Abstract
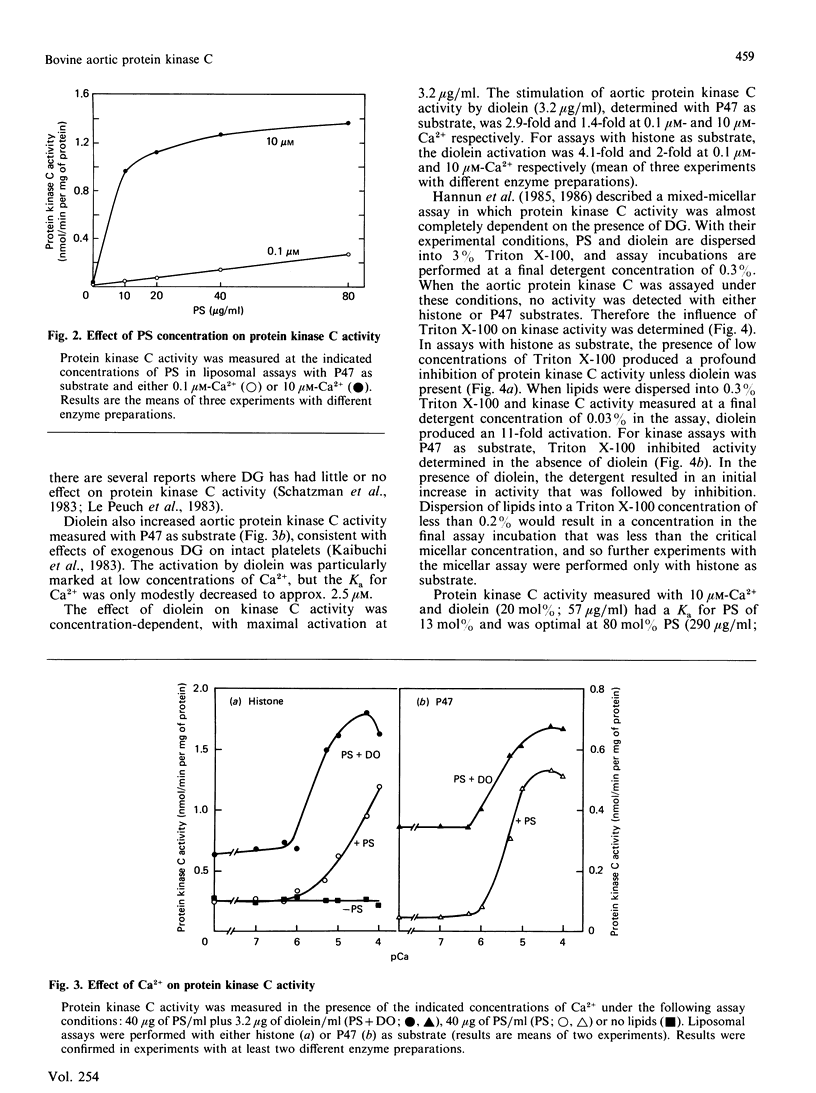
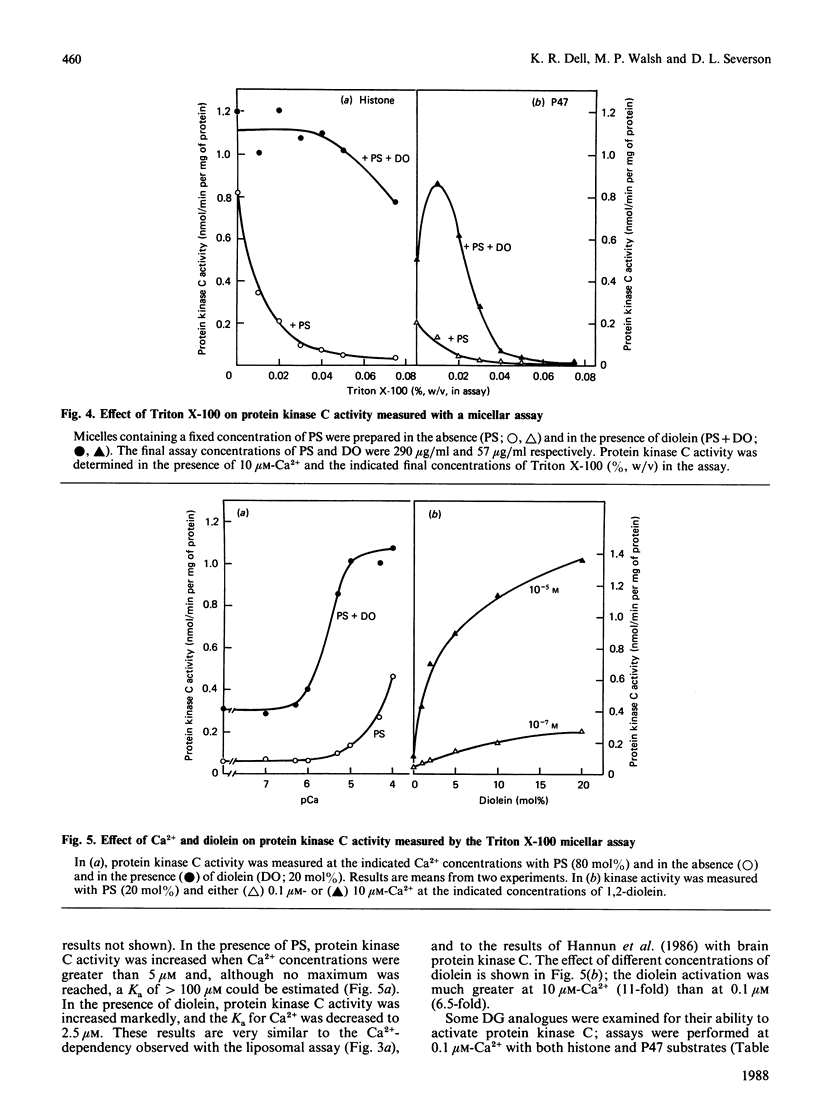
A Ca2+- and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase (protein kinase C) was partially purified from the media of bovine aortas by chromatography on DEAE-Sephacel and phenyl-Sepharose. Enzyme activity was characterized with both histone and a 47 kDa platelet protein (P47) as substrates, because the properties of protein kinase C can be modified by the choice of substrate. Both phosphatidylserine and Ca2+ were required for kinase activity. With P47 as substrate, protein kinase C had a Ka for Ca2+ of 5 microM. Addition of diolein to the enzyme assay caused a marked stimulation of activity, especially at low Ca2+ concentrations, but the Ka for Ca2+ was shifted only slightly, to 2.5 microM. With histone as substrate, the enzyme had a very high Ka (greater than 50 microM) for Ca2+, which was substantially decreased to 3 microM-Ca2+ by diolein. A Triton X-100 mixed-micelle preparation of lipids was also utilized to assay protein kinase C with histone as the substrate. Under these conditions kinase activity was almost totally dependent on the presence of diolein; again, diolein caused a large decrease in the Ka for Ca2+, from greater than 100 microM to 2.5 microM. The increased sensitivity of protein kinase C to Ca2+ with P47 rather than histone, and the ability of diacylglycerol to activate protein kinase C without shifting the Ka for Ca2+, when P47 is the substrate, illustrate that the mechanism of protein kinase C activation is influenced by the exogenous substrate used to assay the enzyme.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad Z., Lee F. T., DePaoli-Roach A., Roach P. J. Phosphorylation of glycogen synthase by the Ca2+- and phospholipid-activated protein kinase (protein kinase C). J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8743–8747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiyar N., Nambi P., Whitman M., Stassen F. L., Crooke S. T. Phorbol ester-mediated inhibition of vasopressin and beta-adrenergic responses in a vascular smooth muscle cell line. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Feb;31(2):180–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander R. W., Brock T. A., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Rittenhouse S. E. Angiotensin increases inositol trisphosphate and calcium in vascular smooth muscle. Hypertension. 1985 May-Jun;7(3 Pt 1):447–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazzi M. D., Nelsestuen G. L. Role of substrate in imparting calcium and phospholipid requirements to protein kinase C activation. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 7;26(7):1974–1982. doi: 10.1021/bi00381a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk B. C., Alexander R. W., Brock T. A., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Webb R. C. Vasoconstriction: a new activity for platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):87–90. doi: 10.1126/science.3485309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk B. C., Aronow M. S., Brock T. A., Cragoe E., Jr, Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Alexander R. W. Angiotensin II-stimulated Na+/H+ exchange in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Evidence for protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5057–5064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R., Seifert R. A. Locally acting growth factors for vascular smooth muscle cells: endogenous synthesis and release from platelets. Circulation. 1985 Oct;72(4):735–740. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.72.4.735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. A., Rittenhouse S. E., Powers C. W., Ekstein L. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Alexander R. W. Phorbol ester and 1-oleoyl-2-acetylglycerol inhibit angiotensin activation of phospholipase C in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14158–14162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. R., de Ruiz Galaretta C. M., Fanjul L. F., Mojsilovic L., Standaert M. L., Pollet R. J., Farese R. V. Insulin but not phorbol ester treatment increases phosphorylation of vinculin by protein kinase C in BC3H-1 myocytes. FEBS Lett. 1987 Apr 6;214(1):122–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80025-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A. Myoplasmic free calcium concentration reached during the twitch of an intact isolated cardiac cell and during calcium-induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of a skinned cardiac cell from the adult rat or rabbit ventricle. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Nov;78(5):457–497. doi: 10.1085/jgp.78.5.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feramisco J. R., Burridge K. A rapid purification of alpha-actinin, filamin, and a 130,000-dalton protein from smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):1194–1199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galizzi J. P., Qar J., Fosset M., Van Renterghem C., Lazdunski M. Regulation of calcium channels in aortic muscle cells by protein kinase C activators (diacylglycerol and phorbol esters) and by peptides (vasopressin and bombesin) that stimulate phosphoinositide breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):6947–6950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganong B. R., Loomis C. R., Hannun Y. A., Bell R. M. Specificity and mechanism of protein kinase C activation by sn-1,2-diacylglycerols. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Go M., Sekiguchi K., Nomura H., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Further studies on the specificity of diacylglycerol for protein kinase C activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 29;144(2):598–605. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habenicht A. J., Glomset J. A., King W. C., Nist C., Mitchell C. D., Ross R. Early changes in phosphatidylinositol and arachidonic acid metabolism in quiescent swiss 3T3 cells stimulated to divide by platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12329–12335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Loomis C. R., Bell R. M. Activation of protein kinase C by Triton X-100 mixed micelles containing diacylglycerol and phosphatidylserine. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10039–10043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Loomis C. R., Bell R. M. Protein kinase C activation in mixed micelles. Mechanistic implications of phospholipid, diacylglycerol, and calcium interdependencies. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7184–7190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang F. L., Yoshida Y., Nakabayashi H., Huang K. P. Differential distribution of protein kinase C isozymes in the various regions of brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15714–15720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikebe M., Inagaki M., Kanamaru K., Hidaka H. Phosphorylation of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase by Ca2+-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4547–4550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaoka T., Lynham J. A., Haslam R. J. Purification and characterization of the 47,000-dalton protein phosphorylated during degranulation of human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11404–11414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Lederis K. Contraction of rat thoracic aorta strips induced by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. Am J Physiol. 