Abstract
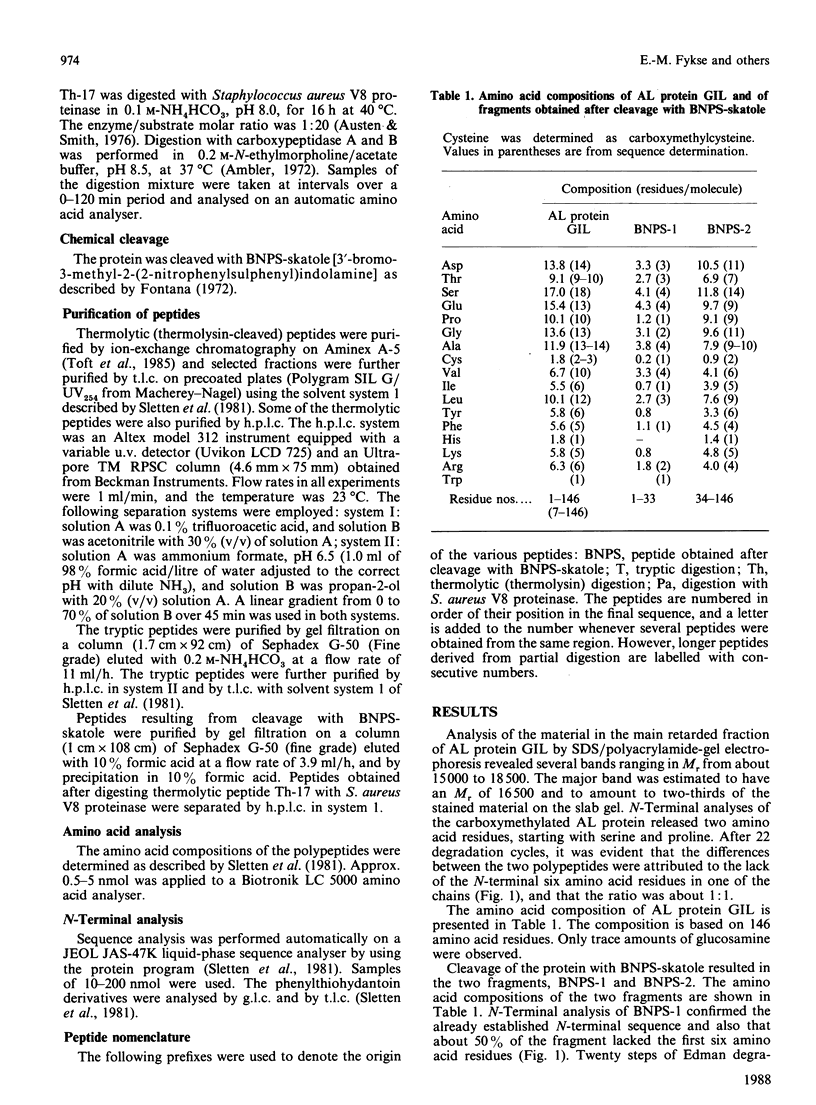
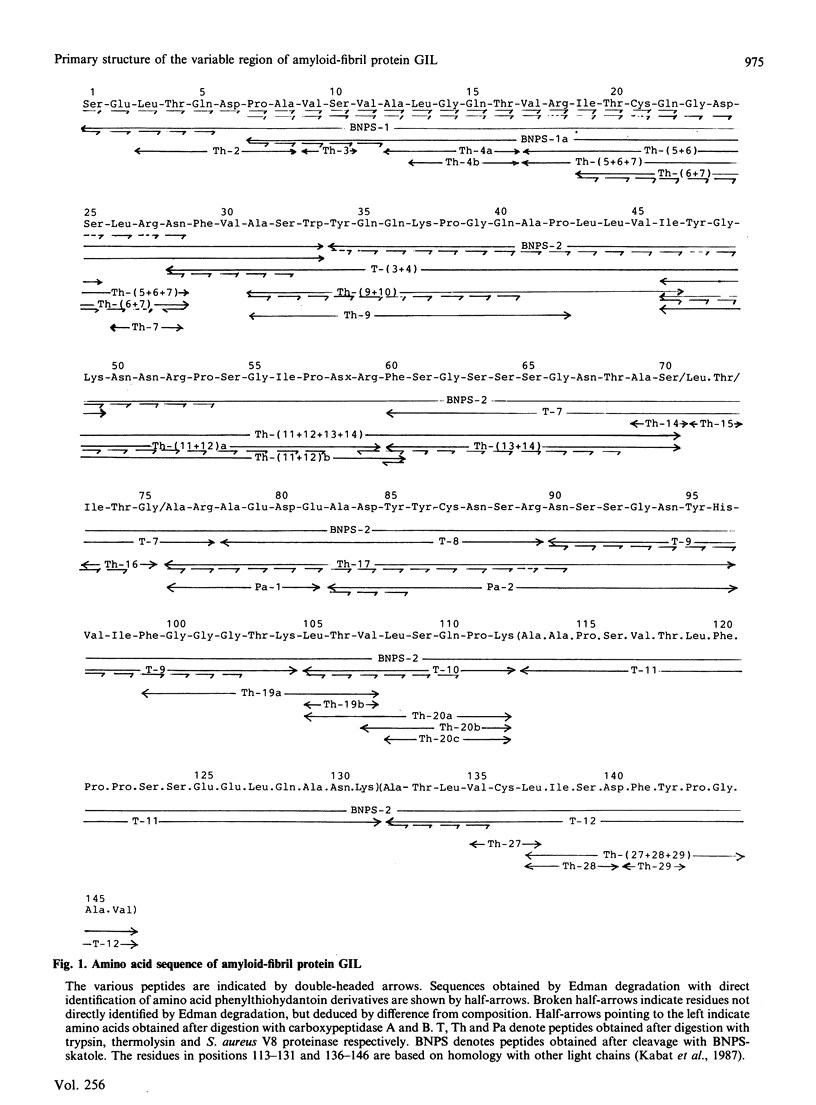
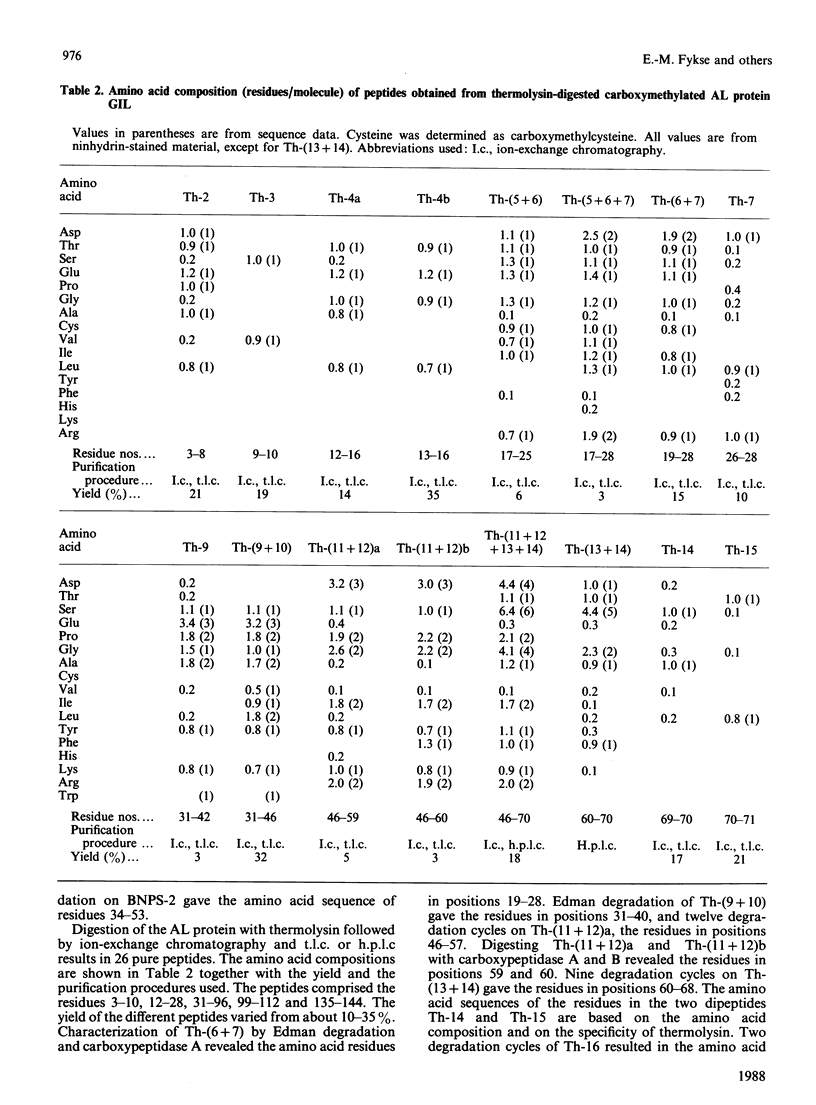
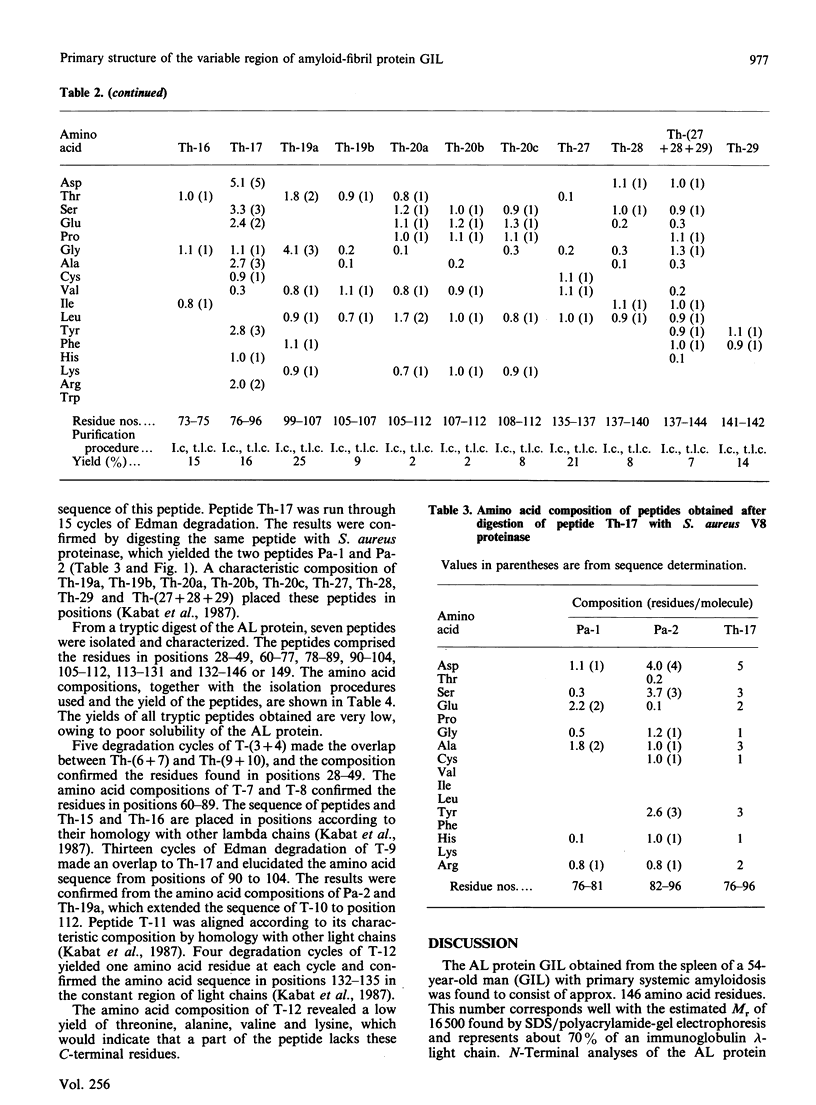
The primary structure of the variable region of an amyloid-fibril protein GIL of immunoglobulin lambda-light-chain origin (AL) was determined. The AL protein obtained from the fibrils in the spleen of a 54-year-old man with primary systemic amyloidosis could be assigned to subgroup IV of the lambda variable-region sequence. About 50% of the protein was found to be truncated in the N-terminus and lacked the first six amino acid residues. The polypeptides consisted of about 146 amino acid residues and contained traces of carbohydrate. An acceptor site for N-glycosylation was found in positions 90-93, but no glycopeptide could be isolated. Comparison of the amino acid sequence of AL protein GIL with that of the only Bence-Jones protein of subgroup IV previously studied revealed a sequence homology of 89%. A similar comparison made with other AL proteins gave sequence homologies below 66%.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austen B. M., Smith E. L. Action of staphylococcal proteinase on peptides of varying chain length and composition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Sep 20;72(2):411–417. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benditt E. P., Eriksen N. Amyloid protein SAA is associated with high density lipoprotein from human serum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4025–4028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESTFIELD A. M., MOORE S., STEIN