Abstract
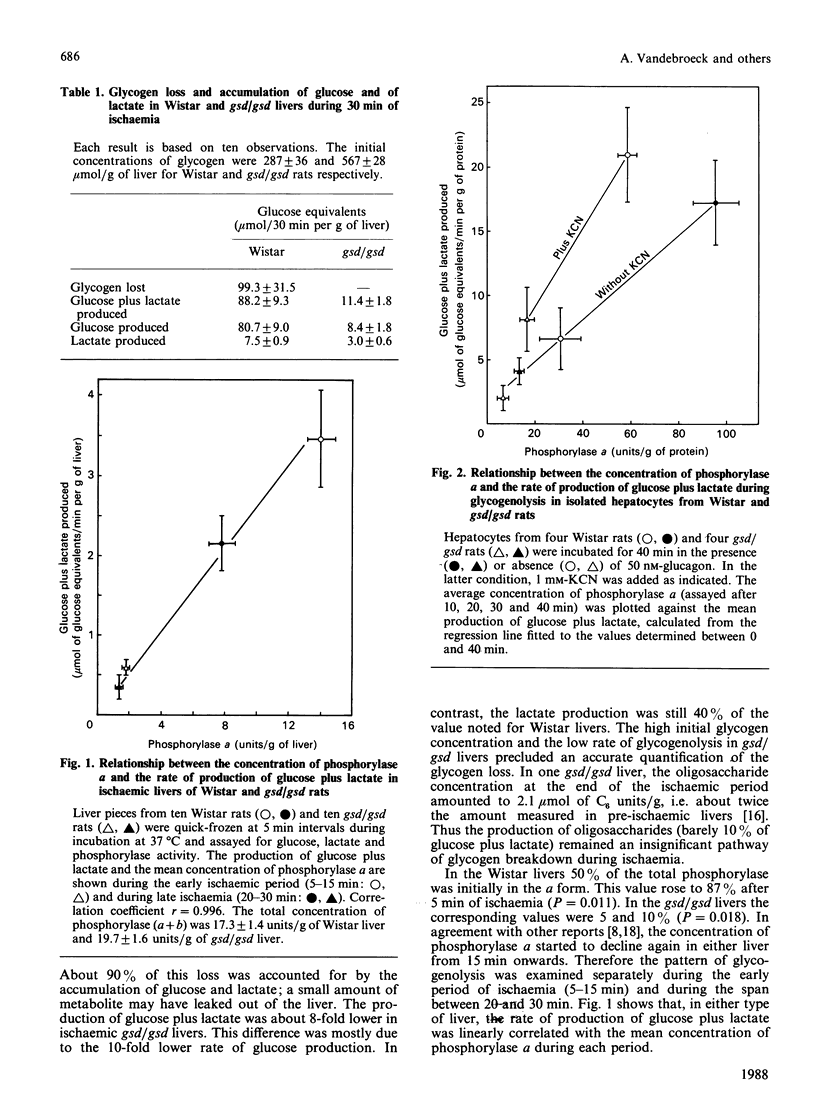
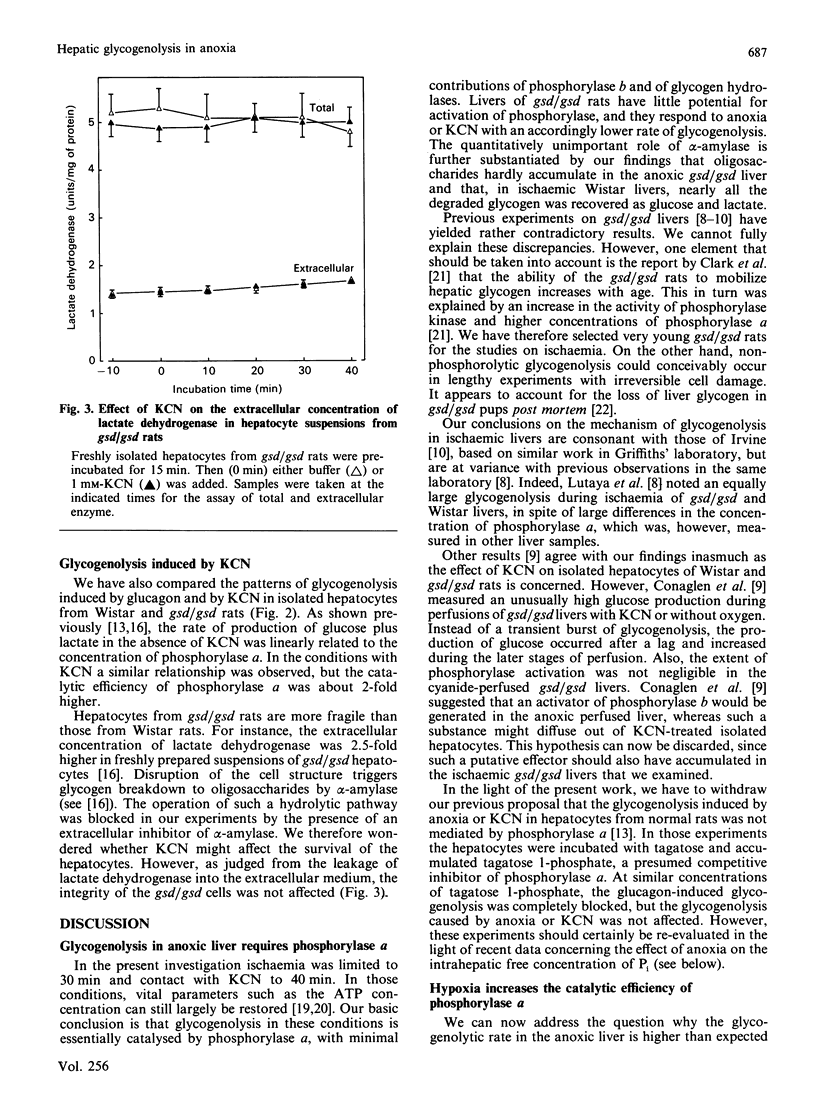
1. Ischaemia was applied for 30 min to the liver of Wistar rats and of gsd/gsd rats, which have a genetic deficiency of phosphorylase kinase. The rate of glycogenolysis corresponded closely to the concentration of phosphorylase a. The loss of glycogen from Wistar livers was accounted for by the intrahepatic increase in glucose plus lactate. Further, the accumulation of oligosaccharides was negligible in the gsd/gsd liver. 2. Isolated hepatocytes from Wistar and gsd/gsd rats were incubated for 40 min in the presence of either KCN or glucagon. Again, the production of glucose plus lactate was strictly dependent on the presence of phosphorylase a. However, the catalytic efficiency of phosphorylase a was about 2-fold higher in the presence of KCN. 3. We conclude that the hepatic glycogenolysis induced by anoxia and by KCN is solely mediated by phosphorylase a. The higher catalytic activity of phosphorylase a under these circumstances could be due to an increased concentration of the substrate Pi.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bollen M., de Ruysscher D., Stalmans W. On the mechanism of hepatic glycogenolysis induced by anoxia or cyanide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Sep 30;115(3):1033–1039. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton S. D., Ishida T. Effect of insulin on potassium and glucose movement in perfused rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1965 Dec;209(6):1145–1151. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.6.1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. G., Neville S. D., Brinkman M., Filsell O. H. Glycogen metabolism in the liver of the neonatal gsd/gsd and control (GSD/GSD) rat. Biochem J. 1982 Mar 15;202(3):623–629. doi: 10.1042/bj2020623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. G., Neville S. D., Brinkman M., Nelson P. V., Illman R. J., Guthberlet A., Haynes W. D. Age-related augmentation of phosphorylase b kinase in hepatic tissue from the glycogen-storage-disease (gsd/gsd) rat. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 15;238(3):811–816. doi: 10.1042/bj2380811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaglen J. V., Malthus R. S., Redshaw-Loten J. C., Sneyd J. G. The action of anoxia and cyanide on glycogen breakdown in the liver of the gsd/gsd rat. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 3;145(2):323–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08556.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glinsmann W. H., Hern E. P., Lynch A. Intrinsic regulation of glucose output by rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1969 Apr;216(4):698–703. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.4.698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hems D. A., Whitton P. D. Control of hepatic glycogenolysis. Physiol Rev. 1980 Jan;60(1):1–50. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iles R. A., Griffiths J. R., Stevens A. N. Perturbations in hepatic energy metabolism. Biochem Soc Trans. 1985 Oct;13(5):843–845. doi: 10.1042/bst0130843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iles R. A., Stevens A. N., Griffiths J. R., Morris P. G. Phosphorylation status of liver by 31P-n.m.r. spectroscopy, and its implications for metabolic control. A comparison of 31P-n.m.r. spectroscopy (in vivo and in vitro) with chemical and enzymic determinations of ATP, ADP and Pi. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 1;229(1):141–151. doi: 10.1042/bj2290141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakob A., Althaus-Salzmann M., Diem S. Non-hormonal activation of glycogenolysis in perfused rat livers. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(1):233–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakob A., Diem S. Activation of glycogenolysis in perfused rat livers by glucagon and metabolic inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 8;362(3):469–479. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90142-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE R. A. EFFECT OF GLYCOGENOLYTIC AGENTS ON PHOSPHORYLASE ACTIVITY OF PERFUSED RAT LIVER. Am J Physiol. 1965 Feb;208:317–323. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.2.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutaya G., Sharma R. J., Griffiths J. R. Glycogenolysis in liver of phosphorylase kinase-deficient rats during liver perfusion and ischaemia. Biochem J. 1983 Aug 15;214(2):645–648. doi: 10.1042/bj2140645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malthus R., Clark D. G., Watts C., Sneyd J. G. Glycogen-storage disease in rats, a genetically determined deficiency of liver phosphorylase kinase. Biochem J. 1980 Apr 15;188(1):99–106. doi: 10.1042/bj1880099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salhany J. M., Stohs S. J., Reinke L. A., Pieper G. M., Hassing J. M. 31P nuclear magnetic resonance of metabolic changes associated with cyanide intoxication in the perfused rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Feb 28;86(4):1077–1083. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90227-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Effects of anaerobiosis, glucose, insulin and glucagon on glycogen metabolism in isolated parenchymal rat liver cells. FEBS Lett. 1973 Nov 1;36(3):309–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80398-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma R. J., Rodrigues L. M., Whitton P. D., Hems D. A. Control mechanisms in the acceleration of hepatic glycogen degradation during hypoxia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul 3;630(3):414–424. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90290-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalmans W., Gevers G. The catalytic activity of phosphorylase b in the liver. With a note on the assay in the glycogenolytic direction. Biochem J. 1981 Nov 15;200(2):327–336. doi: 10.1042/bj2000327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandebroeck A., Bollen M., De Wulf H., Stalmans W. An assessment of the importance of intralysosomal and of alpha-amylolytic glycogenolysis in the liver of normal rats and of rats with a glycogen-storage disease. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Dec 16;153(3):621–628. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09345.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walli A. K., Siebler G., Zepf E., Schimassek H. Glycogen metabolism in isolated perfused rat liver. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1974 Mar;355(3):353–362. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1974.355.1.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods H. F., Krebs H. A. Lactate production in the perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(1):129–139. doi: 10.1042/bj1250129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


