Abstract
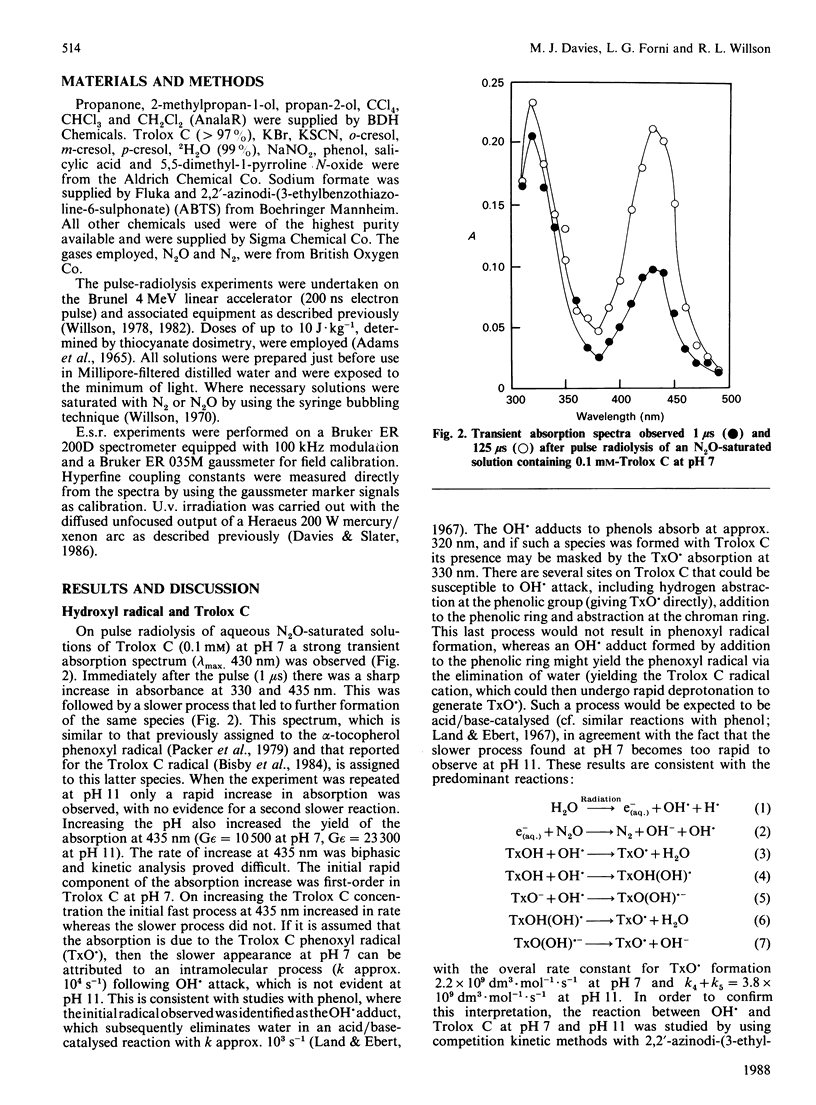
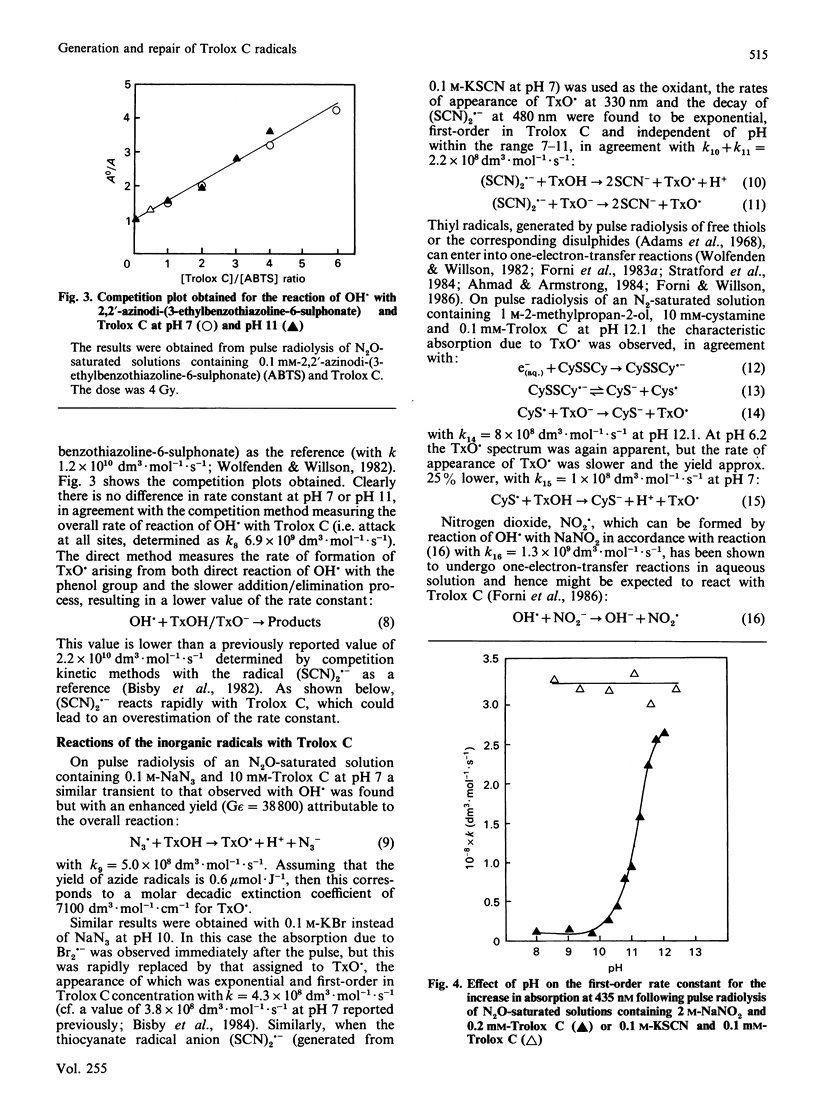
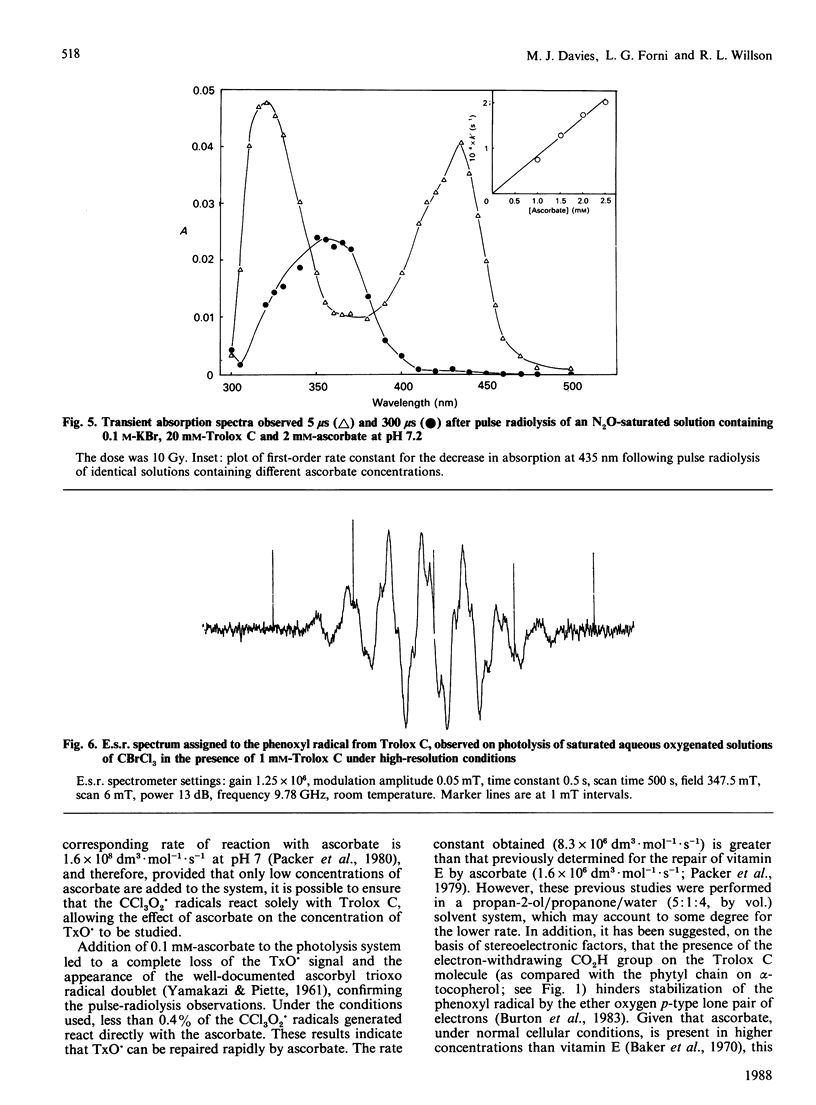
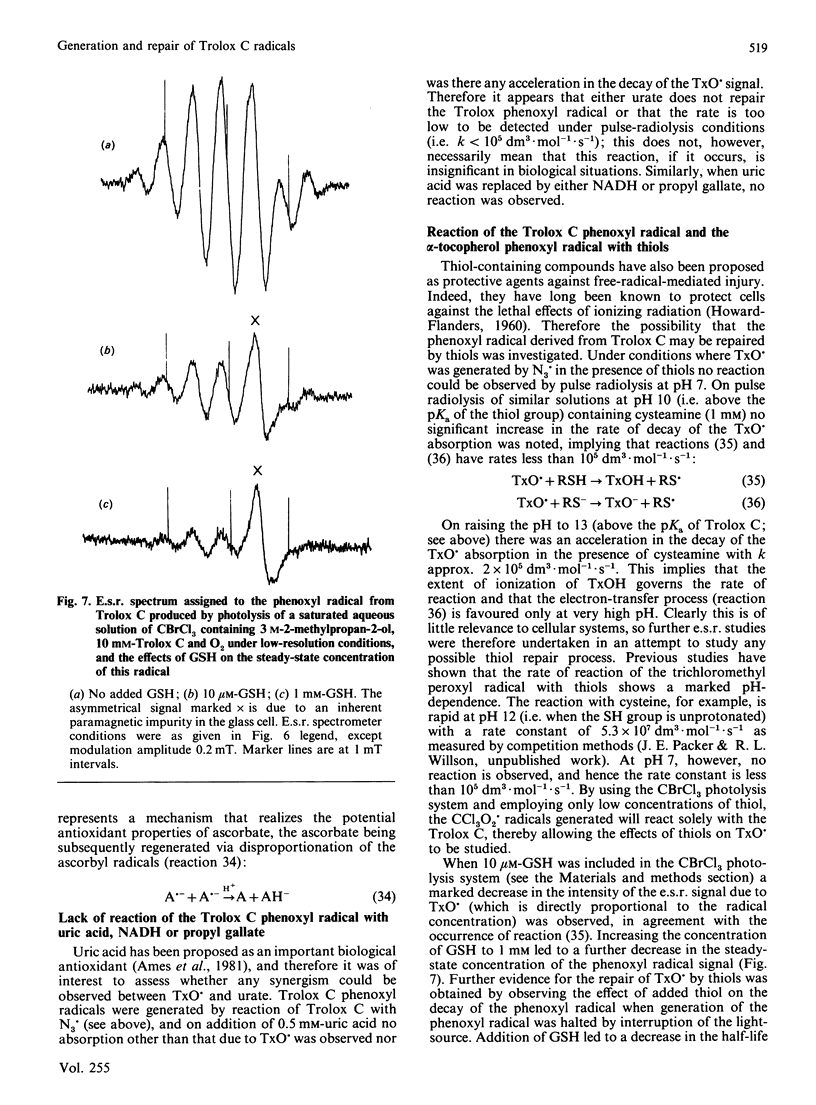
The reactions between Trolox C, a water-soluble vitamin E analogue, and several oxidizing free radicals including the hydroxyl radical and various peroxy radicals were examined by using the pulse-radiolysis technique. The results demonstrate that Trolox C may undergo rapid one-electron-transfer reactions as well as hydrogen-transfer processes; the resulting phenoxyl radical is shown to be relatively stable, in common with the phenoxyl radical derived from vitamin E. The reactions between the Trolox C phenoxyl radical and a variety of biologically relevant reducing compounds were examined by using both pulse radiolysis and e.s.r. The results demonstrate that the Trolox C phenoxyl radical is readily repaired by ascorbate (k = 8.3 x 10(6) dm3.mol-1.s-1) and certain thiols (k less than 10(5) dm3.mol-1.s-1) but not by urate, NADH or propyl gallate. Evidence from e.s.r. studies indicates that thiol-containing compounds may also enter into similar repair reactions with the alpha-tocopherol phenoxyl radical. Kinetic evidence is presented that suggests that Trolox C may 'repair' proteins that have been oxidized by free radicals.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames B. N., Cathcart R., Schwiers E., Hochstein P. Uric acid provides an antioxidant defense in humans against oxidant- and radical-caused aging and cancer: a hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6858–6862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker H., Luisada-Opper A. V., Frank O., Feingold S., Leevy C. M. Effect of CCl4 on the vitamin-protein profile of rat liver subcellular elements. Exp Mol Pathol. 1970 Jun;12(3):306–315. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(70)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bansal K. M., Fessenden R. W. Pulse radiolysis studies of the oxidation of phenols by SO4- and Br2- in aqueous solutions. Radiat Res. 1976 Jul;67(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisby R. H., Ahmed S., Cundall R. B. Repair of amino acid radicals by a vitamin E analogue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Feb 29;119(1):245–251. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91644-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton G. W., Cheeseman K. H., Doba T., Ingold K. U., Slater T. F. Vitamin E as an antioxidant in vitro and in vivo. Ciba Found Symp. 1983;101:4–18. doi: 10.1002/9780470720820.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. J., Forni L. G., Shuter S. L. Electron spin resonance and pulse radiolysis studies on the spin trapping of sulphur-centered radicals. Chem Biol Interact. 1987 Feb;61(2):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(87)90038-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. J., Slater T. F. Electron spin resonance spin trapping studies on the photolytic generation of halocarbon radicals. Chem Biol Interact. 1986 May;58(2):137–147. doi: 10.1016/s0009-2797(86)80093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forni L. G., Packer J. E., Slater T. F., Willson R. L. Reaction of the trichloromethyl and halothane-derived peroxy radicals with unsaturated fatty acids: a pulse radiolysis study. Chem Biol Interact. 1983 Jul 15;45(2):171–177. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(83)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forni L. G., Willson R. L. Thiyl free radicals and the oxidation of ferrocytochrome c. Direct observation of coupled hydrogen-atom- and electron-transfer reactions. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):905–907. doi: 10.1042/bj2400905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuzawa K., Gebicki J. M. Oxidation of alpha-tocopherol in micelles and liposomes by the hydroxyl, perhydroxyl, and superoxide free radicals. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Oct 1;226(1):242–251. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90290-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD-FLANDERS P. Effect of oxygen on the radiosensitivity of bacteriophage in the presence of sulphydryl compounds. Nature. 1960 May 7;186:485–487. doi: 10.1038/186485a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harman L. S., Mottley C., Mason R. P. Free radical metabolites of L-cysteine oxidation. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5606–5611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung H. W., Vang M. J., Mavis R. D. The cooperative interaction between vitamin E and vitamin C in suppression of peroxidation of membrane phospholipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 22;664(2):266–272. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra H. P. Generation of superoxide free radical during the autoxidation of thiols. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2151–2155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niki E., Saito T., Kawakami A., Kamiya Y. Inhibition of oxidation of methyl linoleate in solution by vitamin E and vitamin C. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4177–4182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikimi M., Machlin L. J. Oxidation of alpha-tocopherol model compound by superoxide anion. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Oct;170(2):684–689. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikimi M., Yamada H., Yagi K. Oxidation by superoxide of tocopherols dispersed in aqueous media with deoxycholate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jan 3;627(1):101–108. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa T., Hanaki A., Matsumoto S., Matsuo M. Electron spin resonance studies of radicals obtained by the reaction of alpha-tocopherol and its model compound with superoxide ion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 25;531(1):72–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packer J. E., Mahood J. S., Mora-Arellano V. O., Slater T. F., Willson R. L., Wolfenden B. S. Free radicals and singlet oxygen scavengers: reaction of a peroxy-radical with beta-carotene, diphenyl furan and 1,4-diazobicyclo (2,2,2)-octane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Feb 27;98(4):901–906. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91196-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packer J. E., Slater T. F., Willson R. L. Direct observation of a free radical interaction between vitamin E and vitamin C. Nature. 1979 Apr 19;278(5706):737–738. doi: 10.1038/278737a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packer J. E., Slater T. F., Willson R. L. Reactions of the carbon tetrachloride-related peroxy free radical (CC13O.2) with amino acids: pulse radiolysis evidence. Life Sci. 1978 Dec 25;23(26):2617–2620. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90378-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prütz W. A., Butler J., Land E. J. Phenol coupling initiated by one-electron oxidation of tyrosine units in peptides and histone. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1983 Aug;44(2):183–196. doi: 10.1080/09553008314550981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy C. C., Scholz R. W., Thomas C. E., Massaro E. J. Vitamin E dependent reduced glutathione inhibition of rat liver microsomal lipid peroxidation. Life Sci. 1982 Aug 9;31(6):571–576. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90486-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redpath J. L., Willson R. L. Reducing compounds in radioprotection and radiosensitization: model experiments using ascorbic acid. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1973 Jan;23(1):51–65. doi: 10.1080/09553007314550051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler R. H. Oxidation of ascorbate anion by electron transfer to phenoxyl radicals. Radiat Res. 1977 Mar;69(3):417–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater T. F. Free-radical mechanisms in tissue injury. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 15;222(1):1–15. doi: 10.1042/bj2220001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratford I. J., Adams G. E., Hardy C., Hoe S., O'Neill P., Sheldon P. W. Thiol reactive nitroimidazoles: radiosensitization studies in vitro and in vivo. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1984 Dec;46(6):731–745. doi: 10.1080/09553008414551971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svanholm U., Bechgaard K., Parker V. D. Electrochemistry in media of intermediate acidity. 8. Reversible oxidation products of the alpha-tocopherol model compound. Cation radical, cation, and dication. J Am Chem Soc. 1974 Apr 17;96(8):2409–2413. doi: 10.1021/ja00815a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tappel A. L. Will antioxidant nutrients slow aging processes? Geriatrics. 1968 Oct;23(10):97–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willson R. L. The reaction of oxygen with radiation-induced free radicals in DNA and related compounds. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1970;17(4):349–358. doi: 10.1080/09553007014550411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMAZAKI I., PIETTE L. H. Mechanism of free radical formation and disappearance during the ascorbic acid oxidase and peroxidase reactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Jun 10;50:62–69. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)91060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


