Abstract
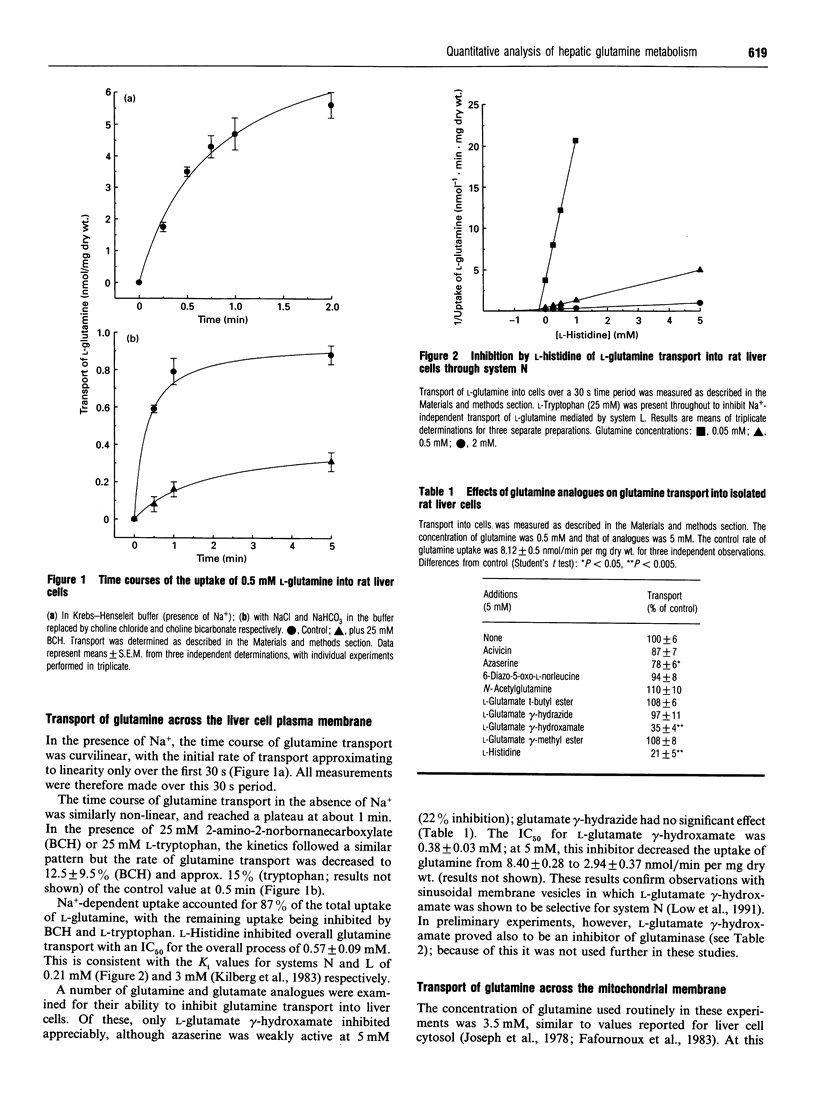
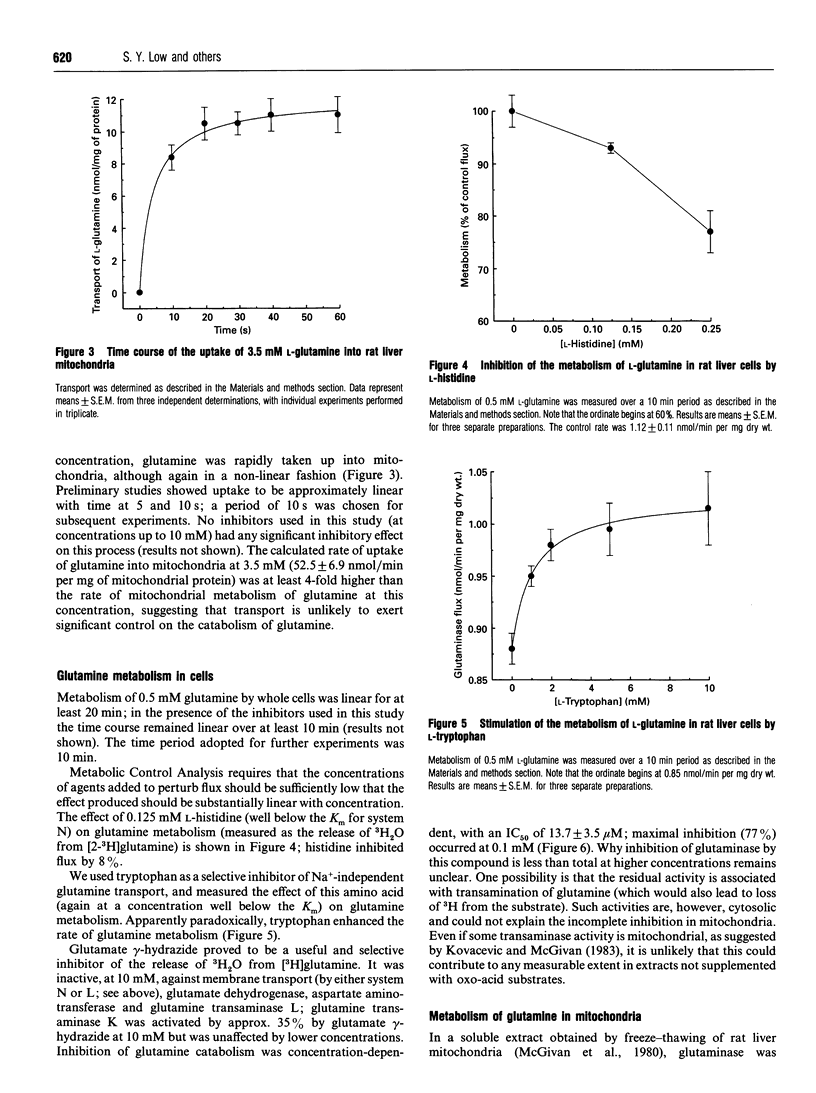
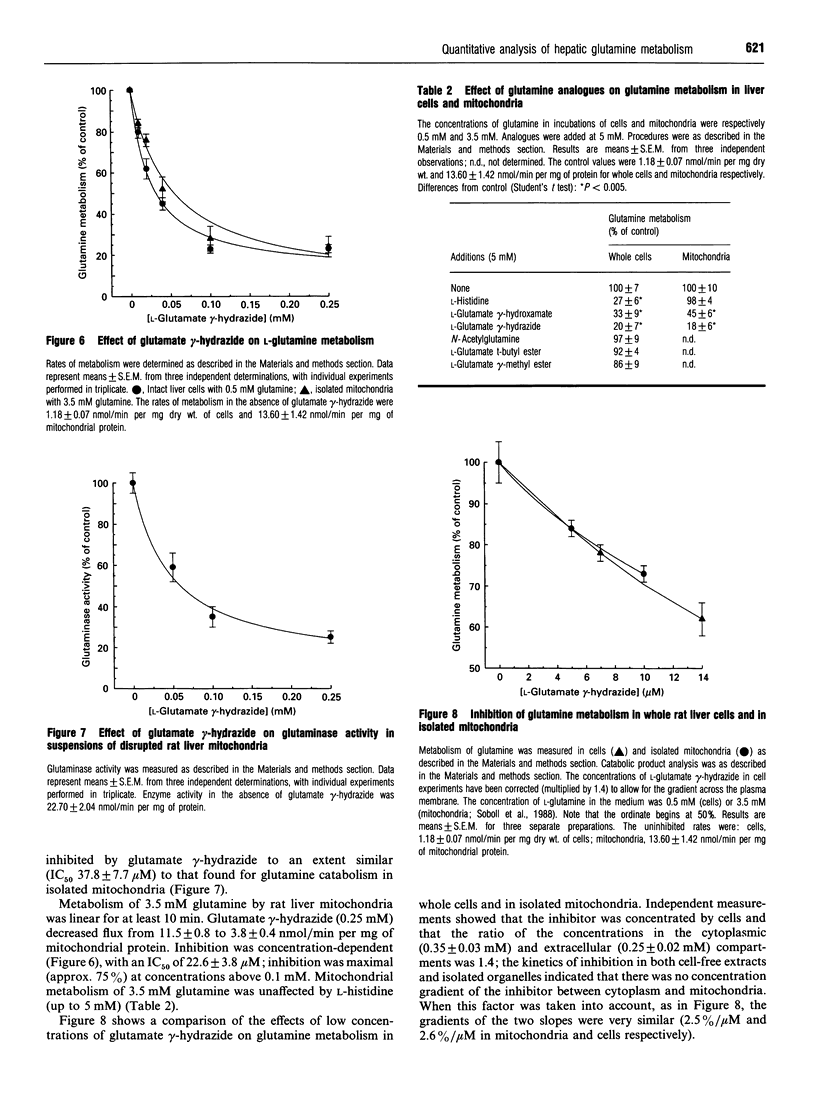
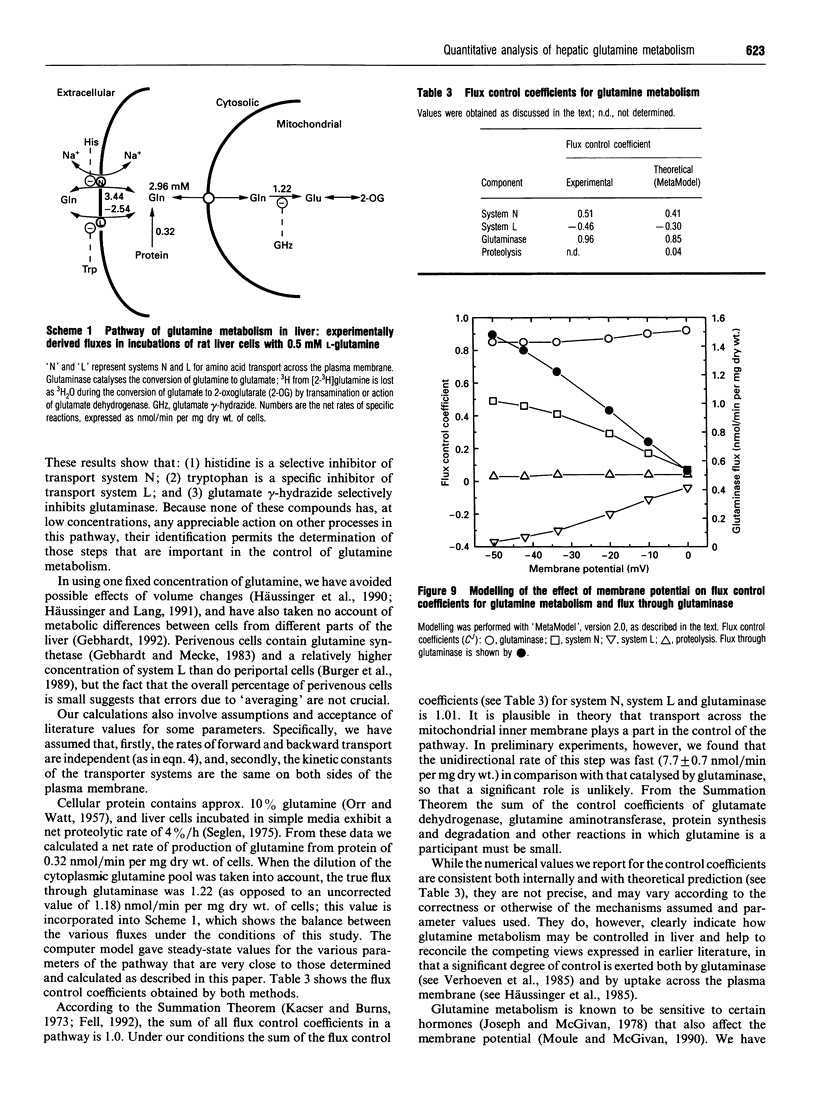
1. At a physiological concentration of glutamine (0.5 mM), 87% of the total transport across the plasma membrane of liver cells isolated from fed rats involved the Na(+)-dependent system N; this was substantially inhibited by L-histidine. The residual Na(+)-independent component was attributed to system L on the basis of inhibition by 2-amino-2-norbornanecarboxylate and L-tryptophan. 2. Catabolism of glutamine by intact liver cells or by isolated mitochondria was inhibited by glutamate gamma-hydrazide with IC50 values of 13.7 +/- 3.5 microM and 22.6 +/- 3.8 microM respectively and a maximal inhibition of approx. 75%. The site of inhibition was identified as glutaminase; glutamate gamma-hydrazide inhibited this enzyme in cell-free extracts (IC50 37.8 +/- 7.7 microM) but had no activity against glutamate dehydrogenase or transport of glutamine, whether across mitochondrial or plasma membranes. 3. The major control site in cells from fed animals incubated with 0.5 mM L-glutamine was glutaminase (flux control coefficient 0.96). Appreciable control also resided in both plasma membrane transport systems, with coefficients of 0.51 for system N and -0.46 for system L, such that both interacted to provide a fine control of the intracellular concentration of the amino acid. Similar values were obtained by computer simulation based on theoretical determination of elasticities. 4. Previous controversy about the locus of regulation of hepatic glutamine metabolism is resolved by this distribution of control.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abumrad N. N., Williams P., Frexes-Steed M., Geer R., Flakoll P., Cersosimo E., Brown L. L., Melki I., Bulus N., Hourani H. Inter-organ metabolism of amino acids in vivo. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1989 May;5(3):213–226. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610050302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger H. J., Gebhardt R., Mayer C., Mecke D. Different capacities for amino acid transport in periportal and perivenous hepatocytes isolated by digitonin/collagenase perfusion. Hepatology. 1989 Jan;9(1):22–28. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840090105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H. N. Role of amino acid transport and countertransport in nutrition and metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jan;70(1):43–77. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. J. Glutamate-aspartate transaminase. Methods Enzymol. 1985;113:66–69. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(85)13014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. J., Meister A. Glutamine transaminase K from rat kidney. Methods Enzymol. 1985;113:344–349. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(85)13047-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. J., Meister A. Glutamine transaminase L from rat liver. Methods Enzymol. 1985;113:338–343. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(85)13046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornish-Bowden A., Hofmeyr J. H. MetaModel: a program for modelling and control analysis of metabolic pathways on the IBM PC and compatibles. Comput Appl Biosci. 1991 Jan;7(1):89–93. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/7.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curthoys N. P., Shapiro R. A. Effect of metabolic acidosis and of phosphate on the presence of glutamine within the matrix space of rat renal mitochondria during glutamine transport. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 10;253(1):63–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fafournoux P., Demigné C., Rémésy C., Le Cam A. Bidirectional transport of glutamine across the cell membrane in rat liver. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 15;216(2):401–408. doi: 10.1042/bj2160401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fell D. A. Metabolic control analysis: a survey of its theoretical and experimental development. Biochem J. 1992 Sep 1;286(Pt 2):313–330. doi: 10.1042/bj2860313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fell D. A., Sauro H. M. Metabolic control and its analysis. Additional relationships between elasticities and control coefficients. Eur J Biochem. 1985 May 2;148(3):555–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08876.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt R., Mecke D. Heterogeneous distribution of glutamine synthetase among rat liver parenchymal cells in situ and in primary culture. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):567–570. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt R. Metabolic zonation of the liver: regulation and implications for liver function. Pharmacol Ther. 1992;53(3):275–354. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(92)90055-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haüssinger D. Nitrogen metabolism in liver: structural and functional organization and physiological relevance. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 15;267(2):281–290. doi: 10.1042/bj2670281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzfeld A., Greengard O. Aspartate aminotransferase in fat tissues: changes with growth and hormones. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 20;237(1):88–98. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häussinger D., Lang F. Cell volume in the regulation of hepatic function: a mechanism for metabolic control. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 12;1071(4):331–350. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90001-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häussinger D., Soboll S., Meijer A. J., Gerok W., Tager J. M., Sies H. Role of plasma membrane transport in hepatic glutamine metabolism. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Nov 4;152(3):597–603. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hüssinger D., Lang F., Bauers K., Gerok W. Control of hepatic nitrogen metabolism and glutathione release by cell volume regulatory mechanisms. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 13;193(3):891–898. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., Bradford N. M., McGivan J. D. Characteristics of the transport of alanine, serine and glutamine across the plasma membrane of isolated rat liver cells. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 15;176(3):827–836. doi: 10.1042/bj1760827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph S. K., McGivan J. D. The effect of ammonium chloride and glucagon on the metabolism of glutamine in isolated liver cells from starved rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 21;543(1):16–28. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90450-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kacser H., Burns J. A. The control of flux. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1973;27:65–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilberg M. S., Handlogten M. E., Christensen H. N. Characteristics of an amino acid transport system in rat liver for glutamine, asparagine, histidine, and closely related analogs. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4011–4019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., McCabe J. P., Beevers S. J., Pogson C. I. The characteristics and site of inhibition of gluconeogenesis in rat liver cells by bacterial endotoxin. Stimulation of phosphofructokinase-1. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 15;242(3):721–728. doi: 10.1042/bj2420721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacevic Z., McGivan J. D. Mitochondrial metabolism of glutamine and glutamate and its physiological significance. Physiol Rev. 1983 Apr;63(2):547–605. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1983.63.2.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low S. Y., Salter M., Knowles R. G., Rennie M. J., Pogson C. I. Effect of L-glutamate-gamma-hydrazide on the transport and metabolism of L-glutamine in rat liver cells and isolated mitochondria. Biochem Soc Trans. 1990 Dec;18(6):1239–1240. doi: 10.1042/bst0181239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low S. Y., Taylor P. M., Ahmed A., Pogson C. I., Rennie M. J. Substrate-specificity of glutamine transporters in membrane vesicles from rat liver and skeletal muscle investigated using amino acid analogues. Biochem J. 1991 Aug 15;278(Pt 1):105–111. doi: 10.1042/bj2780105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGivan J. D., Bradford N. M. Characteristics of the activation of glutaminase by ammonia in sonicated rat liver mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 13;759(3):296–302. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90327-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGivan J. D., Lacey J. H., Joseph S. K. Localization and some properties of phosphate-dependent glutaminase in disrupted liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 15;192(2):537–542. doi: 10.1042/bj1920537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moule S. K., McGivan J. D. Regulation of the plasma membrane potential in hepatocytes--mechanism and physiological significance. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Oct 8;1031(3):383–397. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(90)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pishak M. R., Phillips A. T. A modified radioisotopic assay for measuring glutamine synthetase activity in tissue extracts. Anal Biochem. 1979 Apr 1;94(1):82–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90793-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennie M. J., MacLennan P. A., Hundal H. S., Weryk B., Smith K., Taylor P. M., Egan C., Watt P. W. Skeletal muscle glutamine transport, intramuscular glutamine concentration, and muscle-protein turnover. Metabolism. 