Abstract
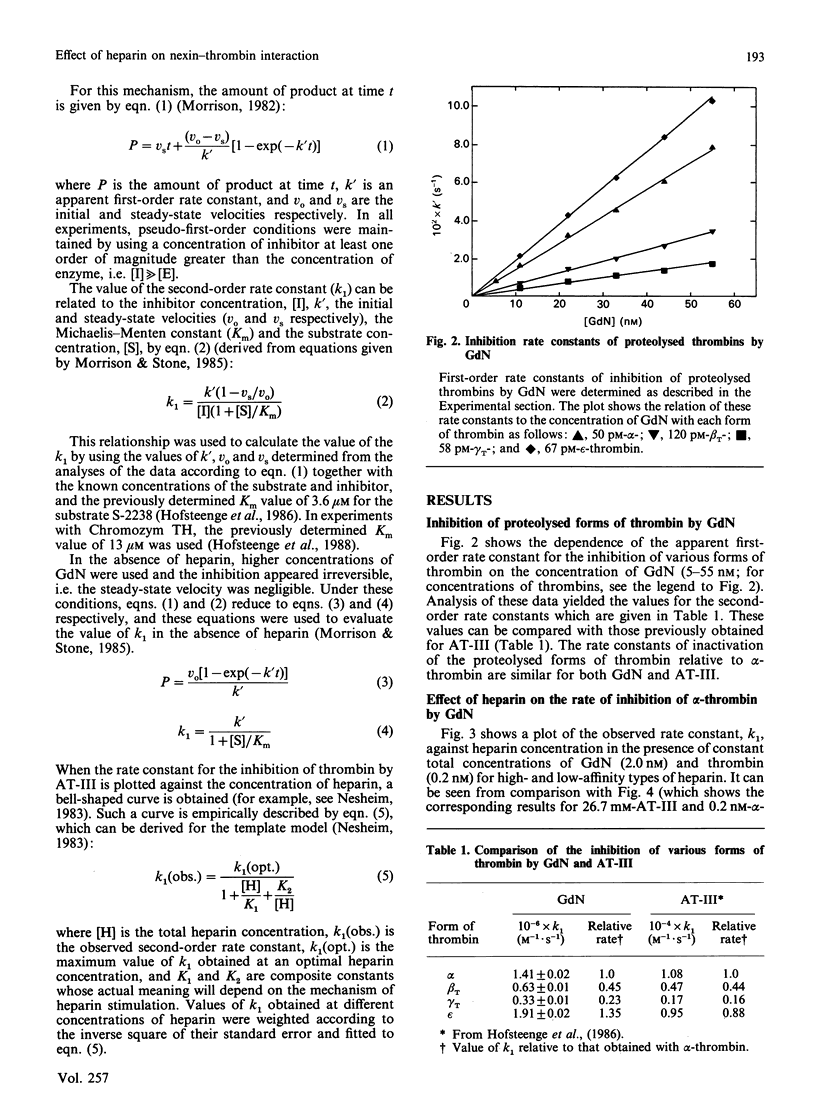
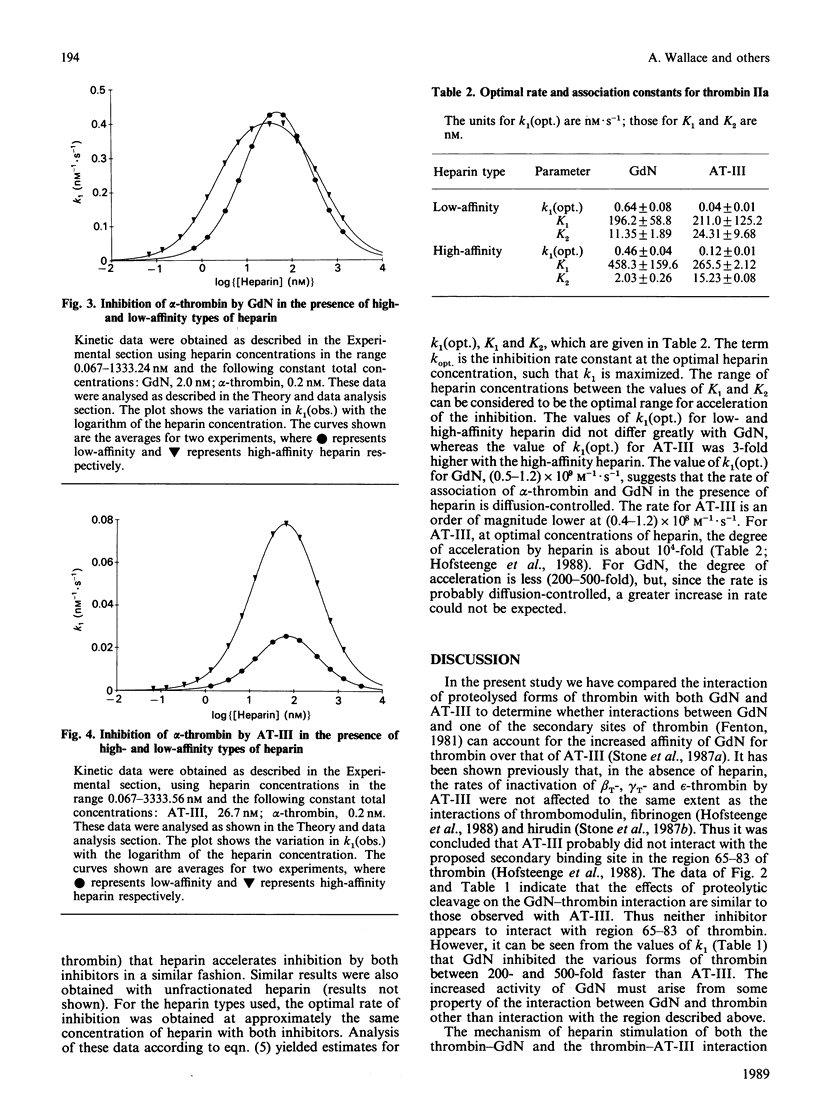
In order to determine the specificity of the interaction between thrombin and glia-derived nexin (GdN), the inactivation of proteolytically modified human thrombin species by GdN has been studied. The second-order rate constants for the inactivation of alpha-, beta T-, gamma T- and epsilon-thrombin by GdN were 1.41, 0.63, 0.33 and 1.91 microM-1.s-1 respectively. The kinetic properties of gdN were also investigated in the presence of different types of heparin, fractionated according to antithrombin III-binding affinity. Association rate constants of both gdN and antithrombin III with alpha-thrombin were obtained using unfractionated, low- and high-affinity heparin types. The different heparin types gave optimal rates of inhibition at similar heparin concentrations for both inhibitors. At optimal heparin concentrations, the rate of inactivation of alpha-thrombin by GdN was 0.5-1.2 nM-1.s-1, which suggests that, under these conditions, the interaction is diffusion-controlled.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atha D. H., Lormeau J. C., Petitou M., Rosenberg R. D., Choay J. Contribution of 3-O- and 6-O-sulfated glucosamine residues in the heparin-induced conformational change in antithrombin III. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 6;26(20):6454–6461. doi: 10.1021/bi00394a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berliner L. J. Structure-function relationships in human alpha- and gamma-thrombins. Mol Cell Biochem. 1984;61(2):159–172. doi: 10.1007/BF00222493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn M. N., Smith R. L., Carson J., Sibley C. C. The heparin-binding site of antithrombin III. Identification of a critical tryptophan in the amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):939–941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun P. J., Hofsteenge J., Chang J. Y., Stone S. R. Preparation and characterization of proteolyzed forms of human alpha-thrombin. Thromb Res. 1988 Apr 15;50(2):273–283. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choay J., Lormeau J. C., Petitou M., Sinaÿ P., Fareed J. Structural studies on a biologically active hexasaccharide obtained from heparin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;370:644–649. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb29770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson A., Raub E., Lindahl U., Björk I. Role of ternary complexes, in which heparin binds both antithrombin and proteinase, in the acceleration of the reactions between antithrombin and thrombin or factor Xa. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15467–15473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eschenbruch M., Bürk R. R. Experimentally improved reliability of ultrasensitive silver staining of protein in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Sep 1;125(1):96–99. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90387-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd Thrombin specificity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;370:468–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb29757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith M. J. Kinetics of the heparin-enhanced antithrombin III/thrombin reaction. Evidence for a template model for the mechanism of action of heparin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7360–7365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronke R. S., Bergman B. L., Baker J. B. Thrombin interaction with platelets. Influence of a platelet protease nexin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3030–3036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guenther J., Nick H., Monard D. A glia-derived neurite-promoting factor with protease inhibitory activity. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):1963–1966. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03878.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofsteenge J., Braun P. J., Stone S. R. Enzymatic properties of proteolytic derivatives of human alpha-thrombin. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):2144–2151. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofsteenge J., Taguchi H., Stone S. R. Effect of thrombomodulin on the kinetics of the interaction of thrombin with substrates and inhibitors. