Abstract
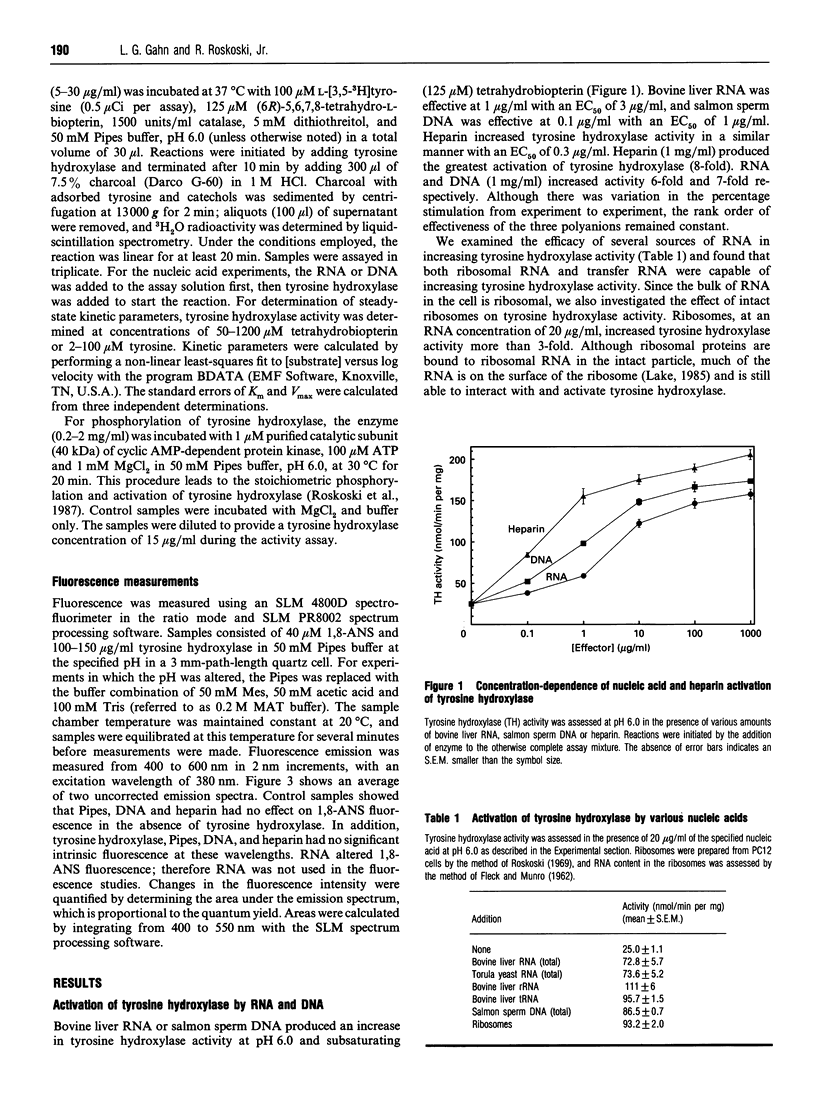
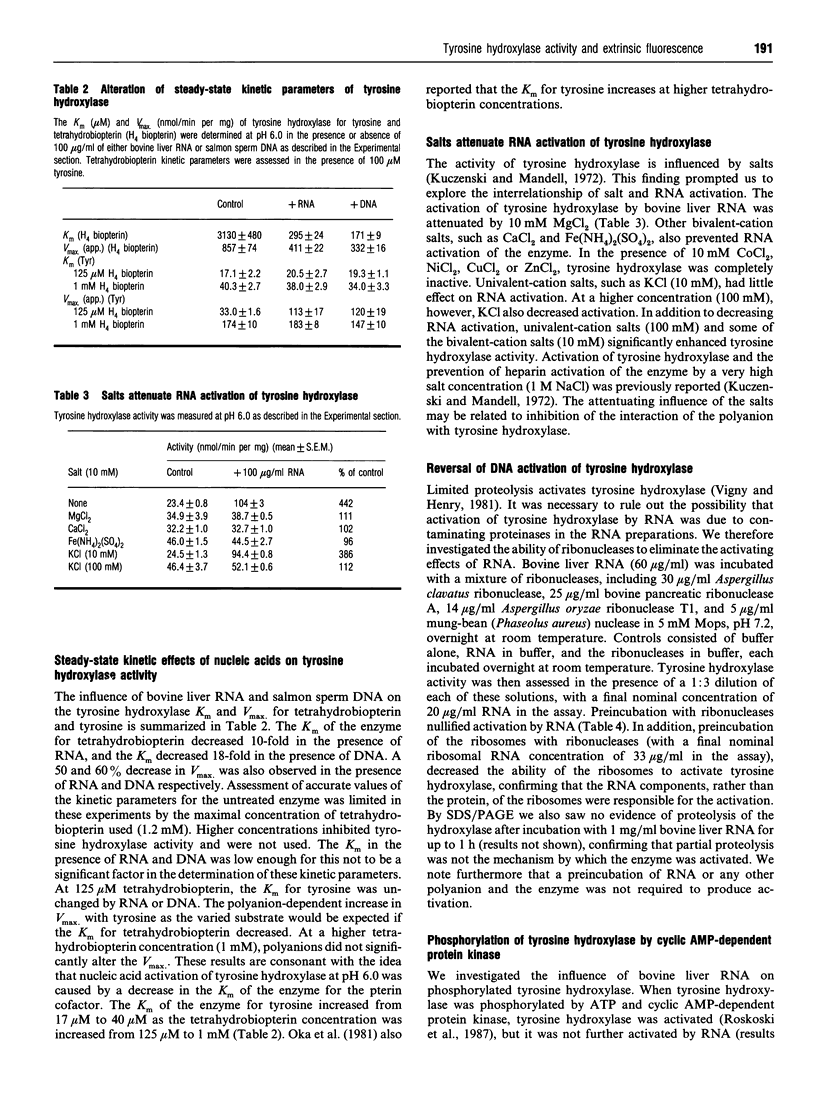
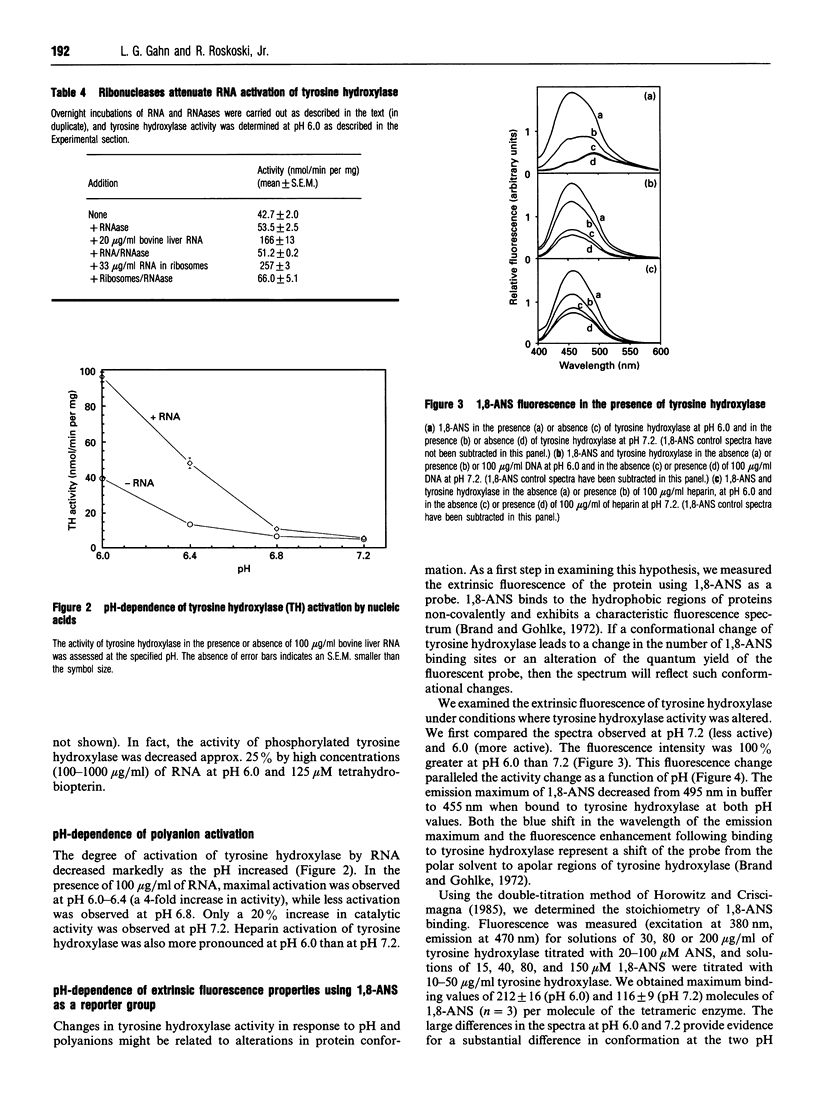
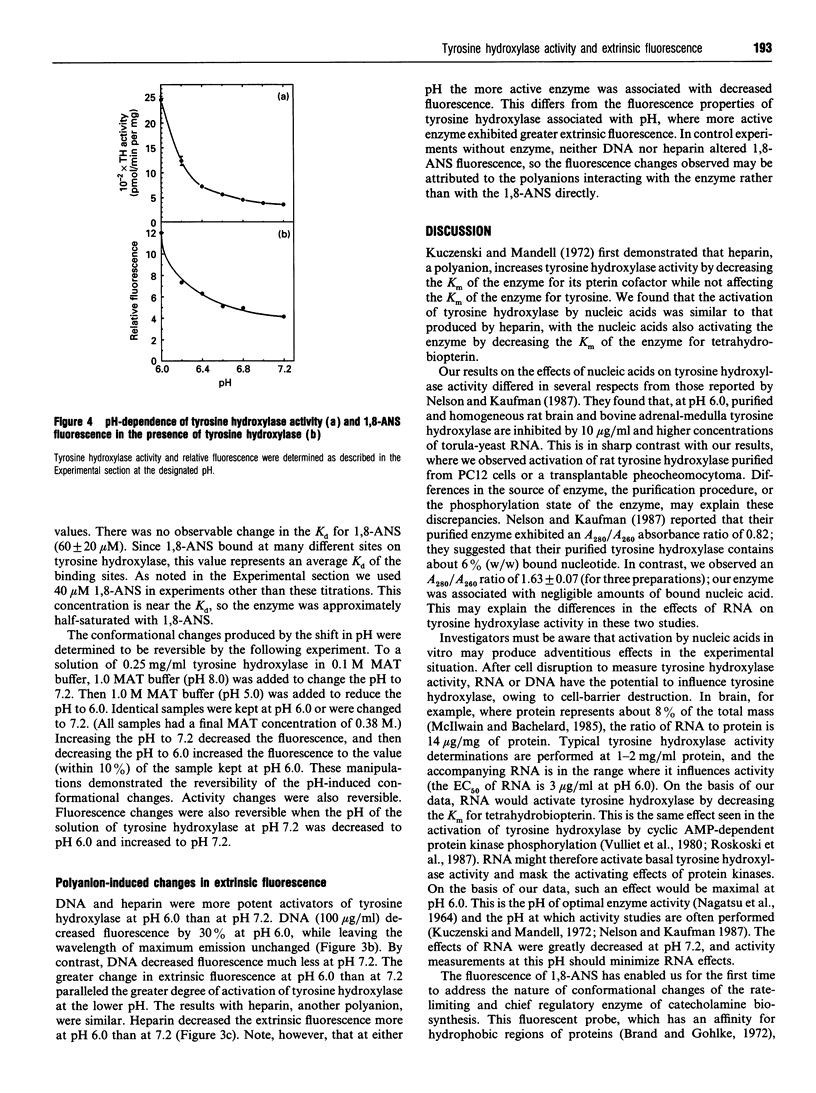
The activity of tyrosine hydroxylase in vitro is affected by many factors, including pH, phosphorylation by several protein kinases, and polyanions. We investigated the activation of tyrosine hydroxylase by RNA or DNA (polyanions), using purified rat PC12 cell enzyme. RNA and DNA each increased tyrosine hydroxylase activity in the presence of subsaturating (125 microM) tetrahydrobiopterin at pH 6. RNA increased enzyme activity up to 6-fold with an EC50 of 3 micrograms/ml. RNA and DNA each increased tyrosine hydroxylase activity by decreasing the Km of the enzyme for tetrahydrobiopterin from 3 mM to 295 microM in the presence of 100 micrograms/ml RNA or 171 microM in the presence of 100 micrograms/ml DNA. We used the apolar fluorescent probe 8-anilino-1-naphthalenesulphonic acid (1,8-ANS) as a reporter group to provide the first evidence for changes in conformation related to changes in activity. At pH 6.0, 1,8-ANS bound to tyrosine hydroxylase and exhibited a characteristic fluorescence spectrum. At pH 7.2, both enzyme activity and fluorescence decreased. DNA or heparin (another polyanion) activated tyrosine hydroxylase and decreased fluorescence of the reporter group 30% at pH 6.0. This decrease suggests that these polyanions altered the conformation of tyrosine hydroxylase. The activating effects of polyanions were diminished at physiological pH (6.8-7.2) or in the presence of bivalent-cation salts (10 mM) or univalentcation salts (100 mM). These results suggest that polyanions play a minimal role, if any, in the physiological regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase activity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson K. K., Vassort C., Brennan B. A., Que L., Jr, Haavik J., Flatmark T., Gros F., Thibault J. Purification and characterization of the blue-green rat phaeochromocytoma (PC12) tyrosine hydroxylase with a dopamine-Fe(III) complex. Reversal of the endogenous feedback inhibition by phosphorylation of serine-40. Biochem J. 1992 Jun 15;284(Pt 3):687–695. doi: 10.1042/bj2840687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand L., Gohlke J. R. Fluorescence probes for structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:843–868. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.004211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLECK A., MUNRO H. N. The precision of ultraviolet absorption measurements in the Schmidt-Thannhauser procedure for nucleic acid estimation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 May 14;55:571–583. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90836-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick P. F. The pH dependence of binding of inhibitors to bovine adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16058–16062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukami M. H., Haavik J., Flatmark T. Phenylalanine as substrate for tyrosine hydroxylase in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochem J. 1990 Jun 1;268(2):525–528. doi: 10.1042/bj2680525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahn L. G., Roskoski R., Jr Tyrosine hydroxylase purification from rat PC12 cells. Protein Expr Purif. 1991 Feb;2(1):10–14. doi: 10.1016/1046-5928(91)90002-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haavik J., Martínez A., Flatmark T. pH-dependent release of catecholamines from tyrosine hydroxylase and the effect of phosphorylation of Ser-40. FEBS Lett. 1990 Mar 26;262(2):363–365. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80230-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl F. T., Roskoski R., Jr Adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate protein kinase from bovine brain: inactivation of the catalytic subunit and holoenzyme by 7-chloro-4-nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 12;21(21):5175–5183. doi: 10.1021/bi00264a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz P. M., Criscimagna N. L. Differential binding of the fluorescent probe 8-anilinonaphthalene-2-sulfonic acid to rhodanese catalytic intermediates. Biochemistry. 1985 May 21;24(11):2587–2593. doi: 10.1021/bi00332a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz I. R., Yamauchi T., Kaufman S. Activation of tyrosine hydroxylase by polyanions and salts. An electrostatic effect. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 11;429(1):84–95. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuczenski R. T., Mandell A. J. Allosteric activation of hypothalamic tyrosine hydroxylase by ions and sulphated mucopolysaccharides. J Neurochem. 