Abstract
1. Nitrogenase activity of a strain of Azotobacter chroococcum lacking the structural genes of Monitrogenase (nifHDK) was associated with a V + Fe-containing protein and an Fe-containing protein [Robson, Eady, Richardson, Miller, Hawkins & Postgate (1986) Nature (London) 322, 388-390; Eady, Robson, Richardson, Miller & Hawkins (1987) Biochem. J. 244, 197-207]. 2. The Fe protein was purified to homogeneity by the criterion of Coomassie Blue staining after electrophoresis in 10% or 17% (w/v) polyacrylamide gels in the presence of SDS. One type of subunit, of Mr 32,000 +/- 2000, was found. 3. The native protein had an Mr of 62,500 +/- 2500 and contained approximately 4 Fe atoms and 4 acid-labile sulphide groups per molecule. The amino acid composition was similar to those of other purified Fe proteins, and, characteristically, tryptophan was absent. The specific activities (nmol of protein/min per mg of protein) when assayed under optimum conditions with the VFe protein from this strain were 1211 for H2 evolution under Ar, 337 for NH3 from N2 formation and 349 for C2H2 reduction. Activity of the Fe protein was O2-labile with a t1/2 of 36 s in air. At low temperatures the dithionite-reduced protein exhibited e.p.r. signals consistent with the presence of both S = 1/2 and S = 3/2 spin states. These signals were similar to those given by other nitrogenase Fe proteins, as were the changes in their line shape that occurred in the presence of MgATP or MgADP. The absorbance spectra showed that an increase in absorption occurred in the visible range on reversible oxidation of the dithionite-reduced protein. The oxidized-minus-reduced epsilon 420 was 6000 M-1.cm-1.
Full text
PDF
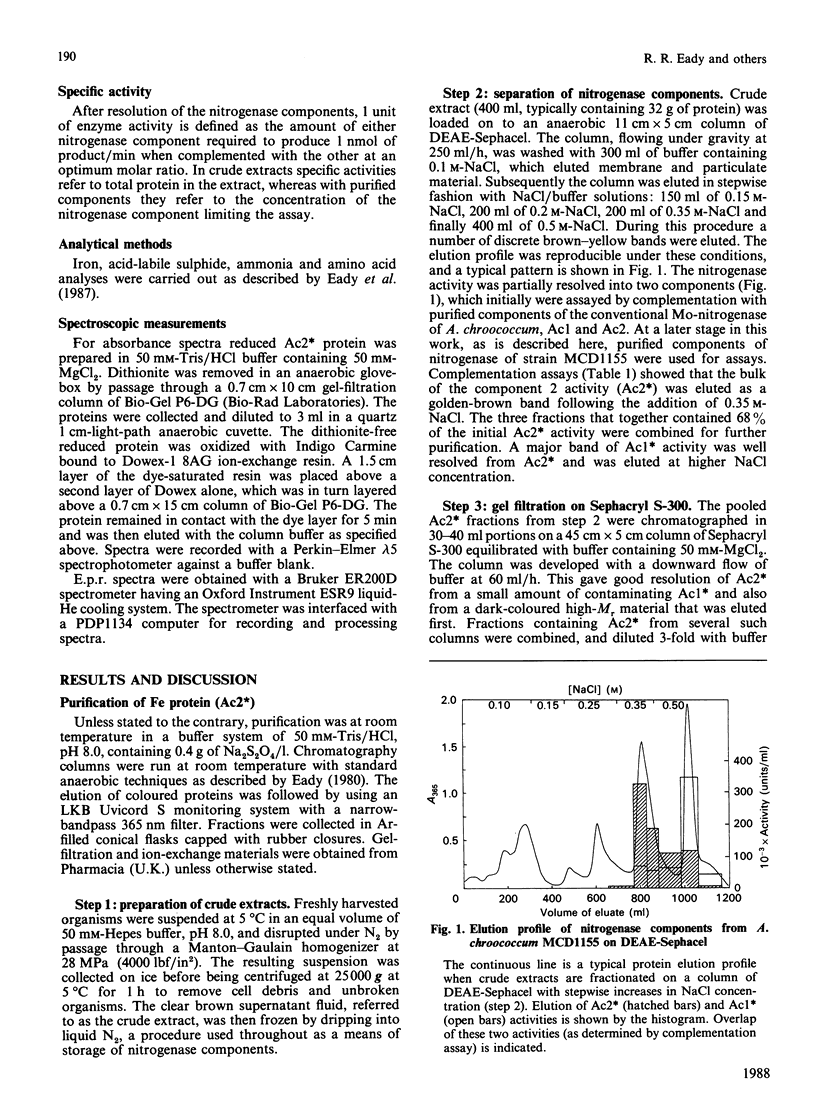
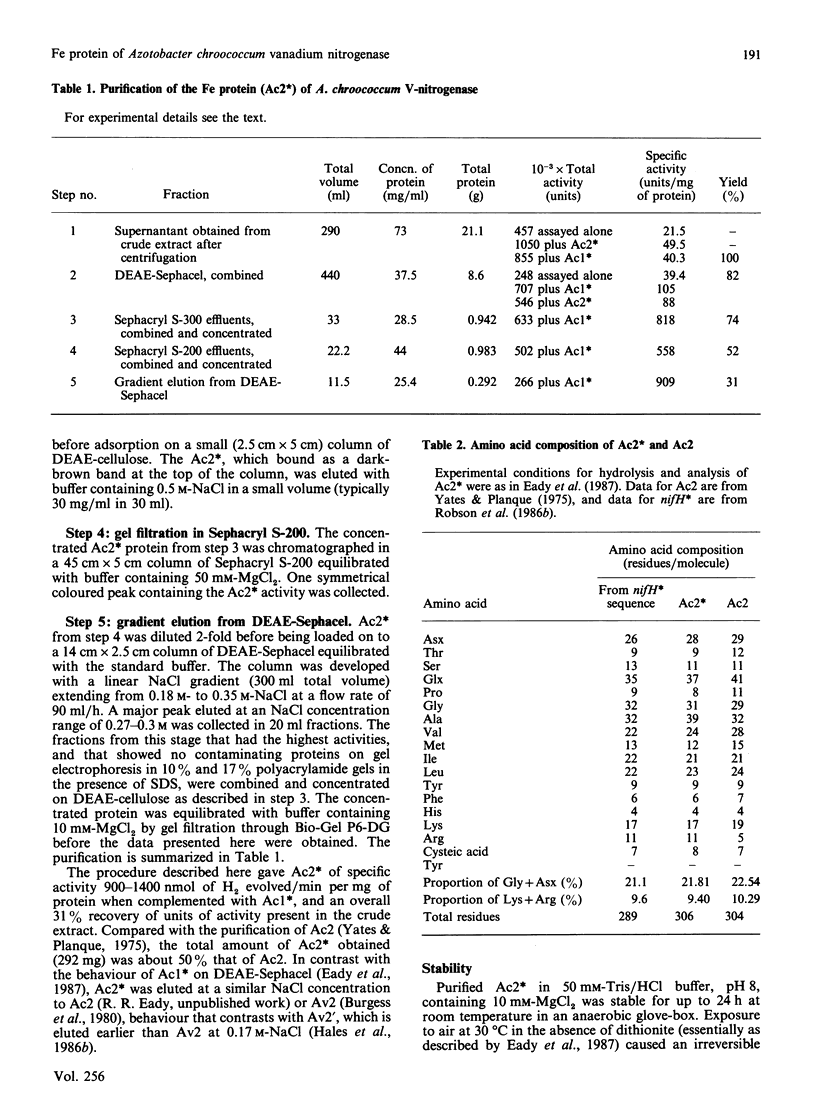
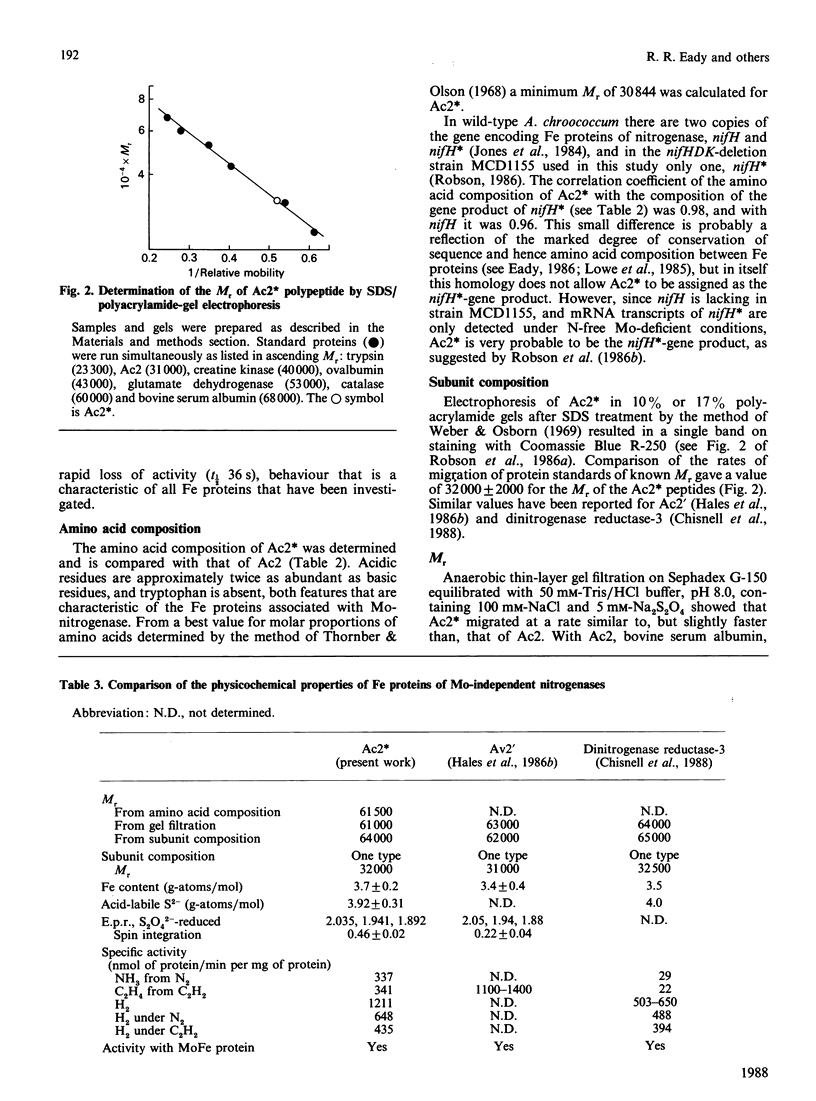
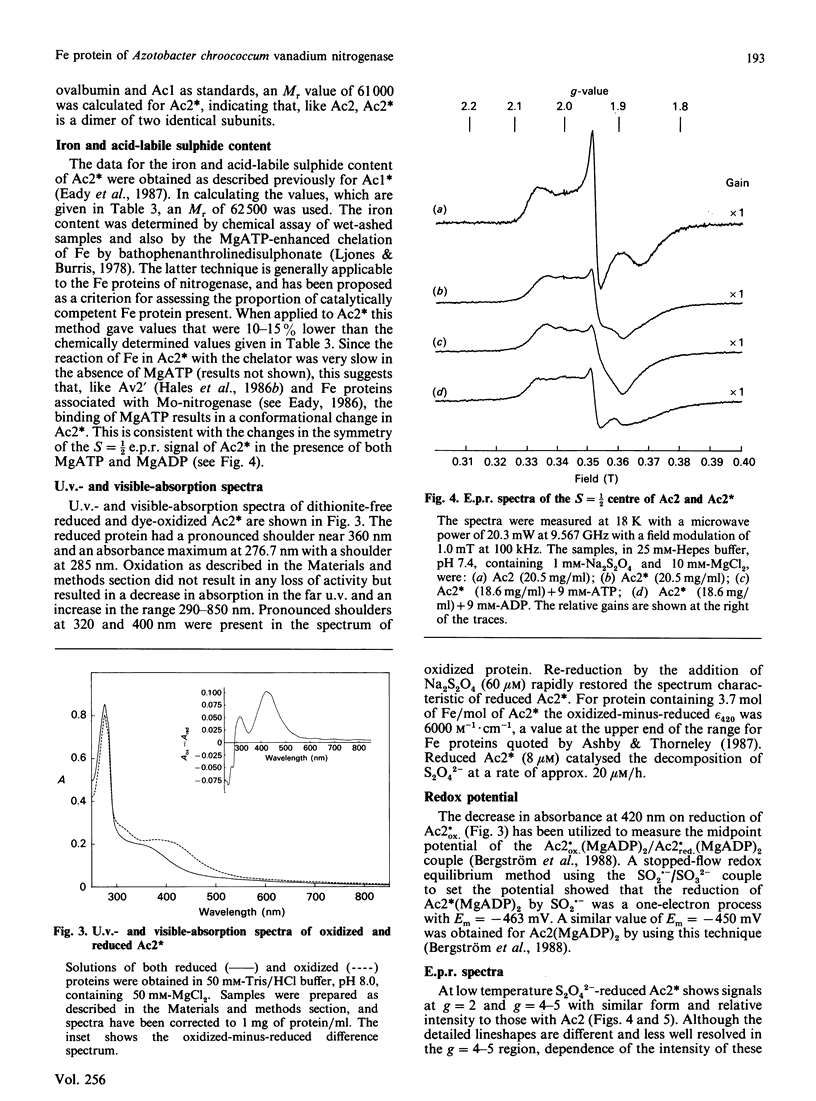


