Abstract
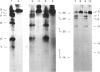
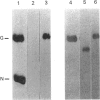
The cysteine residue in the cytoplasmic domain at position 489 of the sequence of the glycoprotein (G protein) isolated from vesicular-stomatitis virions is completely blocked for carboxymethylation. After release of covalently bound fatty acids by hydroxylamine at pH 6.8, this cysteine residue could be specifically labelled by iodo[14C]acetic acid. Reaction products were analysed after specific cleavage of labelled G protein at asparagine-glycine bonds by hydroxylamine at pH 9.3, which generated a C-terminal peptide of Mr 15,300 containing only the single cysteine residue. Bromelain digestion of [3H]palmitic acid-labelled membrane fractions of vesicular-stomatitis-virus-infected baby-hamster kidney cells removed almost completely the 3H radioactivity from the cytoplasmic domain of the G protein, whereas the ectodomain was completely protected by the microsomal membrane. This result indicates that the acylation site of the G protein is exposed on the cytoplasmic side of intracellular membranes. Taken together, both biochemical techniques strongly suggest that the single cysteine-489 residue, which is located six amino acid residues distal to the putative transmembrane domain, is the acylation site. The thioester bond between palmitic acid and the G protein is quite resistant to hydroxylamine treatment (0.32 M at pH 6.8 for 1 h at 37 degrees C) compared with the reactivity of the thioester linkage in palmitoyl-CoA, which is cleaved at relatively low concentrations of hydroxylamine (0.05 M).
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolanowski M. A., Earles B. J., Lennarz W. J. Fatty acylation of proteins during development of sea urchin embryos. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):4934–4940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., Balian G. Cleavage at Asn-Gly bonds with hydroxylamine. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:132–145. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capon D. J., Chen E. Y., Levinson A. D., Seeburg P. H., Goeddel D. V. Complete nucleotide sequences of the T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene and its normal homologue. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):33–37. doi: 10.1038/302033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capone J., Toneguzzo F., Ghosh H. P. Synthesis and assembly of membrane glycoproteins. Membrane anchoring COOH-terminal domain of vesicular stomatitis virus envelope glycoprotein G contains fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):16–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardon J. W., Hammes G. G. Kinetic and structural investigation of acyl-binding sites on avian fatty acid synthase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4802–4807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. Q., Ulsh L. S., DuBois G., Shih T. Y. Posttranslational processing of p21 ras proteins involves palmitylation of the C-terminal tetrapeptide containing cysteine-186. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):607–612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.607-612.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesson L., Larhammar D., Rask L., Peterson P. A. cDNA clone for the human invariant gamma chain of class II histocompatibility antigens and its implications for the protein structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7395–7399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Keller D. S., Helenius A., Balch W. E. Role for adenosine triphosphate in regulating the assembly and transport of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein trimers. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):1957–1969. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garreis-Wabnitz C., Kruppa J. Intracellular appearance of a glycoprotein in VSV-infected BHK cells lacking the membrane-anchoring oligopeptide of the viral G-protein. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1469–1476. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01998.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graeve L., Garreis-Wabnitz C., Zauke M., Breindl M., Kruppa J. The soluble glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus is formed during or shortly after the translation process. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):968–975. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.968-975.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jing S. Q., Trowbridge I. S. Identification of the intermolecular disulfide bonds of the human transferrin receptor and its lipid-attachment site. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):327–331. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J. F., Krangel M. S., Strominger J. L. Cysteines in the transmembrane region of major histocompatibility complex antigens are fatty acylated via thioester bonds. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7230–7238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klockmann U., Deppert W. Acylated simian virus 40 large T-antigen: a new subclass associated with a detergent-resistant lamina of the plasma membrane. EMBO J. 1983;2(7):1151–1157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01560.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch N., Hämmerling G. J. The HLA-D-associated invariant chain binds palmitic acid at the cysteine adjacent to the membrane segment. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3434–3440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambrecht B., Schmidt M. F. Membrane fusion induced by influenza virus hemagglutinin requires protein bound fatty acids. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jun 23;202(1):127–132. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80662-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack D., Berger M., Schmidt M. F., Kruppa J. Cell-free fatty acylation of microsomal integrated and detergent-solubilized glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4297–4302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee A. I., Courtneidge S. A. Two classes of fatty acid acylated proteins exist in eukaryotic cells. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1137–1144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03751.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee A. I., Koyama A. H., Malfer C., Wen D., Schlesinger M. J. Release of fatty acids from virus glycoproteins by hydroxylamine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 10;798(2):156–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90298-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland A., Kühn L. C., Ruddle F. H. The human transferrin receptor gene: genomic organization, and the complete primary structure of the receptor deduced from a cDNA sequence. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):267–274. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIlhinney R. A., Pelly S. J., Chadwick J. K., Cowley G. P. Studies on the attachment of myristic and palmitic acid to cell proteins in human squamous carcinoma cell lines: evidence for two pathways. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1145–1152. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. K., Feuer B. I., Vanderoef R., Lenard J. Reconstituted G protein-lipid vesicles from vesicular stomatitis virus and their inhibition of VSV infection. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):421–429. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. G., McQuain C. O. Assembly of viral membranes: nature of the association of vesicular stomatitis virus proteins to membranes. J Virol. 1978 Apr;26(1):115–125. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.1.115-125.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Glaser L., Merlie J. P. Alpha and beta subunits of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor contain covalently bound lipid. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5364–5367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Towler D. A., Glaser L. Specificity of fatty acid acylation of cellular proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3784–3790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Wagner R. R. Glycoprotein micelles isolated from vesicular stomatitis virus spontaneously partition into sonicated phosphatidylcholine vesicles. Virology. 1980 Dec;107(2):543–547. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90323-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploegh H. L., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L. Major histocompatibility antigens: the human (HLA-A, -B, -C) and murine (H-2K, H-2D) class I molecules. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):287–299. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90318-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein A., McClure M. R., Rice N. R., Luftig R. B., Schultz A. M. Myristylation site in Pr65gag is essential for virus particle formation by Moloney murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7246–7250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Adams G. A., Gallione C. J. The presence of cysteine in the cytoplasmic domain of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein is required for palmitate addition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2050–2054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Gallione C. J. Nucleotide sequences of the mRNA's encoding the vesicular stomatitis virus G and M proteins determined from cDNA clones containing the complete coding regions. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):519–528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.519-528.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saris C. J., van Eenbergen J., Jenks B. G., Bloemers H. P. Hydroxylamine cleavage of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):54–67. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90425-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J., Malfer C. Cerulenin blocks fatty acid acylation of glycoproteins and inhibits vesicular stomatitis and Sindbis virus particle formation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):9887–9890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F., Bracha M., Schlesinger M. J. Evidence for covalent attachment of fatty acids to Sindbis virus glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1687–1691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F. Fatty acid binding: a new kind of posttranslational modification of membrane proteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;102:101–129. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68906-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F., Lambrecht B. On the structure of the acyl linkage and the function of fatty acyl chains in the influenza virus haemagglutinin and the glycoproteins of Semliki Forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1985 Dec;66(Pt 12):2635–2647. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-12-2635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F., Schlesinger M. J. Fatty acid binding to vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein: a new type of post-translational modification of the viral glycoprotein. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):813–819. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Henderson L. E., Oroszlan S., Garber E. A., Hanafusa H. Amino terminal myristylation of the protein kinase p60src, a retroviral transforming protein. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):427–429. doi: 10.1126/science.3917576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slomiany A., Witas H., Aono M., Slomiany B. L. Covalently linked fatty acids in gastric mucus glycoprotein of cystic fibrosis patients. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8535–8538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. Gel electrophoresis of restriction fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:152–176. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoffel W., Hillen H., Schröder W., Deutzmann R. The primary structure of bovine brain myelin lipophilin (proteolipid apoprotein). Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1983 Oct;364(10):1455–1466. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1983.364.2.1455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]