Abstract
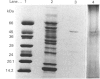
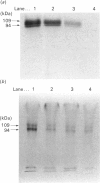
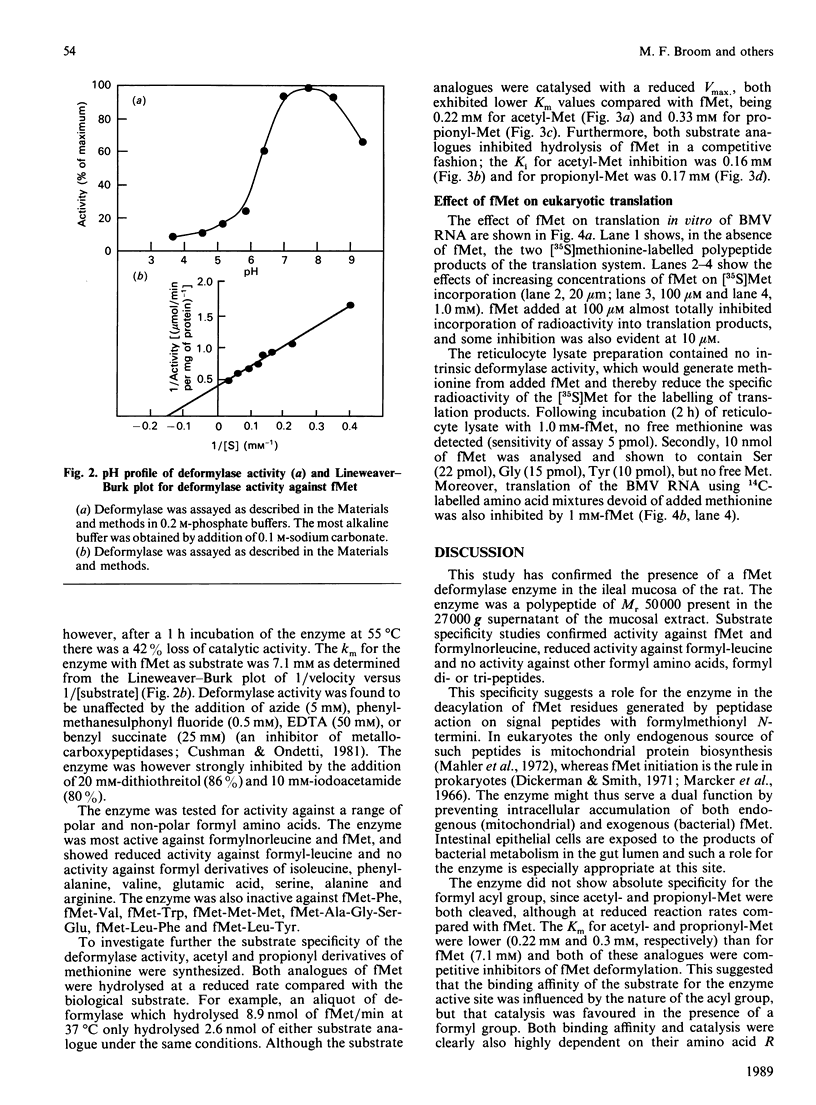
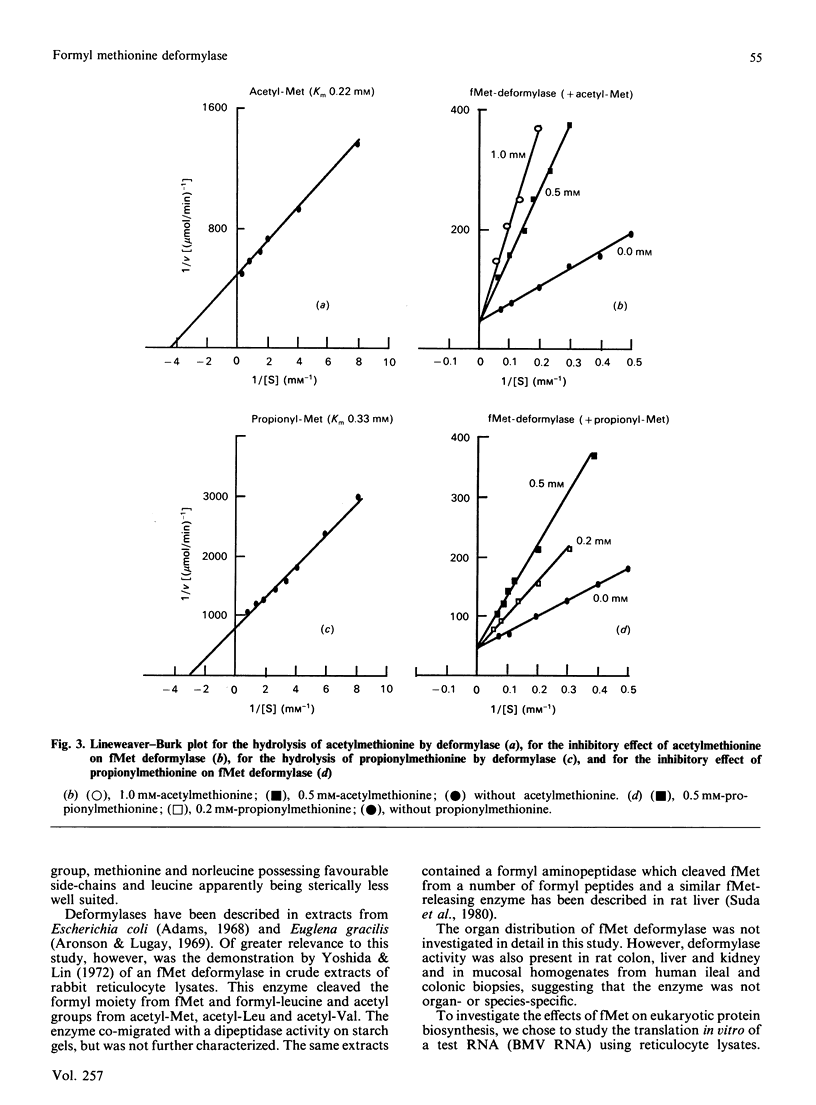
A formylmethionine deformylase from rat small-intestinal mucosa has been isolated, characterized and partially purified. The enzyme catalyses the release of equimolar amounts of formate and the free amino acid. The deformylase was active against formylmethionine (Km 7.1 mM) and formylnorleucine, but showed reduced activity against formyl-leucine. It was inactive against a range of other polar and nonpolar formyl-amino acids and against formyl di- and tri-peptides. The Mr of the native enzyme was between 45,000 and 66,000, as determined by h.p.l.c. gel permeation. Further purification of the enzyme either by h.p.l.c. ion-exchange chromatography and concanavalin A-Sepharose or by isoelectric focusing yielded a preparation with one predominant band of Mr 50,000 on SDS/polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Bacteria in the intestine present the host with substantial amounts of formylmethionine (fMet) from proteinase and carboxypeptidase digestion of bacterial formyl-peptides in the intestinal lumen. fMet (0.01-1.0 mM) inhibited translation of a test RNA from brome mosaic virus in vitro, indicating that it could have adverse effects on cellular metabolism. Gut epithelial fMet deformylase may be required for deformylation of this exogenous (bacterial) and also endogenous (mitochondrial) fMet.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adair W. S., Monk B. C., Cohen R., Hwang C., Goodenough U. W. Sexual agglutinins from the Chlamydomonas flagellar membrane. Partial purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4593–4602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams J. M. On the release of the formyl group from nascent protein. J Mol Biol. 1968 May 14;33(3):571–589. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90307-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson J. N., Lugay J. C. N-Formylmethionine deformylase from Euglena gracilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Feb 7;34(3):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90833-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchetti R., Lucchini G., Sartirana M. L. Endogenous systhesis of formyl-methionine peptides in isolated mitochondria and chloroplasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jan 8;42(1):97–102. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90367-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. C., Smith A. E. Initiator codons in eukaryotes. Nature. 