Abstract
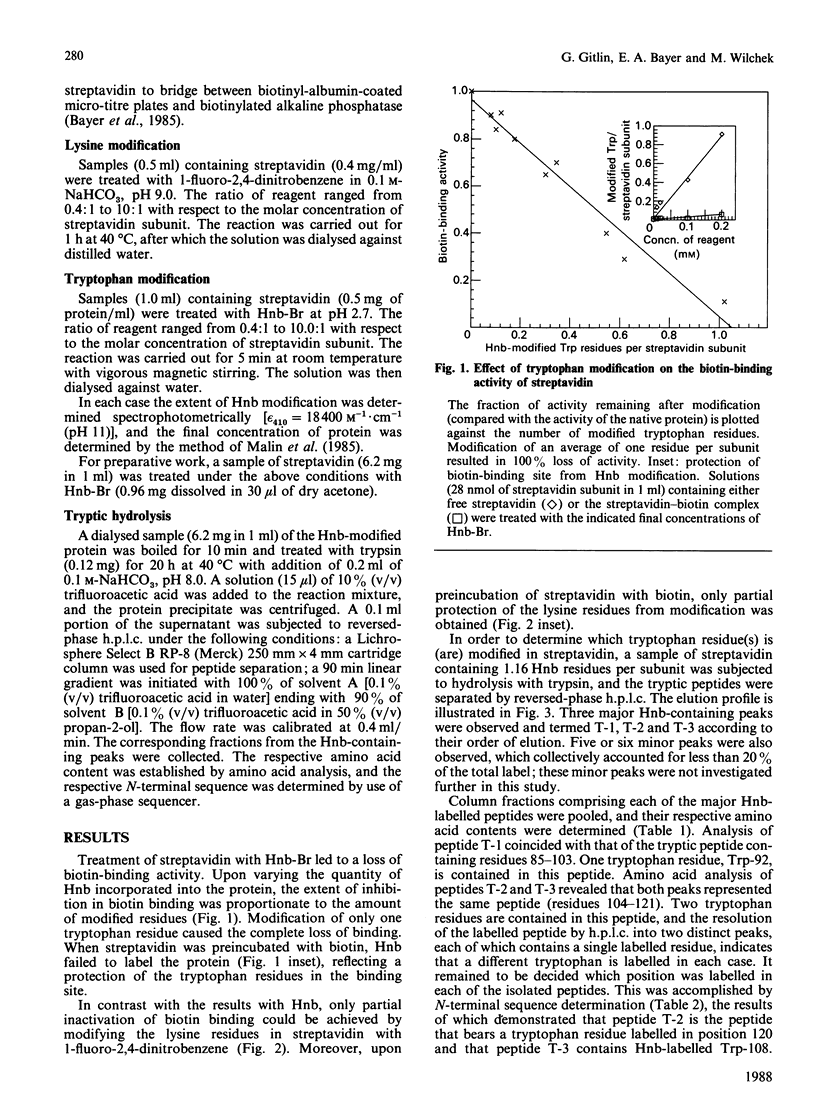
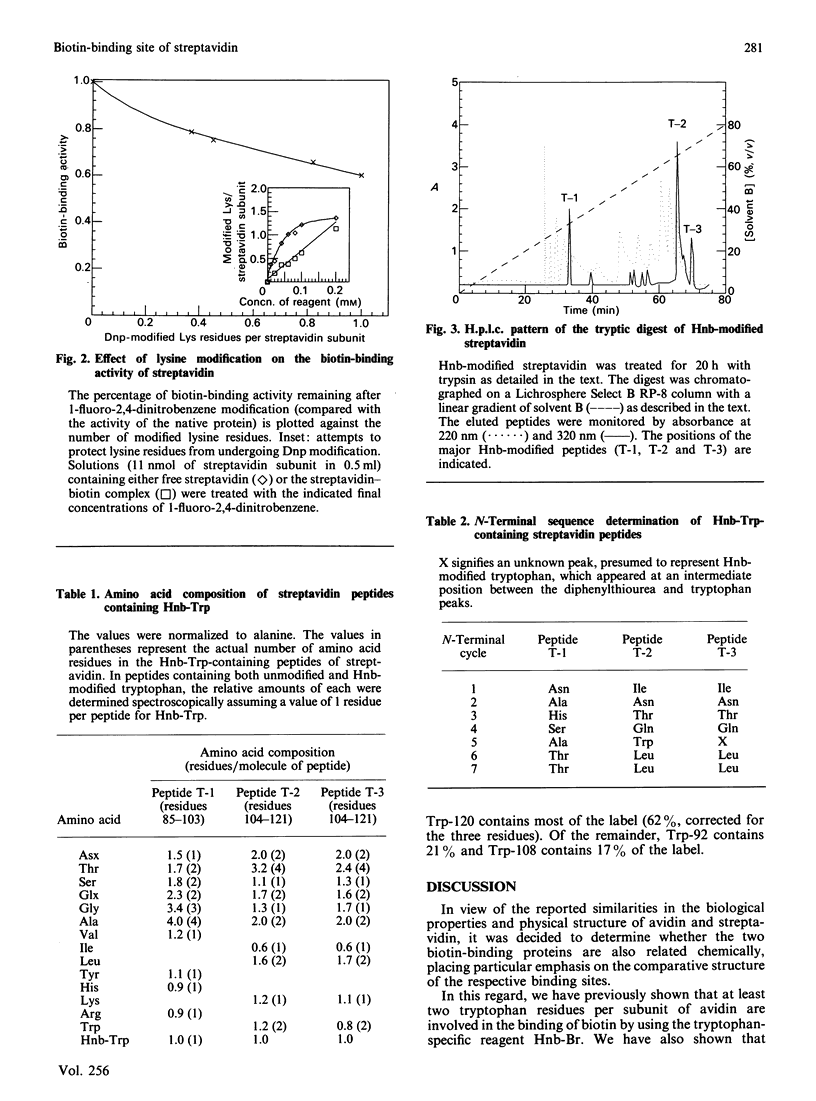
Streptavidin, the non-glycosylated bacterial analogue of the egg-white glycoprotein avidin, was modified with the tryptophan-specific reagent 2-hydroxy-5-nitrobenzyl (Hnb) bromide. As with avidin, complete loss of biotin-binding activity was achieved upon modification of an average of one tryptophan residue per streptavidin subunit. Tryptic peptides obtained from an Hnb-modified streptavidin preparation were fractionated by reversed-phase h.p.l.c., and three major Hnb-containing peptide fractions were isolated. Amino acid and N-terminal sequence analysis revealed that tryptophan residues 92, 108 and 120 are modified and probably comprise part of the biotin-binding site of the streptavidin molecule. Unlike avidin, the modification of lysine residues in streptavidin failed to result in complete loss of biotin-binding activity. The data imply subtle differences in the fine structure of the respective biotin-binding sites of the two proteins.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argaraña C. E., Kuntz I. D., Birken S., Axel R., Cantor C. R. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the streptavidin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1871–1882. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Ben-Hur H., Gitlin G., Wilchek M. An improved method for the single-step purification of streptavidin. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1986 Sep;13(2):103–112. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(86)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Ben-Hur H., Wilchek M. A sensitive enzyme assay for biotin, avidin, and streptavidin. Anal Biochem. 1986 Apr;154(1):367–370. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90538-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. The use of the avidin-biotin complex as a tool in molecular biology. Methods Biochem Anal. 1980;26:1–45. doi: 10.1002/9780470110461.