistance-determining regions analyzed by pyrosequencing. J Clin Microbiol51, 1692–1698. 10.1128/JCM.03049-12 (2013). 10.1128/JCM.03049-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics30, 1312–1313. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033 (2014). 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Didelot, X. & Wilson, D. J. ClonalFrameML: Efficient inference of recombination in whole bacterial genomes. PLoS Comput. Biol.11, e1004041. 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004041 (2015). 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004041 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Letunic, I. & Bork, P. Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v4: Recent updates and new developments. Nucleic Acids Res.47, W256–W259. 10.1093/nar/gkz239 (2019). 10.1093/nar/gkz239 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Li, H. & Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with burrows-wheeler transform. Bioinformatics25, 1754–1760. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324 (2009). 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Quinlan, A. R. & Hall, I. M. BEDTools: A flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics26, 841–842. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq033 (2010). 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Guy, L., Kultima, J. R. & Andersson, S. G. genoPlotR: Comparative gene and genome visualization in R. Bioinformatics26, 2334–2335. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq413 (2010). 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq413 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Zhou, Y., Liang, Y., Lynch, K. H., Dennis, J. J. & Wishart, D. S. PHAST: A fast phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res39, W347-352. 10.1093/nar/gkr485 (2011). 10.1093/nar/gkr485 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Arndt, D. et al. PHASTER: A better, faster version of the PHAST phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res.44, W16-21. 10.1093/nar/gkw387 (2016). 10.1093/nar/gkw387 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Johansson, M. H. K. et al. Detection of mobile genetic elements associated with antibiotic resistance in Salmonella enterica using a newly developed web tool: MobileElementFinder. J. Antimicrob. Chemother.76, 101–109. 10.1093/jac/dkaa390 (2021). 10.1093/jac/dkaa390 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Wishart, D. S. et al. PHASTEST: Faster than PHASTER, better than PHAST. Nucleic Acids Res51, W443–W450. 10.1093/nar/gkad382 (2023). 10.1093/nar/gkad382 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Nordstrom, H. R. et al. Genomic characterization of lytic bacteriophages targeting genetically diverse Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates. iScience25, 104372. 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104372 (2022). 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104372 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Illumina raw reads and genome assemblies for all isolates have been submitted to NCBI under BioProjects PRJNA475751 and PRJNA874473. NCBI accession numbers for genome sequence data are listed in Table S1. All other data are provided in the supplementary information accompanying the manuscript.