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):243–251. doi: 10.1042/bj2370243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hök M., Björk I., Hopwood J., Lindahl U. Anticoagulant activity of heparin: separation of high-activity and low-activity heparin species by affinity chromatography on immobilized antithrombin. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jul 1;66(1):90–93. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80592-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakubowski H. V., Kline M. D., Owen W. G. The effect of bovine thrombomodulin on the specificity of bovine thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3876–3882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jameson G. W., Roberts D. V., Adams R. W., Kyle W. S., Elmore D. T. Determination of the operational molarity of solutions of bovine alpha-chymotrypsin, trypsin, thrombin and factor Xa by spectrofluorimetric titration. Biochem J. 1973 Jan;131(1):107–117. doi: 10.1042/bj1310107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabata S., Morita T., Iwanaga S., Igarashi H. Staphylocoagulase-binding region in human prothrombin. J Biochem. 1985 Jan;97(1):325–331. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koide T., Odani S., Takahashi K., Ono T., Sakuragawa N. Antithrombin III Toyama: replacement of arginine-47 by cysteine in hereditary abnormal antithrombin III that lacks heparin-binding ability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):289–293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam L. H., Silbert J. E., Rosenberg R. D. The separation of active and inactive forms of heparin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 22;69(2):570–577. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90558-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li E. H., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Feinman R. D. The role of heparin in the thrombin-antithrombin III reaction. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jul;175(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90494-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl U., Bäckström G., Thunberg L., Leder I. G. Evidence for a 3-O-sulfated D-glucosamine residue in the antithrombin-binding sequence of heparin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6551–6555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. S., Chang J. Y. The heparin binding site of human antithrombin III. Selective chemical modification at Lys114, Lys125, and Lys287 impairs its heparin cofactor activity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17356–17361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lottenberg R., Jackson C. M. Solution composition dependent variation in extinction coefficients for p-nitroaniline. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Feb 15;742(3):558–564. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90273-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monard D., Solomon F., Rentsch M., Gysin R. Glia-induced morphological differentiation in neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1894–1897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E. A simple rate law that describes the kinetics of the heparin-catalyzed reaction between antithrombin III and thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14708–14717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordenman B., Björk I. Binding of low-affinity and high-affinity heparin to antithrombin. Ultraviolet difference spectroscopy and circular dichroism studies. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 8;17(16):3339–3344. doi: 10.1021/bi00609a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordenman B., Nyström C., Björk I. The size and shape of human and bovine antithrombin III. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Aug 15;78(1):195–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11730.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson S. T., Shore J. D. Demonstration of a two-step reaction mechanism for inhibition of alpha-thrombin by antithrombin III and identification of the step affected by heparin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14891–14895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pecon J. M., Blackburn M. N. Pyridoxylation of essential lysines in the heparin-binding site of antithrombin III. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):935–938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. B., Blackburn M. N. Antithrombin conformation and the catalytic role of heparin. I. Does cleavage by thrombin induce structural changes in the heparin-binding region of antithrombin? J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7552–7558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. B., Noyes C. M., Pecon J. M., Church F. C., Blackburn M. N. Identification of a lysyl residue in antithrombin which is essential for heparin binding. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8061–8065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz M. W., Owen W. G. A catalytic role for heparin. Evidence for a ternary complex of heparin cofactor thrombin and heparin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 21;535(1):66–77. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riesenfeld J., Thunberg L., Hök M., Lindahl U. The antithrombin-binding sequence of heparin. Location of essential N-sulfate groups. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2389–2394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. D., Damus P. S. The purification and mechanism of action of human antithrombin-heparin cofactor. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6490–6505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld L., Danishefsky I. A fragment of antithrombin that binds both heparin and thrombin. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 1;237(3):639–646. doi: 10.1042/bj2370639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. W., Bergman B. L., Bajpai A., Hersh R. T., Rodriguez H., Jones B. N., Barreda C., Watts S., Baker J. B. Protease nexin. Properties and a modified purification procedure. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7029–7034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer J., Gloor S. M., Rovelli G. F., Hofsteenge J., Nick H., Meier R., Monard D. cDNA sequence coding for a rat glia-derived nexin and its homology to members of the serpin superfamily. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 6;26(20):6407–6410. doi: 10.1021/bi00394a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone S. R., Braun P. J., Hofsteenge J. Identification of regions of alpha-thrombin involved in its interaction with hirudin. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 28;26(15):4617–4624. doi: 10.1021/bi00389a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone S. R., Hofsteenge J. Effect of heparin on the interaction between thrombin and hirudin. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 1;169(2):373–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13622.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone S. R., Hofsteenge J. Kinetics of the inhibition of thrombin by hirudin. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 12;25(16):4622–4628. doi: 10.1021/bi00364a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone S. R., Nick H., Hofsteenge J., Monard D. Glial-derived neurite-promoting factor is a slow-binding inhibitor of trypsin, thrombin, and urokinase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Jan;252(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90028-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thunberg L., Bäckström G., Lindahl U. Further characterization of the antithrombin-binding sequence in heparin. Carbohydr Res. 1982 Mar 1;100:393–410. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)81050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefsen D. M., Majerus D. W., Blank M. K. Heparin cofactor II. Purification and properties of a heparin-dependent inhibitor of thrombin in human plasma. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2162–2169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis J., Salvesen G. S. Human plasma proteinase inhibitors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:655–709. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villaneuva G. B., Danishefsky I. Evidence for a heparin-induced conformational change on antithrombin III. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):803–809. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90374-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villanueva G. B. Predictions of the secondary structure of antithrombin III and the location of the heparin-binding site. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2531–2536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