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashby G. A., Thorneley R. N. Nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Kinetic studies on the Fe protein involving reduction by sodium dithionite, the binding of MgADP and a conformation change that alters the reactivity of the 4Fe-4S centre. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 1;246(2):455–465. doi: 10.1042/bj2460455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström J., Eady R. R., Thorneley R. N. The vanadium- and molybdenum-containing nitrogenases of Azotobacter chroococcum. Comparison of mid-point potentials and kinetics of reduction by sodium dithionite of the iron proteins with bound magnesium adenosine 5'-diphosphate. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 1;251(1):165–169. doi: 10.1042/bj2510165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. E., Jarlenski D. M., Hetherington D. R. Expression of an alternative nitrogen fixation system in Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1244–1251. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1244-1251.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. E., Premakumar R., Dean D. R., Jacobson M. R., Chisnell J. R., Rizzo T. M., Kopczynski J. Nitrogen Fixation by Azotobacter vinelandii Strains Having Deletions in Structural Genes for Nitrogenase. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):92–94. doi: 10.1126/science.232.4746.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess B. K., Jacobs D. B., Stiefel E. I. Large-scale purification of high activity Azotobacter vinelandII nitrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul 10;614(1):196–209. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisnell J. R., Premakumar R., Bishop P. E. Purification of a second alternative nitrogenase from a nifHDK deletion strain of Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jan;170(1):27–33. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.1.27-33.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilworth M. J., Eady R. R., Eldridge M. E. The vanadium nitrogenase of Azotobacter chroococcum. Reduction of acetylene and ethylene to ethane. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 1;249(3):745–751. doi: 10.1042/bj2490745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eady R. R., Robson R. L., Richardson T. H., Miller R. W., Hawkins M. The vanadium nitrogenase of Azotobacter chroococcum. Purification and properties of the VFe protein. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):197–207. doi: 10.1042/bj2440197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eady R. R., Smith B. E., Cook K. A., Postgate J. R. Nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Purification and properties of the component proteins. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(3):655–675. doi: 10.1042/bj1280655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerich D. W., Hageman R. V., Burris R. H. Interactions of dinitrogenase and dinitrogenase reductase. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1981;52:1–22. doi: 10.1002/9780470122976.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen W. R., Eady R. R., Dunham W. R., Haaker H. A novel S = 3/2 EPR signal associated with native Fe-proteins of nitrogenase. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 23;189(2):250–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales B. J., Case E. E., Morningstar J. E., Dzeda M. F., Mauterer L. A. Isolation of a new vanadium-containing nitrogenase from Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7251–7255. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales B. J., Langosch D. J., Case E. E. Isolation and characterization of a second nitrogenase Fe-protein from Azotobacter vinelandii. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15301–15306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausinger R. P., Howard J. B. Thiol reactivity of the nitrogenase Fe-protein from Azotobacter vinelandii. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13486–13492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joerger R. D., Premakumar R., Bishop P. E. Tn5-induced mutants of Azotobacter vinelandii affected in nitrogen fixation under Mo-deficient and Mo-sufficient conditions. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):673–682. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.673-682.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R., Woodley P., Robson R. Cloning and organisation of some genes for nitrogen fixation from Azotobacter chroococcum and their expression in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):318–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00330980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljones T., Burris R. H. Nitrogenase: the reaction between the Fe protein and bathophenanthrolinedisulfonate as a probe for interactions with MgATP. Biochemistry. 1978 May 16;17(10):1866–1872. doi: 10.1021/bi00603a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe D. J., Thorneley R. N. The mechanism of Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase action. Pre-steady-state kinetics of H2 formation. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 15;224(3):877–886. doi: 10.1042/bj2240877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson R., Woodley P., Jones R. Second gene (nifH*) coding for a nitrogenase iron protein in Azotobacter chroococcum is adjacent to a gene coding for a ferredoxin-like protein. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1159–1163. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04341.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornber J. P., Olson J. M. The chemical composition of a crystalline bacteriochlorophyll-protein complex isolated from the green bacterium, Chloropseudomonas ethylicum. Biochemistry. 1968 Jun;7(6):2242–2249. doi: 10.1021/bi00846a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates M. G., Planqué K. Nitrogenase from Azotobacter chroococcum. Purification and properties of the component proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Dec 15;60(2):467–476. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb21025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


