Abstract
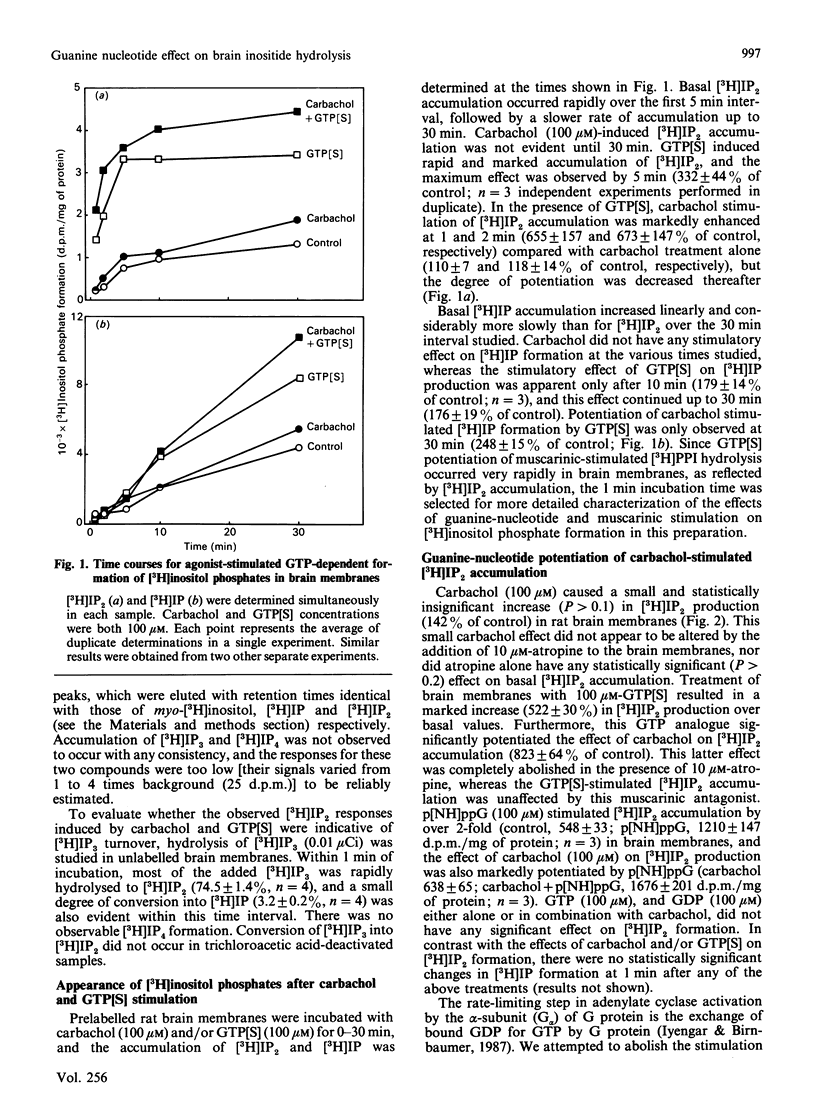
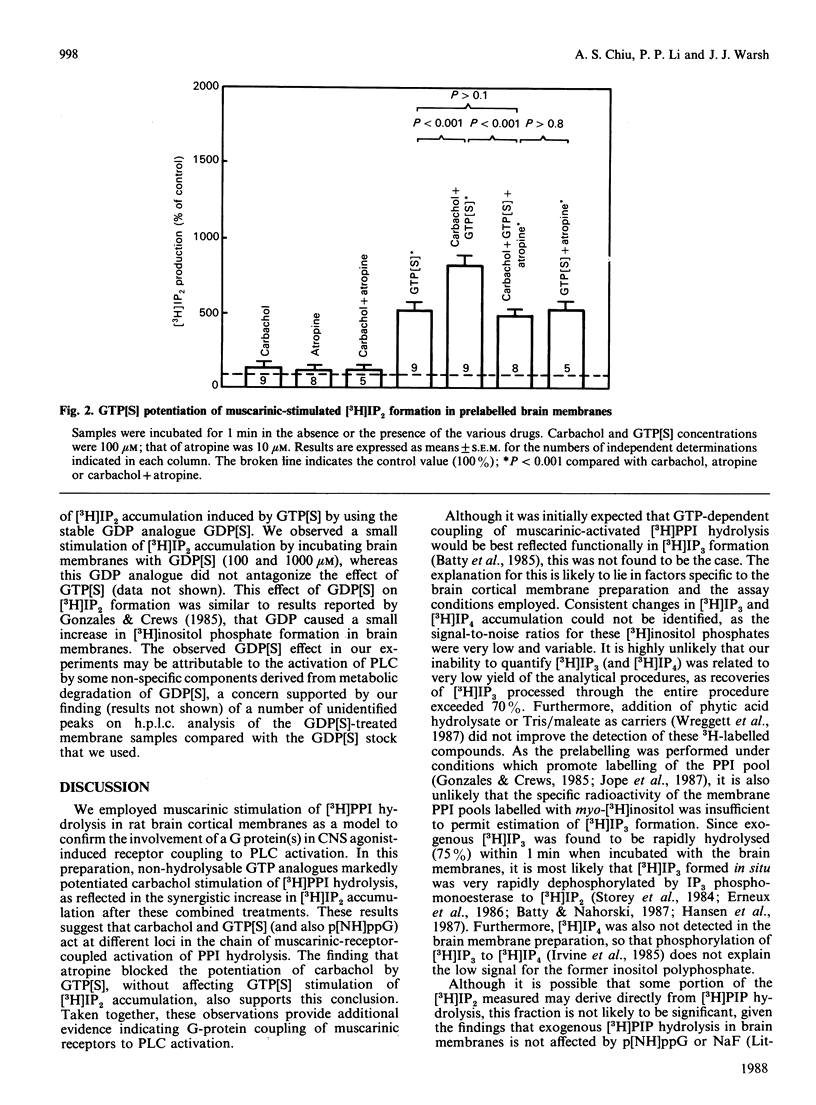
Potentiation of muscarinic-agonist-stimulated polyphosphoinositide (PPI) hydrolysis was demonstrated in a rat cerebral-cortical membrane preparation prelabelled with myo-[3H]inositol. Accumulation of myo-[3H]inositol 1,4-bisphosphate ([3H]IP2) was used to assess brain [3H]phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis as its immediate metabolite, myo-[3H]inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, was rapidly hydrolysed to [3H]IP2. Inclusion of ATP (100 microM) and Mg2+ (5 mM) in the assay medium was necessary to demonstrate the effect of GTP analogues on carbachol-stimulated brain [3H]PPI turnover. Carbachol (100 microM) induced only a small increment in [3H]IP2 accumulation (142% of control) in 1 min. However, its effect was markedly enhanced, to 800% and 300% of control, by 100 microM-guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (GTP[S]) and guanosine 5'-[beta gamma-imido]triphosphate (p[NH]ppG) respectively. GTP[S] and p[NH]ppG also stimulated [3H]IP2 accumulation by over 500% and 200% of control, respectively. The GTP-analogue-potentiated carbachol effect was antagonized by 10 microM-atropine, whereas the GTP-analogue stimulation was unaffected. This report confirms the involvement of a G (GTP-binding) protein(s) in brain PPI metabolism and provides new evidence for the role of G protein(s) in the coupling of stimulated muscarinic receptors to PPI hydrolysis in the central nervous system.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batty I. R., Nahorski S. R., Irvine R. F. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate following muscarinic receptor stimulation of rat cerebral cortical slices. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):211–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2320211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batty I., Nahorski S. R. Lithium inhibits muscarinic-receptor-stimulated inositol tetrakisphosphate accumulation in rat cerebral cortex. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 1;247(3):797–800. doi: 10.1042/bj2470797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erneux C., Delvaux A., Moreau C., Dumont J. E. Characterization of D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate phosphatase in rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 14;134(1):351–358. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90570-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Hepler J. R., Masters S. B., Brown J. H., Harden T. K. Guanine nucleotide regulation of agonist binding to muscarinic cholinergic receptors. Relation to efficacy of agonists for stimulation of phosphoinositide breakdown and Ca2+ mobilization. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 15;232(3):751–757. doi: 10.1042/bj2320751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzales R. A., Crews F. T. Guanine nucleotides stimulate production of inositol trisphosphate in rat cortical membranes. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 15;232(3):799–804. doi: 10.1042/bj2320799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillon G., Mouillac B., Balestre M. N. Activation of polyphosphoinositide phospholipase C by fluoride in WRK1 cell membranes. FEBS Lett. 1986 Aug 18;204(2):183–188. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80808-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen C. A., Johanson R. A., Williamson M. T., Williamson J. R. Purification and characterization of two types of soluble inositol phosphate 5-phosphomonoesterases from rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17319–17326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. M., Sun G. Y. Effects of ATP on phosphatidylinositol-phospholipase C and inositol 1-phosphate accumulation in rat brain synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1988 Feb;50(2):366–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb02921.