Abstract
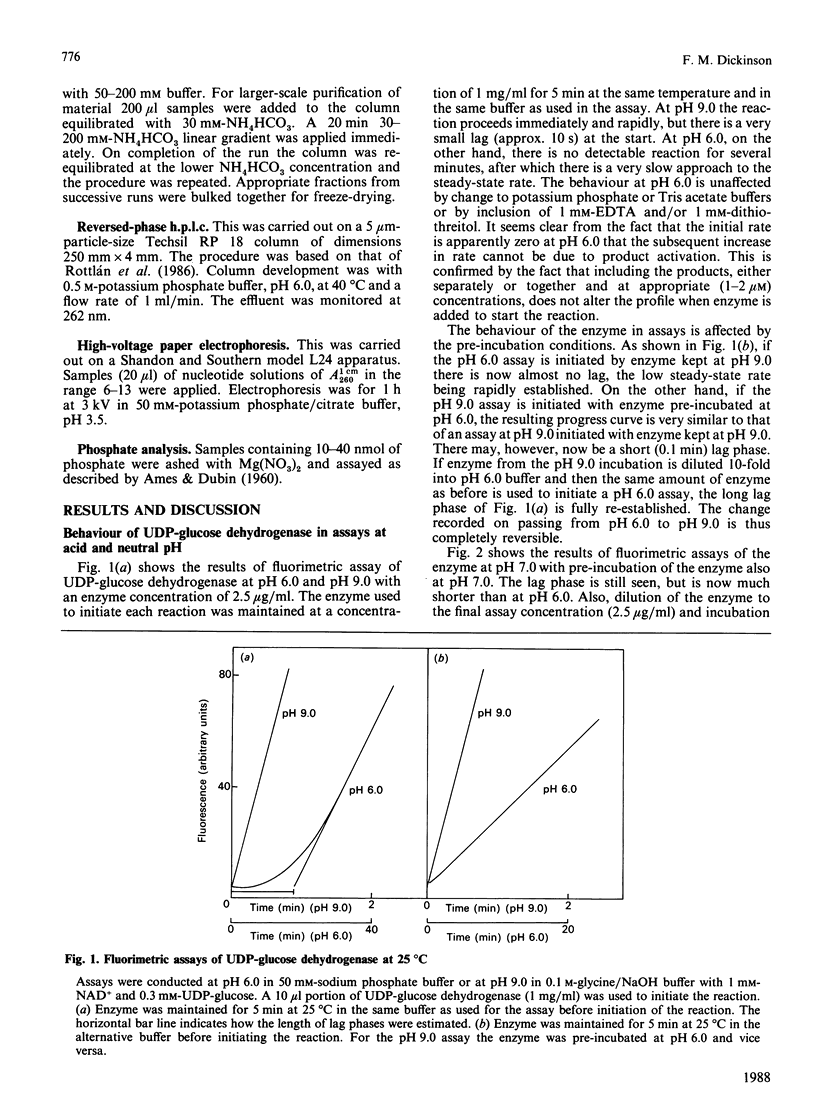
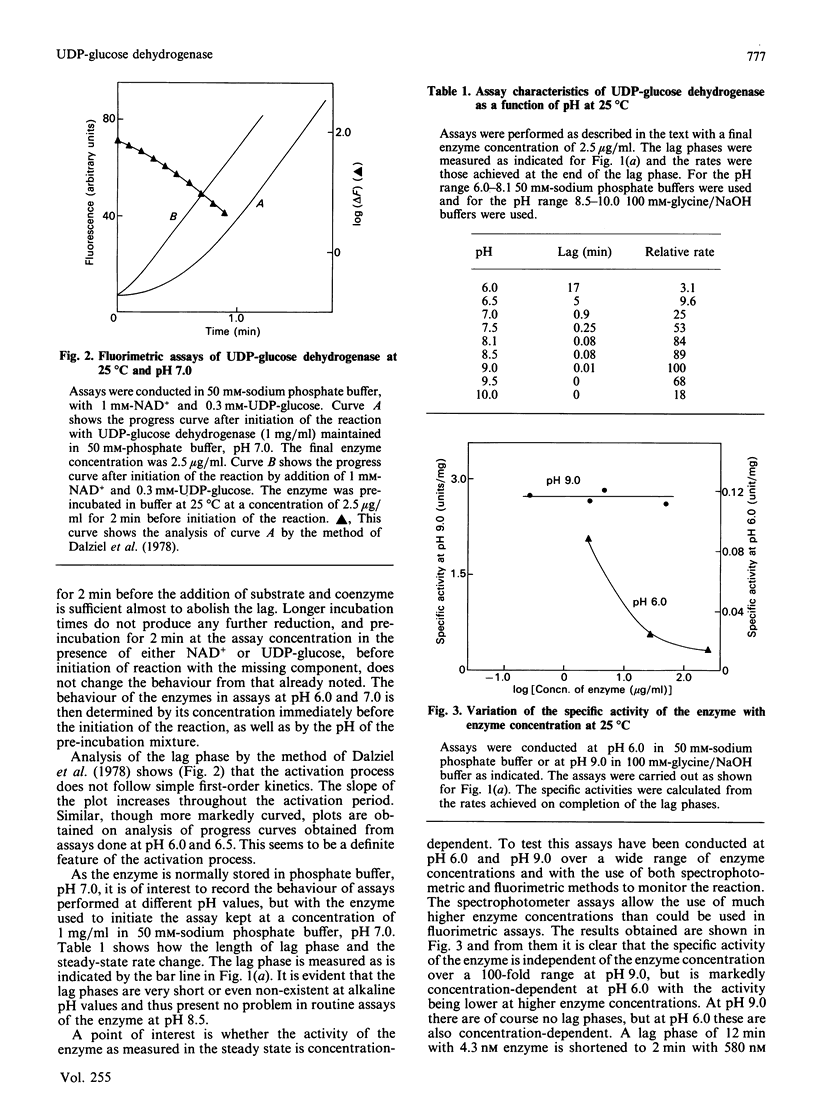
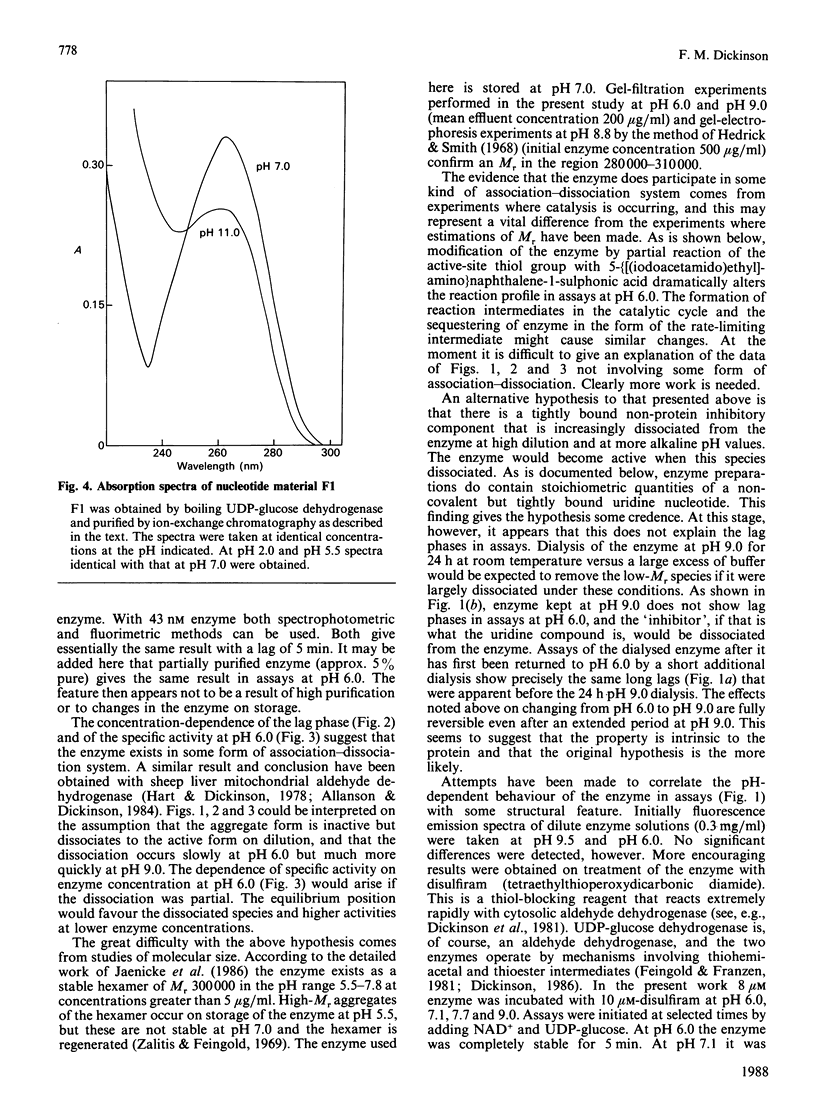
Assays of UDP-glucose dehydrogenase at pH 6.0 show long (10-15 min) lag periods before the steady-state rate is established, but at pH 9.0 no lag is observed. At intermediate pH values the lag is progressively shorter as the pH becomes more alkaline. The behaviour of the enzyme in assays at neutral and acid pH depends on the pH and concentration of the enzyme used to initiate the assay. The steady-state rate at pH 6.0 is strongly concentration-dependent. It is suggested that these phenomena arise because of the slow dissociation of an inactive enzyme species to an active one. Purified preparations of the enzyme release approx. 1 mol of a UDP-sugar/mol of enzyme subunit on denaturation. The identity of the UDP-sugar is unknown.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allanson S., Dickinson F. M. The removal of cytosolic-type aldehyde dehydrogenase from preparations of sheep liver mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase and the unusual properties of the purified mitochondrial enzyme in assays. Biochem J. 1984 Nov 15;224(1):163–169. doi: 10.1042/bj2240163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALZIEL K. Kinetic studies of liver alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1962 Aug;84:244–254. doi: 10.1042/bj0840244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalziel K., McFerran N., Matthews B., Reynolds C. H. Transient kinetics of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate-linked isocitrate dehydrogenase from bovine heart mitochondria. Biochem J. 1978 Jun 1;171(3):743–750. doi: 10.1042/bj1710743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson F. M., Hart G. J., Kitson T. M. The use of pH-gradient ion-exchange chromatography to separate sheep liver cytoplasmic aldehyde dehydrogenase from mitochondrial enzyme contamination, and observations on the interaction between the pure cytoplasmic enzyme and disulfiram. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 1;199(3):573–579. doi: 10.1042/bj1990573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson F. M., Haywood G. W. The effects of Mg2+ on certain steps in the mechanisms of the dehydrogenase and esterase reactions catalysed by sheep liver aldehyde dehydrogenase. Support for the view that dehydrogenase and esterase activities occur at the same site on the enzyme. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 1;233(3):877–883. doi: 10.1042/bj2330877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson F. M., Haywood G. W. The role of the metal ion in the mechanism of the K+-activated aldehyde dehydrogenase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 15;247(2):377–384. doi: 10.1042/bj2470377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson F. M. Studies on the mechanism of sheep liver cytosolic aldehyde dehydrogenase. The effect of pH on the aldehyde binding reactions and a re-examination of the problem of the site of proton release in the mechanism. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 15;238(1):75–82. doi: 10.1042/bj2380075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson F. M. Studies on the mechanism of sheep liver cytosolic aldehyde dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1985 Jan 1;225(1):159–165. doi: 10.1042/bj2250159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccleston E. D., Thayer M. L., Kirkwood S. Mechanisms of action of histidinol dehydrogenase and UDP-Glc dehydrogenase. Evidence that the half-reactions proceed on separate subunits. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11399–11404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzen J. S., Marchetti P. S., Feingold D. S. Resonance energy transfer between catalytic sites of bovine liver uridine diphosphoglucose dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 23;19(26):6080–6089. doi: 10.1021/bi00567a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzen J. S., Marchetti P. S., Lockhart A. H., Feingold D. S. Special effects of UDP-sugar binding to bovine liver uridine diphosphoglucose dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 16;746(3):146–153. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90068-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. J., Dickinson F. M. Kinetic properties of aldehyde dehydrogenase from sheep liver mitochondria. Biochem J. 1978 Dec 1;175(3):899–908. doi: 10.1042/bj1750899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick J. L., Smith A. J. Size and charge isomer separation and estimation of molecular weights of proteins by disc gel electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90569-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenicke R., Rudolph R., Feingold D. S. Dissociation and in vitro reconstitution of bovine liver uridine diphosphoglucose dehydrogenase. The paired subunit nature of the enzyme. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7283–7287. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley W. P., Houchins J. P., Kirkwood S. Mechanism of action of uridine diphosphoglucose dehydrogenase. Evidence for a second reversible dehydrogenation step involving an essential thiol group. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8761–8767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotllán P., Liras A., Llorente P. A set of procedures for resolving purine compounds by reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography: application to the study of purine nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolism. Anal Biochem. 1986 Dec;159(2):377–385. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90356-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalitis J., Feingold D. S. Purification and properties of UDPG dehydrogenase from beef liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Jul;132(2):457–465. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90389-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


