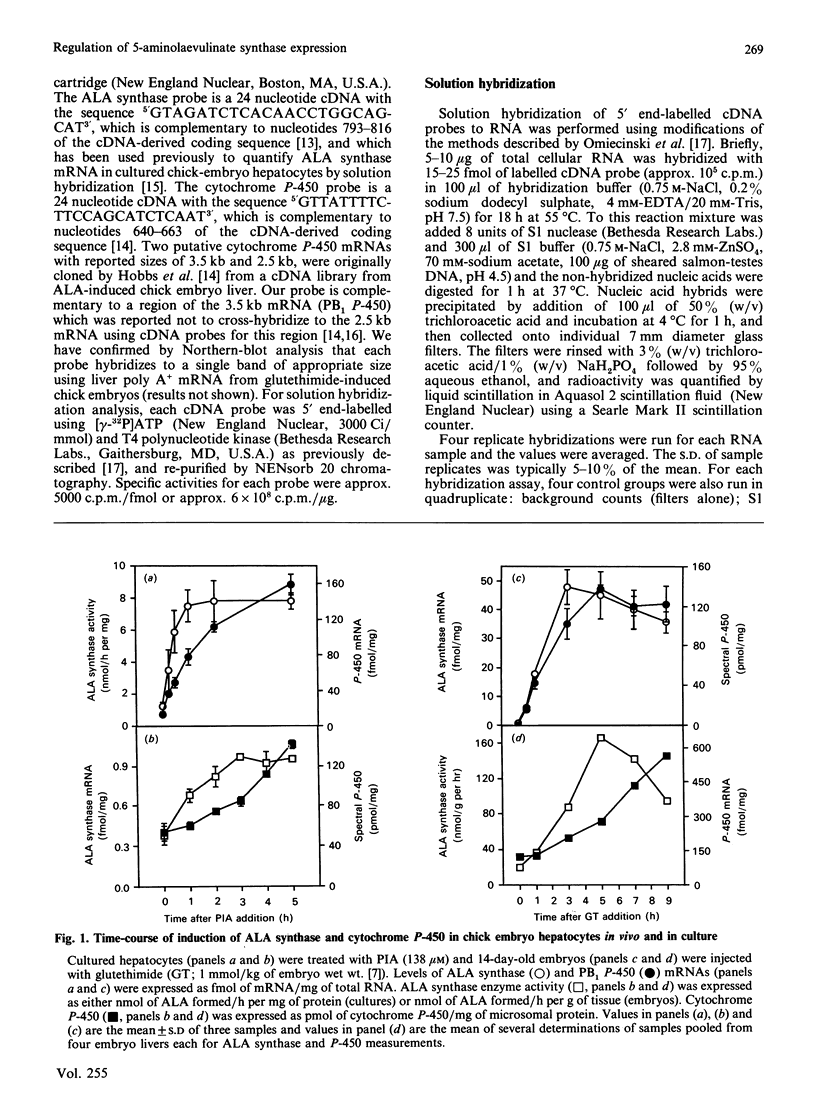
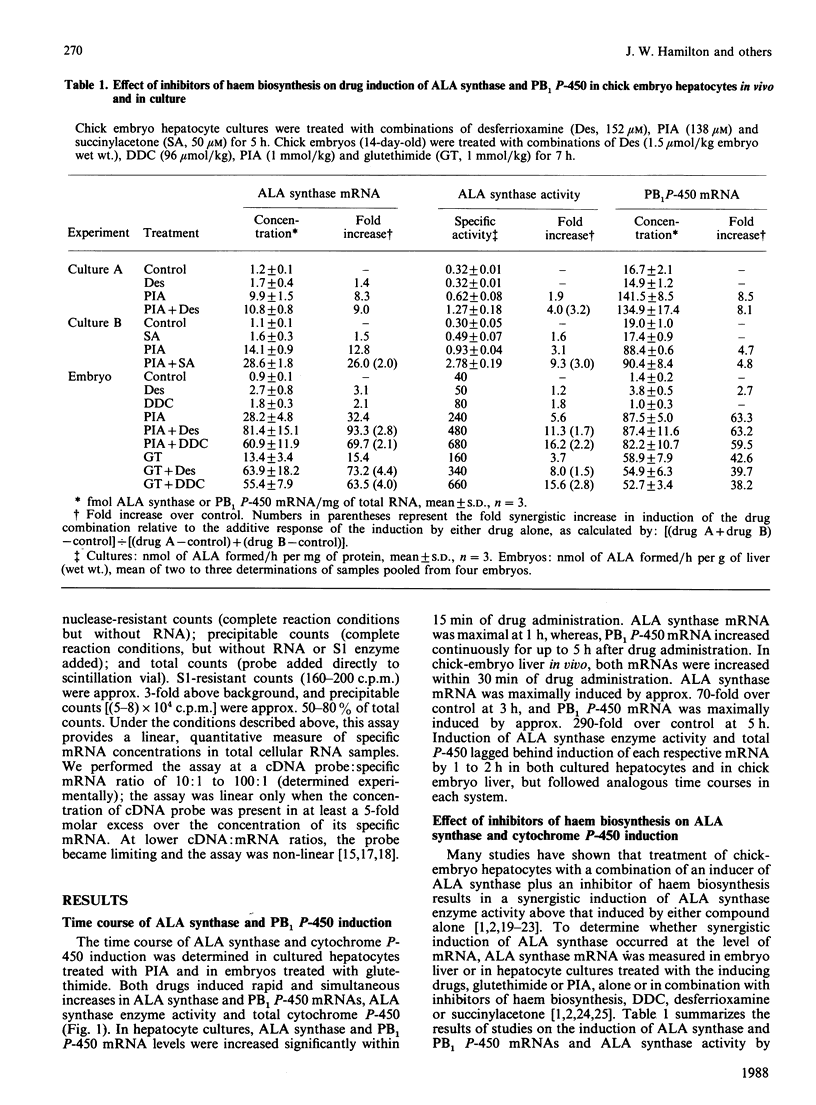
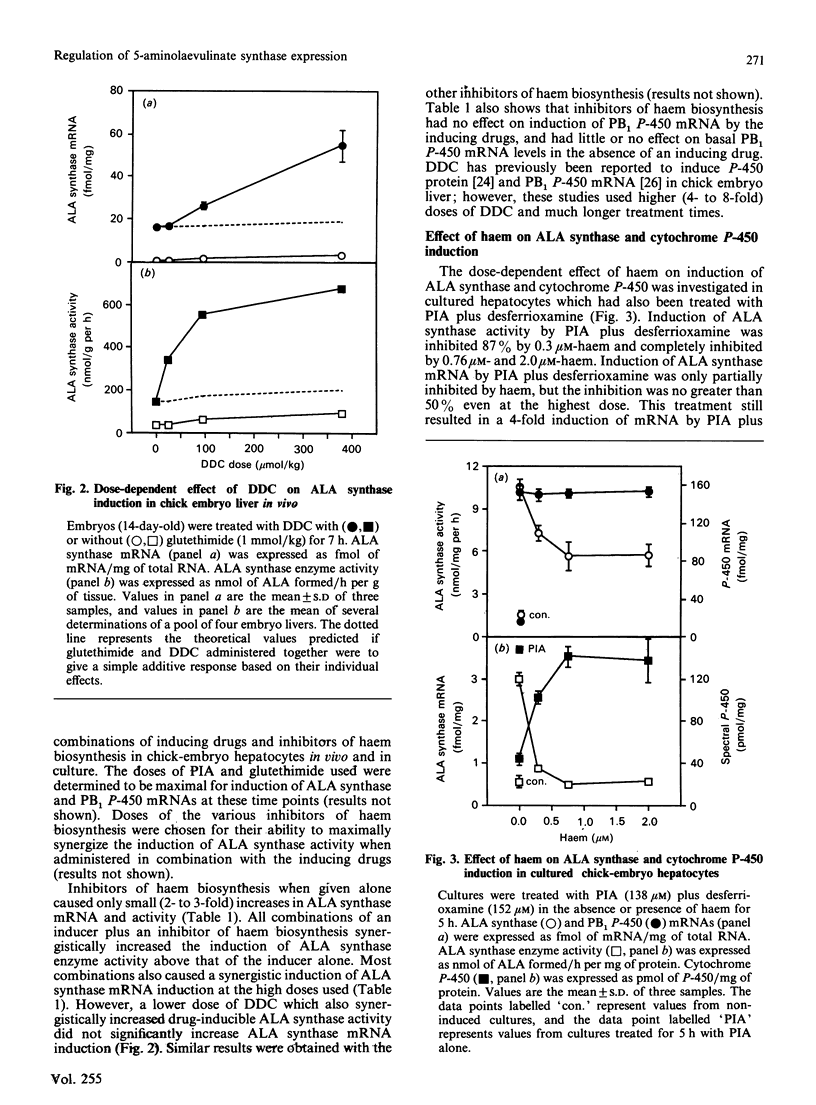
Abstract
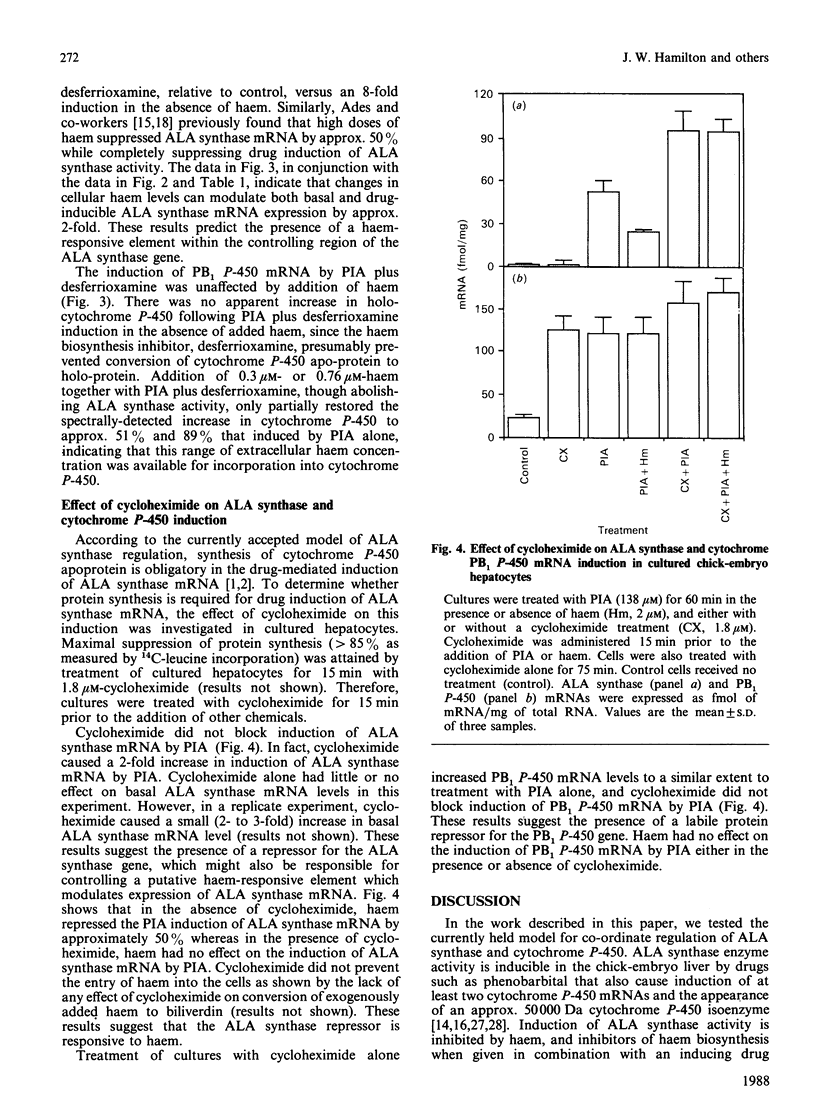
To examine current models for the co-ordinate regulation of 5-aminolaevulinate (ALA) synthase and cytochrome P-450 we have determined the effect of drugs, inhibitors of haem biosynthesis, haem and cycloheximide on the steady-state expression of mRNAs for ALA synthase and a phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450 (PB1 P-450), in chick embryo hepatocytes in vivo and in primary culture. We found that the mRNAs for ALA synthase and PB1 P-450 were rapidly and simultaneously induced by the porphyrinogenic drugs glutethimide and 2-propyl-2-isopropylacetamide. Inhibitors of haem biosynthesis when administered alone had a small effect on ALA synthase mRNA induction, but in combination with the drugs synergistically increased induction of both ALA synthase mRNA and enzyme activity. However, there were concentrations of inhibitors that increased induction of enzyme activity without increasing mRNA induction. Haem suppressed ALA synthase mRNA induction by drugs by only 50%, whereas induction of ALA synthase enzyme activity was completely suppressed. This suppression of ALA synthase mRNA by haem was blocked by cycloheximide treatment which did not block the induction of ALA synthase mRNA by drugs. In fact, cycloheximide synergistically increased the drug induction of ALA synthase mRNA, suggesting the presence of a labile protein factor which may interact with a haem-responsive element of the ALA synthase gene. Cycloheximide treatment alone did not significantly affect ALA synthase mRNA expression, but induced PB1 P-450 mRNA to a similar extent to that caused by porphyrinogenic drugs, suggesting the presence of a labile repressor which modulates PB1 P-450 gene expression. Basal and drug-inducible PB1 P-450 mRNA levels were unaffected by haem or by inhibitors of haem biosynthesis, indicating that the PB1 P-450 gene is not regulated by haem in chick embryo hepatocytes. Our results indicate that drugs simultaneously induce ALA synthase and PB1 P-450 mRNA expression, and that ALA synthase activity is regulated by haem principally at a post-transcriptional site rather than at the transcriptional level.