Abstract
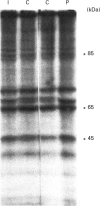
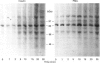
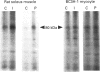
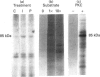
To evaluate the question of whether or not insulin activates protein kinase C (PKC), we compared the effects of insulin and phorbol esters on the phosphorylation of the PKC substrate, i.e. myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate (MARCKS). In rat adipocytes, rat soleus muscle and BC3H-1 myocytes, maximally effective concentrations of insulin and phorbol esters provoked comparable, rapid, 2-fold (on average), non-additive increases in the phosphorylation of immunoprecipitable MARCKS. These effects of insulin and phorbol esters on MARCKS phosphorylation in intact adipocytes and soleus muscles were paralleled by similar increases in the phosphorylation of an exogenous, soluble, 85 kDa PKC substrate (apparently a MARCKS protein) during incubation of post-nuclear membrane fractions in vitro. Increases in the phosphorylation of this 85 kDa PKC substrate in vitro were also observed in assays of both plasma membranes and microsomes obtained from rat adipocytes that had been treated with insulin or phorbol esters. These insulin-induced increases in PKC-dependent phosphorylating activities of adipocyte plasma membrane and microsomes were associated with increases in membrane contents of diacylglycerol, PKC-beta 1 and PKC-beta 2. Our findings suggest that insulin both translocates and activates PKC in rat adipocytes, rat soleus muscles and BC3H-1 myocytes.
Full text
PDF


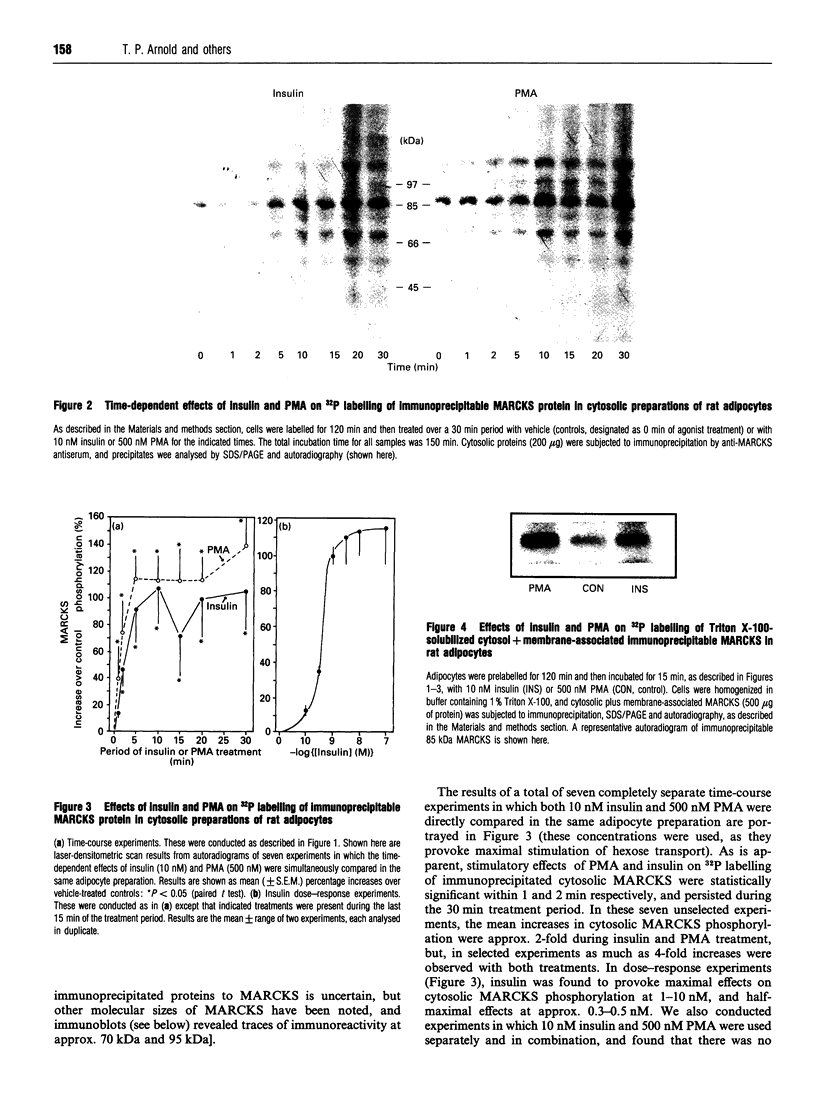
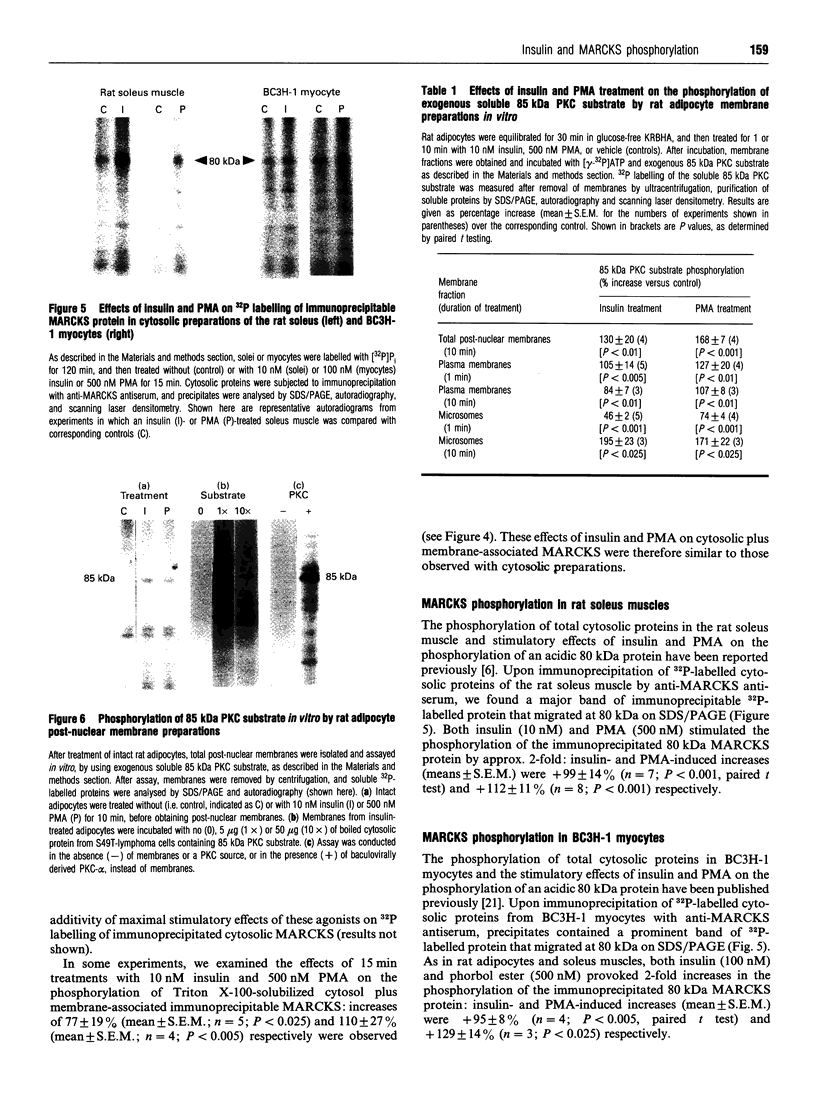
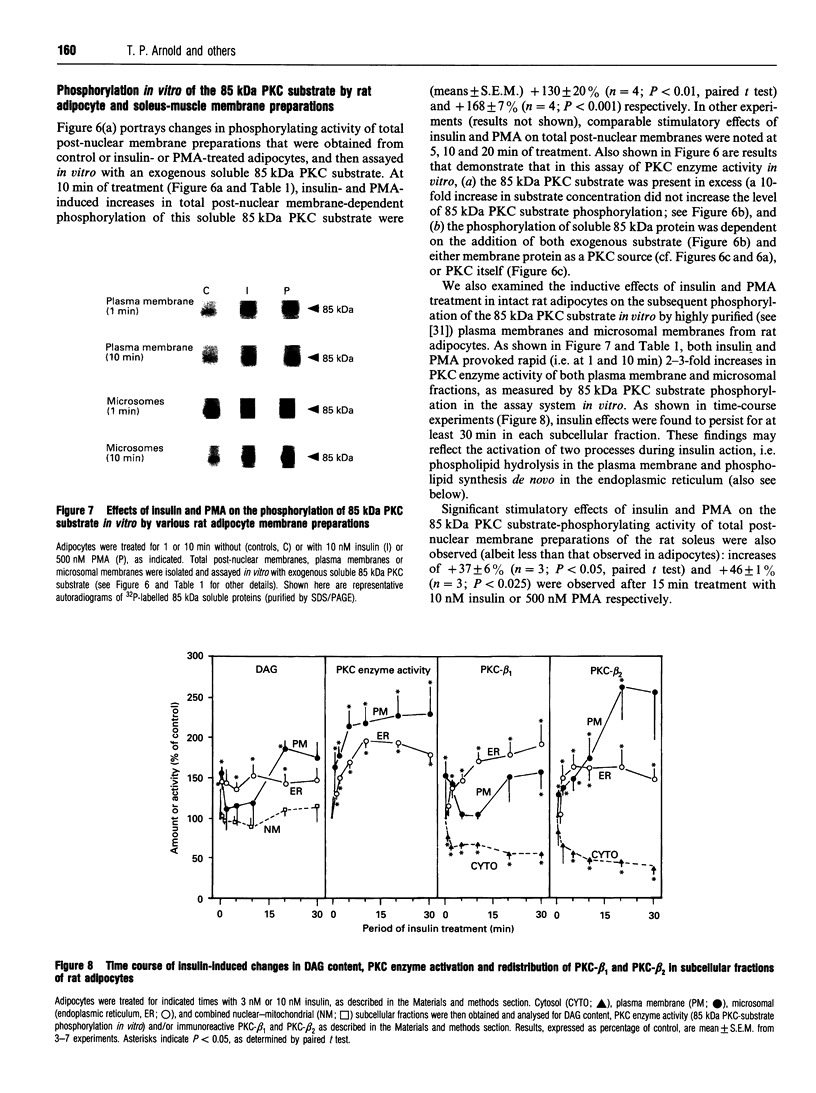




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acevedo-Duncan M., Cooper D. R., Standaert M. L., Farese R. V. Immunological evidence that insulin activates protein kinase C in BC3H-1 myocytes. FEBS Lett. 1989 Feb 13;244(1):174–176. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81186-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albert K. A., Walaas S. I., Wang J. K., Greengard P. Widespread occurrence of "87 kDa," a major specific substrate for protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2822–2826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazzi M. D., Nelsestuen G. L. Properties of the protein kinase C-phorbol ester interaction. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 18;28(8):3577–3585. doi: 10.1021/bi00434a064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs K. P., Farese R. V., Buse M. G. Insulin administration in vivo increases 1,2-diacylglycerol in rat skeletal muscle. Endocrinology. 1991 Jan;128(1):636–638. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-1-636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarthy B. R., Franks D. J., Whitfield J. F., Durkin J. P. A novel method for measuring protein kinase C activity in a native membrane-associated state. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Apr 14;160(1):340–345. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91661-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K. S., Heydrick S., Kurowski T., Ruderman N. B. Diacylglycerol-protein kinase C signalling in skeletal muscle: a possible link to insulin resistance. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1991;104:206–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherqui G., Reynet C., Caron M., Melin B., Wicek D., Clauser E., Capeau J., Picard J. Insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 control insulin stimulation of myristoyl-diacylglycerol generation and subsequent activation of glucose transport. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21254–21261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. R., Hernandez H., Kuo J. Y., Farese R. V. Insulin increases the synthesis of phospholipid and diacylglycerol and protein kinase C activity in rat hepatocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Feb 1;276(2):486–494. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90749-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. R., Ishizuka T., Watson J. E., Standaert M. L., Nair G., Farese R. V. Protein kinase C activation patterns are determined by methodological variations. Studies of insulin action in BC3H-1 myocytes and rat adipose tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 13;1054(1):95–102. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90210-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. R., Konda T. S., Standaert M. L., Davis J. S., Pollet R. J., Farese R. V. Insulin increases membrane and cytosolic protein kinase C activity in BC3H-1 myocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3633–3639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. R., Watson J. E., Acevedo-Duncan M., Pollet R. J., Standaert M. L., Farese R. V. Retention of specific protein kinase C isozymes following chronic phorbol ester treatment in BC3H-1 myocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 May 30;161(1):327–334. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91600-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Laviada I., Larrodera P., Nieto J. L., Cornet M. E., Diaz-Meco M. T., Sanchez M. J., Guddal P. H., Johansen T., Haro A., Moscat J. Mechanism of inhibition of adenylate cyclase by phospholipase C-catalyzed hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine. Involvement of a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1170–1176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draznin B., Leitner J. W., Sussman K. E., Sherman N. A. Insulin and glucose modulate protein kinase C activity in rat adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):570–575. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80880-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan J. J., Saltis J., Wek S. A., Simpson I. A., Londos C. Insulin, oxytocin, and vasopressin stimulate protein kinase C activity in adipocyte plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1052–1056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Davis J. S., Barnes D. E., Standaert M. L., Babischkin J. S., Hock R., Rosic N. K., Pollet R. J. The de novo phospholipid effect of insulin is associated with increases in diacylglycerol, but not inositol phosphates or cytosolic Ca2+. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 15;231(2):269–278. doi: 10.1042/bj2310269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Davis J. S., Barnes D. E., Standaert M. L., Babischkin J. S., Hock R., Rosic N. K., Pollet R. J. The de novo phospholipid effect of insulin is associated with increases in diacylglycerol, but not inositol phosphates or cytosolic Ca2+. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 15;231(2):269–278. doi: 10.1042/bj2310269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Kuo J. Y., Babischkin J. S., Davis J. S. Insulin provokes a transient activation of phospholipase C in the rat epididymal fat pad. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8589–8592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Sabir M. A., Larson R. E., Trudeau W., 3rd Further observations on the increases in inositide phospholipids after stimulation by ACTH, cAMP and insulin, and on discrepancies in phosphatidylinositol mass and 32PO4-labeling during inhibition of hormonal effects by cycloheximide. Cell Calcium. 1983 Jul;4(3):195–218. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(83)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Standaert M. L., Francois A. J., Ways K., Arnold T. P., Hernandez H., Cooper D. R. Effects of insulin and phorbol esters on subcellular distribution of protein kinase C isoforms in rat adipocytes. Biochem J. 1992 Nov 15;288(Pt 1):319–323. doi: 10.1042/bj2880319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves C. B., McDonald J. M. Insulin and phorbol ester stimulate phosphorylation of a 40-kDa protein in adipocyte plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11286–11292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidenreich K. A., Toledo S. P., Brunton L. L., Watson M. J., Daniel-Issakani S., Strulovici B. Insulin stimulates the activity of a novel protein kinase C, PKC-epsilon, in cultured fetal chick neurons. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15076–15082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J. M., Ishizuka T., Farese R. V. Interrelated effects of insulin and glucose on diacylglycerol-protein kinase-C signalling in rat adipocytes and solei muscle in vitro and in vivo in diabetic rats. Endocrinology. 