1972 Jan;19(1):131–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVITT M., SPECTOR S., SJOERDSMA A., UDENFRIEND S. ELUCIDATION OF THE RATE-LIMITING STEP IN NOREPINEPHRINE BIOSYNTHESIS IN THE PERFUSED GUINEA-PIG HEART. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Apr;148:1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. A. Evolving ribosome structure: domains in archaebacteria, eubacteria, eocytes and eukaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:507–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.002451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd T., Kaufman S. The stimulation of partially purified bovine caudate tyrosine hydroxylase by phosphatidyl-L-serine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Aug 19;59(4):1262–1270. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90450-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markey K. A., Kondo H., Shenkman L., Goldstein M. Purification and characterization of tyrosine hydroxylase from a clonal pheochromocytoma cell line. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Jan;17(1):79–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGATSU T., LEVITT M., UDENFRIEND S. TYROSINE HYDROXYLASE. THE INITIAL STEP IN NOREPINEPHRINE BIOSYNTHESIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:2910–2917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson T. J., Kaufman S. Interaction of tyrosine hydroxylase with ribonucleic acid and purification with DNA-cellulose or poly(A)-sepharose affinity chromatography. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Aug 15;257(1):69–84. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90544-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka K., Kato T., Sugimoto T., Matsuura S., Nagatsu T. Kinetic properties of tyrosine hydroxylase with natural tetrahydrobiopterin as cofactor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 15;661(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90082-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhard J. F., Jr, Smith G. K., Nichol C. A. A rapid and sensitive assay for tyrosine-3-monooxygenase based upon the release of 3H2O and adsorption of [3H]-tyrosine by charcoal. Life Sci. 1986 Dec 8;39(23):2185–2189. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90395-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro P., Pigeon D., Kaufman S. The hydroxylation of phenylalanine and tyrosine by tyrosine hydroxylase from cultured pheochromocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):16207–16211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richtand N. M., Inagami T., Misono K., Kuczenski R. Purification and characterization of rat striatal tyrosine hydroxylase. Comparison of the activation by cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation and by other effectors. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8465–8473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roskoski R., Jr Role of divalent cations on the association of rat liver ribosomal subunits. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):561–566. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roskoski R., Jr, Vulliet P. R., Glass D. B. Phosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase by cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase. J Neurochem. 1987 Mar;48(3):840–845. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb05593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saucier A. C., Mariotti S., Anderson S. A., Purich D. L. Ciliary dynein conformational changes as evidenced by the extrinsic fluorescent probe 8-anilino-1-naphthalenesulfonate. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 17;24(26):7581–7585. doi: 10.1021/bi00347a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. The interaction of a naphthalene dye with apomyoglobin and apohemoglobin. A fluorescent probe of non-polar binding sites. J Mol Biol. 1965 Sep;13(2):482–495. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80111-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigny A., Henry J. P. Bovine adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase: comparative study of native and proteolyzed enzyme, and their interaction with anions. J Neurochem. 1981 Feb;36(2):483–489. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb01618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vulliet P. R., Langan T. A., Weiner N. Tyrosine hydroxylase: a substrate of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):92–96. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


