Abstract
Evidence for the modulation of the P2z-purinoceptor for extracellular ATP in dissociated rat parotid cells is presented in studies using compounds that inhibit protein kinases. Preincubation of acinar cells with the protein kinase catalytic-site inhibitors K-252a and staurosporine, as well as with the regulatory-domain inhibitor sphingosine, specifically potentiates the elevation in cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) mediated by extracellular ATP, but has no effect on the [Ca2+]i elevation mediated by muscarinic receptors through phospholipase C activation. Phorbol dibutyrate (PDBu), which activates protein kinase C (PKC), has no modulatory effect on ATP-mediated [Ca2+]i elevation. Further, pretreatment with PDBu does not reverse or block the effects of K-252a or sphinogosine, arguing against the involvement of PKC. Other pharmacological manipulations indicate that neither calmodulin-dependent nor cyclic-AMP-dependent kinases are involved. Neither the peak intracellular Ca2+ mobilization nor the sustained Ca2+ entry in response to carbachol or to a Ca2+ ionophore (4-bromo-A23187) is altered by the kinase inhibitors that potentiate the [Ca2+]i response to ATP, indicating that effects on the ATP response are not due to non-specific permeability changes, nor to decreased Ca2+ removal from the cytosol. ATP-mediated influx of Mn2+ as well as ATP-induced membrane depolarization are potentiated in cells preincubated with K-252a, directly demonstrating that cation influx is enhanced through a P2z-specific route. These results show that P2z responses (or purinoceptors) can be modulated and suggest that phosphorylation events are involved.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bean B. P. ATP-activated channels in rat and bullfrog sensory neurons: concentration dependence and kinetics. J Neurosci. 1990 Jan;10(1):1–10. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-01-00001.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B., Byrne N. G., Large W. A. Action of externally applied adenosine triphosphate on single smooth muscle cells dispersed from rabbit ear artery. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:473–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. D., Tsien R. W. A novel receptor-operated Ca2+-permeable channel activated by ATP in smooth muscle. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):275–278. doi: 10.1038/328275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. P., Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Rat mast cells permeabilized with ATP secrete histamine in response to calcium ions buffered in the micromolar range. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:335–345. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Strasser R. H., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase: identification of a novel protein kinase that phosphorylates the agonist-occupied form of the receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2797–2801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charest R., Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Characterization of responses of isolated rat hepatocytes to ATP and ADP. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15789–15794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. The ATP4- receptor of rat mast cells. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 15;188(3):789–798. doi: 10.1042/bj1880789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlquist R., Diamant B. Interaction of ATP and calcium on the rat mast cell: effect on histamine release. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1974 May;34(5):368–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1974.tb03533.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Togni P., Cabrini G., Di Virgilio F. Cyclic AMP inhibition of fMet-Leu-Phe-dependent metabolic responses in human neutrophils is not due to its effects on cytosolic Ca2+. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 1;224(2):629–635. doi: 10.1042/bj2240629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond A. H. Bidirectional control of cytosolic free calcium by thyrotropin-releasing hormone in pituitary cells. 1985 Jun 27-Jul 3Nature. 315(6022):752–755. doi: 10.1038/315752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. J., Derkach V., Surprenant A. ATP mediates fast synaptic transmission in mammalian neurons. Nature. 1992 Jun 11;357(6378):503–505. doi: 10.1038/357503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faucher M., Gironès N., Hannun Y. A., Bell R. M., Davis R. J. Regulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor phosphorylation state by sphingosine in A431 human epidermoid carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5319–5327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friel D. D., Bean B. P. Two ATP-activated conductances in bullfrog atrial cells. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Jan;91(1):1–27. doi: 10.1085/jgp.91.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda T., Ogurusu T., Furukawa K., Shigekawa M. Protein kinase C-dependent phosphorylation of sarcolemmal Ca2(+)-ATPase isolated from bovine aortic smooth muscle. J Biochem. 1990 Oct;108(4):629–634. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Tawada Y., Shigekawa M. Protein kinase C activation stimulates plasma membrane Ca2+ pump in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4844–4849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L. Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):309–319. doi: 10.1042/bj2330309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S., Di Virgilio F., Steinberg T. H., Silverstein S. C. Extracellular nucleotides mediate Ca2+ fluxes in J774 macrophages by two distinct mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10337–10343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallam T. J., Jacob R., Merritt J. E. Influx of bivalent cations can be independent of receptor stimulation in human endothelial cells. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 1;259(1):125–129. doi: 10.1042/bj2590125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Bell R. M. Regulation of protein kinase C by sphingosine and lysosphingolipids. Clin Chim Acta. 1989 Dec 15;185(3):333–345. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(89)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Loomis C. R., Merrill A. H., Jr, Bell R. M. Sphingosine inhibition of protein kinase C activity and of phorbol dibutyrate binding in vitro and in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12604–12609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson A. B., Schulman H. Sphingosine inhibits calmodulin-dependent enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15241–15244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanagasuntheram P., Randle P. J. Calcium metabolism and amylase release in rat parotid acinar cells. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 15;160(3):547–564. doi: 10.1042/bj1600547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
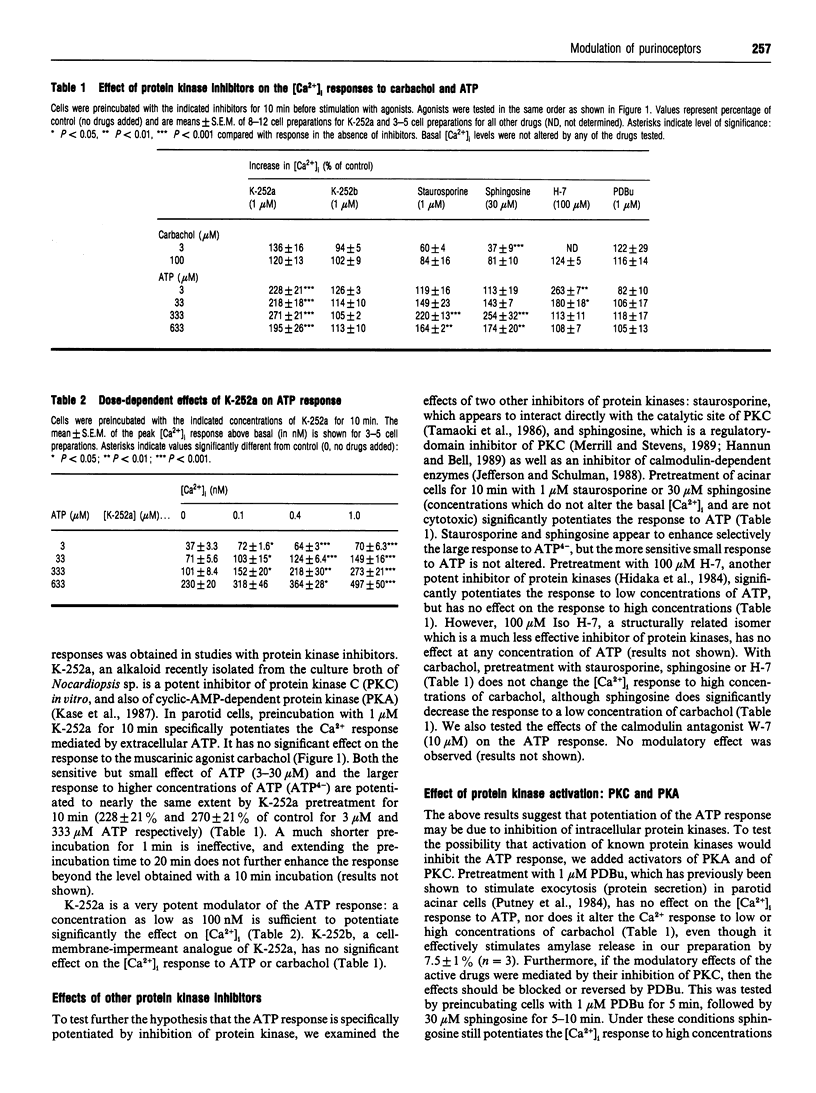
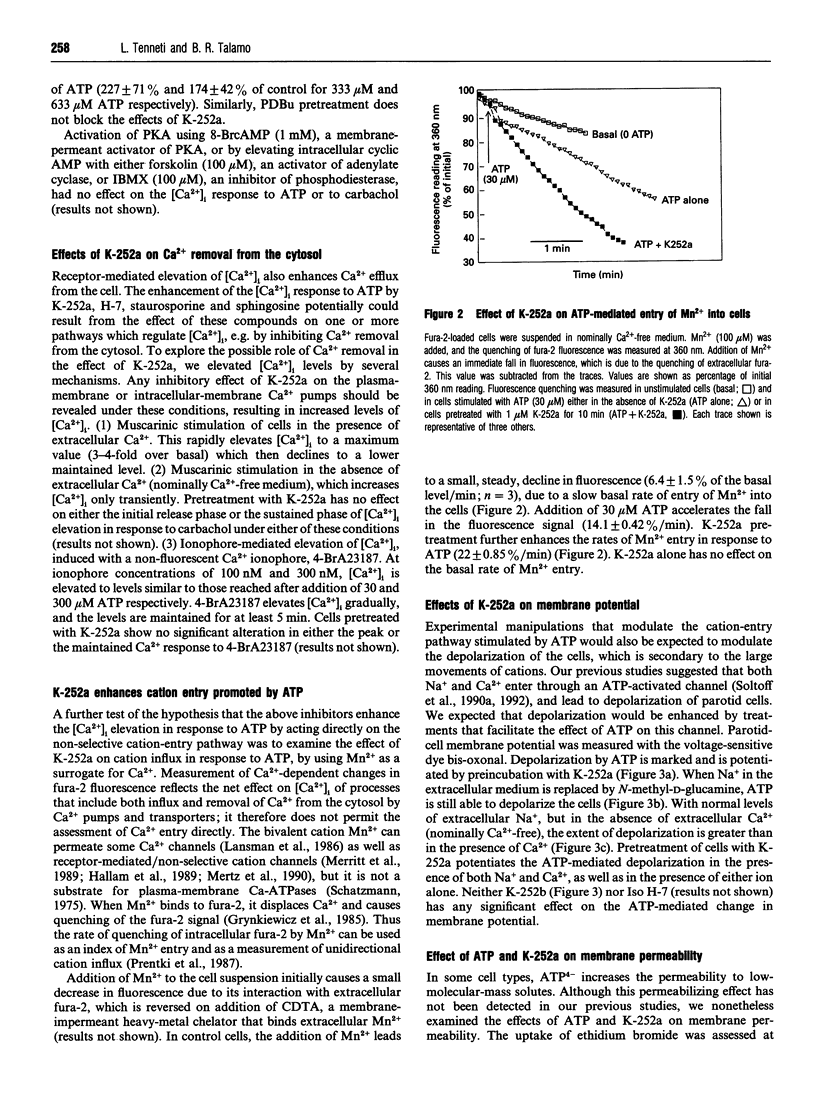
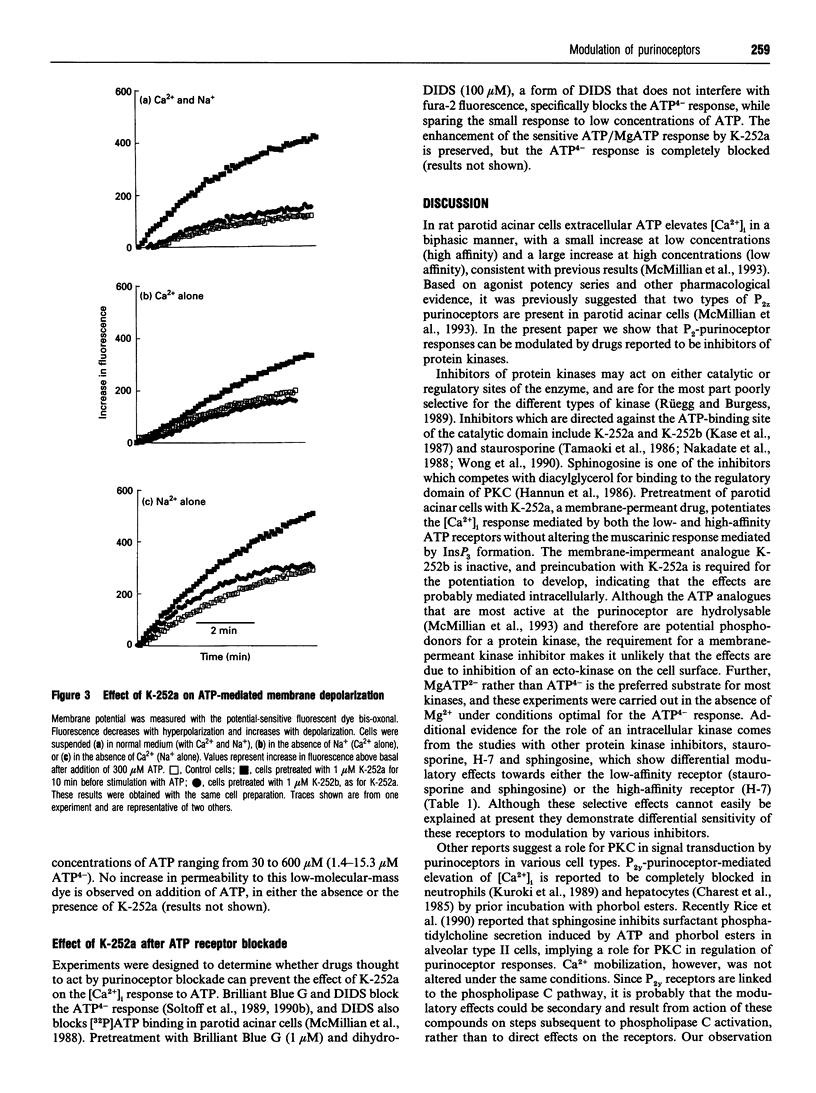
