Abstract
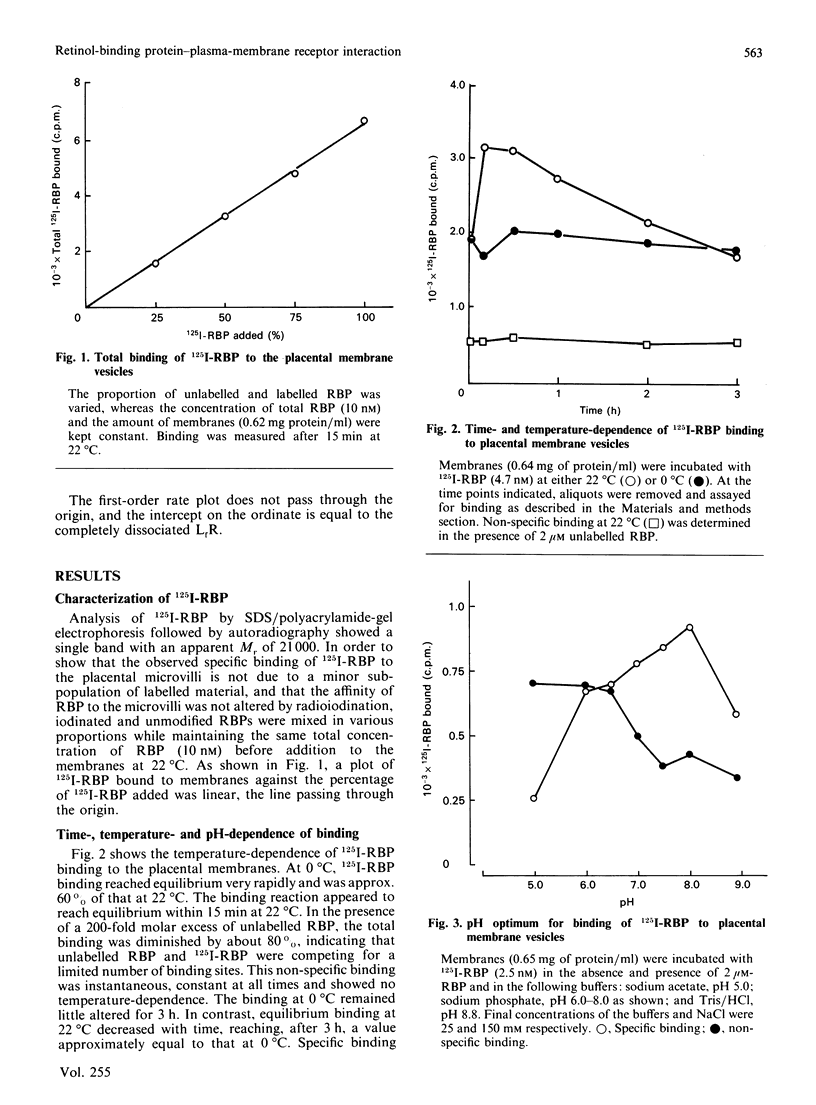
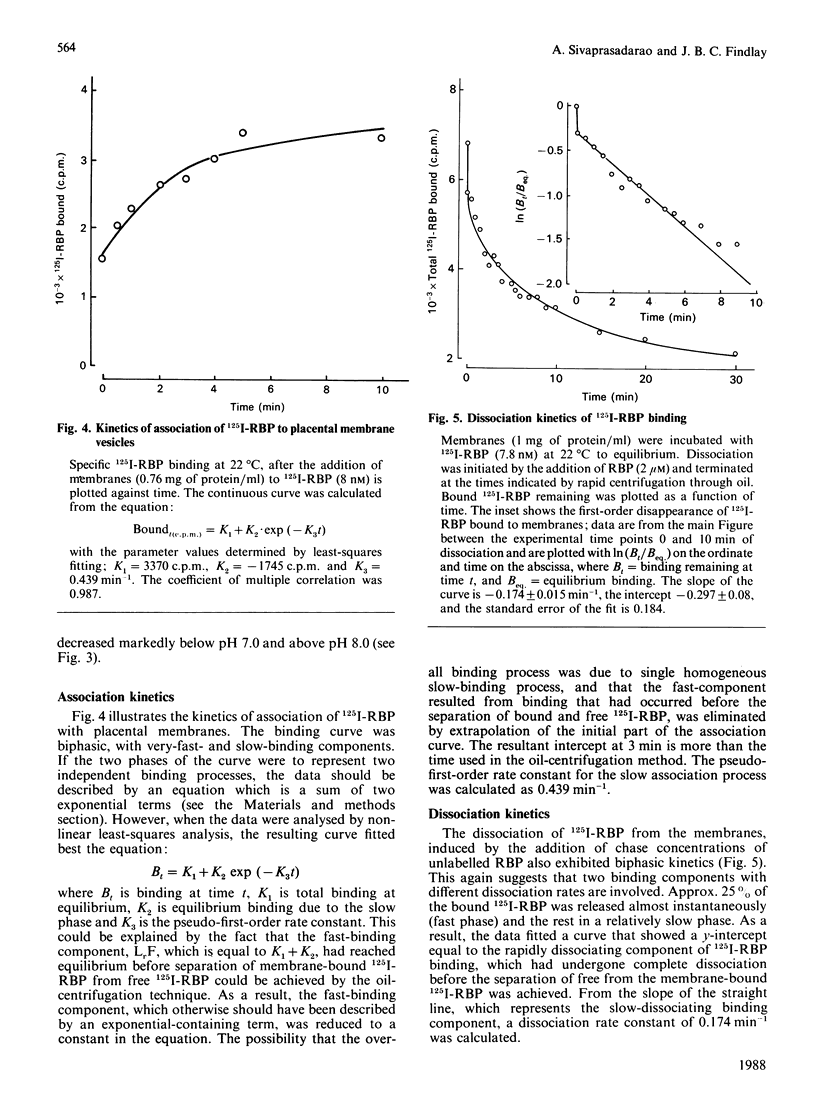
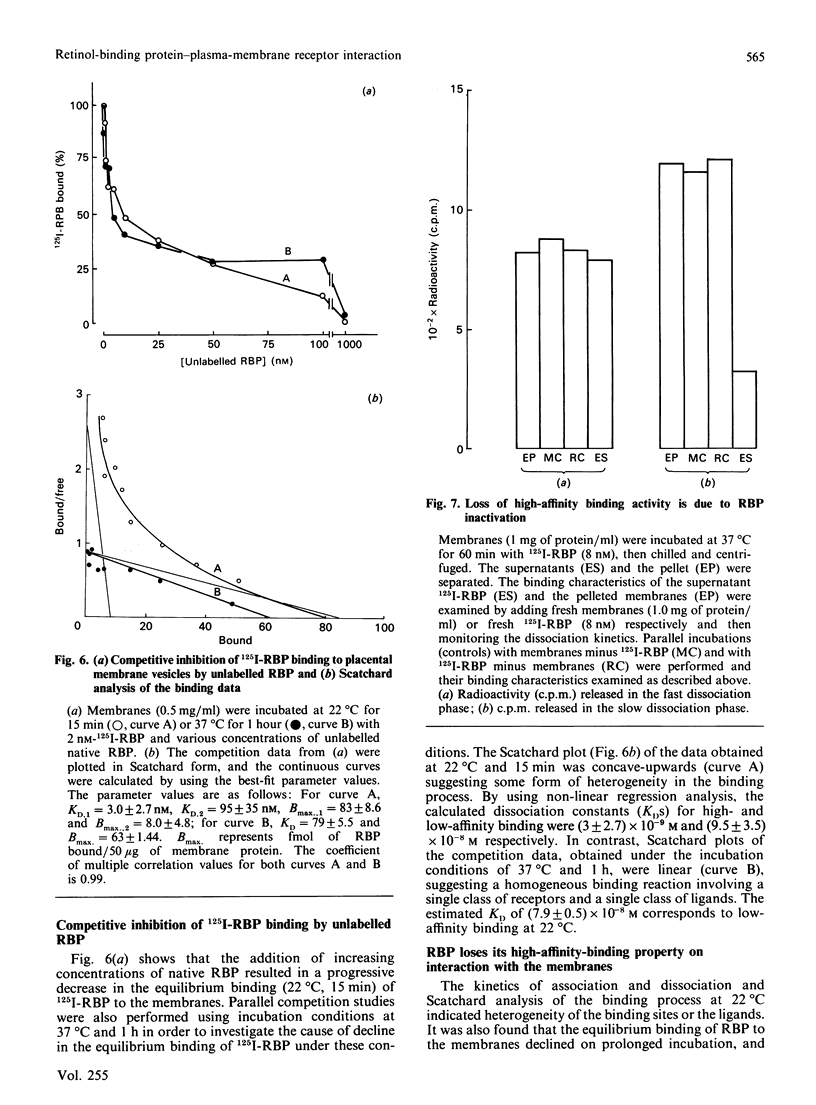
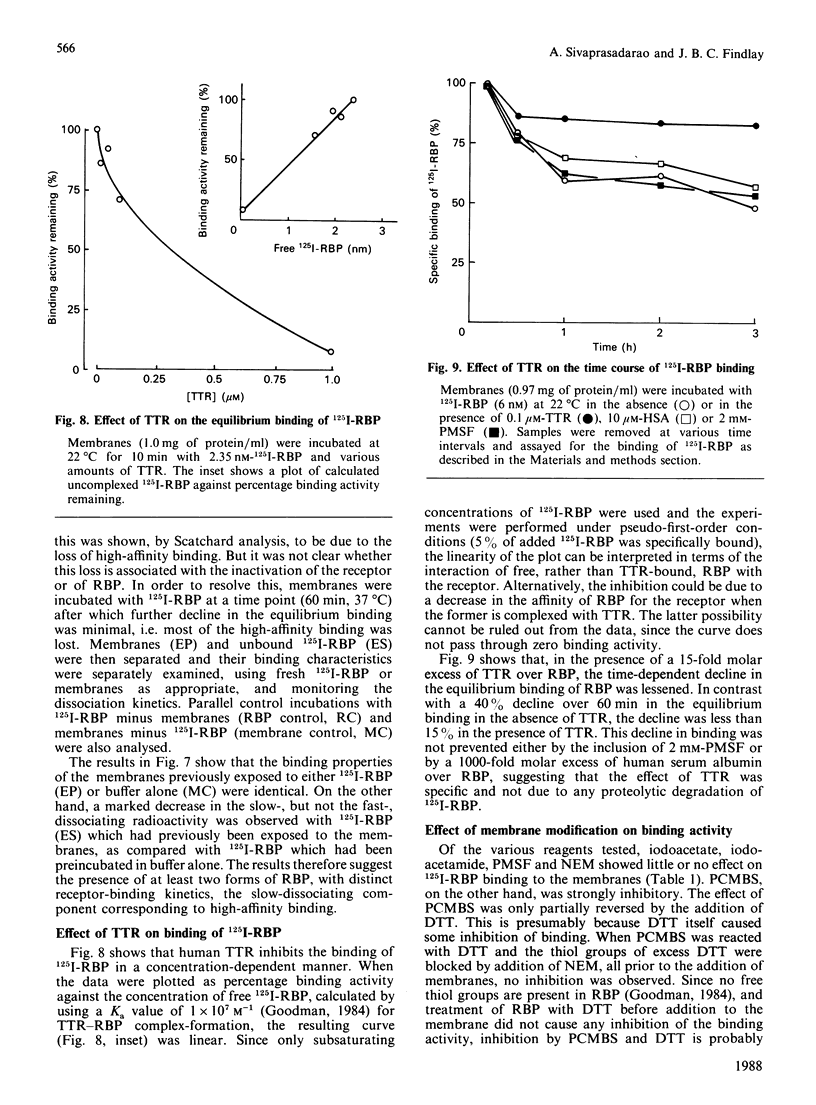
125I-labelled retinol-binding protein (RBP) bound to specific receptors in human placental brush-border membranes. Binding at 22 degrees C reached equilibrium within 15 min, but prolonged incubation caused a subsequent decline. Scatchard analysis of the equilibrium binding data at 22 degrees C and 15 min showed high-(3.0 +/- 2.7 x 10(-9) M) and low-(9.5 +/- 3.5 x 10(-8) M) affinity binding components. 125I-RBP, bound to membranes at 22 degrees C for 15 min and subsequently dissociated with excess unlabelled RBP, exhibited biphasic dissociation kinetics consisting of fast and slow components of release. In contrast, Scatchard analysis and dissociation kinetics of the binding that had taken place at 37 degrees C for 1 h showed the fast-dissociating/low-affinity binding component, but little of the slow-dissociating/higher-affinity binding component. When 125I-RBP, after incubation with membranes at 37 degrees C for 1 h, was re-isolated and subjected to dissociation kinetic analysis using a fresh batch of membranes, the fast-dissociating phase was unchanged, but the slow phase was almost absent. The complex kinetics were interpreted in terms of a heterogeneity in RBP consisting of high- and low-affinity binding forms. The higher-affinity-binding form is thought to be converted into the lower-affinity state on binding to the receptor. Transthyretin inhibited 125I-RBP binding to the membrane, suggesting that free, rather than transthyretin-associated, RBP bound to the receptor. The RBP receptor was trypsin-, heat- and thiol-group-specific-reagent sensitive and was highly specific for RBP.