Abstract
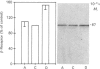
Steroid hormones modulate the ability of cells to respond to hormones that act via cyclic AMP. In adipocytes of adrenalectomized rats, cyclic AMP accumulation and lipolysis in response to adrenaline are attenuated. However, the mechanism(s) of these effects are poorly understood. The effects of altered glucocorticoid status in vivo on the steady-state amounts of components of the hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase were analysed in rat adipocytes. beta-Adrenergic receptors were analysed by using radioligand binding and immunoblotting with an anti-receptor antiserum. Neither the amount of radioligand binding nor the amount of beta-adrenergic-receptor peptide (Mr 67,000) was altered by adrenalectomy, whereas treatment of adrenalectomized rats with dexamethasone was found to increase both parameters by more than 25% with respect to the control. Forskolin-stimulated adenylated cyclase activity was unchanged in membranes isolated from adipocytes of adrenalectomized rats, but was decreased (50%) in those from dexamethasone-treated rats. The alpha-subunit of Gs was probed by using cholera-toxin-catalysed ADP-ribosylation. Immunoblotting was used to analyse the steady-state amounts of G-protein beta-subunits (beta-G35/36). Adrenalectomy was associated with decreases in the steady-state amounts of alpha-Gs (30%) and beta-G35/36 (50%). Dexamethasone treatment of adrenalectomized animals partially restored the lipolytic response of adipocytes to adrenaline and the amounts of alpha-Gs, increased the amounts of beta-G35/36 subunits from 50% to 150% of control values, increased beta-adrenergic receptors by more than 25% and decreased adenylate cyclase activity (50%). These results suggest that the steady-state amounts of components of hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase are differentially regulated by glucocorticoids.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen D. O., Beck R. R. Alterations in lipolysis, adenylate cyclase and adenosine 3', 5'-monophosphate levels in isolated fat cells following adrenalectomy. Endocrinology. 1972 Aug;91(2):504–510. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-2-504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. H., Bourne H. R. Dexamethasone increases adenylyl cyclase activity and expression of the alpha-subunit of Gs in GH3 cells. Endocrinology. 1987 Nov;121(5):1711–1715. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-5-1711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codina J., Stengel D., Woo S. L., Birnbaumer L. Beta-subunits of the human liver Gs/Gi signal-transducing proteins and those of bovine retinal rod cell transducin are identical. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 27;207(2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81486-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Beta-adrenergic receptors in hamster smooth muscle cells are transcriptionally regulated by glucocorticoids. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9067–9070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubero A., Malbon C. C. The fat cell beta-adrenergic receptor. Purification and characterization of a mammalian beta 1-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1344–1350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P., Malbon C. C., Kerman K., Gitomer W., Pilch P. F. Effect of thyroid status on insulin action in rat adipocytes and skeletal muscle. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):574–582. doi: 10.1172/JCI109889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Brown M. L., Fraser E. D., Northup J. K. Purification of the major GTP-binding proteins from human placental membranes. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):7052–7059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Fawzi A., Fraser E. D., Brown M. L., Northup J. K. Purification of a beta 35 form of the beta gamma complex common to G-proteins from human placental membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):176–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H., Friedmann N., Wong E. H., Brineaux J. P., Corbin J. D., Park C. R. Interaction of glucocorticoids with glucagon and epinephrine in the control of gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis in liver and of lipolysis in adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 10;247(11):3579–3588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong H. K., Amatruda T. T., 3rd, Birren B. W., Simon M. I. Distinct forms of the beta subunit of GTP-binding regulatory proteins identified by molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3792–3796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudenrich C. C., Borle A. B. The effects of adrenalectomy on the alpha-adrenergic regulation of cytosolic free calcium in hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8604–8610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George S. T., Berrios M., Hadcock J. R., Wang H. Y., Malbon C. C. Receptor density and cAMP accumulation: analysis in CHO cells exhibiting stable expression of a cDNA that encodes the beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jan 29;150(2):665–672. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90443-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guellaen G., Yates-Aggerbeck M., Vauquelin G., Strosberg D., Hanoune J. Characterization with [3H] dihydroergocryptine of the alpha-adrenergic receptor of the hepatic plasma membrane. Comparison with the beta-adrenergic receptor in normal and adrenalectomized rats. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1114–1120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Oinuma M., Ui M. Mechanisms for inhibition of the catalytic activity of adenylate cyclase by the guanine nucleotide-binding proteins serving as the substrate of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):5215–5221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacasa D., Agli B., Giudicelli Y. Permissive action of glucocorticoids on catecholamine-induced lipolysis: direct "in vitro" effects on the fat cell beta-adrenoreceptor-coupled-adenylate cyclase system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 16;153(2):489–497. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Rosen O. M., Rubin C. S. Differentiation-dependent expression of catecholamine-stimulated adenylate cyclase. Roles of the beta-receptor and G/F protein in differentiating 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12866–12874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamberts S. W., Timmermans H. A., Kramer-Blankestijn M., Birkenhäger J. C. The mechanism of the potentiating effect of glucocorticoids on catecholamine-induced lipolysis. Metabolism. 1975 Jun;24(6):681–689. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malbon C. C., Gill D. M. ADP-ribosylation of membrane proteins and activation of adenylate cyclase by cholera toxin in fat cell ghosts from euthyroid and hypothyroid rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Sep 3;586(3):518–527. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90042-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malbon C. C., Graziano M. P., Johnson G. L. Fat cell beta-adrenergic receptor in the hypothyroid rat. Impaired interaction with the stimulatory regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3254–3260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malbon C. C., Hadcock J. R. Evidence that glucocorticoid response elements in the 5'-noncoding region of the hamster beta 2-adrenergic receptor gene are obligate for glucocorticoid regulation of receptor mRNA levels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jul 29;154(2):676–681. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90192-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malbon C. C., Li S., Fain J. N. Hormonal activation of glycogen phosphorylase in hepatocytes from hypothyroid rats. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8820–8825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malbon C. C., Rapiejko P. J., Mangano T. J. Fat cell adenylate cyclase system. Enhanced inhibition by adenosine and GTP in the hypothyroid rat. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2558–2564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malbon C. C., Rapiejko P. J., Watkins D. C. Permissive hormone regulation of hormone-sensitive effector systems. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Jan;9(1):33–36. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90240-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malbon C. C. The effects of thyroid status on the modulation of fat cell beta-adrenergic receptor agonist affinity by guanine nucleotides. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Sep;18(2):193–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manganiello V., Vaughan M. An effect of insulin on cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase activity in fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7164–7170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeel D. W., Jarett L. Preparation and characterization of a plasma membrane fraction from isolated fat cells. J Cell Biol. 1970 Feb;44(2):417–432. doi: 10.1083/jcb.44.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Spiegel A. M., Unson C. G., Saggerson E. D. Chemically induced hypothyroidism produces elevated amounts of the alpha subunit of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide binding protein (Gi) and the beta subunit common to all G-proteins. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 1;247(1):223–227. doi: 10.1042/bj2470223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxham C. P., George S. T., Graziano M. P., Brandwein H. J., Malbon C. C. Mammalian beta 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors. Immunological and structural comparisons. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14562–14570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxham C. P., Ross E. M., George S. T., Malbon C. C. Beta-adrenergic receptors display intramolecular disulfide bridges in situ: analysis by immunoblotting and functional reconstitution. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 May;33(5):486–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajerison R., Marchetti J., Roy C., Bockaert J., Jard S. The vasopressin-sensitive adenylate cyclase of the rat kidney. Effect of adrenalectomy and corticosteroids on hormonal receptor-enzyme coupling. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 25;249(20):6390–6400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapiejko P. J., Malbon C. C. Short-term hyperthyroidism modulates adenosine receptors and catalytic activity of adenylate cyclase in adipocytes. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 1;241(3):765–771. doi: 10.1042/bj2410765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ros M., Northup J. K., Malbon C. C. Steady-state levels of G-proteins and beta-adrenergic receptors in rat fat cells. Permissive effects of thyroid hormones. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4362–4368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggerson E. D. Sensitivity of adipocyte lipolysis to stimulatory and inhibitory agonists in hypothyroidism and starvation. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):387–394. doi: 10.1042/bj2380387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles G. L., Stadel J. M., De Lean A., Lefkowitz R. J. Hypothyroidism modulates beta adrenergic receptor adenylate cyclase interactions in rat reticulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1450–1455. doi: 10.1172/JCI110397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studer R. K., Borle A. B. Effect of adrenalectomy on cellular calcium metabolism and on the response to adrenergic stimulation of hepatocytes isolated from male and female rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jul 20;804(3):377–385. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(84)90142-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins D. C., Northup J. K., Malbon C. C. Regulation of G-proteins in differentiation. Altered ratio of alpha- to beta-subunits in 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10651–10657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe B. B., Harden T. K., Molinoff P. B. beta-adrenergic receptors in rat liver: effects of adrenalectomy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1343–1347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]