Abstract
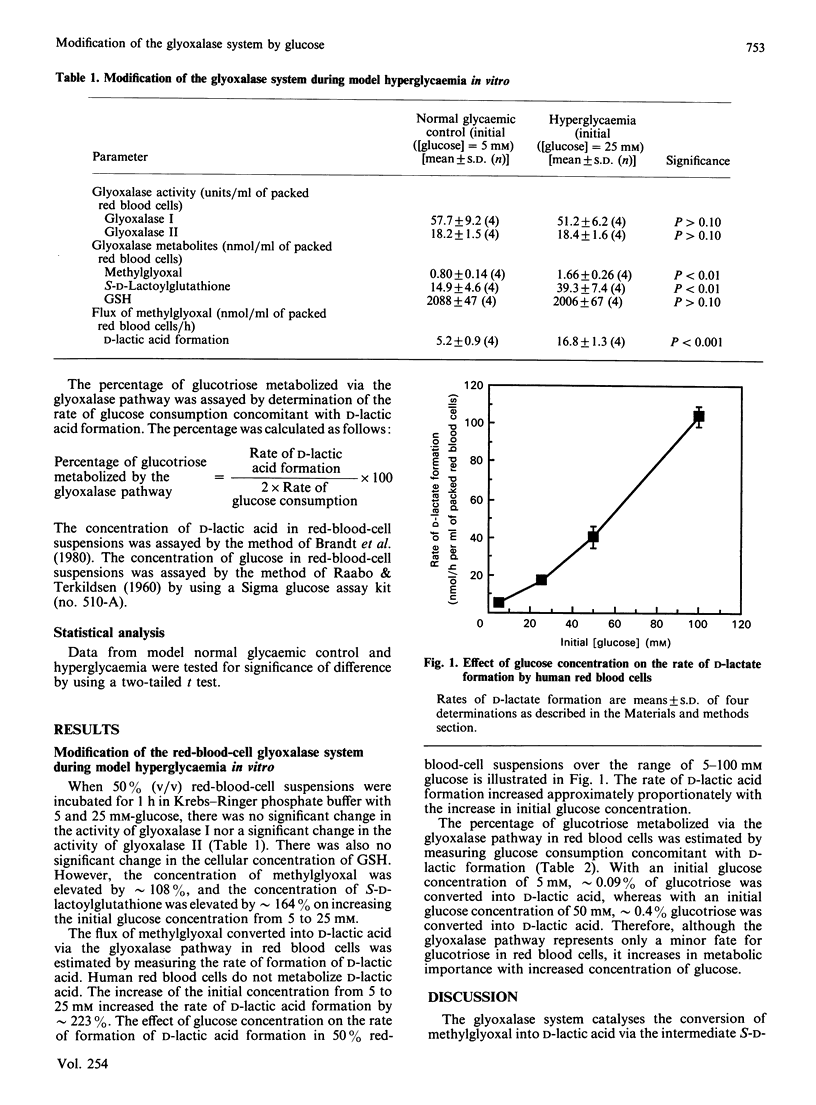
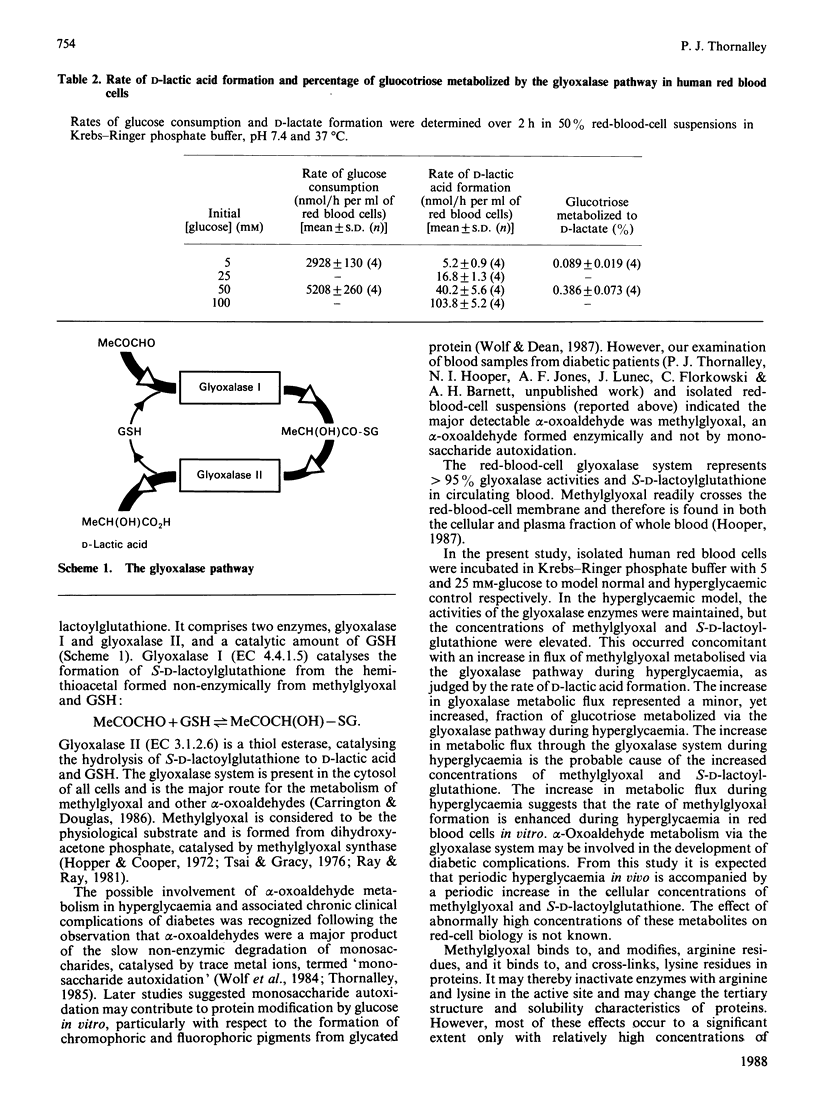
The human red-blood-cell glyoxalase system was modified by incubation with high concentrations of glucose in vitro. Red-blood-cell suspensions (50%, v/v) were incubated with 5 mM- and 25 mM-glucose to model normal and hyperglycaemic glucose metabolism. There was an increase in the flux of methylglyoxal metabolized to D-lactic acid via the glyoxalase pathway with high glucose concentration. The increase was approximately proportional to initial glucose concentration over the range studied (5-100 mM). The activities of glyoxalase I and glyoxalase II were not significantly changed, but the concentrations of the glyoxalase substrates, methylglyoxal and S-D-lactoylglutathione, and the percentage of glucotriose metabolized via the glyoxalase pathway, were significantly increased. The increase in the flux of intermediates metabolized via the glyoxalase pathway during periodic hyperglycaemia may be a biochemical factor involved in the development of chronic clinical complications associated with diabetes mellitus.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Betz A. L., Bowman P. D., Goldstein G. W. Hexose transport in microvascular endothelial cells cultured from bovine retina. Exp Eye Res. 1983 Feb;36(2):269–277. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(83)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt R. B., Siegel S. A., Waters M. G., Bloch M. H. Spectrophotometric assay for D-(-)-lactate in plasma. Anal Biochem. 1980 Feb;102(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90314-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee M., Vlassara H., Cerami A. Nonenzymatic glycosylation and the pathogenesis of diabetic complications. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Oct;101(4):527–537. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-101-4-527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. H., Birt D. F., Schnell R. C. Direct enzymatic assay for reduced and oxidized glutathione. J Pharmacol Methods. 1984 Oct;12(3):191–194. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(84)90059-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie E. Effects of S-lactoylglutathione and inhibitors of glyoxalase I on histamine release from human leukocytes. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):135–137. doi: 10.1038/277135a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonen B., Rubenstein A., Rochman H., Tanega S. P., Horwitz D. L. Haemoglobin A1: An indicator of the metabolic control of diabetic patients. Lancet. 1977 Oct 8;2(8041):734–737. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhan I., Vague P., Buonocore M., Moulin J. P., Jouve R., Vialettes B. Abnormalities of erythrocyte deformability and platelet aggregation in insulin-dependent diabetics corrected by insulin in vivo and in vitro. Lancet. 1982 Mar 6;1(8271):535–537. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92045-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leoncini G., Maresca M., Bonsignore A. The effect of methylglyoxal on the glycolytic enzymes. FEBS Lett. 1980 Aug 11;117(1):17–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80903-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone J. I., Leavengood H., Peterson M. J., O'Brien M. M., Page M. G., Aldinger C. E. Red blood cell sorbitol as an indicator of polyol pathway activity. Inhibition by sorbinil in insulin-dependent diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1984 Jan;33(1):45–49. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monnier V. M., Vishwanath V., Frank K. E., Elmets C. A., Dauchot P., Kohn R. R. Relation between complications of type I diabetes mellitus and collagen-linked fluorescence. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 13;314(7):403–408. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602133140702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmori S., Mori M., Kawase M., Tsuboi S. Determination of methylglyoxal as 2-methylquinoxaline by high-performance liquid chromatography and its application to biological samples. J Chromatogr. 1987 Feb 20;414(1):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(87)80033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. M., Jones R. L., Koenig R. J., Melvin E. T., Lehrman M. L. Reversible hematologic sequelae of diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Apr;86(4):425–429. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-4-425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAABO E., TERKILDSEN T. C. On the enzymatic determination of blood glucose. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1960;12(4):402–407. doi: 10.3109/00365516009065404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray S., Ray M. Isolation of methylglyoxal synthase from goat liver. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):6230–6233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava S. K., Ansari N. H., Hair G. A., Das B. Aldose and aldehyde reductases in human tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Aug 21;800(3):220–227. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90399-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornalley P. J. Monosaccharide autoxidation in health and disease. Environ Health Perspect. 1985 Dec;64:297–307. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8564297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai P. K., Gracy R. W. Isolation and characterization of crystalline methylglyoxal synthetase from Proteus vulgaris. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):364–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uotila L. Purification and characterization of S-2-hydroxyacylglutathione hydrolase (glyoxalase II) from human liver. Biochemistry. 1973 Sep 25;12(20):3944–3951. doi: 10.1021/bi00744a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander Jagt D. L., Han L. P., Lehman C. H. Kinetic evaluation of substrate specificity in the glyoxalase-I-catalyzed disproportionation of -ketoaldehydes. Biochemistry. 1972 Sep 26;11(20):3735–3740. doi: 10.1021/bi00770a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff S. P., Dean R. T. Glucose autoxidation and protein modification. The potential role of 'autoxidative glycosylation' in diabetes. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 1;245(1):243–250. doi: 10.1042/bj2450243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



