Abstract
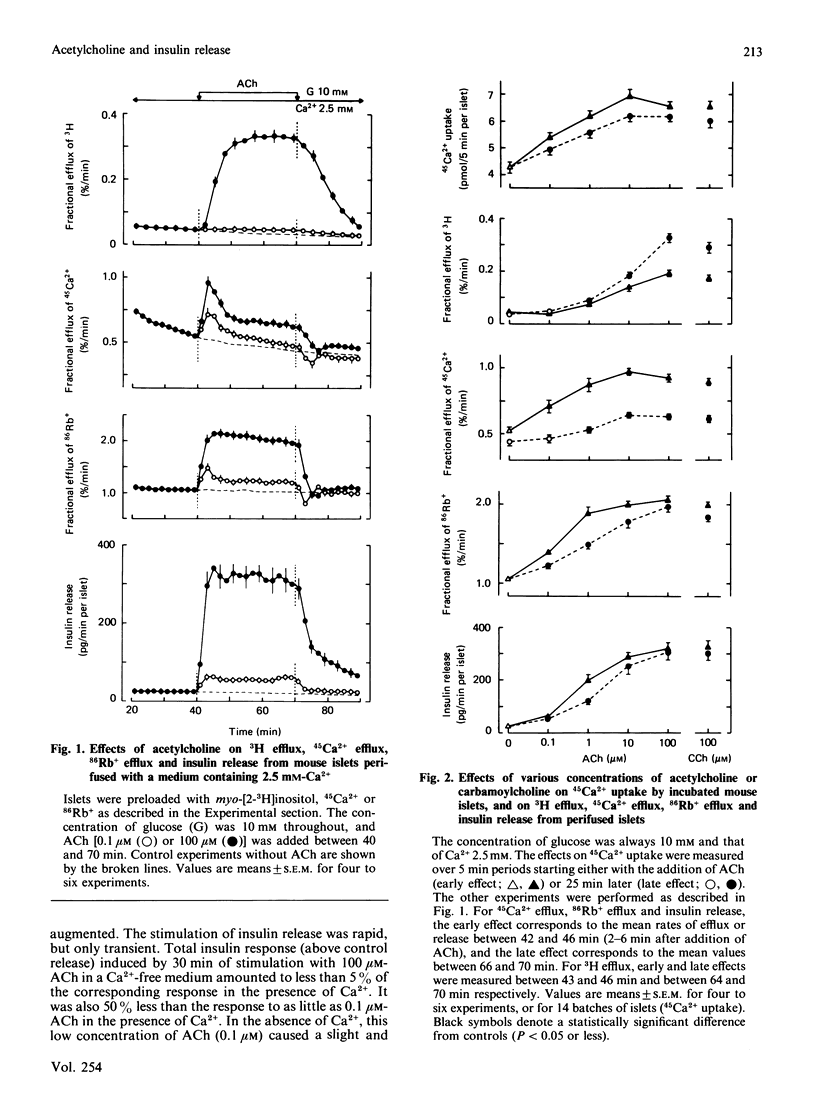
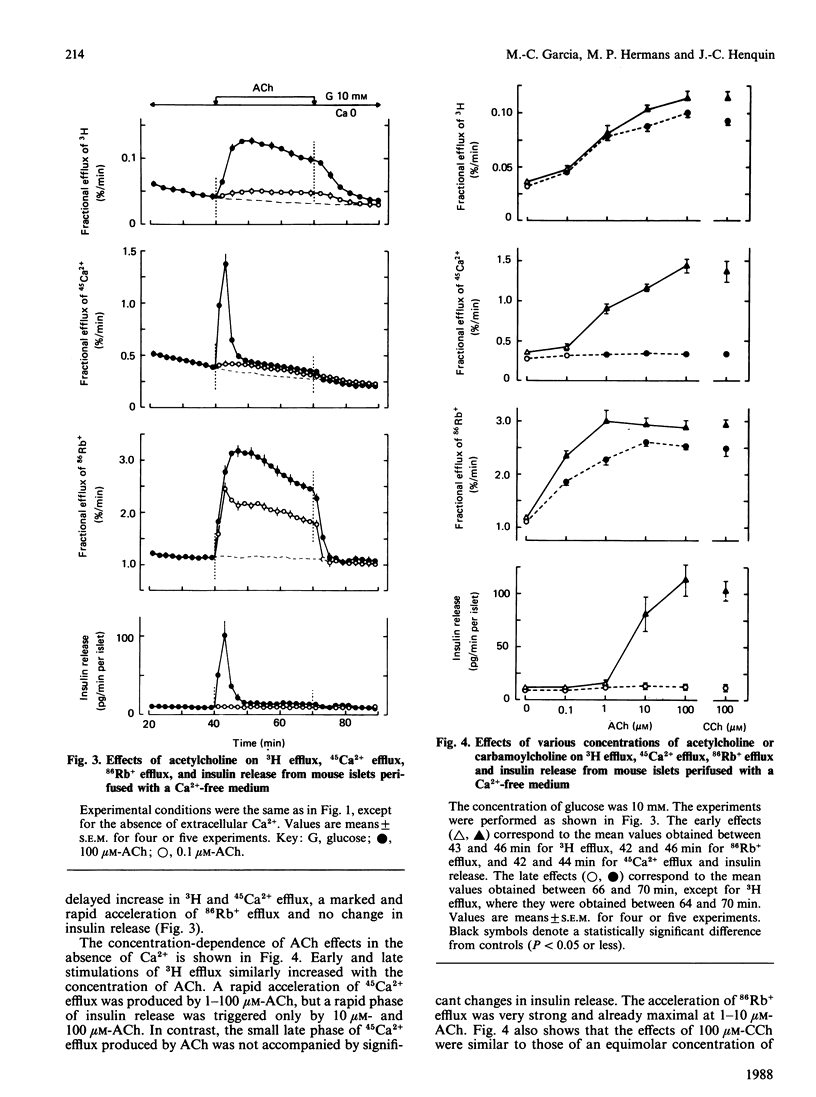
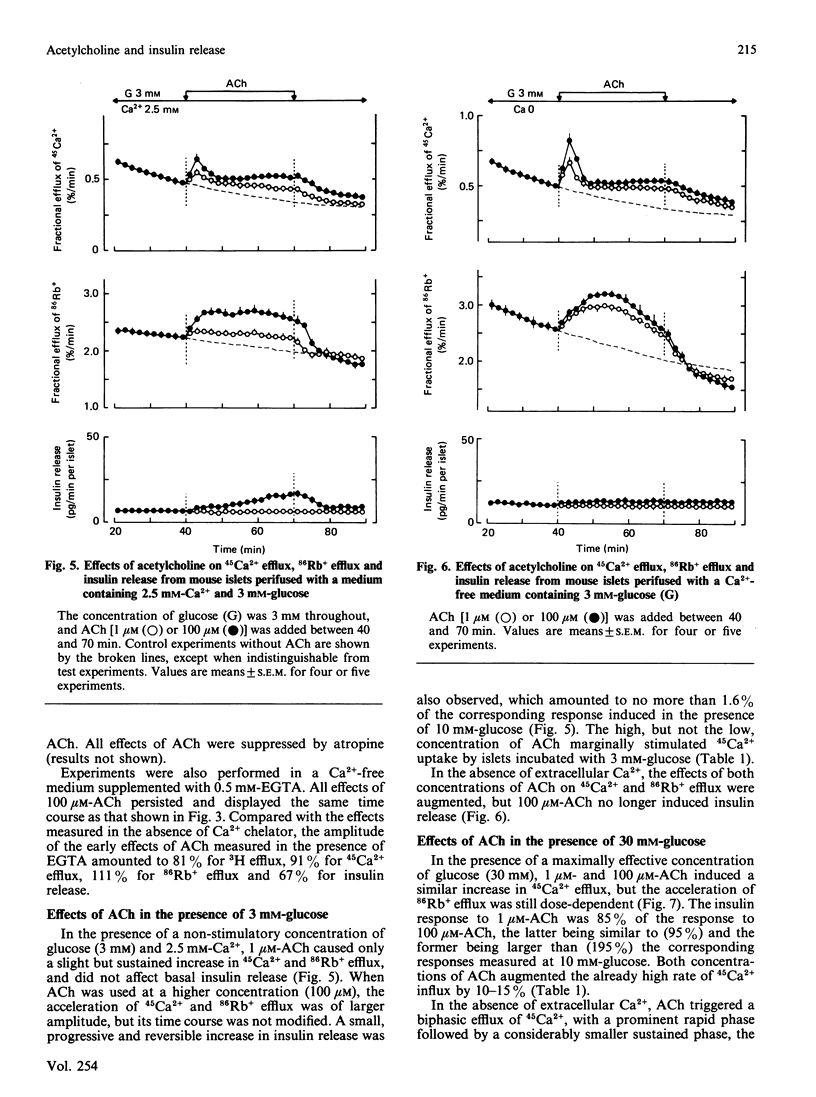
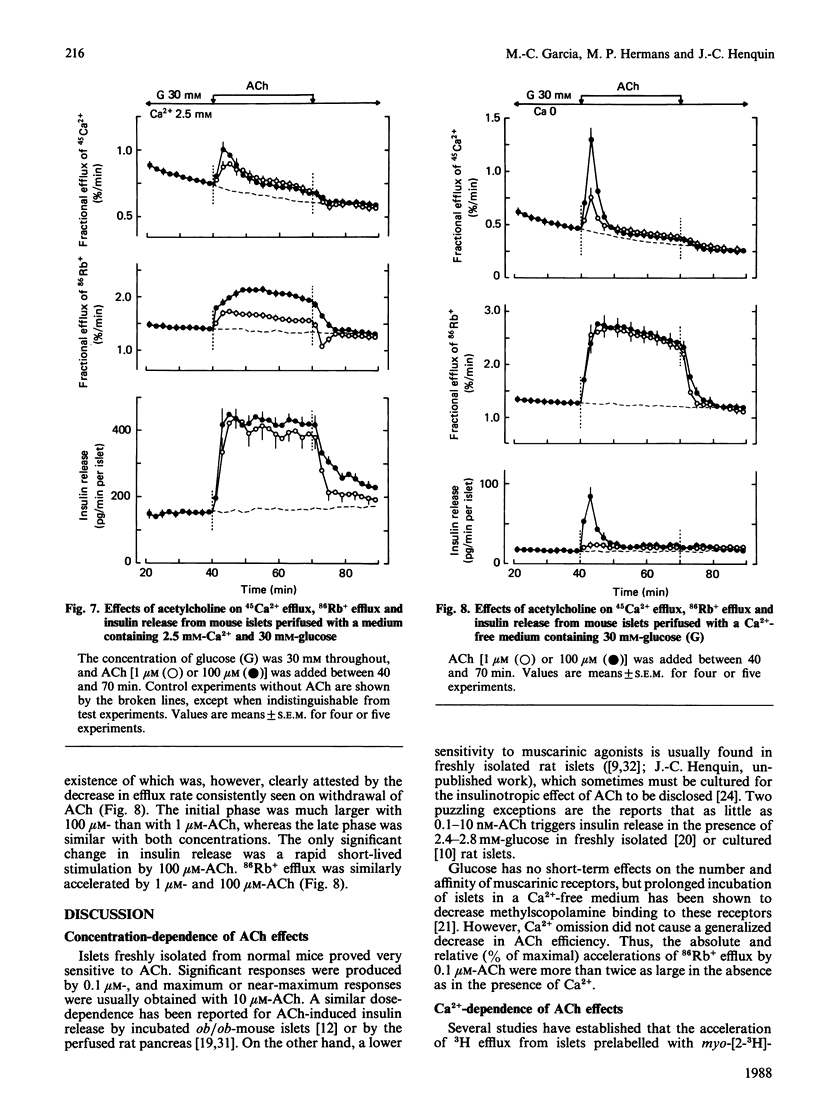
Mouse islets were used to define the glucose-dependence and extracellular Ca2+ requirement of muscarinic stimulation of pancreatic beta-cells. In the presence of a stimulatory concentration of glucose (10 mM) and of Ca2+, acetylcholine (0.1-100 microM) accelerated 3H efflux from islets preloaded with myo-[3H]inositol. It also stimulated 45Ca2+ influx and efflux, 86Rb+ efflux and insulin release. In the absence of Ca2+, only 10-100 microM-acetylcholine mobilized enough intracellular Ca2+ to trigger an early but brief peak of insulin release. At a non-stimulatory concentration of glucose (3 mM), 1 microM- and 100 microM-acetylcholine increased 45Ca2+ and 86Rb+ efflux in the presence and absence of extracellular Ca2+. However, only 100 microM-acetylcholine marginally increased 45Ca2+ influx and caused a small, delayed, stimulation of insulin release, which was abolished by omission of Ca2+. At a maximally effective concentration of glucose (30 mM), 1 microM- and 100 microM-acetylcholine increased 45Ca2+ influx and efflux only slightly, but markedly amplified insulin release. Again, only 100 microM-acetylcholine mobilized enough Ca2+ to trigger a peak of insulin release in the absence of Ca2+. The results thus show that only high concentrations of acetylcholine (greater than or equal to 10 microM) can induce release at low glucose or in a Ca2+-free medium. beta-Cells exhibit their highest sensitivity to acetylcholine in the presence of Ca2+ and stimulatory glucose. Under these physiological conditions, the large amplification of insulin release appears to be the result of combined effects of the neurotransmitter on Ca2+ influx, on intracellular Ca2+ stores and on the efficiency with which Ca2+ activates the releasing machinery.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axen K. V., Schubart U. K., Blake A. D., Fleischer N. Role of Ca2+ in secretagogue-stimulated breakdown of phosphatidylinositol in rat pancreatic islets. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):13–21. doi: 10.1172/JCI110951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best L. A role for calcium in the breakdown of inositol phospholipids in intact and digitonin-permeabilized pancreatic islets. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 15;238(3):773–779. doi: 10.1042/bj2380773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biden T. J., Peter-Riesch B., Schlegel W., Wollheim C. B. Ca2+-mediated generation of inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate and inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate in pancreatic islets. Studies with K+, glucose, and carbamylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3567–3571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozem M., Nenquin M., Henquin J. C. The ionic, electrical, and secretory effects of protein kinase C activation in mouse pancreatic B-cells: studies with a phorbol ester. Endocrinology. 1987 Sep;121(3):1025–1033. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-3-1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr I. M., Slonim A. E., Burke V., Fletcher T. Extracellular calcium and adrenergic and cholinergic effects on islet beta-cell function. Am J Physiol. 1976 Oct;231(4):1246–1249. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.4.1246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campfield L. A., Smith F. J. Neural control of insulin secretion: interaction of norepinephrine and acetylcholine. Am J Physiol. 1983 May;244(5):R629–R634. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1983.244.5.R629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng P. Y., Yasuda H., Katori T., Oka H. Phosphoinositides turnover and insulin secretion in pancreatic islets. Endocrinol Jpn. 1987 Apr;34(2):189–202. doi: 10.1507/endocrj1954.34.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements R. S., Jr, Rhoten W. B. Phosphoinositide metabolism and insulin secretion from isolated rat pancreatic islets. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):684–691. doi: 10.1172/JCI108325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook D. L., Crill W. E., Porte D., Jr Glucose and acetylcholine have different effects on the plateau pacemaker of pancreatic islet cells. Diabetes. 1981 Jul;30(7):558–561. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.7.558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel P. M., Henderson J. R. The effect of vagal stimulation on plasma insulin and glucose levels in the baboon. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):317–327. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman L. A., Ezdinli E. Z., Javid R. Effect of vagotomy and vagal stimulation on insulin secretion. Diabetes. 1967 Jul;16(7):443–448. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.7.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagerman E., Idahl L. A., Meissner H. P., Täljedal I. B. Insulin release, cGMP, cAMP, and membrane potential in acetylcholine-stimulated islets. Am J Physiol. 1978 Nov;235(5):E493–E500. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.5.E493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagerman E., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Effects of acetylcholine on ion fluxes and chlorotetracycline fluorescence in pancreatic islets. J Physiol. 1980 Mar;300:505–513. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffey M. A., Conaway H. H., Whitney J. E. Extracellular calcium and acetylcholine-stimualted insulin secretion. Diabetes. 1974 Jun;23(6):494–498. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.6.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grill V., Fåk K. Influence of thiol groups, calcium, and glucose metabolism on cholinergic-induced insulin release and on methylscopolamine binding to muscarinic receptors in pancreatic islets of the rat. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1985 Jul;109(3):355–360. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1090355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Gylfe E. Mobilization of different intracellular calcium pools after activation of muscarinic receptors in pancreatic beta-cells. Pharmacology. 1986;32(5):257–267. doi: 10.1159/000138178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Gylfe E., Wesslén N. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate mobilizes glucose-incorporated calcium from pancreatic islets. Biochem Int. 1986 Aug;13(2):383–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Bozem M., Schmeer W., Nenquin M. Distinct mechanisms for two amplification systems of insulin release. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 1;246(2):393–399. doi: 10.1042/bj2460393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Garcia M. C., Bozem M., Hermans M. P., Nenquin M. Muscarinic control of pancreatic B cell function involves sodium-dependent depolarization and calcium influx. Endocrinology. 1988 May;122(5):2134–2142. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-5-2134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C., Lambert A. E. Cobalt inhibition of insulin secretion and calcium uptake by isolated rat islets. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jun;228(6):1669–1677. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.6.1669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. Opposite effects of intracellular Ca2+ and glucose on K+ permeability of pancreatic islet cells. Nature. 1979 Jul 5;280(5717):66–68. doi: 10.1038/280066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. Regulation of insulin release by ionic and electrical events in B cells. Horm Res. 1987;27(3):168–178. doi: 10.1159/000180806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans M. P., Schmeer W., Henquin J. C. Modulation of the effect of acetylcholine on insulin release by the membrane potential of B cells. Endocrinology. 