1991 Jun;128(6):2937–2948. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-6-2937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman J. M., Standaert M. L., Nair G. P., Farese R. V. Differential effects of pertussis toxin on insulin-stimulated phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis and glycerolipid synthesis de novo. Studies in BC3H-1 myocytes and rat adipocytes. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 2;30(13):3315–3322. doi: 10.1021/bi00227a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- House C., Kemp B. E. Protein kinase C contains a pseudosubstrate prototope in its regulatory domain. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1726–1728. doi: 10.1126/science.3686012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuka T., Cooper D. R., Farese R. V. Insulin stimulates the translocation of protein kinase C in rat adipocytes. FEBS Lett. 1989 Nov 6;257(2):337–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81565-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuka T., Cooper D. R., Hernandez H., Buckley D., Standaert M., Farese R. V. Effects of insulin on diacylglycerol-protein kinase C signaling in rat diaphragm and soleus muscles and relationship to glucose transport. Diabetes. 1990 Feb;39(2):181–190. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.2.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manenti S., Sorokine O., Van Dorsselaer A., Taniguchi H. Affinity purification and characterization of myristoylated alanine-rich protein kinase C substrate (MARCKS) from bovine brain. Comparison of the cytoplasmic and the membrane-bound forms. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22310–22315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messina J. L., Standaert M. L., Ishizuka T., Weinstock R. S., Farese R. V. Role of protein kinase C in insulin's regulation of c-fos transcription. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9223–9228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochly-Rosen D., Khaner H., Lopez J., Smith B. L. Intracellular receptors for activated protein kinase C. Identification of a binding site for the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):14866–14868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley S. J., Traugh J. A. Differential stimulation of phosphorylation of initiation factors eIF-4F, eIF-4B, eIF-3, and ribosomal protein S6 by insulin and phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10611–10616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouimet C. C., Wang J. K., Walaas S. I., Albert K. A., Greengard P. Localization of the MARCKS (87 kDa) protein, a major specific substrate for protein kinase C, in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1990 May;10(5):1683–1698. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-05-01683.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J., Loomis C. R., Bishop W. R., Stein R., Niedel J. E., Bell R. M. Quantitative measurement of sn-1,2-diacylglycerols present in platelets, hepatocytes, and ras- and sis-transformed normal rat kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8597–8600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowell M. O., Boggs K. P., Robinson K. A., Dutton S. L., Buse M. G. Effects of insulin and phospholipase C in control and denervated rat skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1991 Feb;260(2 Pt 1):E247–E256. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1991.260.2.E247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spach D. H., Nemenoff R. A., Blackshear P. J. Protein phosphorylation and protein kinase activities in BC3H-1 myocytes. Differences between the effects of insulin and phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12750–12753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standaert M. L., Sasse J., Cooper D. R., Farese R. V. Protein kinase C(19-31) pseudosubstrate inhibition of insulin action in rat adipocytes. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 22;282(1):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80463-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelen M., Rosen A., Nairn A. C., Aderem A. Regulation by phosphorylation of reversible association of a myristoylated protein kinase C substrate with the plasma membrane. Nature. 1991 May 23;351(6324):320–322. doi: 10.1038/351320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vila M. C., Cooper D. R., Davis J. S., Standaert M. L., Farese R. V. Studies of in vivo phosphorylated proteins in BC3H-1 myocytes suggest that protein kinase C is involved in insulin action. FEBS Lett. 1989 Feb 13;244(1):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81187-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walaas S. I., Horn R. S., Adler A., Albert K. A., Walaas O. Insulin increases membrane protein kinase C activity in rat diaphragm. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 17;220(2):311–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80837-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu B., Standaert M., Arnold T., Hernandez H., Watson J., Ways K., Cooper D. R., Farese R. V. Effects of insulin on diacylglycerol/protein kinase-C signalling and glucose transport in rat skeletal muscles in vivo and in vitro. Endocrinology. 1992 Jun;130(6):3345–3355. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.6.1597146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]