Abstract
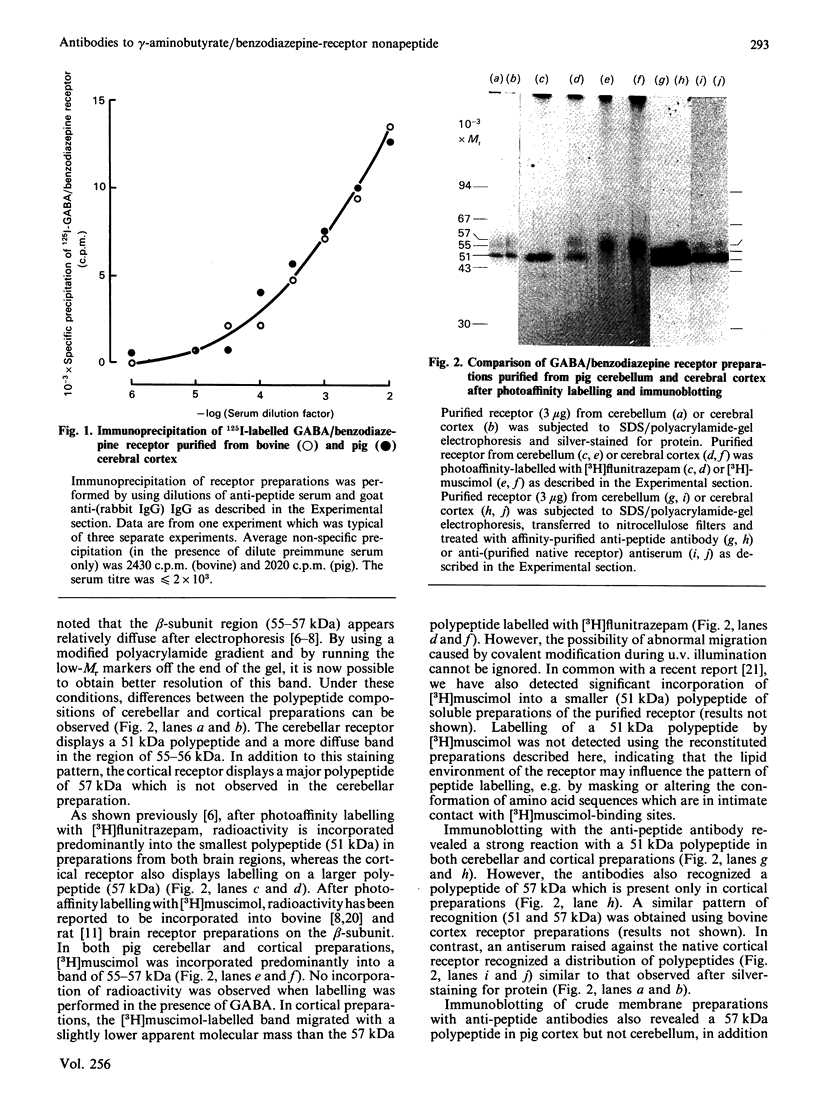
A synthetic peptide, corresponding to amino acid residues 101-109 of the bovine gamma-aminobutyrate/benzodiazepine receptor alpha-subunit, was used to raise a polyclonal antiserum. The reactivity of this antiserum towards polypeptides of both bovine and pig receptor preparations was established by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting. Anti-peptide antibodies recognized the alpha-subunit (51 kDa) of receptor prepared from pig cerebellum or cerebral cortex. However, a polypeptide of 57 kDa was additionally recognized in cortical, but not cerebellar, preparations. This alpha-like polypeptide appeared larger than the band of polypeptides labelled irreversibly with [3H]muscimol (beta-subunit, 55-57 kDa) and corresponds to a polypeptide detected only in cortex after silver-staining or irreversible labelling with [3H]flunitrazepam. These results support the idea that the distinct regional patterns of polypeptides labelled irreversibly with [3H]flunitrazepam reflect the existence of heterologous distributions of distinct alpha-like subunits.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown J. P., Tamerius J. D., Hellström I. Indirect 125I-labeled protein A assay for monoclonal antibodies to cell surface antigens. J Immunol Methods. 1979;31(3-4):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90132-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bureau M., Olsen R. W. gamma-Aminobutyric acid/benzodiazepine receptor protein carries binding sites for both ligands on both two major peptide subunits. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 30;153(3):1006–1011. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81328-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casalotti S. O., Stephenson F. A., Barnard E. A. Separate subunits for agonist and benzodiazepine binding in the gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor oligomer. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15013–15016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalla D., Neff N. H. Photoaffinity labeling of the GABAA receptor with [3H]muscimol. J Neurochem. 1985 Mar;44(3):916–921. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb12904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng L., Ransom R. W., Olsen R. W. [3H]muscimol photolabels the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor binding site on a peptide subunit distinct from that labeled with benzodiazepines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 14;138(3):1308–1314. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80425-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs K., Möhler H., Sieghart W. Various proteins from rat brain, specifically and irreversibly labeled by [3H]flunitrazepam, are distinct alpha-subunits of the GABA-benzodiazepine receptor complex. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Aug 1;90(3):314–319. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90208-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Alexander H., Olson A., Alexander S., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A. Immunogenic structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkness E. F., Turner A. J. Characterization of a cytosolic protein (P36) isolated from pig brain by benzodiazepine-affinity chromatography. J Neurochem. 1988 Feb;50(2):356–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb02920.