Abstract
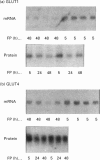
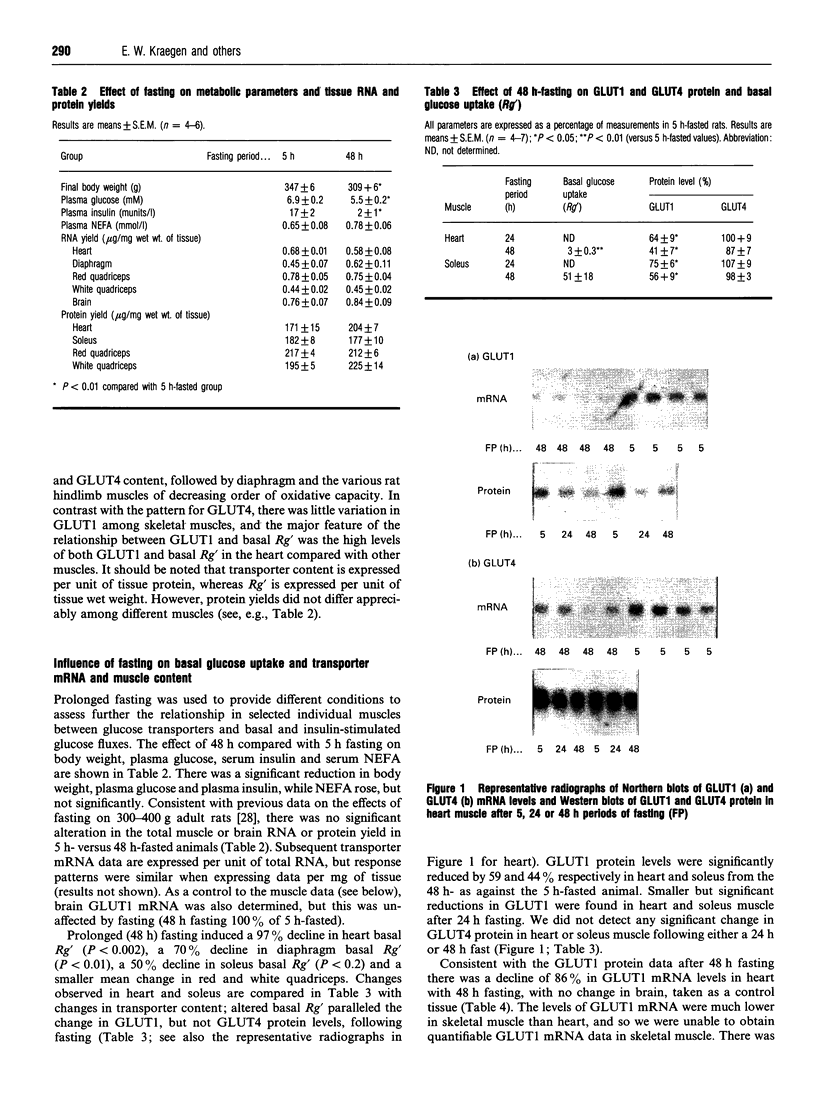
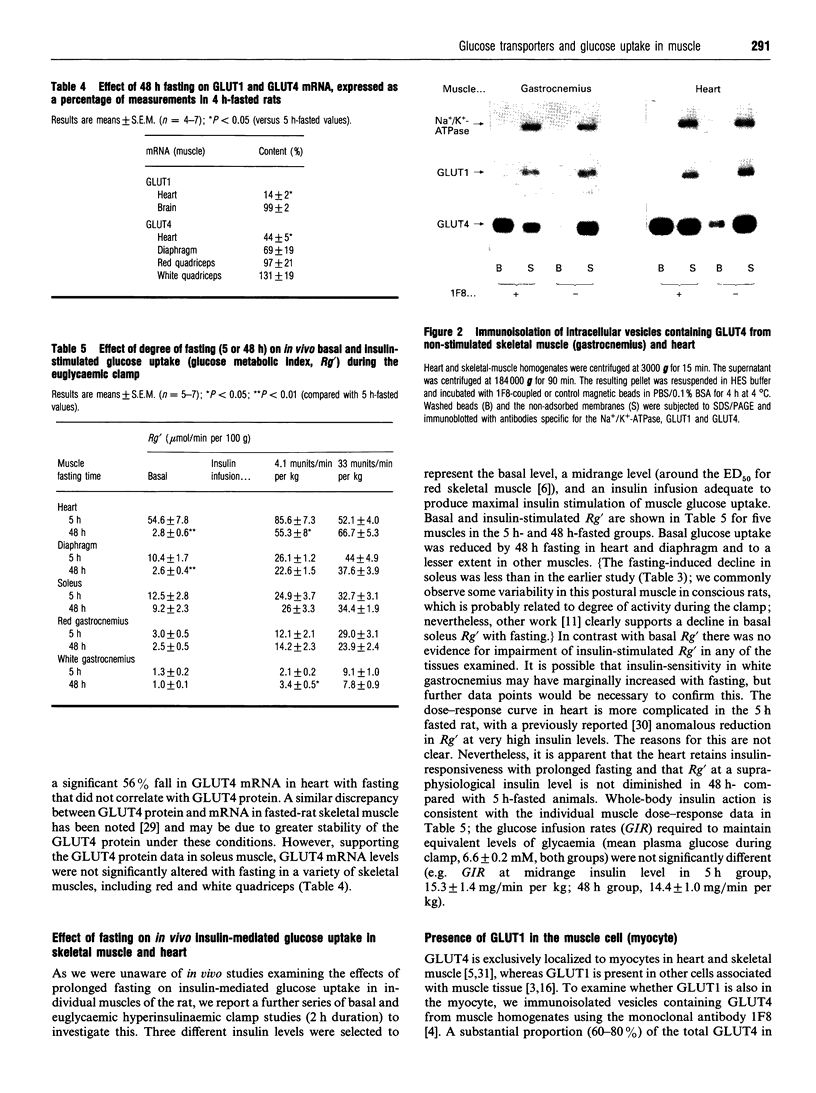
Our aim was to study glucose transporters GLUT1 and GLUT4 in relation to in vivo glucose uptake in rat cardiac and skeletal muscle. The levels of both transporters were of a similar order of magnitude in whole muscle tissue (GLUT1/GLUT4 ratio varied from 0.1 to 0.6), suggesting that both may have an important physiological role in regulating muscle glucose metabolism. GLUT4 correlated very strongly (r2 = 0.97) with maximal insulin-stimulated glucose uptake (Rg' max., estimated using the glucose clamp plus 2-deoxy[3H]glucose bolus technique) in six skeletal muscles and heart. A distinct difference in regulation of the two transporters was evident in heart: in 5 h-fasted rats, basal glucose uptake and GLUT1 levels in heart were very high and both were reduced, by 90 and 60% respectively, by 48 h fasting. However, in heart (and in red skeletal muscle), neither GLUT4 levels nor Rg' max. were reduced by 48 h fasting. GLUT1 was shown to be specifically expressed in cardiac myocytes, because intracellular vesicles enriched in GLUT4 contained significant levels of GLUT1. In conclusion, the high association of muscle GLUT4 content with insulin responsiveness in different muscles, and the preservation of both with fasting, supports a predominant role of GLUT4 in insulin-mediated glucose uptake. GLUT1 may play an important role in mediating cardiac muscle glucose uptake in the basal metabolic state. Marked changes in GLUT1 expression with alterations in the metabolic state, such as prolonged fasting, may play an important role in cardiac glucose metabolism.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourey R. E., Koranyi L., James D. E., Mueckler M., Permutt M. A. Effects of altered glucose homeostasis on glucose transporter expression in skeletal muscle of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1990 Aug;86(2):542–547. doi: 10.1172/JCI114742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderhead D. M., Kitagawa K., Lienhard G. E., Gould G. W. Translocation of the brain-type glucose transporter largely accounts for insulin stimulation of glucose transport in BC3H-1 myocytes. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 1;269(3):597–601. doi: 10.1042/bj2690597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camps M., Castelló A., Muñoz P., Monfar M., Testar X., Palacín M., Zorzano A. Effect of diabetes and fasting on GLUT-4 (muscle/fat) glucose-transporter expression in insulin-sensitive tissues. Heterogeneous response in heart, red and white muscle. Biochem J. 1992 Mar 15;282(Pt 3):765–772. doi: 10.1042/bj2820765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron M. J., Kahn B. B. Divergent molecular mechanisms for insulin-resistant glucose transport in muscle and adipose cells in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):7994–8000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douen A. G., Ramlal T., Rastogi S., Bilan P. J., Cartee G. D., Vranic M., Holloszy J. O., Klip A. Exercise induces recruitment of the "insulin-responsive glucose transporter". Evidence for distinct intracellular insulin- and exercise-recruitable transporter pools in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13427–13430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M. N., Ruderman N. B. Starvation in the rat. I. Effect of age and obesity on organ weights, RNA, DNA, and protein. Am J Physiol. 1980 Oct;239(4):E269–E276. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.239.4.E269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenberg J., Howell K. E. Immuno-isolation of vesicles using antigenic sites either located on the cytoplasmic or the exoplasmic domain of an implanted viral protein. A quantitative analysis. Eur J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;38(2):312–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handberg A., Kayser L., Høyer P. E., Vinten J. A substantial part of GLUT-1 in crude membranes from muscle originates from perineurial sheaths. Am J Physiol. 1992 May;262(5 Pt 1):E721–E727. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1992.262.5.E721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holness M. J., Howard R. M., Sugden M. C. Glucose utilization and disposition by skeletal muscle during unrestricted feeding. Biochem J. 1992 Sep 1;286(Pt 2):395–398. doi: 10.1042/bj2860395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holness M. J., Sugden M. C. Glucose utilization in heart, diaphragm and skeletal muscle during the fed-to-starved transition. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 15;270(1):245–249. doi: 10.1042/bj2700245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issad T., Pénicaud L., Ferré P., Kandé J., Baudon M. A., Girard J. Effects of fasting on tissue glucose utilization in conscious resting rats. Major glucose-sparing effect in working muscles. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 15;246(1):241–244. doi: 10.1042/bj2460241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Burleigh K. M., Chisholm D. J., Kraegen E. W. In vivo dose response curves of insulin action in heart: anomalous effects at high insulin doses. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1985 Oct;17(10):981–985. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(85)80078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Jenkins A. B., Kraegen E. W. Heterogeneity of insulin action in individual muscles in vivo: euglycemic clamp studies in rats. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):E567–E574. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.5.E567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Kraegen E. W., Chisholm D. J. Effects of exercise training on in vivo insulin action in individual tissues of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):657–666. doi: 10.1172/JCI112019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Strube M., Mueckler M. Molecular cloning and characterization of an insulin-regulatable glucose transporter. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):83–87. doi: 10.1038/338083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern M., Wells J. A., Stephens J. M., Elton C. W., Friedman J. E., Tapscott E. B., Pekala P. H., Dohm G. L. Insulin responsiveness in skeletal muscle is determined by glucose transporter (Glut4) protein level. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 1;270(2):397–400. doi: 10.1042/bj2700397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraegen E. W., James D. E., Jenkins A. B., Chisholm D. J. Dose-response curves for in vivo insulin sensitivity in individual tissues in rats. Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 1):E353–E362. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.3.E353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraegen E. W., Storlien L. H., Jenkins A. B., James D. E. Chronic exercise compensates for insulin resistance induced by a high-fat diet in rats. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 1):E242–E249. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.256.2.E242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruszynska Y. T., McCormack J. G. Effect of nutritional status on insulin sensitivity in vivo and tissue enzyme activities in the rat. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 15;258(3):699–707. doi: 10.1042/bj2580699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Freychet P. Effect of fasting and streptozotocin diabetes on insulin binding and action in the isolated mouse soleus muscle. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1505–1515. doi: 10.1172/JCI109609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marette A., Richardson J. M., Ramlal T., Balon T. W., Vranic M., Pessin J. E., Klip A. Abundance, localization, and insulin-induced translocation of glucose transporters in red and white muscle. Am J Physiol. 1992 Aug;263(2 Pt 1):C443–C452. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.2.C443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M. Family of glucose-transporter genes. Implications for glucose homeostasis and diabetes. Diabetes. 1990 Jan;39(1):6–11. doi: 10.2337/diacare.39.1.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper R. C., Hess L. J., James D. E. Differential sorting of two glucose transporters expressed in insulin-sensitive cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Mar;260(3 Pt 1):C570–C580. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.3.C570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. M., Balon T. W., Treadway J. L., Pessin J. E. Differential regulation of glucose transporter activity and expression in red and white skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12690–12694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson L. J., James D. E. Insulin-regulated sorting of glucose transporters in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Am J Physiol. 1992 Aug;263(2 Pt 1):E383–E393. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1992.263.2.E383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodnick K. J., Holloszy J. O., Mondon C. E., James D. E. Effects of exercise training on insulin-regulatable glucose-transporter protein levels in rat skeletal muscle. Diabetes. 1990 Nov;39(11):1425–1429. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.11.1425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodnick K. J., Slot J. W., Studelska D. R., Hanpeter D. E., Robinson L. J., Geuze H. J., James D. E. Immunocytochemical and biochemical studies of GLUT4 in rat skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6278–6285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Gigengack S., James D. E., Lienhard G. E. Translocation of the glucose transporter GLUT4 in cardiac myocytes of the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7815–7819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Moxley R., Geuze H. J., James D. E. No evidence for expression of the insulin-regulatable glucose transporter in endothelial cells. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):369–371. doi: 10.1038/346369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake S. A., Sowden J. A., Storlien L. H., James D. E., Clark P. W., Shine J., Chisholm D. J., Kraegen E. W. Effects of exercise training and dietary manipulation on insulin-regulatable glucose-transporter mRNA in rat muscle. Diabetes. 1991 Feb;40(2):275–279. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.2.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziel F. H., Venkatesan N., Davidson M. B. Glucose transport is rate limiting for skeletal muscle glucose metabolism in normal and STZ-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1988 Jul;37(7):885–890. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.7.885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]