1970 May 16;226(5246):610–612. doi: 10.1038/226610a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caffier H., Raskas H. J., Parsons T. J., Green M. Initiation of mammalian viral protein synthesis. Nat New Biol. 1971 Feb 24;229(8):239–241. doi: 10.1038/newbio229239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadwick V. S., Mellor D. M., Myers D. B., Selden A. C., Keshavarzian A., Broom M. F., Hobson C. H. Production of peptides inducing chemotaxis and lysosomal enzyme release in human neutrophils by intestinal bacteria in vitro and in vivo. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1988 Jan;23(1):121–128. doi: 10.3109/00365528809093861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai U., Kreutzer D. L., Showell H., Arroyave C. V., Ward P. A. Acute inflammatory pulmonary reactions induced by chemotactic factors. Am J Pathol. 1979 Jul;96(1):71–83. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerman H. W., Smith B. C. Formymethionyl transfer ribonucleic acid transformylase: the specific interaction of the enzyme with its transfer ribonucleic acid substrate. J Mol Biol. 1971 Aug 14;59(3):425–445. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90308-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz A. C., Movat H. Z. The in vivo quantitation and kinetics of rabbit neutrophil leukocyte accumulation in the skin in response to chemotactic agents and Escherichia coli. Lab Invest. 1980 Mar;42(3):310–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. G., Richardson D. L., Kay A. B. Neutrophil accumulation in vivo following the administration of chemotactic factors. Br J Haematol. 1977 Jan;35(1):19–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1977.tb00558.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahler H. R., Dawidowicz K., Feldman F. Formate as a specific label for mitochondrial translational products. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7439–7442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makar A. B., McMartin K. E., Palese M., Tephly T. R. Formate assay in body fluids: application in methanol poisoning. Biochem Med. 1975 Jun;13(2):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(75)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marasco W. A., Phan S. H., Krutzsch H., Showell H. J., Feltner D. E., Nairn R., Becker E. L., Ward P. A. Purification and identification of formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine as the major peptide neutrophil chemotactic factor produced by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5430–5439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcker K. A., Clark B. F., Anderson J. S. N-formyl-methionyl-sRNA and its relation to protein biosynthesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:279–285. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. T., Burgess D. R. SDS microslab linear gradient polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jul 1;87(2):386–396. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90688-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor D. M., Myers D. B., Chadwick V. S. The cored sponge model of in vivo leucocyte chemotaxis. Agents Actions. 1986 Aug;18(5-6):550–554. doi: 10.1007/BF01964963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Showell H. V., Corcoran B. A., Ward P. A., Smith E., Becker E. L. The isolation and partial characterization of neutrophil chemotactic factors from Escherichia coli. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1831–1837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showell H. J., Freer R. J., Zigmond S. H., Schiffmann E., Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Becker E. L. The structure-activity relations of synthetic peptides as chemotactic factors and inducers of lysosomal secretion for neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1154–1169. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchowitz L., Spilberg I. Generation of superoxide radicals by human peripheral neutrophils activated by chemotactic factor. Evidence for the role of calcium. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Apr;93(4):583–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Hollers J. C. Motility and adhesiveness in human neutrophils. Redistribution of chemotactic factor-induced adhesion sites. J Clin Invest. 1980 Apr;65(4):804–812. doi: 10.1172/JCI109731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda H., Yamamoto K., Aoyagi T., Umezawa H. Purification and properties of N-formylmethionine aminopeptidase from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 6;616(1):60–67. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90263-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Lepow I. H., Newman L. J. Bacterial factors chemotactic for polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Am J Pathol. 1968 Apr;52(4):725–736. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida A., Lin M. NH 2 -terminal formylmethionine- and NH 2 -terminal methionine-cleaving enzymes in rabbits. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):952–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]