Abstract
A comparison of the effect of temperature on the reduction of N2 by purified molybdenum nitrogenase and vanadium nitrogenase of Azotobacter chroococcum showed differences in behaviour. As the assay temperature was lowered from 30 degrees C to 5 degrees C N2 remained an effective substrate for V nitrogenase, but not Mo nitrogenase, since the specific activity for N2 reduction by Mo nitrogenase decreased 10-fold more than that of V nitrogenase. Activity cross-reactions between nitrogenase components showed the enhanced low-temperature activity to be associated with the Fe protein of V nitrogenase. The lower activity of homologous Mo nitrogenase components, although dependent on the ratio of MoFe protein to Fe protein, did not equal that of V nitrogenase even under conditions of high electron flux obtained at a 12-fold molar excess of Fe protein.
Full text
PDF
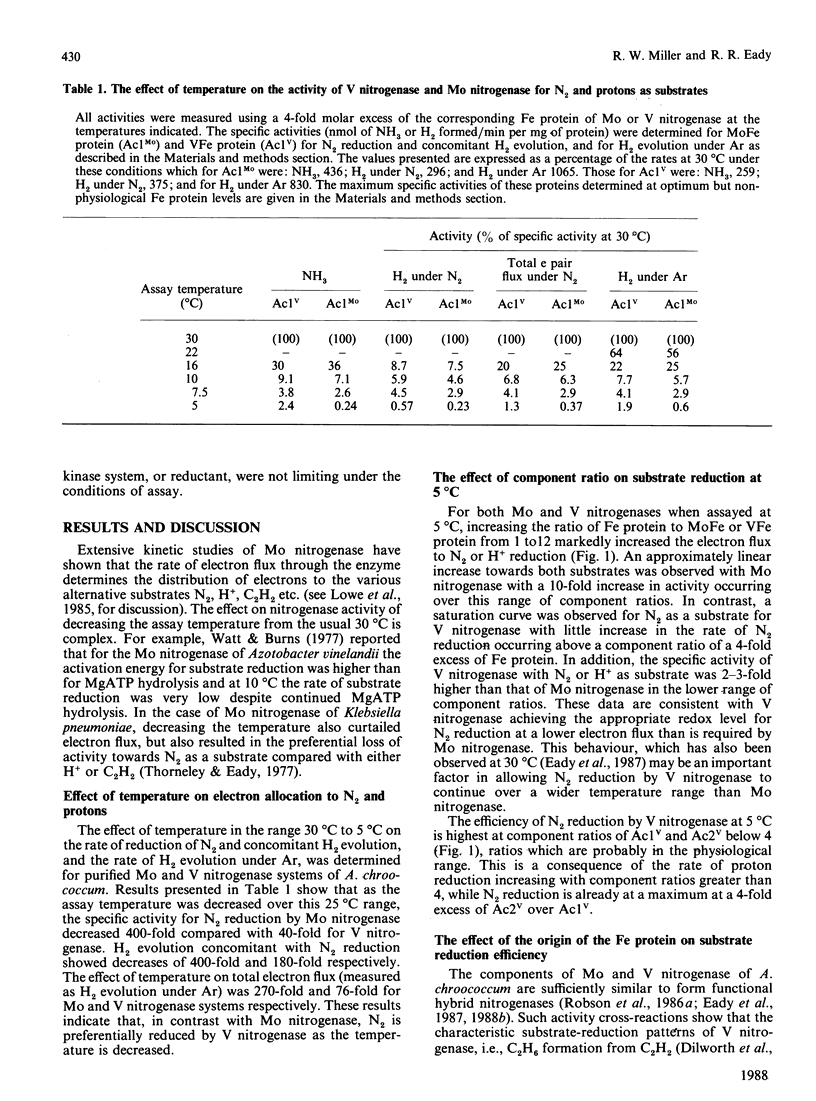
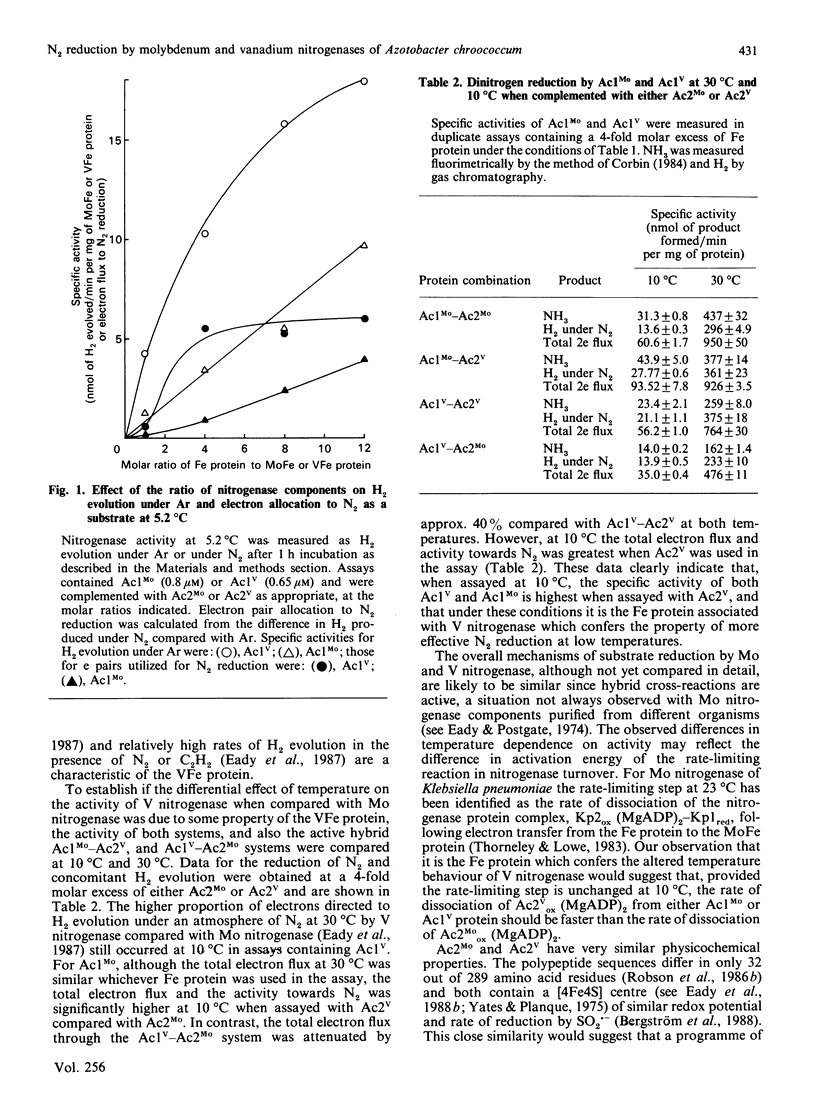

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergström J., Eady R. R., Thorneley R. N. The vanadium- and molybdenum-containing nitrogenases of Azotobacter chroococcum. Comparison of mid-point potentials and kinetics of reduction by sodium dithionite of the iron proteins with bound magnesium adenosine 5'-diphosphate. Biochem J. 1988 Apr 1;251(1):165–169. doi: 10.1042/bj2510165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. E., Jarlenski D. M., Hetherington D. R. Evidence for an alternative nitrogen fixation system in Azotobacter vinelandii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7342–7346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. E., Jarlenski D. M., Hetherington D. R. Expression of an alternative nitrogen fixation system in Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1244–1251. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1244-1251.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. L. Liquid chromatographic-fluorescence determination of ammonia from nitrogenase reactions: a 2-min assay. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 May;47(5):1027–1030. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.5.1027-1030.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilworth M. J., Eady R. R., Eldridge M. E. The vanadium nitrogenase of Azotobacter chroococcum. Reduction of acetylene and ethylene to ethane. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 1;249(3):745–751. doi: 10.1042/bj2490745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eady R. R., Postgate J. R. Nitrogenase. Nature. 1974 Jun 28;249(460):805–810. doi: 10.1038/249805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eady R. R., Richardson T. H., Miller R. W., Hawkins M., Lowe D. J. The vanadium nitrogenase of Azotobacter chroococcum. Purification and properties of the Fe protein. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 15;256(1):189–196. doi: 10.1042/bj2560189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eady R. R., Robson R. L., Richardson T. H., Miller R. W., Hawkins M. The vanadium nitrogenase of Azotobacter chroococcum. Purification and properties of the VFe protein. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):197–207. doi: 10.1042/bj2440197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eady R. R., Smith B. E., Cook K. A., Postgate J. R. Nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Purification and properties of the component proteins. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(3):655–675. doi: 10.1042/bj1280655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales B. J., Case E. E., Morningstar J. E., Dzeda M. F., Mauterer L. A. Isolation of a new vanadium-containing nitrogenase from Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 18;25(23):7251–7255. doi: 10.1021/bi00371a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales B. J., Langosch D. J., Case E. E. Isolation and characterization of a second nitrogenase Fe-protein from Azotobacter vinelandii. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15301–15306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson R., Woodley P., Jones R. Second gene (nifH*) coding for a nitrogenase iron protein in Azotobacter chroococcum is adjacent to a gene coding for a ferredoxin-like protein. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1159–1163. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04341.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson F. B., Burris R. H. A nitrogen pressure of 50 atmospheres does not prevent evolution of hydrogen by nitrogenase. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1095–1097. doi: 10.1126/science.6585956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorneley R. N., Eady R. R. Nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Distinction between proton-reducing and acetylene-reducing forms of the enzyme: effect of temperature and component protein ratio on substrate-reduction kinetics. Biochem J. 1977 Nov 1;167(2):457–461. doi: 10.1042/bj1670457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorneley R. N., Lowe D. J. Nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Kinetics of the dissociation of oxidized iron protein from molybdenum-iron protein: identification of the rate-limiting step for substrate reduction. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 1;215(2):393–403. doi: 10.1042/bj2150393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt G. D., Burns A. Kinetics of dithionite ion utilization and ATP hydrolysis for reactions catalyzed by the nitrogenase complex from Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochemistry. 1977 Jan 25;16(2):264–270. doi: 10.1021/bi00621a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates M. G., Planqué K. Nitrogenase from Azotobacter chroococcum. Purification and properties of the component proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Dec 15;60(2):467–476. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb21025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