W. H. The preparation and enzymatic hydrolysis of reduced and S-carboxymethylated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:622–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornwell G. G., 3rd, Sletten K., Olofsson B. O., Johansson B., Westermark P. Prealbumin: its association with amyloid. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Feb;40(2):226–231. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.2.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwulet F. E., O'Connor T. P., Benson M. D. Polymorphism in a kappa I primary (AL) amyloid protein (BAN). Mol Immunol. 1986 Jan;23(1):73–78. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90173-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eulitz M., Linke R. P. Primary structure of the variable part of an amyloidogenic Bence-Jones Protein (Mev.). An unusual insertion in the third hypervariable region of a human kappa-immunoglobulin light chain. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1982 Nov;363(11):1347–1358. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1982.363.2.1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eulitz M., Linke R. Amyloid fibrils derived from V-region together with C-region fragments from a lambda II-immunoglobulin light chain (HAR). Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1985 Sep;366(9):907–915. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1985.366.2.907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G. Amyloid deposits and amyloidosis. The beta-fibrilloses (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1980 Jun 5;302(23):1283–1292. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198006053022305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G. Amyloid deposits and amyloidosis: the beta-fibrilloses (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1980 Jun 12;302(24):1333–1343. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198006123022403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm E., Sletten K., Husby G. Structural studies of a carbohydrate-containing immunoglobulin-lambda-light-chain amyloid-fibril protein (AL) of variable subgroup III. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 1;239(3):545–551. doi: 10.1042/bj2390545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husby G., Sletten K. Chemical and clinical classification of amyloidosis 1985. Scand J Immunol. 1986 Mar;23(3):253–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb01966.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Møyner K., Sletten K., Husby G., Natvig J. B. An unusually large (83 amino acid residues) amyloid fibril protein AA from a patient with Waldenström's macroglobulinaemia and amyloidosis. Scand J Immunol. 1980;11(5):549–554. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00023.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitkänen P., Westermark P., Cornwell G. G., 3rd Senile systemic amyloidosis. Am J Pathol. 1984 Dec;117(3):391–399. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras M., Schubert M., Zucker-Franklin D., Rimon A., Franklin E. C. The characterization of soluble amyloid prepared in water. J Clin Invest. 1968 Apr;47(4):924–933. doi: 10.1172/JCI105784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sletten K., Husby G., Natvig J. B. N-terminal amino acid sequence of amyloid fibril protein AR, prototype of a new lambda-variable subgroup, V lambda V. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(6):833–836. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01319.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sletten K., Natvig J. B., Husby G., Juul J. The complete amino acid sequence of a prototype immunoglobulin-lambda light-chain-type amyloid-fibril protein AR. Biochem J. 1981 Jun 1;195(3):561–572. doi: 10.1042/bj1950561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Wikler M., Shinoda T., Putnam F. W. The amino acid sequence of a lambda type Bence-Jones protein. 3. The complete amino acid sequence and the location of the disulfide bridges. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 25;245(8):2171–2176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toft K. G., Sletten K., Husby G. The amino-acid sequence of the variable region of a carbohydrate-containing amyloid fibril protein EPS (immunoglobulin light chain, type lambda). Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1985 Jul;366(7):617–625. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1985.366.2.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tveteraas T., Sletten K., Westermark P. The amino acid sequence of a carbohydrate-containing immunoglobulin-light-chain-type amyloid-fibril protein. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):183–190. doi: 10.1042/bj2320183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