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkness E. F., Turner A. J. The gamma-aminobutyrate/benzodiazepine receptor from pig brain. Purification and characterization of the receptor complex from cerebral cortex and cerebellum. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 1;233(1):265–270. doi: 10.1042/bj2330265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klepner C. A., Lippa A. S., Benson D. I., Sano M. C., Beer B. Resolution of two biochemically and pharmacologically distinct benzodiazepine receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1979 Oct;11(4):457–462. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(79)90125-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Battersby M. K., Richards J. G. Benzodiazepine receptor protein identified and visualized in brain tissue by a photoaffinity label. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1666–1670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T. N., Neale J. H. The type I and type II gamma-aminobutyric acid/benzodiazepine receptor: 1. Purification and two-dimensional electrophoretic analysis of the receptor from cortex and cerebellum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Jul 31;146(2):568–574. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90566-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Darlison M. G., Fujita N., Burt D. R., Stephenson F. A., Rodriguez H., Rhee L. M., Ramachandran J., Reale V., Glencorse T. A. Sequence and functional expression of the GABA A receptor shows a ligand-gated receptor super-family. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):221–227. doi: 10.1038/328221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieghart W., Drexler G. Irreversible binding of [3H]flunitrazepam to different proteins in various brain regions. J Neurochem. 1983 Jul;41(1):47–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb11812.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel E., Barnard E. A. A gamma-aminobutyric acid/benzodiazepine receptor complex from bovine cerebral cortex. Improved purification with preservation of regulatory sites and their interactions. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7219–7223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel E., Stephenson F. A., Mamalaki C., Barnard E. A. A gamma-aminobutyric acid/benzodiazepine receptor complex of bovine cerebral cortex. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6965–6971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauber G. B., Ransom R. W., Dilber A. I., Olsen R. W. The gamma-aminobutyric-acid/benzodiazepine-receptor protein from rat brain. Large-scale purification and preparation of antibodies. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Aug 17;167(1):125–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson F. A. Understanding the GABAA receptor: a chemically gated ion channel. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 1;249(1):21–32. doi: 10.1042/bj2490021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi J., Kuriyama K. Purification of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor from rat brain by affinity column chromatography using a new benzodiazepine, 1012-S, as an immobilized ligand. Brain Res. 1984 Dec 10;323(2):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90292-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]