1987 Feb;252(2 Pt 1):C244–C247. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.252.2.C244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Takai Y., Sawamura M., Hoshijima M., Fujikura T., Nishizuka Y. Synergistic functions of protein phosphorylation and calcium mobilization in platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6701–6704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kariya K. I., Kawahara Y., Tsuda T., Fukuzaki H., Takai Y. Possible involvement of protein kinase C in platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated DNA synthesis in vascular smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis. 1987 Feb;63(2-3):251–255. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(87)90128-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh N., Kuo J. F. Subcellular distribution of phospholipid-sensitive calcium-dependent protein kinase in guinea pig heart, spleen and cerebral cortex, and inhibition of the enzyme by Triton X-100. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):590–595. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91151-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Minakuchi R., Takai Y., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase (protein kinase C) from rat brain. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:288–298. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Inohara S., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase from rat brain. Subcellular distribution, purification, and properties. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13341–13348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto A., Takai Y., Mori T., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Activation of calcium and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by diacylglycerol, its possible relation to phosphatidylinositol turnover. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2273–2276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Andersson R. G., Wise B. C., Mackerlova L., Salomonsson I., Brackett N. L., Katoh N., Shoji M., Wrenn R. W. Calcium-dependent protein kinase: widespread occurrence in various tissues and phyla of the animal kingdom and comparison of effects of phospholipid, calmodulin, and trifluoperazine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7039–7043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Peuch C. J., Ballester R., Rosen O. M. Purified rat brain calcium- and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates ribosomal protein S6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6858–6862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim M. S., Sutherland C., Walsh M. P. Phosphorylation of bovine cardiac C-protein by protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Nov 15;132(3):1187–1195. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91932-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Connolly T. M., Deckmyn H., Ross T. S., Bross T. E., Ishii H., Bansal V. S., Wilson D. B. The metabolism of phosphoinositide-derived messenger molecules. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1519–1526. doi: 10.1126/science.3024320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. R., Gröschel-Stewart U., Walsh M. P. Properties and distribution of the protein inhibitor (Mr 17,000) of protein kinase C. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 15;242(3):695–705. doi: 10.1042/bj2420695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa M., Sellers J. R., Adelstein R. S., Hidaka H. Protein kinase C modulates in vitro phosphorylation of the smooth muscle heavy meromyosin by myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8808–8814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi M., Adachi H., Gardner J. D., Jensen R. T. Calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in pancreatic acinar cells. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jun;248(6 Pt 1):G692–G701. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1985.248.6.G692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen N. E. Platelet-derived growth factor stimulates Na+ influx in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1984 Nov;247(5 Pt 1):C501–C505. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1984.247.5.C501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park S., Rasmussen H. Carbachol-induced protein phosphorylation changes in bovine tracheal smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15734–15739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano K., Takai Y., Yamanishi J., Nishizuka Y. A role of calcium-activated phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in human platelet activation. Comparison of thrombin and collagen actions. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):2010–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzman R. C., Raynor R. L., Fritz R. B., Kuo J. F. Purification to homogeneity, characterization and monoclonal antibodies of phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase from spleen. Biochem J. 1983 Feb 1;209(2):435–443. doi: 10.1042/bj2090435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. M., Campbell G. R., Campbell J. H. Replication of smooth muscle cells in vascular disease. Circ Res. 1986 Apr;58(4):427–444. doi: 10.1161/01.res.58.4.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severson D. L., Hee-Cheong M. Diacylglycerol lipase and kinase activities in rabbit aorta and coronary microvessels. Biochem Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;64(10):976–983. doi: 10.1139/o86-130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector T. Refinement of the coomassie blue method of protein quantitation. A simple and linear spectrophotometric assay for less than or equal to 0.5 to 50 microgram of protein. Anal Biochem. 1978 May;86(1):142–146. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90327-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh M. P., Hinkins S., Dabrowska R., Hartshorne D. J. Smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:279–288. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werth D. K., Niedel J. E., Pastan I. Vinculin, a cytoskeletal substrate of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11423–11426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werth D. K., Pastan I. Vinculin phosphorylation in response to calcium and phorbol esters in intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5264–5270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise B. C., Raynor R. L., Kuo J. F. Phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase from heart. I. Purification and general properties. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8481–8488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]