Abstract
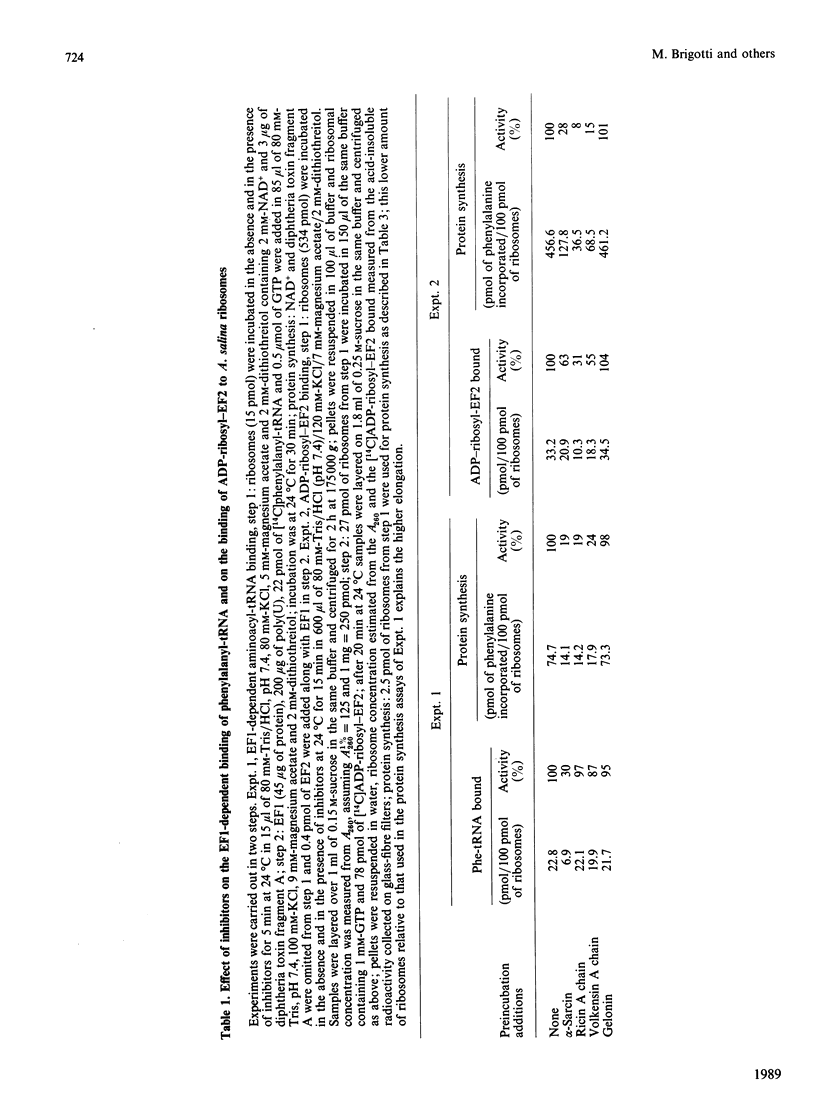
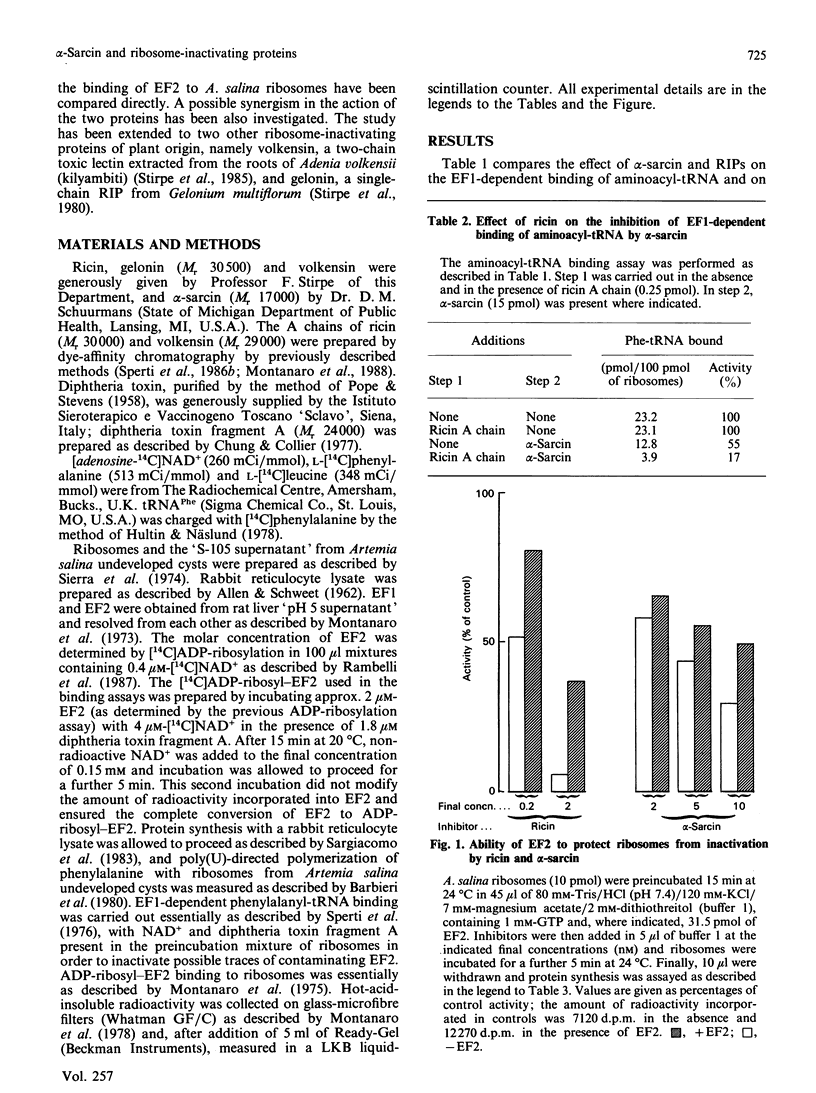
alpha-Sarcin from Aspergillus giganteus and the ribosome-inactivating proteins (RIPs) from higher plants inactivate the 60 S ribosomal subunit. The former is an RNAase, whereas RIPs are N-glycosidases. The site of cleavage of RNA and that of N-glycosidic depurinization are at one nucleotide distance in 28 S rRNA [Endo & Tsurugi (1987) J. Biol. Chem. 262, 8128-8130]. The effect of alpha-sarcin and that of RIPs on the interaction of elongation factors with Artemia salina (brine shrimp) ribosomes have been investigated. alpha-Sarcin inhibits both the EF1 (elongation factor 1)-dependent binding of aminoacyl-tRNA and the GTP-dependent binding of EF2 (elongation factor 2) to ribosomes, whereas two of the RIPs tested, ricin from Ricinus communis (castor bean) and volkensin from Adenia volkensii (kilyambiti), inhibit only the latter reaction. EF2 protects ribosomes from inactivation by both alpha-sarcin and ricin. The EF1-binding site is affected only by alpha-sarcin. The sensitivity of this site to alpha-sarcin is increased by pretreatment of ribosomes with ricin. A. salina ribosomes were highly resistant to the third RIP tested, namely gelonin from Gelonium multiflorum. All four proteins tested have, however, a comparable activity on the rabbit reticulocyte-lysate system.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN E. H., SCHWEET R. S. Synthesis of hemoglobin in a cell-free system. I. Properties of the complete system. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:760–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri L., Zamboni M., Lorenzoni E., Montanaro L., Sperti S., Stirpe F. Inhibition of protein synthesis in vitro by proteins from the seeds of Momordica charantia (bitter pear melon). Biochem J. 1980 Feb 15;186(2):443–452. doi: 10.1042/bj1860443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson S., Olsnes S., Pihl A., Skorve J., Abraham A. K. On the mechanism of protein-synthesis inhibition by abrin and ricin. Inhibition of the GTP-hydrolysis site on the 60-S ribosomal subunit. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Nov 15;59(2):573–580. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cenini P., Battelli M. G., Bolognesi A., Stirpe F., Villemez C. L. Effect of ribosome-inactivating proteins on ribosomes from Tetrahymena pyriformis and Acanthamoeba castellanii. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 29;148(2):521–527. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90907-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cenini P., Bolognesi A., Stirpe F. Ribosome-inactivating proteins from plants inhibit ribosome activity of Trypanosoma and Leishmania. J Protozool. 1988 Aug;35(3):384–387. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1988.tb04113.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung D. W., Collier R. J. The mechanism of ADP-ribosylation of elongation factor 2 catalyzed by fragment A from diphtheria toxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 11;483(2):248–257. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Huber P. W., Wool I. G. The ribonuclease activity of the cytotoxin alpha-sarcin. The characteristics of the enzymatic activity of alpha-sarcin with ribosomes and ribonucleic acids as substrates. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2662–2667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Mitsui K., Motizuki M., Tsurugi K. The mechanism of action of ricin and related toxic lectins on eukaryotic ribosomes. The site and the characteristics of the modification in 28 S ribosomal RNA caused by the toxins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5908–5912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K., Lambert J. M. The site of action of six different ribosome-inactivating proteins from plants on eukaryotic ribosomes: the RNA N-glycosidase activity of the proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 15;150(3):1032–1036. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90733-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K. RNA N-glycosidase activity of ricin A-chain. Mechanism of action of the toxic lectin ricin on eukaryotic ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8128–8130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Tsurugi K., Yutsudo T., Takeda Y., Ogasawara T., Igarashi K. Site of action of a Vero toxin (VT2) from Escherichia coli O157:H7 and of Shiga toxin on eukaryotic ribosomes. RNA N-glycosidase activity of the toxins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):45–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Wool I. G. The site of action of alpha-sarcin on eukaryotic ribosomes. The sequence at the alpha-sarcin cleavage site in 28 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):9054–9060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Puentes C., Benson S., Olsnes S., Pihl A. Protective effect of elongation factor 2 on the inactivation of ribosomes by the toxic lectins abrin and ricin. Eur J Biochem. 1976 May 1;64(2):437–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10320.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Puentes C., Vazquez D. Effects of some proteins that inactivate the eukaryotic ribosome. FEBS Lett. 1977;78(1):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80292-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobden A. N., Cundliffe E. The mode of action of alpha sarcin and a novel assay of the puromycin reaction. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 15;170(1):57–61. doi: 10.1042/bj1700057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultin T., Náslund P. H. Stimulation of enzymatic phe-tRNA binding to mammalian ribosomes by thallium ions at concentrations blocking other ribosomal functions. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jul 17;88(1):143–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvin J. D. Purification and partial characterization of the antiviral protein from Phytolacca americana which inhibits eukaryotic protein synthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Aug;169(2):522–528. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90195-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montanaro L., Sperti S., Mattioli A., Testoni G., Stirpe F. Inhibition by ricin of protein synthesis in vitro. Inhibition of the binding of elongation factor 2 and of adenosine diphosphate-ribosylated elongation factor 2 to ribosomes. Biochem J. 1975 Jan;146(1):127–131. doi: 10.1042/bj1460127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montanaro L., Sperti S., Stirpe F. Inhibition by ricin of protein synthesis in vitro. Ribosomes as the target of the toxin. Biochem J. 1973 Nov;136(3):677–683. doi: 10.1042/bj1360677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montanaro L., Sperti S., Zamboni M., Denaro M., Testoni G., Gasperi-Campani A., Stirpe F. Effect of modeccin on the steps of peptide-chain elongation. Biochem J. 1978 Nov 15;176(2):371–379. doi: 10.1042/bj1760371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson L., Nygård O. The mechanism of the protein-synthesis elongation cycle in eukaryotes. Effect of ricin on the ribosomal interaction with elongation factors. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 17;161(1):111–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10130.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPE C. G., STEVENS M. F. The purification of diphtheria toxin and the isolation of crystalline toxin-protein. Br J Exp Pathol. 1958 Apr;39(2):139–149. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paleologue A., Reboud J. P., Reboud A. M. Modifications of 60 S ribosomal subunits induced by the ricin A chain. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 24;208(2):373–377. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambelli F., Brigotti M., Sperti S., Montanaro L. Interaction of diphtheria toxin fragment A and of elongation factor 2 with cibacron blue. Biosci Rep. 1987 Sep;7(9):737–743. doi: 10.1007/BF01116867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. K., Selitrennikoff C. P. Plant proteins that inactivate foreign ribosomes. Biosci Rep. 1986 Jan;6(1):19–29. doi: 10.1007/BF01145175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler D. G., Davies J. E. Specific cleavage of ribosomal RNA caused by alpha sarcin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Apr;4(4):1097–1110. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.4.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra J. M., Meier D., Ochoa S. Effect of development on the translation of messenger RNA in Artemia salina embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2693–2697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperti S., Montanaro L., Mattioli A., Stirpe F. Inhibition by ricin of protein synthesis in vitro: 60 S ribosomal subunit as the target of the toxin. Biochem J. 1973 Nov;136(3):813–815. doi: 10.1042/bj1360813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperti S., Montanaro L., Mattioli A., Testoni G. Relationship between elongation factor I- and elongation factor II- dependent guanosine triphosphatase activities of ribosomes. Inhibition of both activities by ricin. Biochem J. 1975 Jun;148(3):447–451. doi: 10.1042/bj1480447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperti S., Montanaro L., Mattioli A., Testoni G., Stirpe F. Inhibition of protein synthesis in vitro by crotins and ricin. Effect on the steps of peptide chain elongation. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 15;156(1):7–13. doi: 10.1042/bj1560007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperti S., Montanaro L., Rambelli F. Dye affinity chromatography of ricin subunits. Biosci Rep. 1986 Dec;6(12):1035–1040. doi: 10.1007/BF01141024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperti S., Montanaro L. Ricin and modeccin do not inhibit the elongation factor 1-dependent binding of aminoacyl-tRNA to ribosomes. Biochem J. 1979 Jan 15;178(1):233–236. doi: 10.1042/bj1780233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Bailey S., Miller S. P., Bodley J. W. Modification of ribosomal RNA by ribosome-inactivating proteins from plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 25;16(4):1349–1357. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.4.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Barbieri L., Abbondanza A., Falasca A. I., Brown A. N., Sandvig K., Olsnes S., Pihl A. Properties of volkensin, a toxic lectin from Adenia volkensii. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14589–14595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Barbieri L. Ribosome-inactivating proteins up to date. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 20;195(1-2):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80118-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Olsnes S., Pihl A. Gelonin, a new inhibitor of protein synthesis, nontoxic to intact cells. Isolation, characterization, and preparation of cytotoxic complexes with concanavalin A. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6947–6953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. A., Endo Y., Wheat W. H., Wool I. G., Pace N. R. Location of 5.8 S rRNA contact sites in 28 S rRNA and the effect of alpha-sarcin on the association of 5.8 S rRNA with 28 S rRNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):333–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


