Abstract
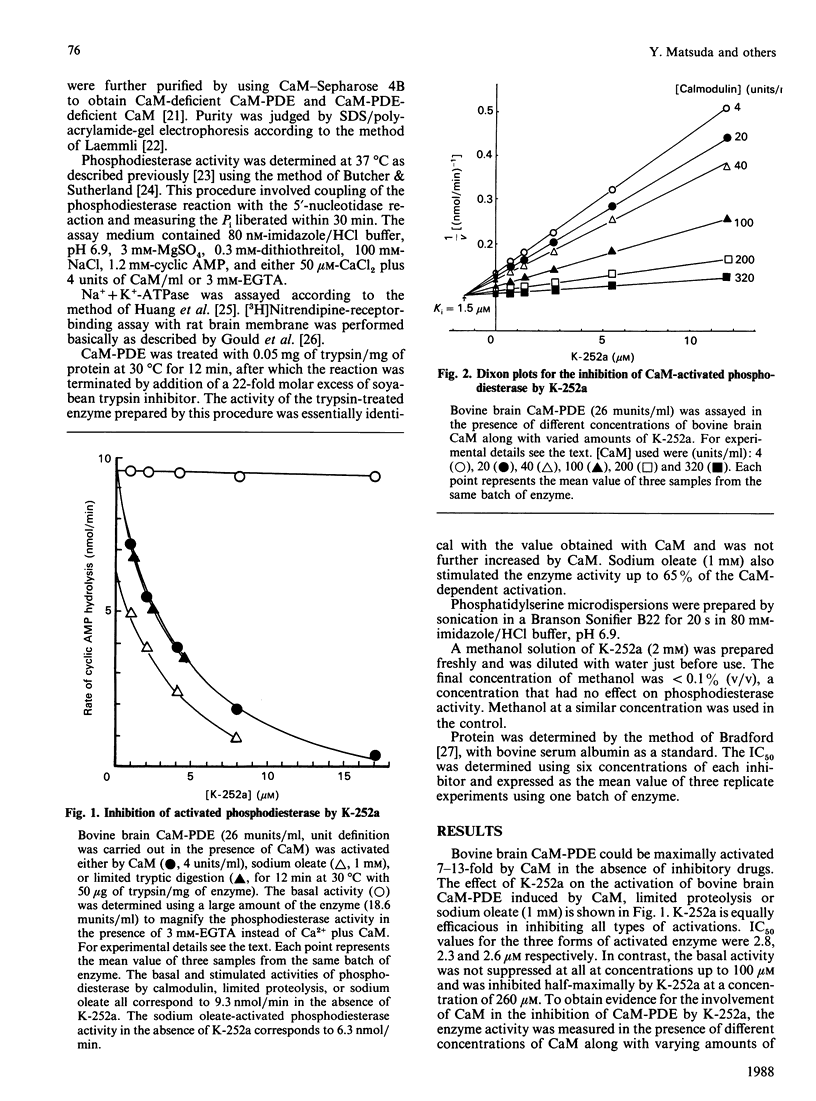
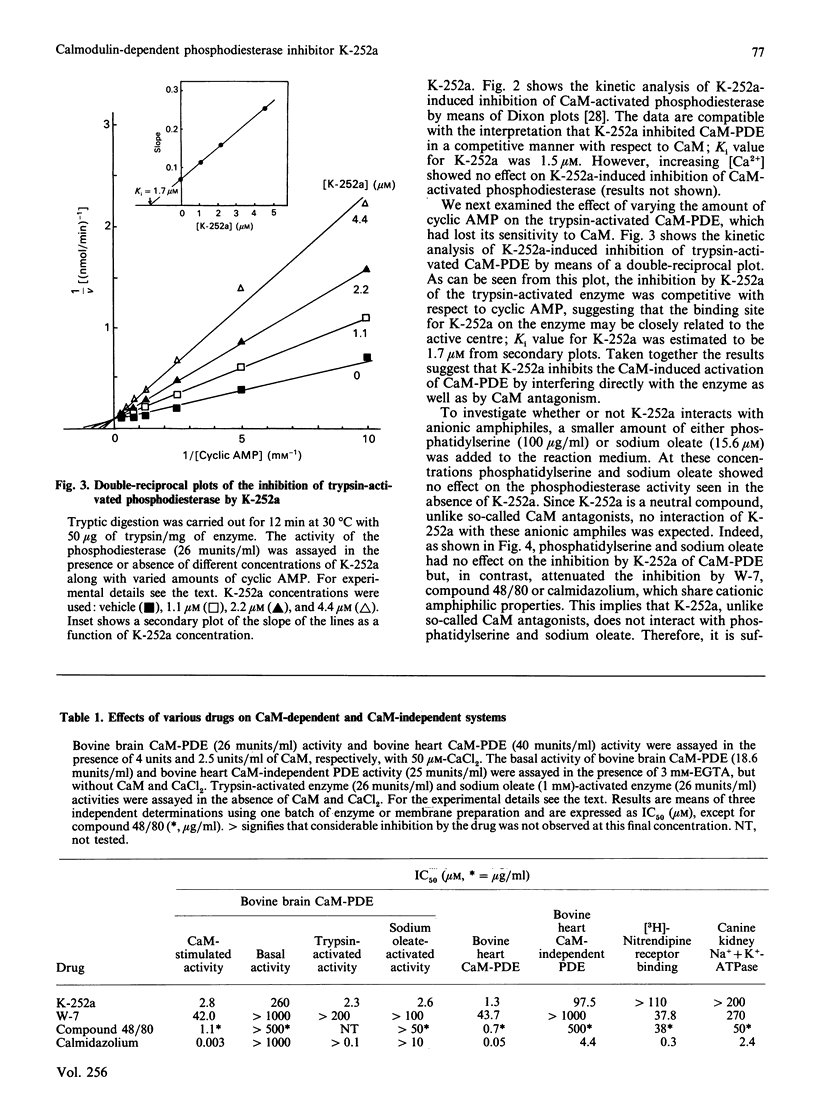
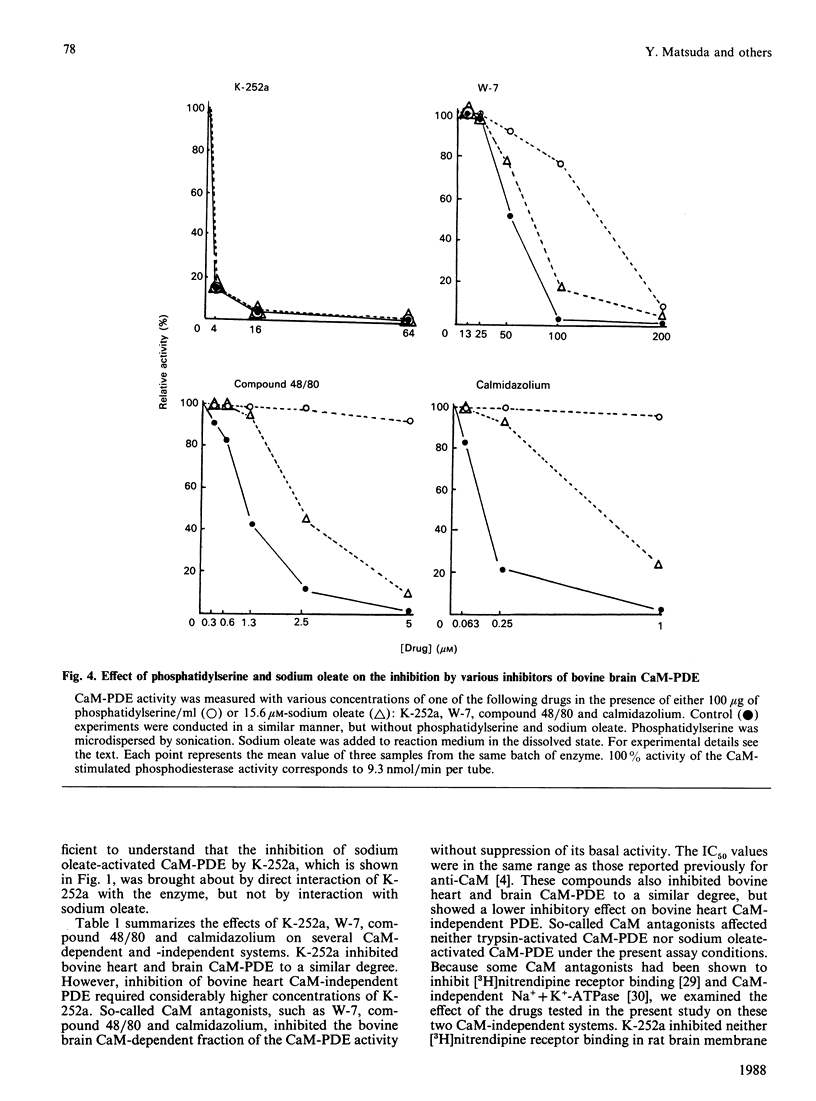
K-252a, an indole carbazol compound of microbial origin, inhibited activation of bovine brain phosphodiesterase induced by calmodulin (CaM), sodium oleate, or limited proteolysis with almost equal potency. Kinetic analysis revealed that the CaM-activated phosphodiesterase (CaM-PDE) was competitively inhibited by K-252a with respect to CaM. On the other hand, inhibition of the trypsin-activated phosphodiesterase was competitive with respect to cyclic AMP. Addition of a lower amount of phosphatidylserine or sodium oleate to the reaction medium was efficacious in attenuating the inhibition of the CaM-PDE by W-7, compound 48/80, or calmidazolium but, in contrast, had no effect on the inhibition by K-252a. Furthermore, CaM-independent systems such as [3H]nitrendipine receptor binding or Na+ + K+-ATPase were influenced less by K-252a compared with W-7, compound 48/80 and calmidazolium. In conclusion, K-252a is an inhibitor of CaM-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase and it appears that it inhibits the enzyme not only via CaM antagonism but possibly also by interfering with the enzyme.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adunyah E. S., Niggli V., Carafoli E. The anticalmodulin drugs trifluoperazine and R24571 remove the activation of the purified erythrocyte Ca2+-ATPase by acidic phospholipids and by controlled proteolysis. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jun 21;143(1):65–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80274-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTCHER R. W., SUTHERLAND E. W. Adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in biological materials. I. Purification and properties of cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase and use of this enzyme to characterize adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in human urine. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1244–1250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):170–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0550170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein P. M., Fiss K., Hachisu R., Andrenyak D. M. Interaction of calcium antagonists with cyclic AMP phosphodiesterases and calmodulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Apr 14;105(3):1142–1149. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91089-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietzen K., Adamczyk-Engelmann P., Wüthrich A., Konstantinova A., Bader H. Compound 48/80 is a selective and powerful inhibitor of calmodulin-regulated functions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 7;736(1):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietzen K., Sadorf I., Bader H. A model for the regulation of the calmodulin-dependent enzymes erythrocyte Ca2+-transport ATPase and brain phosphodiesterase by activators and inhibitors. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 1;207(3):541–548. doi: 10.1042/bj2070541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould R. J., Murphy K. M., Snyder S. H. [3H]nitrendipine-labeled calcium channels discriminate inorganic calcium agonists and antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3656–3660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L., Albers-Schonberg G., Monaghan R. L., Jakubas K., Pong S. S., Hensens O. D., Burg R. W., Ostlind D. A., Conroy J., Stapley E. O. Discovery, production and purification of the Na+, K+ activated ATPase inhibitor, L-681,110 from the fermentation broth of Streptomyces sp. MA-5038. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1984 Sep;37(9):970–975. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.37.970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikebe M., Stepinska M., Kemp B. E., Means A. R., Hartshorne D. J. Proteolysis of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase. Formation of inactive and calmodulin-independent fragments. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13828–13834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh H., Hidaka H. Direct interaction of calmodulin antagonists with Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. J Biochem. 1984 Dec;96(6):1721–1726. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakiuchi S., Yamazaki R., Teshima Y., Uenishi K., Miyamoto E. Multiple cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase activities from rat tissues and occurrence of a calcium-plus-magnesium-ion-dependent phosphodiesterase and its protein activator. Biochem J. 1975 Jan;146(1):109–120. doi: 10.1042/bj1460109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kase H., Iwahashi K., Matsuda Y. K-252a, a potent inhibitor of protein kinase C from microbial origin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1986 Aug;39(8):1059–1065. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.39.1059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kase H., Iwahashi K., Nakanishi S., Matsuda Y., Yamada K., Takahashi M., Murakata C., Sato A., Kaneko M. K-252 compounds, novel and potent inhibitors of protein kinase C and cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jan 30;142(2):436–440. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90293-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Crouch T. H., Krinks M. H. Subunit structure and catalytic properties of bovine brain Ca2+-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):722–729. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Crouch T. H., Richman P. G. Calmodulin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:489–515. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi S., Contreras M. L., Matsuda Y., Hama T., Lazarovici P., Guroff G. K-252a: a specific inhibitor of the action of nerve growth factor on PC 12 cells. J Neurosci. 1988 Feb;8(2):715–721. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-02-00715.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo K., Matsuda Y., Kase H., Yamada K. Inhibition of calmodulin-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase by flunarizine, a calcium-entry blocker. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 30;124(2):315–321. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91555-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luchowski E. M., Yousif F., Triggle D. J., Maurer S. C., Sarmiento J. G., Janis R. A. Effects of metal cations and calmodulin antagonists on [3H] nitrendipine binding in smooth and cardiac muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Sep;230(3):607–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda Y., Fukuda J. Inhibition by K-252a, a new inhibitor of protein kinase, of nerve growth factor-induced neurite outgrowth of chick embryo dorsal root ganglion cells. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Apr 22;87(1-2):11–17. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90137-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori T., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Yu B., Nishizuka Y. Inhibitory action of chlorpromazine, dibucaine, and other phospholipid-interacting drugs on calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8378–8380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S., Yamada K., Kase H., Nakamura S., Nonomura Y. K-252a, a novel microbial product, inhibits smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6215–6219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niggli V., Adunyah E. S., Carafoli E. Acidic phospholipids, unsaturated fatty acids, and limited proteolysis mimic the effect of calmodulin on the purified erythrocyte Ca2+ - ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8588–8592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sezaki M., Sasaki T., Nakazawa T., Takeda U., Iwata M., Watanabe T., Koyama M., Kai F., Shomura T., Kojima M. A new antibiotic SF-2370 produced by Actinomadura. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1985 Oct;38(10):1437–1439. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.38.1437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Ohmura T., Yamakado T., Hidaka H. Two types of calcium-dependent protein phosphorylations modulated by calmodulin antagonists. Naphthalenesulfonamide derivatives. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;22(2):408–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taverna R. D., Hanahan D. J. Modulation of human erythrocyte Ca2+/Mg2+ ATPase activity by phospholipase A2 and proteases. A comparison with calmodulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 May 30;94(2):652–659. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91282-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise B. C., Kuo J. F. Modes of inhibition by acylcarnitines, adriamycin and trifluoperazine of cardiac phospholipid-sensitive calcium-dependent protein kinase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Apr 1;32(7):1259–1265. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff D. J., Brostrom C. O. Calcium-dependent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase from brain identification of phospholipids as calcium-independent activators. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Apr;173(2):720–731. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Y. H., Liu J., Zhang S. P., Liu L. H. The effect of berbamine derivatives on activated Ca2+-stimulated Mg2+-dependent ATPase in erythrocyte membranes. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 15;248(3):985–988. doi: 10.1042/bj2480985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K., Iwahashi K., Kase H. K252a, a new inhibitor of protein kinase C, concomitantly inhibits 40K protein phosphorylation and serotonin secretion in a phorbol ester-stimulated platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 14;144(1):35–40. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80471-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K., Iwahashi K., Kase H. Parallel inhibition of platelet-activating factor-induced protein phosphorylation and serotonin release by K-252a, a new inhibitor of protein kinases, in rabbit platelets. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Mar 15;37(6):1161–1166. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90525-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuzawa T., Iida T., Yoshida M., Hirayama N., Takahashi M., Shirahata K., Sano H. The structures of the novel protein kinase C inhibitors K-252a, b, c and d. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1986 Aug;39(8):1072–1078. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.39.1072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


