Abstract
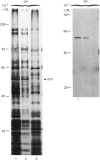
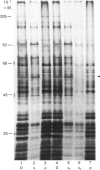
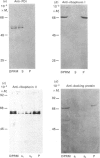
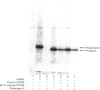
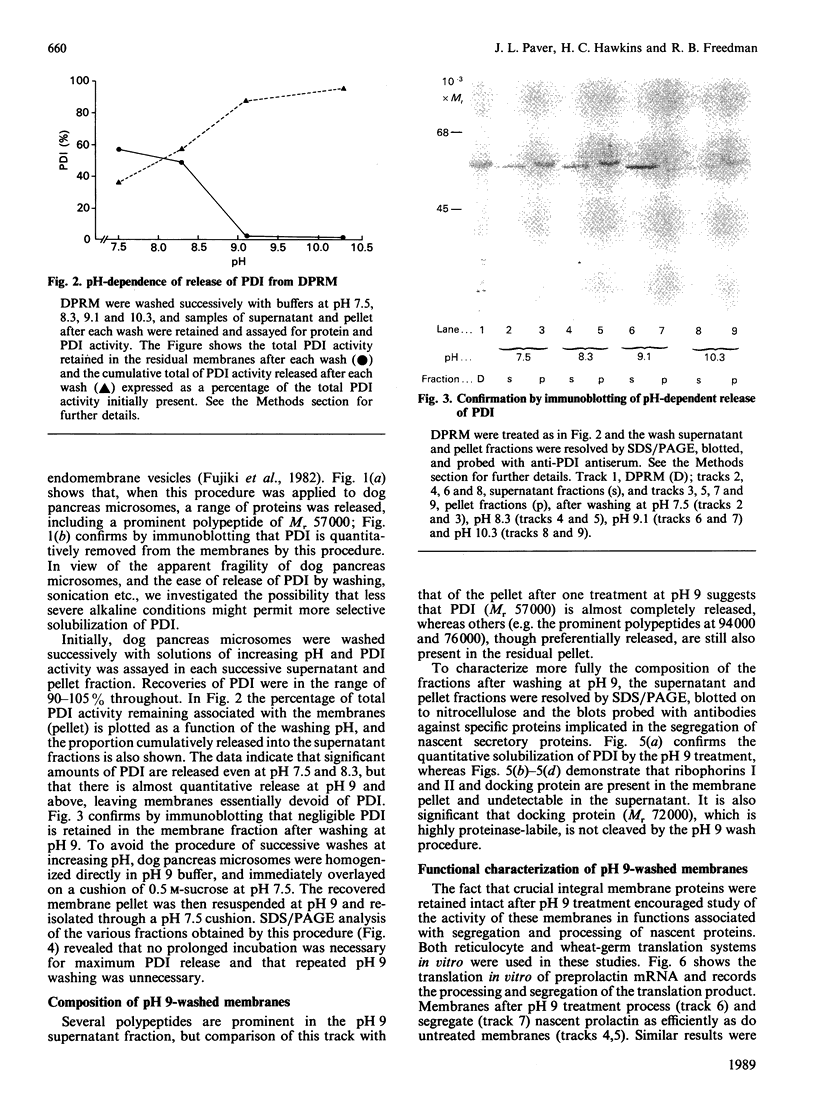
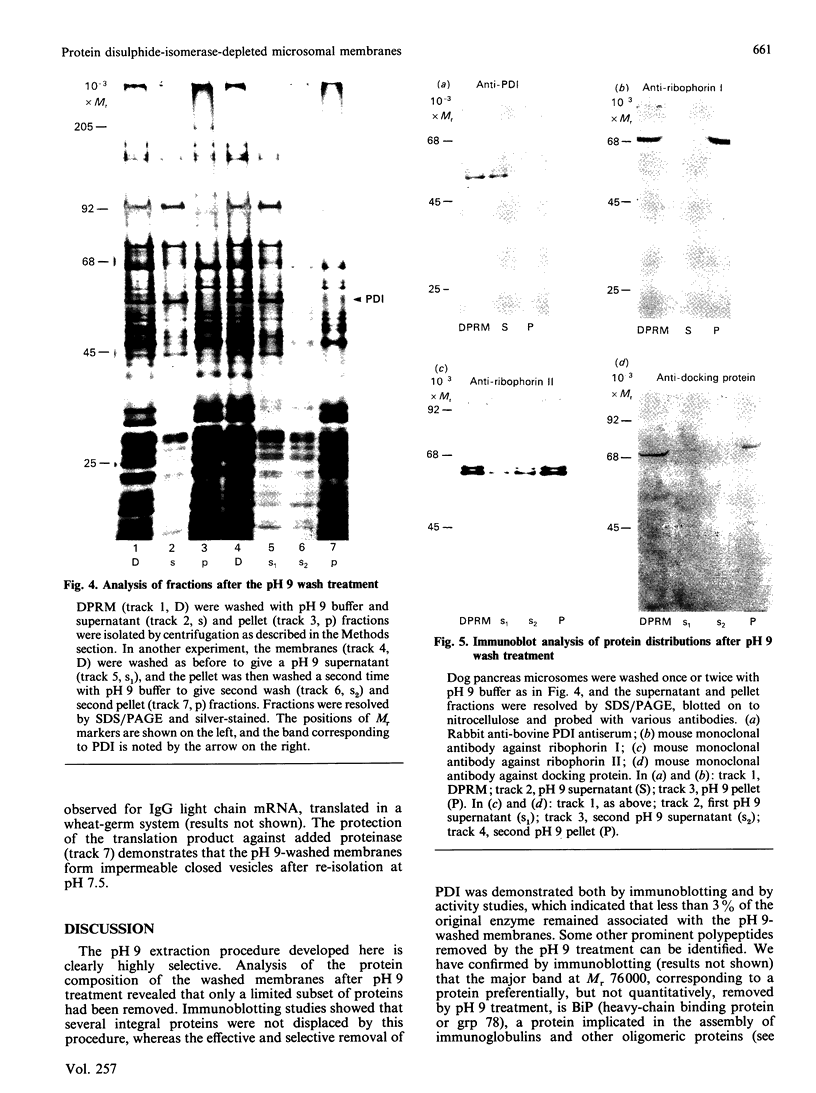
1. The selective release of protein disulphide-isomerase from dog pancreas and rat liver microsomal membranes was studied to throw light on the mechanisms of retention of this enzyme within the endoplasmic reticulum, and in order to prepare microsomal membranes specifically depleted of the enzyme. 2. Protein disulphide-isomerase was quantitatively released from dog pancreas microsomal membranes by washing at pH 9 and above, as demonstrated both by enzyme assay and by immunoblotting analysis. 3. Integral membrane proteins implicated in the process of translocation and segregation of secretory proteins were retained in pH 9-washed dog pancreas microsomal membranes. 4. After pH 9 washing, dog pancreas microsomal membranes were fully active in the translocation, segregation and processing of nascent secretory proteins; these membranes therefore provide a useful experimental system for testing the action of protein disulphide-isomerase on nascent secretory proteins. 5. Protein disulphide-isomerase was not released from rat liver microsomal membranes by pH 9 washing, and was much less readily released from these membranes by sonication, washing etc. than from dog pancreas microsomal membranes. 6. The mechanism of retention of protein disulphide-isomerase, and of other resident proteins of the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum, is discussed in the light of these findings.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. W., Straus J. W., Dudock B. S. Preparation of a cell-free protein-synthesizing system from wheat germ. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:635–644. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansorge W. Fast and sensitive detection of protein and DNA bands by treatment with potassium permanganate. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1985 May;11(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(85)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulleid N. J., Freedman R. B. Defective co-translational formation of disulphide bonds in protein disulphide-isomerase-deficient microsomes. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):649–651. doi: 10.1038/335649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman J. C., Ellis L., Blacher R. W., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Sequence of protein disulphide isomerase and implications of its relationship to thioredoxin. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):267–270. doi: 10.1038/317267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman R. B., Brockway B. E., Lambert N. Protein disulphide-isomerase and the formation of native disulphide bonds. Biochem Soc Trans. 1984 Dec;12(6):929–932. doi: 10.1042/bst0120929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki Y., Hubbard A. L., Fowler S., Lazarow P. B. Isolation of intracellular membranes by means of sodium carbonate treatment: application to endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):97–102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins H. C., Freedman R. B. Thiol-protein disulphide oxidoreductases. Differences between protein disulphide-isomerase and glutathione-insulin transhydrogenase activities in ox liver. Biochem J. 1976 Nov;159(2):385–393. doi: 10.1042/bj1590385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins J. A., Pigott C. A. Asymmetric distribution of phosphatidylethanolamine in the endoplasmic reticulum demonstrated using trinitrobenzenesulphonic acid as a probe. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec 8;693(1):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90481-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillson D. A., Lambert N., Freedman R. B. Formation and isomerization of disulfide bonds in proteins: protein disulfide-isomerase. Methods Enzymol. 1984;107:281–294. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(84)07018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hortsch M., Avossa D., Meyer D. I. A structural and functional analysis of the docking protein. Characterization of active domains by proteolysis and specific antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9137–9145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaderbhai M. A., Austen B. M. Dog pancreatic microsomal-membrane polypeptides analysed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1984 Jan 1;217(1):145–157. doi: 10.1042/bj2170145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaderbhai M. A., Austen B. M. Studies on the formation of intrachain disulphide bonds in newly biosynthesised bovine prolactin. Role of protein-disulphide isomerase. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Nov 15;153(1):167–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09283.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch G. L. Reticuloplasmins: a novel group of proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Sci. 1987 May;87(Pt 4):491–492. doi: 10.1242/jcs.87.4.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7057–7070. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert N., Freedman R. B. Structural properties of homogeneous protein disulphide-isomerase from bovine liver purified by a rapid high-yielding procedure. Biochem J. 1983 Jul 1;213(1):225–234. doi: 10.1042/bj2130225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert N., Freedman R. B. The latency of rat liver microsomal protein disulphide-isomerase. Biochem J. 1985 Jun 15;228(3):635–645. doi: 10.1042/bj2280635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macer D. R., Koch G. L. Identification of a set of calcium-binding proteins in reticuloplasm, the luminal content of the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Sci. 1988 Sep;91(Pt 1):61–70. doi: 10.1242/jcs.91.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. An Hsp70-like protein in the ER: identity with the 78 kd glucose-regulated protein and immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90746-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohba H., Harano T., Omura T. Intracellular and intramembranous localization of a protein disulfide isomerase in rat liver. J Biochem. 1981 Mar;89(3):889–900. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Evidence that luminal ER proteins are sorted from secreted proteins in a post-ER compartment. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):913–918. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Speculations on the functions of the major heat shock and glucose-regulated proteins. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):959–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90693-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pihlajaniemi T., Helaakoski T., Tasanen K., Myllylä R., Huhtala M. L., Koivu J., Kivirikko K. I. Molecular cloning of the beta-subunit of human prolyl 4-hydroxylase. This subunit and protein disulphide isomerase are products of the same gene. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):643–649. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04803.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A., Pierce S. B. In vivo cross-linking of protein disulfide isomerase to immunoglobulins. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4179–4182. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi K., Yamamoto T., Hayashi H., Koya S., Takikawa H., Toyoshima K., Horiuchi R. Sequence of membrane-associated thyroid hormone binding protein from bovine liver: its identity with protein disulphide isomerase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 14;146(3):1485–1492. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90817-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]