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAIET L., WOLF F. J. THE PROPERTIES OF STREPTAVIDIN, A BIOTIN-BINDING PROTEIN PRODUCED BY STREPTOMYCETES. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jul 20;106:1–5. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90150-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin G., Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. Studies on the biotin-binding site of avidin. Lysine residues involved in the active site. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 15;242(3):923–926. doi: 10.1042/bj2420923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin G., Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. Studies on the biotin-binding site of avidin. Tryptophan residues involved in the active site. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 15;250(1):291–294. doi: 10.1042/bj2500291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M. Avidin. Adv Protein Chem. 1975;29:85–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60411-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malin E. L., Greenberg R., Farrell H. M., Jr Spectrophotometric estimation of protein concentration in the presence of tryptophan modified by 2-hydroxy-5-nitrobenzyl bromide. Anal Biochem. 1985 Feb 1;144(2):356–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90128-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pähler A., Hendrickson W. A., Kolks M. A., Argaraña C. E., Cantor C. R. Characterization and crystallization of core streptavidin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):13933–13937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAPLEY E. O., MATA J. M., MILLER I. M., DEMNY T. C., WOODRUFF H. B. ANTIBIOTIC MSD-235. I. PRODUCTION BY STREPTOMYCES AVIDINII AND STREPTOMYCES LAVENDULAE. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1963;161:20–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilchek M., Bayer E. A. The avidin-biotin complex in bioanalytical applications. Anal Biochem. 1988 May 15;171(1):1–32. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


