Abstract
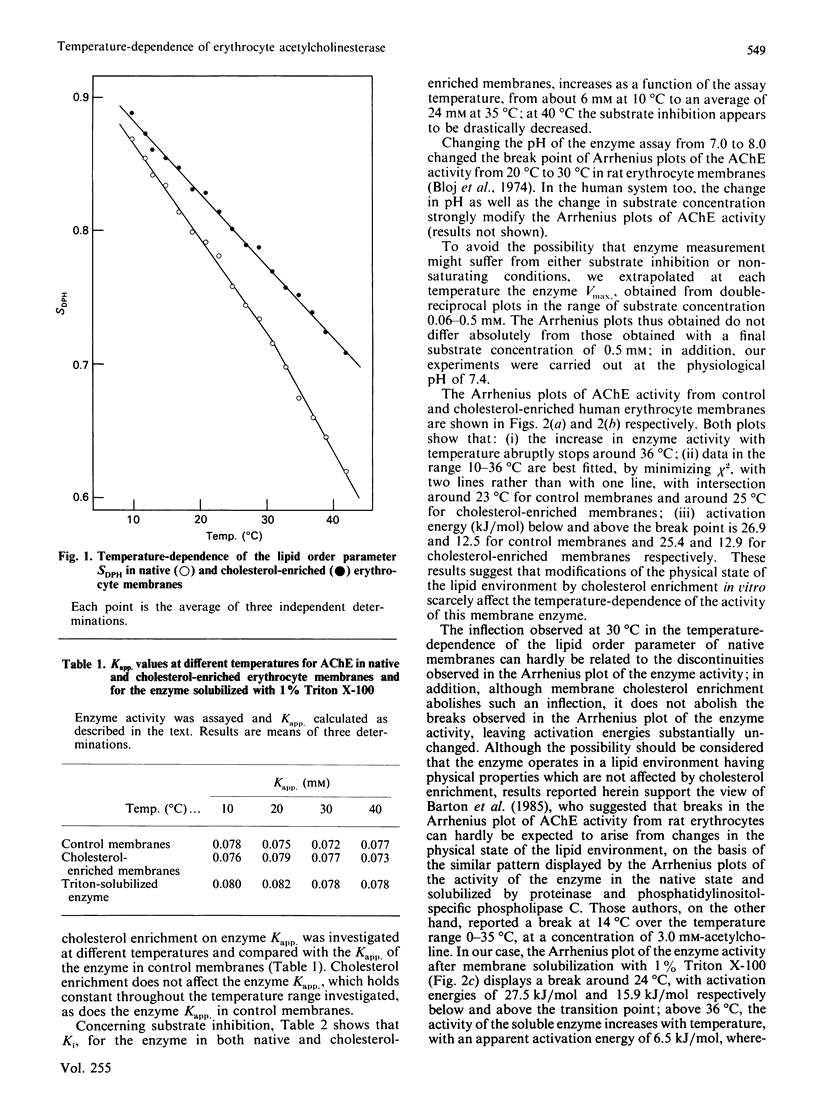
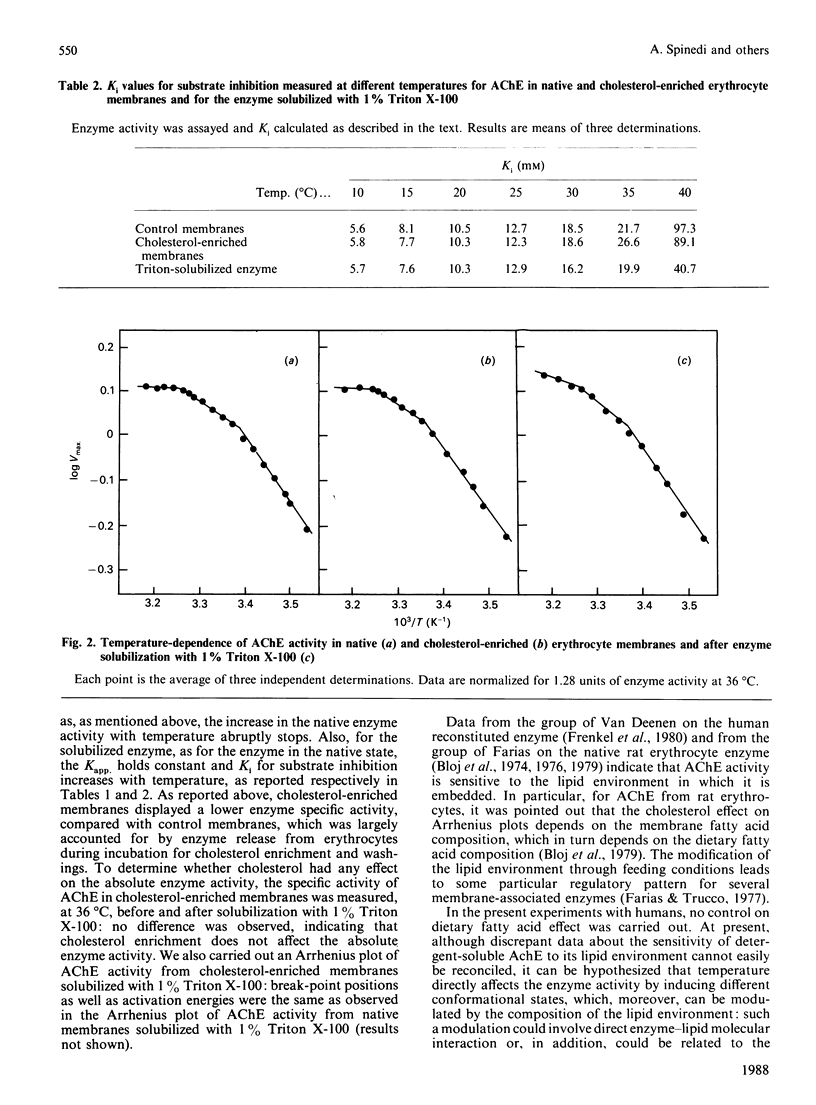
The temperature-dependence of both the lipid order parameter (SDPH) and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity from native and cholesterol-enriched human erythrocyte membranes was investigated. Cholesterol enrichment abolishes an inflection observed around 30 degrees C in the temperature-dependence of native membrane lipid order parameter, whereas the Arrhenius plot of the enzymic activity is substantially unaffected. These results support the view that the breaks in the Arrhenius plot of the enzyme activity are not related to sudden changes of bulk membrane physical state, but arise from a direct effect of temperature on enzyme conformation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aberlin M. E., Litman G. W. Differential perturbation of erythrocyte membrane-associated transport and enzyme activities by structurally related lipophilic compounds. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 3;553(1):96–106. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton P. L., Futerman A. H., Silman I. Arrhenius plots of acetylcholinesterase activity in mammalian erythrocytes and in Torpedo electric organ. Effect of solubilization by proteinases and by a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Biochem J. 1985 Oct 1;231(1):237–240. doi: 10.1042/bj2310237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauregard G., Roufogalis B. D. Characterization of lipid-protein interactions in acetylcholinesterase lipoprotein extracted from bovine erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1979 Apr 1;179(1):109–117. doi: 10.1042/bj1790109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauregard G., Roufogalis B. D. Involvement of calcium ions in the properties of cardiolipin-associated erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 19;557(1):102–111. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90093-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloj B., Galo M. G., Morero R. D., Farias R. N. Kinetic modifications of the acetylcholinesterase and (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase in rat erythrocytes by cholesterol feeding. J Nutr. 1976 Dec;106(12):1827–1834. doi: 10.1093/jn/106.12.1827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloj B., Galo M. G., Morero R. D., Farías R. N. Heterogeneous effect of dietary cholesterol on acetylcholinesterase and ATPases of rat erythrocytes: Arrhenius plots. J Nutr. 1979 Jan;109(1):63–69. doi: 10.1093/jn/109.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloj B., Morero R. D., Farías R. N. Effect of essential fatty acid deficiency on the arrhenius plot of acetylcholinesterase from rat erythrocytes. J Nutr. 1974 Oct;104(10):1265–1272. doi: 10.1093/jn/104.10.1265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deliconstantinos G., Tsakiris S. Differential effect of anionic and cationic drugs on the synaptosome-associated acetylcholinesterase activity of dog brain. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 1;229(1):81–86. doi: 10.1042/bj2290081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devaux P. F., Seigneuret M. Specificity of lipid-protein interactions as determined by spectroscopic techniques. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jun 12;822(1):63–125. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(85)90004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta-Choudhury T. A., Rosenberry T. L. Human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase is an amphipathic protein whose short membrane-binding domain is removed by papain digestion. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5653–5660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L., COURTNEY K. D., ANDRES V., Jr, FEATHER-STONE R. M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1961 Jul;7:88–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farías R. N., Trucco R. E. Membrane structure and function with different lipid-supplemented diets. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1977;83:591–607. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3276-3_53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel E. J., Roelofsen B., Brodbeck U., van Deenen L. L., Ott P. Lipid-protein interactions in human erythrocyte-membrane acetylcholinesterase. Modulation of enzyme activity by lipids. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(2):377–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04804.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futerman A. H., Low M. G., Michaelson D. M., Silman I. Solubilization of membrane-bound acetylcholinesterase by a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. J Neurochem. 1985 Nov;45(5):1487–1494. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas R., Brandt P. T., Knight J., Rosenberry T. L. Identification of amine components in a glycolipid membrane-binding domain at the C-terminus of human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3098–3105. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Incerpi S., Baldini P., Luly P. Cholesterol modulation in vitro of plasma membrane-bound enzymes in human erythrocytes. Cell Mol Biol. 1983;29(4):285–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inestrosa N. C., Roberts W. L., Marshall T. L., Rosenberry T. L. Acetylcholinesterase from bovine caudate nucleus is attached to membranes by a novel subunit distinct from those of acetylcholinesterases in other tissues. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4441–4444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Futerman A. H., Ackermann K. E., Sherman W. R., Silman I. Removal of covalently bound inositol from Torpedo acetylcholinesterase and mammalian alkaline phosphatases by deamination with nitrous acid. Evidence for a common membrane-anchoring structure. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 15;241(2):615–619. doi: 10.1042/bj2410615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massoulié J., Bon S. The molecular forms of cholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase in vertebrates. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1982;5:57–106. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.05.030182.000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzanti L., Pastuszko A., Lenaz G. Effects of ketamine anesthesia on rat-brain membranes: fluidity changes and kinetics of acetylcholinesterase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Sep 25;861(1):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90376-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogiso T., Iwaki M., Mori K. Fluidity of human erythrocyte membrane and effect of chlorpromazine on fluidity and phase separation of membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 7;649(2):325–335. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90422-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott P. Membrane acetylcholinesterases: purification, molecular properties and interactions with amphiphilic environments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Dec 9;822(3-4):375–392. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(85)90016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. L., Rosenberry T. L. Identification of covalently attached fatty acids in the hydrophobic membrane-binding domain of human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Dec 17;133(2):621–627. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90950-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. L., Rosenberry T. L. Selective radiolabeling and isolation of the hydrophobic membrane-binding domain of human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3091–3098. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberry T. L., Scoggin D. M. Structure of human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Characterization of intersubunit disulfide bonding and detergent interaction. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5643–5652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinitzky M., Barenholz Y. Fluidity parameters of lipid regions determined by fluorescence polarization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 15;515(4):367–394. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(78)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silvius J. R., Read B. D., McElhaney R. N. Membrane enzymes: artifacts in Arrhenius plots due to temperature dependence of substrate-binding affinity. Science. 1978 Feb 24;199(4331):902–904. doi: 10.1126/science.146257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinedi A., Rufini S., Luly P. Lipid composition and temperature adaptation of the nervous system of the leech Hirudo medicinalis L. J Neurochem. 1987 Jul;49(1):45–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb03392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K. I., Ohnishi S. Heterogeneity in the fluidity of intact erythrocyte membrane and its homogenization upon hemolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Mar 5;426(2):218–231. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90333-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Blitterswijk W. J., Van Hoeven R. P., Van der Meer B. W. Lipid structural order parameters (reciprocal of fluidity) in biomembranes derived from steady-state fluorescence polarization measurements. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 22;644(2):323–332. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90390-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whetton A. D., Gordon L. M., Houslay M. D. Elevated membrane cholesterol concentrations inhibit glucagon-stimulated adenylate cyclase. Biochem J. 1983 Feb 15;210(2):437–449. doi: 10.1042/bj2100437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedmer T., Di Francesco C., Brodbeck U. Effects of amphiphiles on structure and activity of human erythrocyte membrane acetylcholinesterase. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Dec;102(1):59–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb06262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



