Abstract
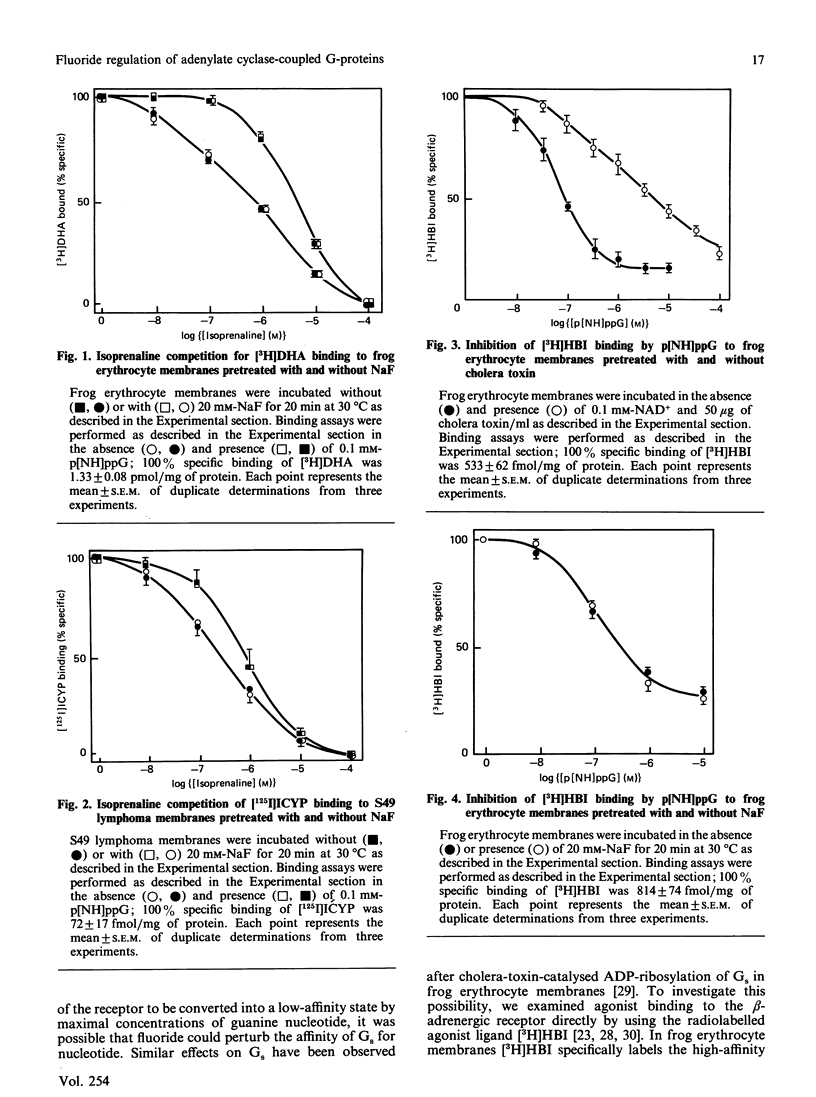
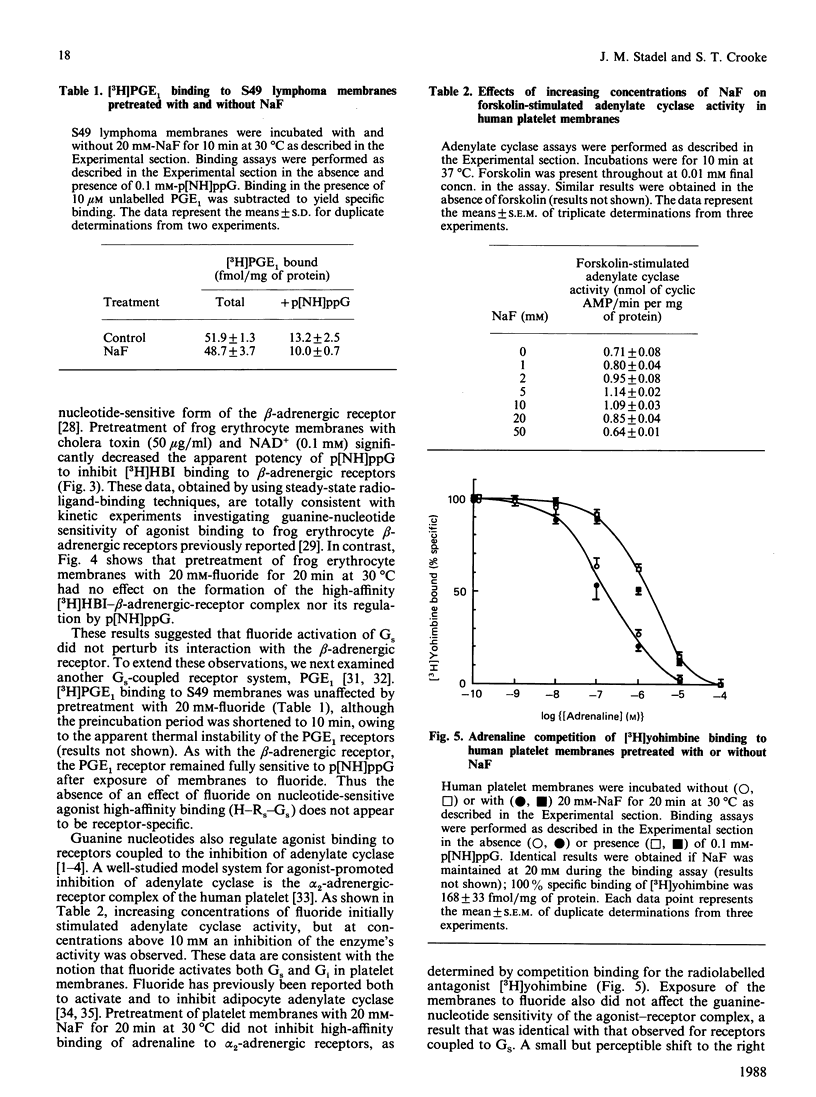
Fluoride ion, presumably an Al3+-F- complex, has been proposed to activate the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein (G-protein) of the visual system, transducin, by associating with GDP at the nucleotide-binding site and thus mimicking the effects of non-hydrolysable GTP analogues [Bigay, Deterre, Pfister & Chabre (1985) FEBS Lett. 191, 181-85]. We have examined this proposed model by using the adenylate cyclase complexes of frog erythrocytes, S49 lymphoma cells and human platelets. Preincubation of plasma membranes from frog erythrocytes and S49 cells with 20 mM-fluoride for 20 min at 30 degrees C strongly stimulated adenylate cyclase activity. In contrast, the preactivated membranes were still able to bind beta-adrenergic agonist with high affinity, as determined by radioligand-binding techniques. Moreover, high-affinity agonist binding in fluoride-treated membranes was fully sensitive to guanine nucleotide, which decreased beta-adrenergic-receptor affinity for agonist. Very similar results were obtained for [3H]prostaglandin E1 binding to S49 membranes pretreated with fluoride. Incubation of human platelet membranes with increasing concentrations of fluoride (1-50 mM) resulted in biphasic regulation of adenylate cyclase activity, with inhibition observed at concentrations greater than 10 mM. Preincubation of platelet membranes with 20 mM-fluoride did not affect agonist high-affinity binding to alpha 2-adrenergic receptors, nor receptor regulation by guanine nucleotide. These results suggest that the model developed from the study of transducin may not be generally applicable to the G-proteins of the adenylate cyclase system.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERTHET J., RALL T. W., SUTHERLAND E. W. The relationship of epinephrine and glucagon to liver phosphorylase. IV. Effect of epinephrine and glucagon on the reactivation of phosphorylase in liver homogenates. J Biol Chem. 1957 Jan;224(1):463–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigay J., Deterre P., Pfister C., Chabre M. Fluoroaluminates activate transducin-GDP by mimicking the gamma-phosphate of GTP in its binding site. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 28;191(2):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Bocckino S. B., Waynick L. E., Exton J. H. Role of a guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein in the hydrolysis of hepatocyte phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate by calcium-mobilizing hormones and the control of cell calcium. Studies utilizing aluminum fluoride. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14477–14483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore P. F., Exton J. H. Studies on the hepatic calcium-mobilizing activity of aluminum fluoride and glucagon. Modulation by cAMP and phorbol myristate acetate. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11056–11063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt D. R., Ross E. M. Effect of Al3+ plus F- on the catecholamine-stimulated GTPase activity of purified and reconstituted Gs. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):7036–7041. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunton L. L., Wiklund R. A., Van Arsdale P. M., Gilman A. G. Binding of (3H)prostaglandin E1 to putative receptors linked to adenylate cyclase of cultured cell clones. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 25;251(10):3037–3044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Pfeuffer T. Mechanism of cholera toxin action: covalent modification of the guanyl nucleotide-binding protein of the adenylate cyclase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2669–2673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Selinger Z. Catecholamine-stimulated GTPase activity in turkey erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 8;452(2):538–551. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90206-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerione R. A., Codina J., Benovic J. L., Lefkowitz R. J., Birnbaumer L., Caron M. G. The mammalian beta 2-adrenergic receptor: reconstitution of functional interactions between pure receptor and pure stimulatory nucleotide binding protein of the adenylate cyclase system. Biochemistry. 