Abstract
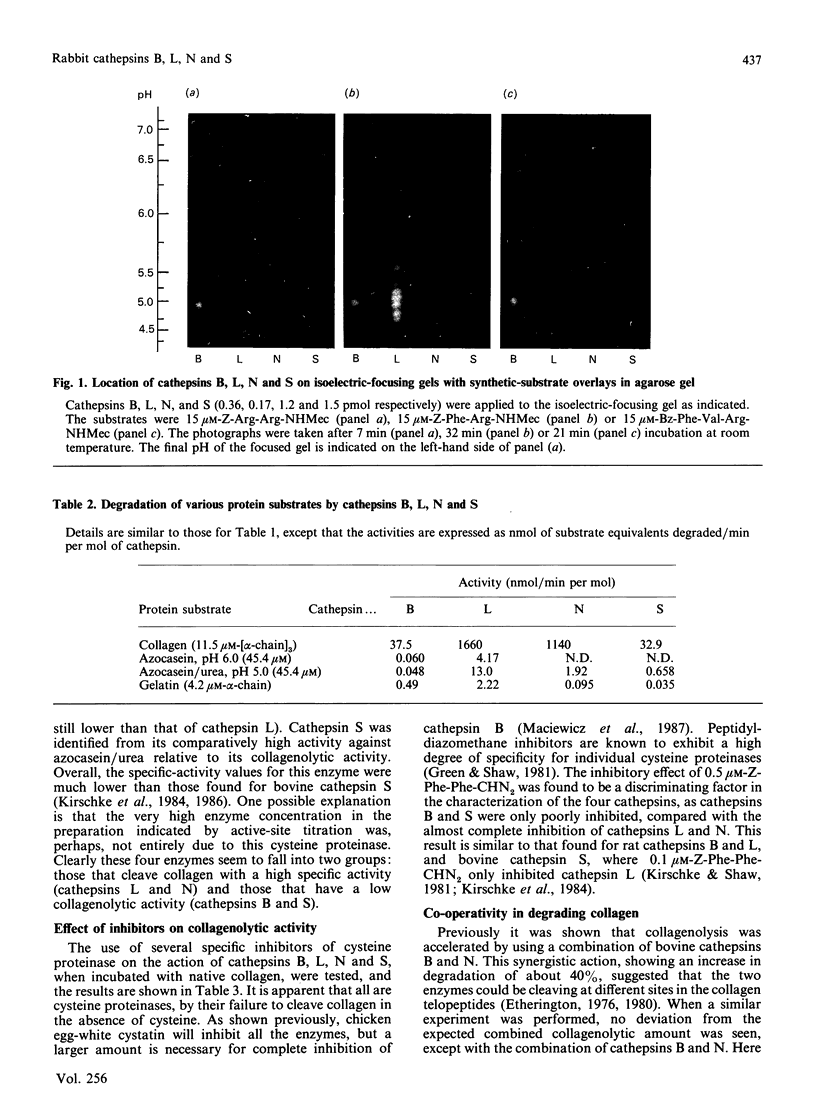
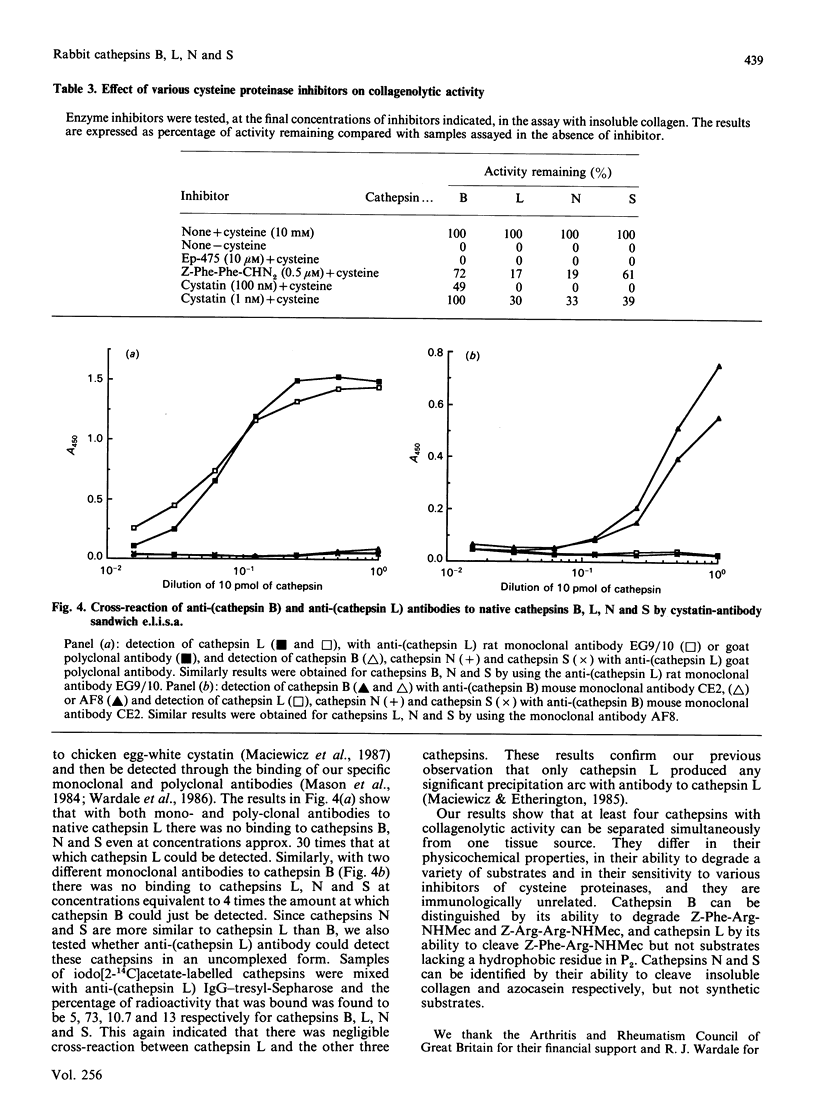
We have separated four cathepsins (B, L, N and S) from rabbit spleen. They are all collagen-degrading cysteine proteinases, with Mr values of 25,250, 23,500, 34,000 and 30,000 for cathepsin B, L, N and S respectively. Cathepsins B, N and S have isoelectric points of 5.4, 6.2 and 6.8 respectively, whereas cathepsin L exhibited multiple charge forms in the range 5.0-5.7. A comparison of their specific activity against a variety of protein and synthetic substrates shows many differences. These differences can be visually illustrated through isoelectric focusing and detection of enzymic activity with protein and synthetic-substrate overlays. By using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on the binding to chicken cystatin and detection with polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies to native cathepsins B and L, no cross-reactivity of the four native enzymes was observed. Studies on the co-operative or synergistic effect in degrading collagen indicated that, of the different combinations tested, only the combination of cathepsin B and N exhibited enhanced collagenolysis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron R., Neff L., Louvard D., Courtoy P. J. Cell-mediated extracellular acidification and bone resorption: evidence for a low pH in resorbing lacunae and localization of a 100-kD lysosomal membrane protein at the osteoclast ruffled border. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2210–2222. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Kirschke H. Cathepsin B, Cathepsin H, and cathepsin L. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):535–561. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burleigh M. C., Barrett A. J., Lazarus G. S. Cathepsin B1. A lysosomal enzyme that degrades native collagen. Biochem J. 1974 Feb;137(2):387–398. doi: 10.1042/bj1370387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett D., Stockley R. A. Cathepsin B-like cysteine proteinase activity in sputum and bronchoalveolar lavage samples: relationship to inflammatory cells and effects of corticosteroids and antibiotic treatment. Clin Sci (Lond) 1985 Apr;68(4):469–474. doi: 10.1042/cs0680469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clezardin P., McGregor J. L., Manach M., Boukerche H., Dechavanne M. One-step procedure for the rapid isolation of mouse monoclonal antibodies and their antigen binding fragments by fast protein liquid chromatography on a mono Q anion-exchange column. J Chromatogr. 1985 Jan 25;319(1):67–77. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)90540-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducastaing A., Etherington D. J. Purification of bovine spleen collagenolytic cathepsin, (cathepsin N). Biochem Soc Trans. 1978;6(5):938–940. doi: 10.1042/bst0060938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etherington D. J., Birkedahl-Hansen H. The influence of dissolved calcium salts on the degradation of hard-tissue collagens by lysosomal cathepsins. Coll Relat Res. 1987 Aug;7(3):185–199. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(87)80009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etherington D. J. Bovine spleen cathepsin B1 and collagenolytic cathepsin. A comparative study of the properties of the two enzymes in the degradation of native collagen. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):199–209. doi: 10.1042/bj1530199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etherington D. J., Mason R. W., Taylor M. A., Wardale R. J. Production of a monospecific antiserum to cathepsin L: the histochemical location of enzyme in rabbit fibroblasts. Biosci Rep. 1984 Feb;4(2):121–127. doi: 10.1007/BF01120308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etherington D. J. Proteinases in connective tissue breakdown. Ciba Found Symp. 1979;(75):87–103. doi: 10.1002/9780470720585.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etherington D. J., Taylor M. A., Henderson B. Elevation of cathepsin L levels in the synovial lining of rabbits with antigen-induced arthritis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1988 Apr;69(2):281–289. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etherington D. J. The purification of bovine cathepsin B1 and its mode of action on bovine collagens. Biochem J. 1974 Mar;137(3):547–557. doi: 10.1042/bj1370547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G. D., Shaw E. Peptidyl diazomethyl ketones are specific inactivators of thiol proteinases. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1923–1928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr, Krane S. M. An endopeptidase from rheumatoid synovial tissue culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;258(2):566–576. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. S., Cleary E. G. The determination of collagen and elastin. Methods Biochem Anal. 1967;15:25–76. doi: 10.1002/9780470110331.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katunuma N., Kominami E. Structures and functions of lysosomal thiol proteinases and their endogenous inhibitor. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1983;22:71–101. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152822-5.50007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschke H., Kembhavi A. A., Bohley P., Barrett A. J. Action of rat liver cathepsin L on collagen and other substrates. Biochem J. 1982 Feb 1;201(2):367–372. doi: 10.1042/bj2010367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschke H., Locnikar P., Turk V. Species variations amongst lysosomal cysteine proteinases. FEBS Lett. 1984 Aug 20;174(1):123–127. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81089-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschke H., Schmidt I., Wiederanders B. Cathepsin S. The cysteine proteinase from bovine lymphoid tissue is distinct from cathepsin L (EC 3.4.22.15). Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):455–459. doi: 10.1042/bj2400455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschke H., Shaw E. Rapid interaction of cathepsin L by Z-Phe-PheCHN12 and Z-Phe-AlaCHN2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jul 30;101(2):454–458. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami E., Kunio I., Katunuma N. Activation of the intramyofibral autophagic-lysosomal system in muscular dystrophy. Am J Pathol. 1987 Jun;127(3):461–466. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn K. R., Labow R. S. A comparison of four sulfhydryl cathepsins (B, C, H, and L) from porcine spleen. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;62(12):1301–1308. doi: 10.1139/o84-166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciewicz R. A., Etherington D. J., Kos J., Turk V. Collagenolytic cathepsins of rabbit spleen: a kinetic analysis of collagen degradation and inhibition by chicken cystatin. Coll Relat Res. 1987 Sep;7(4):295–304. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(87)80035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. W., Green G. D., Barrett A. J. Human liver cathepsin L. Biochem J. 1985 Feb 15;226(1):233–241. doi: 10.1042/bj2260233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. W., Taylor M. A., Etherington D. J. The purification and properties of cathepsin L from rabbit liver. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 1;217(1):209–217. doi: 10.1042/bj2170209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich D. H., Brown M. A., Barrett A. J. Purification of cathepsin B by a new form of affinity chromatography. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):731–734. doi: 10.1042/bj2350731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochefort H., Capony F., Garcia M., Cavaillès V., Freiss G., Chambon M., Morisset M., Vignon F. Estrogen-induced lysosomal proteases secreted by breast cancer cells: a role in carcinogenesis? J Cell Biochem. 1987 Sep;35(1):17–29. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240350103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver I. A., Murrills R. J., Etherington D. J. Microelectrode studies on the acid microenvironment beneath adherent macrophages and osteoclasts. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Apr;175(2):266–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90191-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk V., Brzin J., Longer M., Ritonja A., Eropkin M., Borchart U., Machleidt W. Protein inhibitors of cysteine proteinases. III. Amino-acid sequence of cystatin from chicken egg white. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1983 Nov;364(11):1487–1496. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1983.364.2.1487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E. A simple method for detecting antibodies to rubella. Br J Exp Pathol. 1975 Aug;56(4):338–339. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardale R. J., Maciewicz R. A., Etherington D. J. Monoclonal antibodies to rabbit liver cathepsin B. Biosci Rep. 1986 Jul;6(7):639–646. doi: 10.1007/BF01114758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