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Anggård E. E., Letcher A. J., Downes C. P. Metabolism of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 15;229(2):505–511. doi: 10.1042/bj2290505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jope R. S., Casebolt T. L., Johnson G. V. Modulation of carbachol-stimulated inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in rat cerebral cortex. Neurochem Res. 1987 Aug;12(8):693–700. doi: 10.1007/BF00970524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li P. P., Warsh J. J., Sibony D., Chiu A. Assessment of rat brain alpha 1-adrenoceptor binding and activation of inositol phospholipid turnover following chronic imipramine treatment. Neurochem Res. 1988 Dec;13(12):1111–1118. doi: 10.1007/BF00971627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litosch I., Fain J. N. Regulation of phosphoinositide breakdown by guanine nucleotides. Life Sci. 1986 Jul 21;39(3):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90529-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litosch I. Guanine nucleotide and NaF stimulation of phospholipase C activity in rat cerebral-cortical membranes. Studies on substrate specificity. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):35–40. doi: 10.1042/bj2440035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litosch I., Wallis C., Fain J. N. 5-Hydroxytryptamine stimulates inositol phosphate production in a cell-free system from blowfly salivary glands. Evidence for a role of GTP in coupling receptor activation to phosphoinositide breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5464–5471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Taylor C. W., Rubin R. P., Putney J. W., Jr Evidence suggesting that a novel guanine nucleotide regulatory protein couples receptors to phospholipase C in exocrine pancreas. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 1;236(2):337–343. doi: 10.1042/bj2360337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J., Bauer C. Different effects of phorbol ester on angiotensin II- and stable GTP analogue-induced activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase in membranes isolated from rat renal mesangial cells. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 15;248(1):209–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2480209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedmak J. J., Grossberg S. E. A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using Coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 1;79(1-2):544–552. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Cox C. C., Snyderman R. Receptor-coupled activation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C by an N protein. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):97–100. doi: 10.1126/science.3006254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey D. J., Shears S. B., Kirk C. J., Michell R. H. Stepwise enzymatic dephosphorylation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate to inositol in liver. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):374–376. doi: 10.1038/312374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wreggett K. A., Howe L. R., Moore J. P., Irvine R. F. Extraction and recovery of inositol phosphates from tissues. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 1;245(3):933–934. doi: 10.1042/bj2450933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