- Kase H., Iwahashi K., Nakanishi S., Matsuda Y., Yamada K., Takahashi M., Murakata C., Sato A., Kaneko M. K-252 compounds, novel and potent inhibitors of protein kinase C and cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jan 30;142(2):436–440. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90293-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishtal O. A., Marchenko S. M., Pidoplichko V. I. Receptor for ATP in the membrane of mammalian sensory neurones. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Jan 31;35(1):41–45. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90524-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki M., Minakami S. Extracellular ATP triggers superoxide production in human neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jul 14;162(1):377–380. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki M., Takeshige K., Minakami S. ATP-induced calcium mobilization in human neutrophils. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jun 15;1012(1):103–106. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lansman J. B., Hess P., Tsien R. W. Blockade of current through single calcium channels by Cd2+, Mg2+, and Ca2+. Voltage and concentration dependence of calcium entry into the pore. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Sep;88(3):321–347. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.3.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillian M. K., Soltoff S. P., Cantley L. C., Rudel R., Talamo B. R. Two distinct cytosolic calcium responses to extracellular ATP in rat parotid acinar cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;108(2):453–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillian M. K., Soltoff S. P., Cantley L. C., Talamo B. R. Extracellular ATP elevates intracellular free calcium in rat parotid acinar cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 16;149(2):523–530. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90399-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillian M. K., Soltoff S. P., Lechleiter J. D., Cantley L. C., Talamo B. R. Extracellular ATP increases free cytosolic calcium in rat parotid acinar cells. Differences from phospholipase C-linked receptor agonists. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):291–300. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillian M. K., Soltoff S. P., Talamo B. R. Rapid desensitization of substance P- but not carbachol-induced increases in inositol trisphosphate and intracellular Ca++ in rat parotid acinar cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 13;148(3):1017–1024. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80233-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill A. H., Jr, Stevens V. L. Modulation of protein kinase C and diverse cell functions by sphingosine--a pharmacologically interesting compound linking sphingolipids and signal transduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 9;1010(2):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Jacob R., Hallam T. J. Use of manganese to discriminate between calcium influx and mobilization from internal stores in stimulated human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1522–1527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz L. M., Baum B. J., Ambudkar I. S. Refill status of the agonist-sensitive Ca2+ pool regulates Mn2+ influx into parotid acini. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15010–15014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakadate T., Jeng A. Y., Blumberg P. M. Comparison of protein kinase C functional assays to clarify mechanisms of inhibitor action. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Apr 15;37(8):1541–1545. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa K., Matsuki N. Adenosine triphosphate-activated inward current in isolated smooth muscle cells from rat vas deferens. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Aug;409(6):644–646. doi: 10.1007/BF00584668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Tokumitsu Y., Kondo Y., Ui M. P2-purinergic receptors are coupled to two signal transduction systems leading to inhibition of cAMP generation and to production of inositol trisphosphate in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13483–13490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poggioli J., Putney J. W., Jr Net calcium fluxes in rat parotid acinar cells: evidence for a hormone-sensitive calcium pool in or near the plasma membrane. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Jan;392(3):239–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00584303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Glennon M. C., Geschwind J. F., Matschinsky F. M., Corkey B. E. Cyclic AMP raises cytosolic Ca2+ and promotes Ca2+ influx in a clonal pancreatic beta-cell line (HIT T-15). FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 10;220(1):103–107. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80884-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney J. W., Jr, McKinney J. S., Aub D. L., Leslie B. A. Phorbol ester-induced protein secretion in rat parotid gland. Relationship to the role of inositol lipid breakdown and protein kinase C activation in stimulus-secretion coupling. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;26(2):261–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice W. R., Dorn C. C., Singleton F. M. P2-purinoceptor regulation of surfactant phosphatidylcholine secretion. Relative roles of calcium and protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1990 Mar 1;266(2):407–413. doi: 10.1042/bj2660407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink T. J., Sage S. O. Stimulated calcium efflux from fura-2-loaded human platelets. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;393:513–524. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Heppel L. A. Reciprocal control of membrane permeability of transformed cultures of mouse cell lines by external and internal ATP. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):708–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüegg U. T., Burgess G. M. Staurosporine, K-252 and UCN-01: potent but nonspecific inhibitors of protein kinases. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Jun;10(6):218–220. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Gallacher D. V. Extracellular ATP activates receptor-operated cation channels in mouse lacrimal acinar cells to promote calcium influx in the absence of phosphoinositide metabolism. FEBS Lett. 1990 May 7;264(1):130–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80782-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smallwood J. I., Gügi B., Rasmussen H. Regulation of erythrocyte Ca2+ pump activity by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2195–2202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltoff S. P., McMillian M. K., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Cantley L. C., Talamo B. R. Effects of extracellular ATP on ion transport systems and [Ca2+]i in rat parotid acinar cells. Comparison with the muscarinic agonist carbachol. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Feb;95(2):319–346. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltoff S. P., McMillian M. K., Lechleiter J. D., Cantley L. C., Talamo B. R. Elevation of [Ca2+]i and the activation of ion channels and fluxes by extracellular ATP and phospholipase C-linked agonists in rat parotid acinar cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;603:76–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb37663.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltoff S. P., McMillian M. K., Talamo B. R. ATP activates a cation-permeable pathway in rat parotid acinar cells. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 1):C934–C940. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.4.C934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltoff S. P., McMillian M. K., Talamo B. R. Coomassie Brilliant Blue G is a more potent antagonist of P2 purinergic responses than Reactive Blue 2 (Cibacron Blue 3GA) in rat parotid acinar cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 29;165(3):1279–1285. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92741-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg T. H., Newman A. S., Swanson J. A., Silverstein S. C. ATP4- permeabilizes the plasma membrane of mouse macrophages to fluorescent dyes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8884–8888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutts M. J., Chinet T. C., Mason S. J., Fullton J. M., Clarke L. L., Boucher R. C. Regulation of Cl- channels in normal and cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells by extracellular ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1621–1625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nomoto H., Takahashi I., Kato Y., Morimoto M., Tomita F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatham P. E., Cusack N. J., Gomperts B. D. Characterisation of the ATP4- receptor that mediates permeabilisation of rat mast cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Feb 16;147(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90628-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatham P. E., Lindau M. ATP-induced pore formation in the plasma membrane of rat peritoneal mast cells. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Mar;95(3):459–476. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.3.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K. K., Wright L. C., Machan C. L., Allen B. G., Conigrave A. D., Roufogalis B. D. Protein kinase C phosphorylates the carboxyl terminus of the plasma membrane Ca(2+)-ATPase from human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9078–9085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Cunningham T. W., McCulloch K. K., Johnson K. J. Regulatory effects of adenosine and adenine nucleotides on oxygen radical responses of neutrophils. Lab Invest. 1988 Apr;58(4):438–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilden U., Hall S. W., Kühn H. Phosphodiesterase activation by photoexcited rhodopsin is quenched when rhodopsin is phosphorylated and binds the intrinsic 48-kDa protein of rod outer segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1174–1178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winicov I., Gershengorn M. C. Sphingosine inhibits thyrotropin-releasing hormone binding to pituitary cells by a mechanism independent of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12179–12182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. C., Remold-O'Donnell E., Vercelli D., Sancho J., Terhorst C., Rosen F., Geha R., Chatila T. Signal transduction via leukocyte antigen CD43 (sialophorin). Feedback regulation by protein kinase C. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1455–1460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