1989 Aug;38(8 Suppl 1):47–51. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(89)90140-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter M., Knowles R. G., Pogson C. I. Quantification of the importance of individual steps in the control of aromatic amino acid metabolism. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 15;234(3):635–647. doi: 10.1042/bj2340635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter M., Knowles R. G., Pogson C. I. Transport of the aromatic amino acids into isolated rat liver cells. Properties of uptake by two distinct systems. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):499–506. doi: 10.1042/bj2330499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauro H. M., Small J. R., Fell D. A. Metabolic control and its analysis. Extensions to the theory and matrix method. Eur J Biochem. 1987 May 15;165(1):215–221. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11214.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Protein degradation in isolated rat hepatocytes is inhibited by ammonia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 2;66(1):44–52. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80292-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soboll S., Lenzen C., Rettich D., Gründel S., Ziegler B. Characterisation of glutamine uptake in rat liver mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Apr 10;197(1):113–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15888.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley P. E., Williams S. G. Use of the liquid scintillation spectrometer for determining adenosine triphosphate by the luciferase enzyme. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jun;29(3):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90323-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. M., Egan C. J., Rennie M. J. Transport of glutamine across blood-facing membranes of perfused rat jejunum. Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 1):E550–E558. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.256.4.E550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeven A. J., Estrela J. M., Meijer A. J. Alpha-adrenergic stimulation of glutamine metabolism in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1985 Sep 1;230(2):457–463. doi: 10.1042/bj2300457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