1987 May;120(5):1765–1773. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-5-1765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans M. P., Schmeer W., Henquin J. C. The permissive effect of glucose, tolbutamide and high K+ on arginine stimulation of insulin release in isolated mouse islets. Diabetologia. 1987 Aug;30(8):659–665. doi: 10.1007/BF00277325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. J., Christie M. R., Ashcroft S. J. Potentiators of insulin secretion modulate Ca2+ sensitivity in rat pancreatic islets. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1987 Apr;50(3):231–236. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(87)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen J. Effect of acetyl choline on the secretion of glucagon and insulin from the isolated, perfused canine pancreas. Diabetes. 1973 May;22(5):381–387. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.5.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. M., Stutchfield J., Howell S. L. Effects of Ca2+ and a phorbol ester on insulin secretion from islets of Langerhans permeabilised by high-voltage discharge. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 21;191(1):102–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneto A., Kosaka K., Nakao K. Effects of stimulation of the vagus nerve on insulin secretion. Endocrinology. 1967 Mar;80(3):530–536. doi: 10.1210/endo-80-3-530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loubatières-Mariani M. M., Chapal J., Alric R., Loubatières A. Studies of the cholinergic receptors involved in the secretion of insulin using isolated perfused rat pancreas. Diabetologia. 1973 Dec;9(6):439–446. doi: 10.1007/BF00461685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W., Malaisse-Lagae F., Wright P. H., Ashmore J. Effects of adrenergic and cholinergic agents upon insulin secretion in vitro. Endocrinology. 1967 May;80(5):975–978. doi: 10.1210/endo-80-5-975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias P. C., Best L., Malaisse W. J. Stimulation by glucose and carbamylcholine of phospholipase C in pancreatic islets. Cell Biochem Funct. 1985 Jul;3(3):173–177. doi: 10.1002/cbf.290030303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias P. C., Carpinelli A. R., Billaudel B., Garcia-Morales P., Valverde I., Malaisse W. J. Cholinergic stimulation of ion fluxes in pancreatic islets. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Oct 1;34(19):3451–3457. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90717-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan N. G., Rumford G. M., Montague W. Studies on the role of inositol trisphosphate in the regulation of insulin secretion from isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Biochem J. 1985 Jun 15;228(3):713–718. doi: 10.1042/bj2280713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nenquin M., Awouters P., Mathot F., Henquin J. C. Distinct effects of acetylcholine and glucose on 45calcium and 86rubidium efflux from mouse pancreatic islets. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 29;176(2):457–461. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81218-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostenson C. G., Grill V. Evidence that hyperglycemia increases muscarinic binding in pancreatic islets of the rat. Endocrinology. 1987 Nov;121(5):1705–1710. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-5-1705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp R., Culbert S., Cook J., Jennings A., Burr I. M. Cholinergic modification of glucose-induced biphasic insulin release in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1974 Mar;53(3):710–716. doi: 10.1172/JCI107609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamagawa T., Niki H., Niki A. Insulin release independent of a rise in cytosolic free Ca2+ by forskolin and phorbol ester. FEBS Lett. 1985 Apr 22;183(2):430–432. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80825-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trus M. D., Hintz C. S., Weinstein J. B., Williams A. D., Pagliara A. S., Matschinsky F. M. A comparison of the effects of glucose and acetylcholine on insulin release and intermediary metabolism in rat pancreatic islets. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3921–3929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B. A., Comens P. G., Ackermann K. E., Sherman W. R., McDaniel M. L. The digitonin-permeabilized pancreatic islet model. Effect of myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate on Ca2+ mobilization. Biochem J. 1985 May 1;227(3):965–969. doi: 10.1042/bj2270965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Biden T. J. Second messenger function of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Early changes in inositol phosphates, cytosolic Ca2+, and insulin release in carbamylcholine-stimulated RINm5F cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8314–8319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollheim C. B., Siegel E. G., Sharp G. W. Dependency of acetylcholine-induced insulin release on Ca++ uptake by rat pancreatic islets. Endocrinology. 1980 Oct;107(4):924–929. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-4-924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