1984 Sep 25;23(20):4519–4525. doi: 10.1021/bi00315a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerione R. A., Regan J. W., Nakata H., Codina J., Benovic J. L., Gierschik P., Somers R. L., Spiegel A. M., Birnbaumer L., Lefkowitz R. J. Functional reconstitution of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor with guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins in phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3901–3909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Taylor J. A. Fluoroaluminates mimic guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate in activating the polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase of hepatocyte membranes. Role for the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein Gp in signal transduction. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 15;241(2):409–414. doi: 10.1042/bj2410409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codina J., Hildebrandt J. D., Birnbaumer L., Sekura R. D. Effects of guanine nucleotides and Mg on human erythrocyte Ni and Ns, the regulatory components of adenylyl cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11408–11418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lean A., Stadel J. M., Lefkowitz R. J. A ternary complex model explains the agonist-specific binding properties of the adenylate cyclase-coupled beta-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7108–7117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downs R. W., Jr, Spiegel A. M., Singer M., Reen S., Aurbach G. D. Fluoride stimulation of adenylate cyclase is dependent on the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):949–954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson K. M., Higashijima T., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. The influence of bound GDP on the kinetics of guanine nucleotide binding to G proteins. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7393–7399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Meren R. ADP-ribosylation of membrane proteins catalyzed by cholera toxin: basis of the activation of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3050–3054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood J. P., Rodbell M. Inhibition by fluoride ion of hormonal activation of fat cell adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 25;248(14):4901–4904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman B. B., Michel T., Brenneman T. B., Lefkowitz R. J. Interactions of agonists with platelet alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. Endocrinology. 1982 Mar;110(3):926–932. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-3-926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. M. Are guanine nucleotide binding proteins a distinct class of regulatory proteins? FEBS Lett. 1983 Nov 28;164(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobs K. H. Inhibition of adenylate cyclase by hormones and neurotransmitters. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1979 Dec;16(3):147–156. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(79)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanaho Y., Moss J., Vaughan M. Mechanism of inhibition of transducin GTPase activity by fluoride and aluminum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11493–11497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Bokoch G. M., Northup J. K., Ui M., Gilman A. G. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Properties and function of the purified protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3568–3577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Mullikin D., Wood C. L., Gore T. B., Mukherjee C. Regulation of prostaglandin receptors by prostaglandins and guanine nucleotides in frog erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5295–5303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Williams L. T. Catecholamine binding to the beta-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):515–519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limbird L. E., Gill D. M., Lefkowitz R. J. Agonist-promoted coupling of the beta-adrenergic receptor with the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein of the adenylate cyclase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):775–779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limbird L. E., Speck J. L., Smith S. K. Sodium ion modulates agonist and antagonist interactions with the human platelet alpha 2-adrenergic receptor in membrane and solubilized preparations. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 May;21(3):609–617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manganiello V. C., Vaughan M. Activation and inhibition of fat cell adenylate cyclase by fluoride. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 25;251(20):6205–6209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northup J. K., Smigel M. D., Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. The subunits of the stimulatory regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Resolution of the activated 45,000-dalton (alpha) subunit. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11369–11376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northup J. K., Sternweis P. C., Smigel M. D., Schleifer L. S., Ross E. M., Gilman A. G. Purification of the regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6516–6520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S. E., Ross E. M. Functional reconstitution of beta-adrenergic receptors and the stimulatory GTP-binding protein of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7228–7232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins J. P. Adenyl cyclase. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1973;3:1–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeuffer T. GTP-binding proteins in membranes and the control of adenylate cyclase activity. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7224–7234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Howlett A. C., Ferguson K. M., Gilman A. G. Reconstitution of hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase activity with resolved components of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6401–6412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadel J. M., De Lean A., Lefkowitz R. J. Molecular mechanisms of coupling in hormone receptor-adenylate cyclase systems. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1982;53:1–43. doi: 10.1002/9780470122983.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadel J. M., Lefkowitz R. J. Differential effects of cholera toxin on guanine nucleotide regulation of beta-adrenergic agonist high affinity binding and adenylate cyclase activation in frog erythrocyte membranes. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1981;7(6):363–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadel J. M., Lefkowitz R. J. Multiple reactive sulfhydryl groups modulate the function of adenylate cyclase coupled beta-adrenergic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;16(3):709–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadel J. M., Strulovici B., Nambi P., Lavin T. N., Briggs M. M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Desensitization of the beta-adrenergic receptor of frog erythrocytes. Recovery and characterization of the down-regulated receptors in sequestered vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3032–3038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein P. J., Halliday K. R., Rasenick M. M. Photoreceptor GTP binding protein mediates fluoride activation of phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9081–9084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. Aluminum: a requirement for activation of the regulatory component of adenylate cyclase by fluoride. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4888–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Bourne H. R. G proteins: a family of signal transducers. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:391–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