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barclay P. L., Findlay J. B. Labelling of the cytoplasmic domains of ovine rhodopsin with hydrophilic chemical probes. Biochem J. 1984 May 15;220(1):75–84. doi: 10.1042/bj2200075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benga G., Popescu O., Pop V. I., Holmes R. P. p-(Chloromercuri)benzenesulfonate binding by membrane proteins and the inhibition of water transport in human erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 8;25(7):1535–1538. doi: 10.1021/bi00355a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomhoff R., Norum K. R., Berg T. Hepatic uptake of [3H]retinol bound to the serum retinol binding protein involves both parenchymal and perisinusoidal stellate cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13571–13575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth A. G., Olaniyan R. O., Vanderpuye O. A. An improved method for the preparation of human placental syncytiotrophoblast microvilli. Placenta. 1980 Oct-Dec;1(4):327–336. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4004(80)80034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. C., Heller J., Ding L. L., Horwitz J. Retinol transfer from rat liver cytosol retinyl ester lipoprotein complex to serum retinol-binding protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Apr 1;207(2):392–398. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. C., Heller J. Uptake of retinol and retinoic acid from serum retinol-binding protein by retinal pigment epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5216–5221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Hollenberg M. D. Membrane receptors and hormone action. Adv Protein Chem. 1976;30:251–451. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60481-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller J. Interactions of plasma retinol-binding protein with its receptor. Specific binding of bovine and human retinol-binding protein to pigment epithelium cells from bovine eyes. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):3613–3619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketis M. V., Grant C. W. Co-operative binding of concanavalin A to a glycoprotein in lipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jul 28;689(2):194–202. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90251-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire B. W., Chytil F. Three-step purification of retinol-binding protein from rat serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Feb 27;621(2):324–331. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90184-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomer M. E., Jones T. A., Aqvist J., Sundelin J., Eriksson U., Rask L., Peterson P. A. The three-dimensional structure of retinol-binding protein. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1451–1454. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01995.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rask L., Geijer C., Bill A., Peterson P. A. Vitamin A supply of the cornea. Exp Eye Res. 1980 Aug;31(2):201–211. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(80)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rask L., Peterson P. A. In vitro uptake of vitamin A from the retinol-binding plasma protein to mucosal epithelial cells from the monkey's small intestine. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 25;251(20):6360–6366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rask L., Peterson P. A., Nilsson S. F. The subunit structure of human thyroxine-binding prealbumin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 10;246(19):6087–6097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandblom P., Aqvist J., Jones T. A., Newcomer M. E., van Gunsteren W. F., Tapia O. Structural changes in retinol binding protein induced by retinol removal. A molecular dynamics study. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 14;139(2):564–570. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivaprasadarao A., Findlay J. B. The mechanism of uptake of retinol by plasma-membrane vesicles. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 15;255(2):571–579. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. E., Milch P. O., Muto Y., Goodman D. S. The plasma transport and metabolism of retinoic acid in the rat. Biochem J. 1973 Apr;132(4):821–827. doi: 10.1042/bj1320821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi Y. I., Smith J. E., Goodman D. S. Vitamin A and retinol-binding protein metabolism during fetal development in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1977 Oct;233(4):E263–E272. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1977.233.4.E263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf G. Multiple functions of vitamin A. Physiol Rev. 1984 Jul;64(3):873–937. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.3.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