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ades I. Z., Stevens T. M., Drew P. D. Biogenesis of embryonic chick liver delta-aminolevulinate synthase: regulation of the level of mRNA by hemin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Mar;253(2):297–304. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90182-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. E. Effects of antihypertensive drugs on hepatic heme biosynthesis, and evaluation of ferrochelatase inhibitors to simplify testing of drugs for heme pathway induction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 18;543(3):313–327. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat G. J., Rangarajan P. N., Padmanaban G. Differential effects of cycloheximide on rat liver cytochrome P-450 gene transcription in the whole animal and hepatoma cell culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 13;148(3):1118–1123. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80248-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borthwick I. A., Srivastava G., Day A. R., Pirola B. A., Snoswell M. A., May B. K., Elliott W. H. Complete nucleotide sequence of hepatic 5-aminolaevulinate synthase precursor. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Aug 1;150(3):481–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooker J. D., O'Connor R. cDNA cloning and analysis of chick-embryo-liver cytochrome P-450 mRNA induced by porphyrinogenic drugs. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec 15;129(2):325–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07055.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooker J. D., Srivastava G., Borthwick I. A., May B. K., Elliott W. H. Evidence that 2-allyl-2-isopropylacetamide, phenobarbital and 3,5-diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-dihydrocollidine induce the same cytochrome P450 mRNA in chick embryo liver. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Nov 2;136(2):327–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07745.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chianale J., Mulholland L., Traber P. G., Gumucio J. J. Phenobarbital induction of cytochrome P-450 b,e genes is dependent on protein synthesis. Hepatology. 1988 Mar-Apr;8(2):327–331. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Matteis F., Gibbs A. Stimulation of liver 5-aminolaevulinate synthetase by drugs and its relevance to drug-induced accumulation of cytochrome P-450. Studies with phenylbutazone and 3,5-diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-dihydrocollidine. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;126(5):1149–1160. doi: 10.1042/bj1261149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew P. D., Ades I. Z. Regulation of production of embryonic chick liver delta-aminolevulinate synthase: effects of testosterone and of hemin on the mRNA of the enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Oct 15;140(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwarki V. J., Francis V. N., Bhat G. J., Padmanaban G. Regulation of cytochrome P-450 messenger RNA and apoprotein levels by heme. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):16958–16962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granick S., Sinclair P., Sassa S., Grieninger G. Effects by heme, insulin, and serum albumin on heme and protein synthesis in chick embryo liver cells cultured in a chemically defined medium, and a spectrofluorometric assay for porphyrin composition. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 25;250(24):9215–9225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. W., Denison M. S., Bloom S. E. Development of basal and induced aryl hydrocarbon (benzo[a]pyrene) hydroxylase activity in the chicken embryo in ovo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3372–3376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs A. A., Mattschoss L. A., May B. K., Williams K. E., Elliott W. H. The cDNA and protein sequence of a phenobarbital-induced chicken cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9444–9449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel D. I., Estolano M. G., Galeazzi D. R., Whitlock J. P., Jr Superinduction of cytochrome P1-450 gene transcription by inhibition of protein synthesis in wild type and variant mouse hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5648–5653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattschoss L. A., Hobbs A. A., Steggles A. W., May B. K., Elliott W. H. Isolation and characterization of genomic clones for two chicken phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450 genes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9438–9443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May B. K., Borthwick I. A., Srivastava G., Pirola B. A., Elliott W. H. Control of 5-aminolevulinate synthase in animals. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1986;28:233–262. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152828-7.50008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Adesnik M., Coon M. J., Estabrook R. W., Gonzalez F. J., Guengerich F. P., Gunsalus I. C., Johnson E. F., Kemper B., Levin W. The P450 gene superfamily: recommended nomenclature. DNA. 1987 Feb;6(1):1–11. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omiecinski C. J. Tissue-specific expression of rat mRNAs homologous to cytochromes P-450b and P-450e. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1525–1539. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omiecinski C. J., Walz F. G., Jr, Vlasuk G. P. Phenobarbital induction of rat liver cytochromes P-450b and P-450e. Quantitation of specific RNAs by hybridization to synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide probes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3247–3250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike S. F., Shephard E. A., Rabin B. R., Phillips I. R. Induction of cytochrome P-450 by phenobarbital is mediated at the level of transcription. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Jul 15;34(14):2489–2494. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90531-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkind A. B. Maintenance of microsomal hemoprotein concentrations following inhibition of ferrochelatase activity by 3,5-diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-dihydrocollidine in chick embryo liver. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4636–4644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassa S., Granick S. Induction of -aminolevulinic acid synthetase in chick embryo liver cells in cluture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):517–522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassa S., Kappas A. Hereditary tyrosinemia and the heme biosynthetic pathway. Profound inhibition of delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase activity by succinylacetone. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):625–634. doi: 10.1172/JCI110809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassa S., Kappas A. Induction of aminolevulinate synthase and porphyrins in cultured liver cells maintained in chemically defined medium. Permissive effects of hormones on induction process. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2428–2436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair J. F., Sinclair P. R., Bonkowsky H. L. Hormonal requirements for the induction of cytochrome P-450 in hepatocytes cultured in a serum-free medium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Feb 14;86(3):710–717. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91771-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair J. F., Smith L., Bement W. J., Sinclair P. R., Bonkowsky H. L. Increases in cytochrome p-450 in cultured hepatocytes mediated by 3- and 4-carbon alcohols. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Sep 1;31(17):2811–2815. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair P., Granick S. Two methods for determining the activity of delta-aminolevulinate synthetase within intact liver cells in culture. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 1;79(1-2):380–393. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90412-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava G., Borthwick I. A., Maguire D. J., Elferink C. J., Bawden M. J., Mercer J. F., May B. K. Regulation of 5-aminolevulinate synthase mRNA in different rat tissues. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5202–5209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand L. J., Manning J., Marver H. S. The induction of -aminolevulinic acid synthetase in cultured liver cells. The effects of end product and inhibitors of heme synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2820–2827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell D. L., Marks G. S. Drug-induced porphyrin biosynthesis. V. Effect of protohemin on the transcriptional and post-transcriptional phases of -aminolevulinic acid synthetase induction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Aug 1;21(15):2077–2093. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiting M. J., Granick S. Delta-Aminolevulinic acid synthase from chick embryo liver mitochondria. I. Purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1340–1346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr The regulation of cytochrome P-450 gene expression. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1986;26:333–369. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.26.040186.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr The regulation of gene expression by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Pharmacol Rev. 1987 Jun;39(2):147–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]